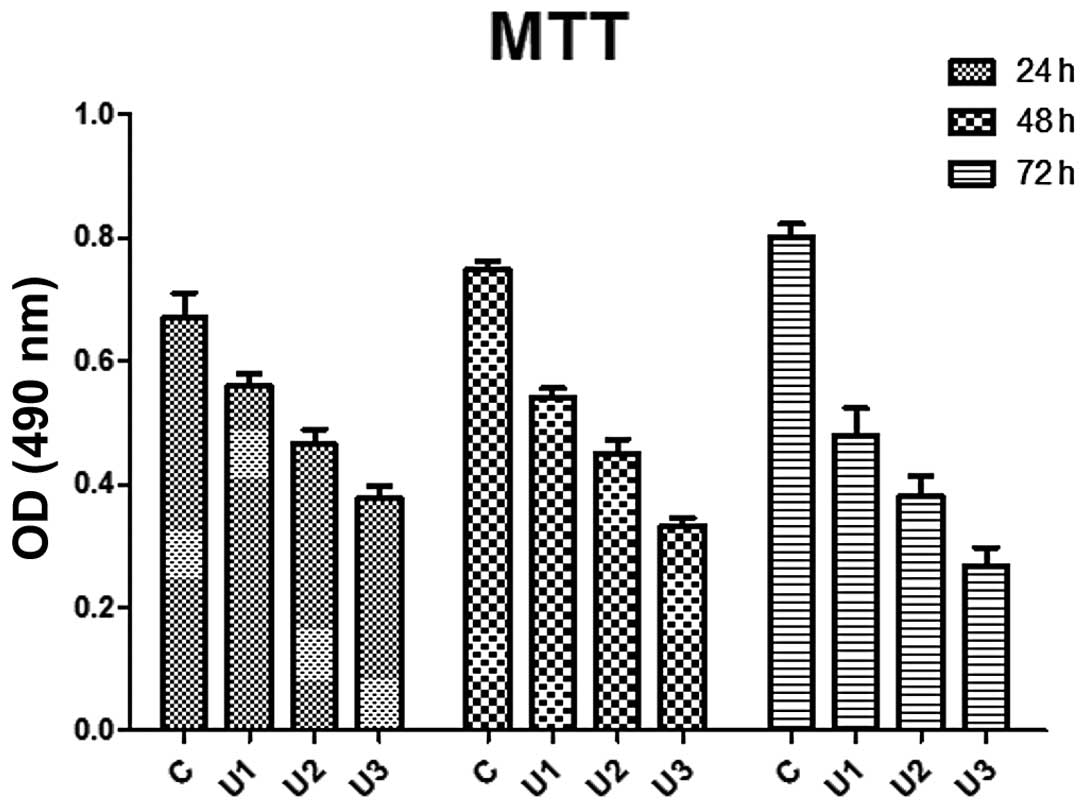
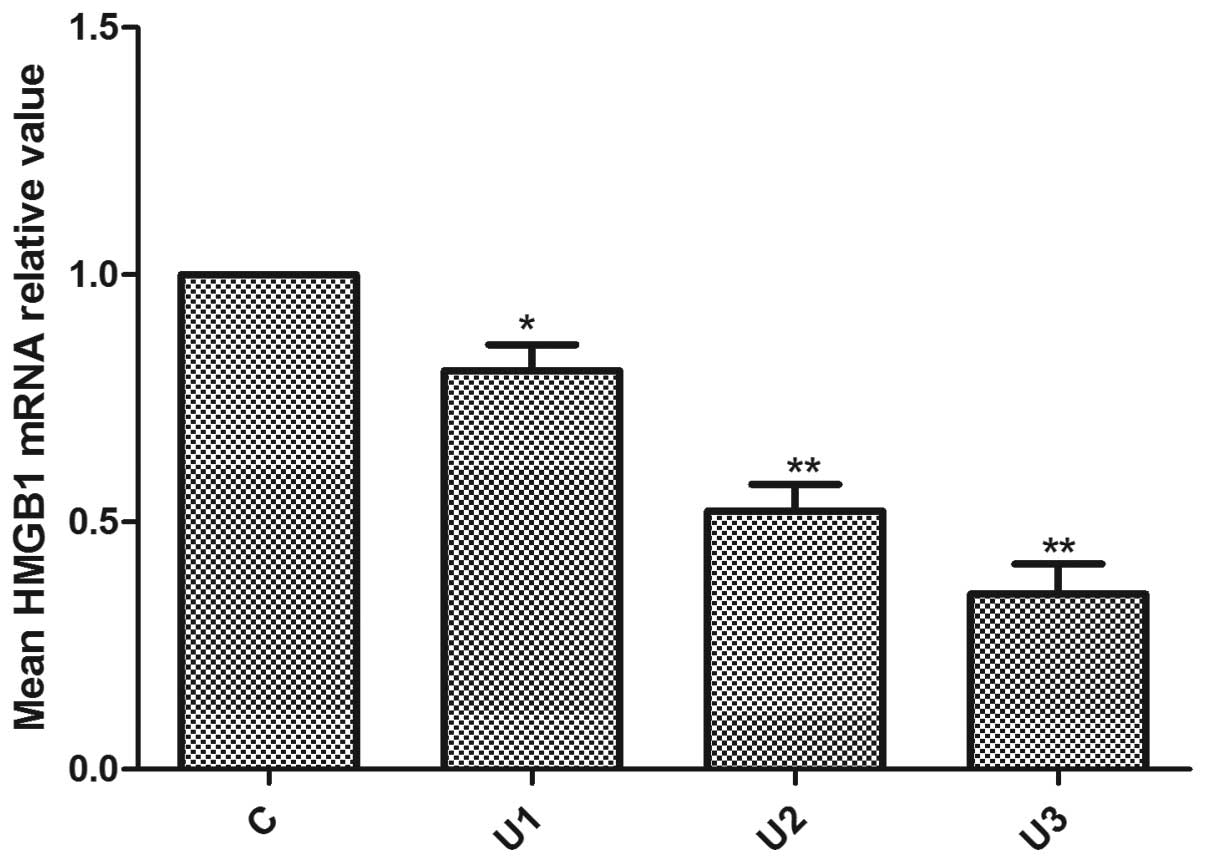
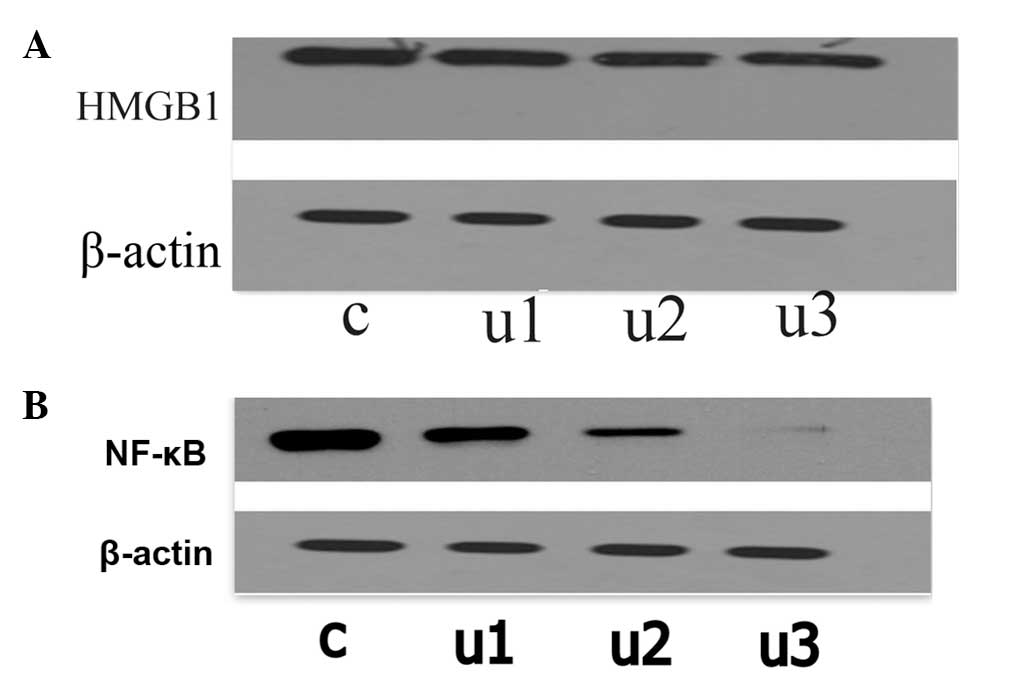
|
1
|
Czura CJ, Wang H and Tracey KJ: Dual roles
for HMGB1: DNA binding and cytokine. J Endotoxin Res. 7:315–321.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Agresti A and Bianchi ME: HMGB proteins
and gene expression. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2:170–178. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Andersson U, Erlandsson-Harris H, Yang H
and Tracey KJ: HMGB1 as a DNA-binding cytokine. J Leukoc Biol.
6:1084–1091. 2002.
|
|
4
|
Muller S, Scaffidi P, Degryse B, et al:
New EMBO members’ review: the double life of HMGB1 chromatin
protein: architectural factor and extracellular signal. Embo J.
20:4337–4340. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Bustin M, Lehn DA and Landsman D:
Structural features of the HMG chromosomal proteins and their
genes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1049:231–243. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Andersson U, Wang H, Palmblad K, et al:
High mobility group 1 protein (HMG-1) stimulates proinflammatory
cytokine synthesis in human monocytes. J Exp Med. 192:565–570.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang H, Wang H and Tracey KJ: HMG-1
rediscovered as a cytokine. Shock. 15:247–253. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Scaffidi P, Misteli T and Bianchi ME:
Release of chromatin protein HMGB1 by necrotic cells triggers
inflammation. Nature. 418:191–195. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Czura CJ and Tracey KJ: Targeting high
mobility group box 1 as a late-acting mediator of inflammation.
Crit Care Med. 31:S46–S50. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: The hallmarks
of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sun KK, Ji C, Li X, et al: Overexpression
of high mobility group protein B1 correlates with the proliferation
and metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma cells. Mol Med Rep.
7:1678–1682. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Taguchi A, Blood DC, Del TG, et al:
Blockade of RAGE-amphoterin signalling suppresses tumour growth and
metastases. Nature. 405:354–360. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xiang YY, Wang DY, Tanaka M, et al:
Expression of high-mobility group-1 mRNA in human gastrointestinal
adenocarcinoma and corresponding non-cancerous mucosa. Int J
Cancer. 74:1–6. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Poser I, Golob M, Buettner R and
Bosserhoff AK: Upregulation of HMG1 leads to melanoma inhibitory
activity expression in malignant melanoma cells and contributes to
their malignancy phenotype. Mol Cell Biol. 23:2991–2998. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cabart P, Kalousek I, Jandová and Hrkai Z:
Differential expression of nuclear HMG1, HMG2 proteins and H1(zero)
histone in various blood cells. Cell Biochem Funct. 13:125–133.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Flohr AM, Rogalla P, Meiboom M, et al:
Variation of HMGB1 expression in breast cancer. Anticancer Res.
21:3881–3885. 2001.
|
|
17
|
Muller S, Ronfani L and Bianchi ME:
Regulated expression and subcellular localization of HMGB1, a
chromatin protein with a cytokine function. J Intern Med.
255:332–343. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Degryse B, Bonaldi T, Scaffidi P, et al:
The high mobility group (HMG) boxes of the nuclear protein HMG1
induce chemotaxis and cytoskeleton reorganization in rat smooth
muscle cells. J Cell Biol. 152:1197–1206. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Guazzi S, Strangio A, Franzi AT and
Bianchi ME: HMGB1, an architectural chromatin protein and
extracellular signalling factor, has a spatially and temporally
restricted expression pattern in mouse brain. Gene Expr Patterns.
3:29–33. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hori O, Brett J, Slattery T, et al: The
receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) is a cellular
binding site for amphoterin. Mediation of neurite outgrowth and
co-expression of rage and amphoterin in the developing nervous
system. J Biol Chem. 270:25752–25761. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ono M, Torisu H, Fukushi J, et al:
Biological implications of macrophage infiltration in human tumor
angiogenesis. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 43:69–71. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Schlueter C, Weber H, Meyer B, et al:
Angiogenetic signaling through hypoxia: HMGB1: an angiogenetic
switch molecule. Am J Pathol. 166:1259–12563. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chuangui C, Peng T and Zhentao Y: The
expression of high mobility group box 1 is associated with lymph
node metastasis and poor prognosis in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Pathol Oncol Res. 18:1021–1027. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Völp K, Brezniceanu ML, Bösser S, et al:
Increased expression of high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) is
associated with an elevated level of the antiapoptotic c-IAP2
protein in human colon carcinomas. Gut. 55:234–242. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Dong YD, Cui L, Peng CH, et al: Expression
and clinical significance of HMGB1 in human liver cancer: Knockdown
inhibits tumor growth and metastasis in vitro and in vivo. Oncol
Rep. 29:87–94. 2013.
|
|
26
|
Zeh HR 3rd and Lotze MT: Addicted to
death: invasive cancer and the immune response to unscheduled cell
death. J Immunother. 28:1–9. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Lindqvist A, Rouet P, Salier JP and
Akerström B: The alpha1-microglobulin/bikunin gene:
characterization in mouse and evolution. Gene. 234:329–336. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kanayama N, Halim A, Maehara K, et al:
Kunitz-type trypsin inhibitor prevents LPS-induced increase of
cytosolic free Ca2+ in human neutrophils and HUVEC
cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 207:324–330. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kobayashi H, Gotoh J, Fujie M and Terao T:
Characterization of the cellular binding site for the urinary
trypsin inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 269:20642–20647. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kobayashi H, Shinohara H, Ohi H, et al:
Urinary trypsin inhibitor (UTI) and fragments derived from UTI by
limited proteolysis efficiently inhibit tumor cell invasion. Clin
Exp Metastasis. 12:117–128. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kobayashi H, Fujie M, Shinohara H, et al:
Effects of urinary trypsin inhibitor on the invasion of
reconstituted basement membranes by ovarian cancer cells. Int J
Cancer. 57:378–384. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kobayashi H, Sugino D and Terao T: Urinary
trypsin inhibitor, a Kunitz-type protease inhibitor, modulates
tumor necrosis factor-stimulated activation and translocation of
protein kinase C in U937 cells. Int J Oncol. 12:95–105.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tanaka R, Fujita M, Tsuruta R, et al:
Urinary trypsin inhibitor suppresses excessive generation of
superoxide anion radical, systemic inflammation, oxidative stress,
and endothelial injury in endotoxemic rats. Inflamm Res.
59:597–606. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Albini A, Iwamoto Y, Kleinman HK, et al: A
rapid in vitro assay for quantitating the invasive potential of
tumor cells. Cancer Res. 47:3239–3245. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ellerman JE, Brown CK, de Vera M, et al:
Masquerader: high mobility group box-1 and cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
13:2836–2848. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sasahira T, Akama Y, Fujii K and Kuniyasu
H: Expression of receptor for advanced glycation end products and
HMGB1/amphoterin in colorectal adenomas. Virchows Arch.
446:411–415. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ishiguro H, Nakaigawa N, Miyoshi Y, et al:
Receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) and its ligand,
amphoterin are overexpressed and associated with prostate cancer
development. Prostate. 64:92–100. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yao Xingjun, Zhao Gang, Yang Hongfa, et
al: Overexpression of high-mobility group box 1 correlates with
tumor progression and poor prognosis in human colorectal carcinoma.
J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 136:677–684. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Yao X, Zhao G, Yang H, et al:
Overexpression of high-mobility group box 1 correlates with tumor
progression and poor prognosis in human colorectal carcinoma. J
Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 136:677–684. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Srikrishna G and Freeze HH: Endogenous
damage-associated molecular pattern molecules at the crossroads of
inflammation and cancer. Neoplasia. 11:615–28. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Srikrishna G and Freeze HH: Endogenous
damage-associated molecular pattern molecules at the crossroads of
inflammation and cancer. Neoplasia. 11:615–628. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Le Bitoux MA and Stamenkovic I: Tumor-host
interactions: the role of inflammation. Histochem Cell Biol.
6:1079–1090. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Kobayashi H, Shinohara H, Fujie M, et al:
Inhibition of metastasis of Lewis lung carcinoma by urinary trypsin
inhibitor in experimental and spontaneous metastasis models. Int J
Cancer. 63:455–462. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Shu H, Liu K, He Q, et al: Ulinastatin, a
protease inhibitor, may inhibit allogeneic blood
transfusion-associated pro-inflammatory cytokines and systemic
inflammatory response syndrome and improve postoperative recovery.
Blood Transfus. 109–118. 2014.
|
|
45
|
Kobayashi H, Suzuki M, Hirashima Y and
Terao T: The protease inhibitor bikunin, a novel anti-metastatic
agent. Biol Chem. 384:749–754. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Sun ZJ, Yu T, Chen JS, et al: Effects of
ulinastatin and cyclophosphamide on the growth of xenograft breast
cancer and expression of CXC chemokine receptor 4 and matrix
metalloproteinase-9 in cancers. J Int Med Res. 38:967–976. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Palumbo R, Galvez BG, Pusterla T, et al:
Cells migrating to sites of tissue damage in response to the danger
signal HMGB1 require NF-kappaB activation. J Cell Biol. 179:33–40.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wang H, Sun X, Gao F, et al: Effect of
ulinastatin on growth inhibition, apoptosis of breast carcinoma
cells is related to a decrease in signal conduction of JNk-2 and
NF-kappaB. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 31:22012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Brezniceanu ML, Völp K, Bösser S, et al:
HMGB1 inhibits cell death in yeast and mammalian cells and is
abundantly expressed in human breast carcinoma. Faseb J.
17:1295–1297. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Jones LG, Ella KM, Bradshaw CD, et al:
Activations of mitogen-activated protein kinases and phospholipase
D in A7r5 vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem.
269:23790–23799. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Nguyen DH, Catling AD, Webb DJ, et al:
Myosin light chain kinase functions downstream of Ras/ERK to
promote migration of urokinase-type plasminogen
activator-stimulated cells in an integrin-selective manner. J Cell
Biol. 146:149–164. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Olson MF, Ashworth A and Hall A: An
essential role for Rho, Rac, and Cdc42 GTPases in cell cycle
progression through G1. Science. 269:1270–1272. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Kobayashi H, Suzuki M, Kanayama N, et al:
Suppression of urokinase receptor expression by bikunin is
associated with inhibition of upstream targets of extracellular
signal-regulated kinase-dependent cascade. Eur J Biochem.
269:3945–3957. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Kang HJ, Lee H, Choi HJ, et al:
Non-histone nuclear factor HMGB1 is phosphorylated and secreted in
colon cancers. Lab Invest. 89:948–959. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Nishizuka Y: Intracellular signaling by
hydrolysis of phospholipids and activation of protein kinase C.
Science. 5082:607–614. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Paolucci L and Rozengurt E: Protein kinase
D in small cell lung cancer cells: rapid activation through protein
kinase C. Cancer Res. 3:572–577. 1999.
|
|
57
|
Goode N, Hughes K, Woodgett R and Parker
PJ: Differential regulation of glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta by
protein kinase C isotypes. J Biol Chem. 267:16878–16882.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Burgering BM, de Vries-Smits AM, Medema
RH, et al: Epidermal growth factor induces phosphorylation of
extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2 via multiple pathways. Mol
Cell Biol. 13:7248–7256. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Wisniewski JR, Schulze E and Sapetto B:
DNA binding and nuclear translocation of insect
high-mobility-group-protein-1 (HMG1) proteins are inhibited by
phosphorylation. Eur J Biochem. 225:687–693. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Kobayashi H, Suzuki M, Tanaka Y, et al:
Suppression of urokinase expression and invasiveness by urinary
trypsin inhibitor is mediated through inhibition of protein kinase
C- and MEK/ERK/c-Jun-dependent signaling pathways. J Biol Chem.
276:2015–2022. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|