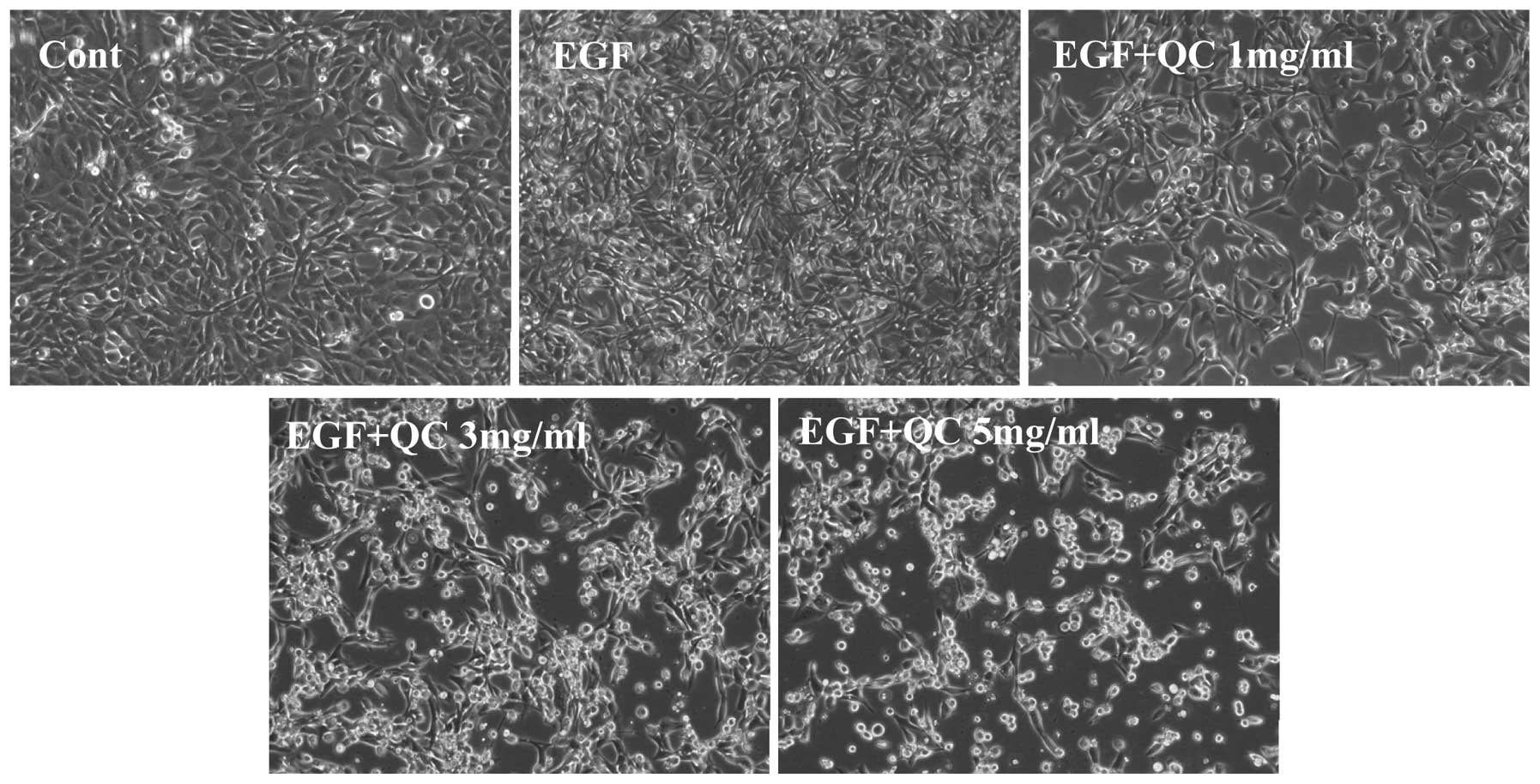
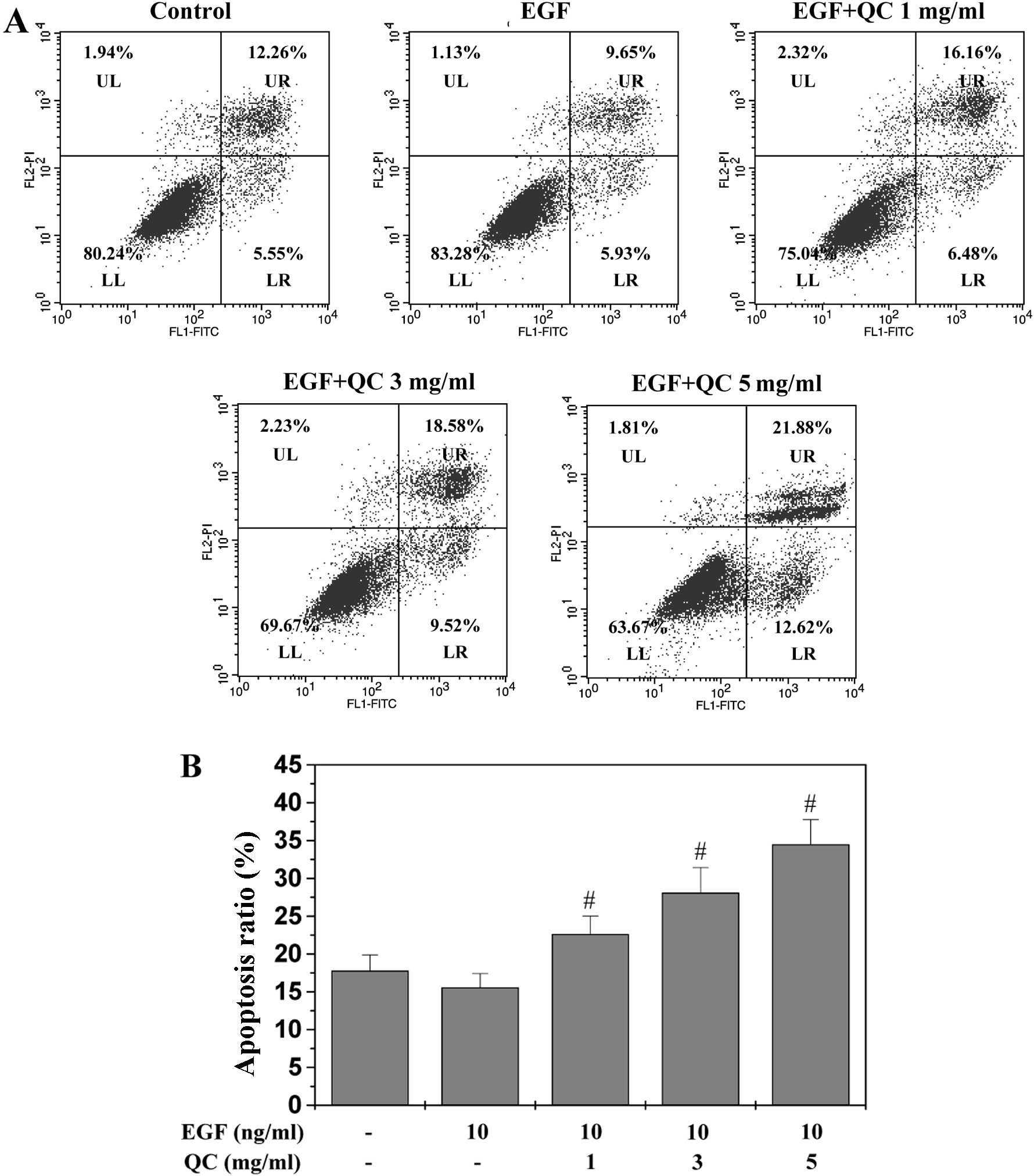
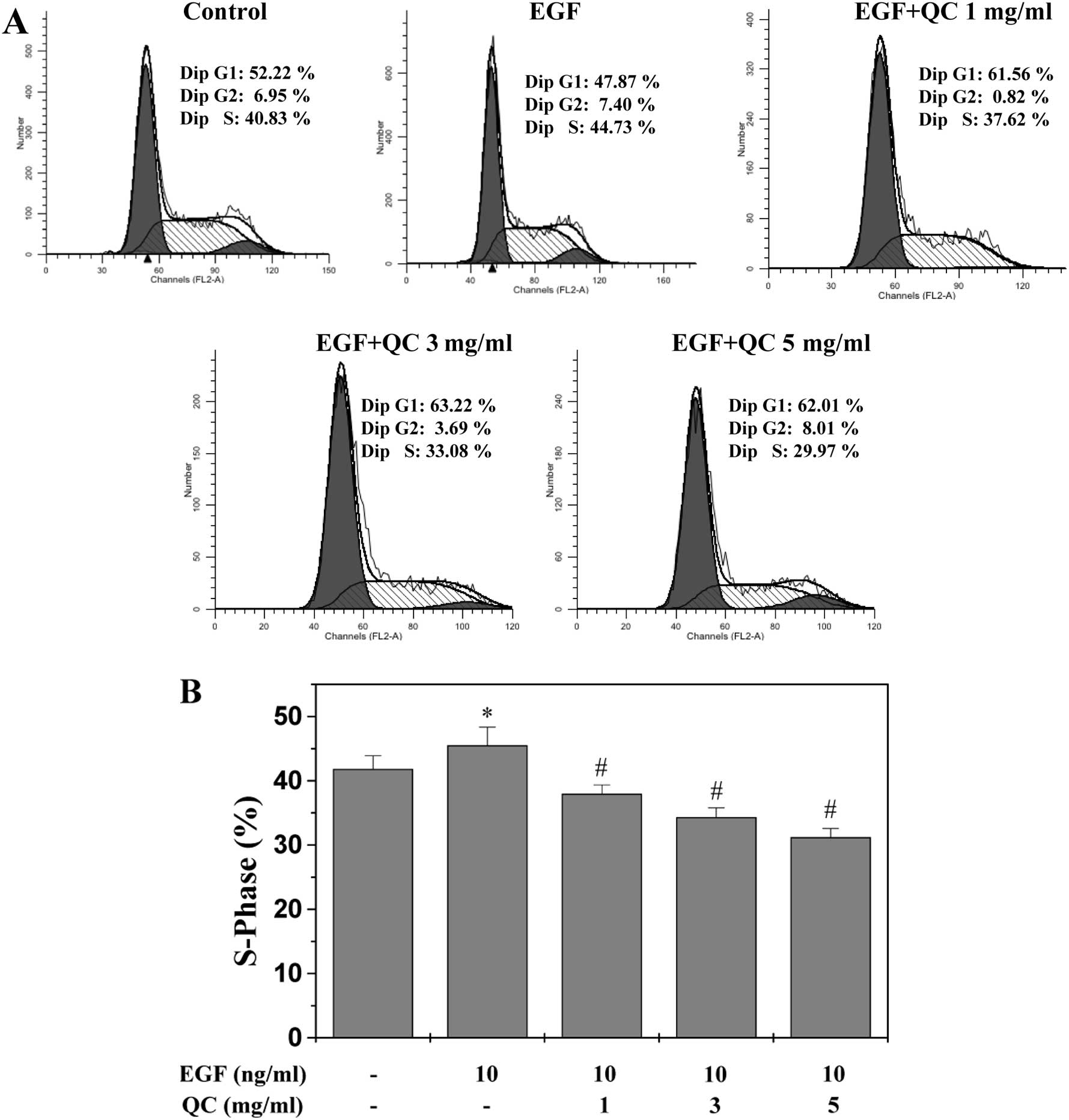
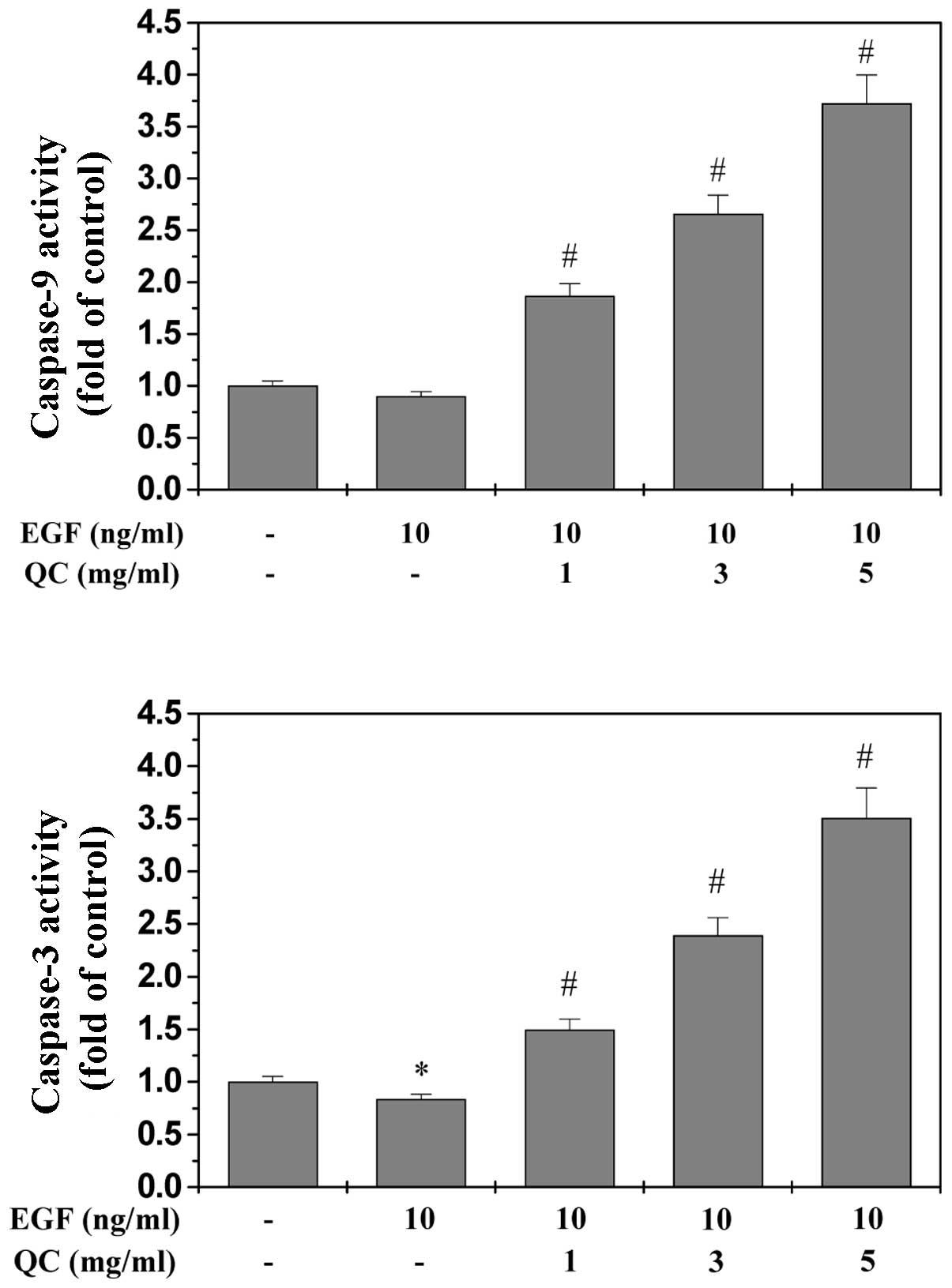
|
1
|
Sirab N, Robert G, Fasolo V, et al:
Lipidosterolic extract of Serenoa repens modulates the expression
of inflammation related-genes inbenign prostatic hyperplasia
epithelial and stromal cells. Int J Mol Sci. 14:14301–14320. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Atawia RT, Tadros MG, Khalifa AE, Mosli HA
and Abdel-Naim AB: Role of the phytoestrogenic, pro-apoptotic and
anti-oxidative properties of silymarin in inhibiting experimental
benign prostatic hyperplasia in rats. Toxicol Lett. 219:160–169.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pollan MC, Benghuzzi HA and Tucci M:
Growth factor expression in early stages of benign prostatic
hyperplasia upon exposure to sustained delivery of androgens.
Biomed Sci Instrum. 39:329–334. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Paolone DR: Benign prostatic hyperplasia.
Clin Geriatr Med. 26:223–239. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Roehrborn CG: Male lower urinary tract
symptoms (LUTS) and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). Med Clin
North Am. 95:87–100. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Gat Y, Gornish M, Heiblum M and Joshua S:
Reversal of benign prostate hyperplasia by selective occlusion of
impaired venous drainage in the male reproductive system: novel
mechanism, new treatment. Andrologia. 40:273–281. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Steiner MS: Review of peptide growth
factors in benign prostatic hyperplasia and urological malignancy.
J Urol. 153:1085–1096. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang Z and Olumi AF: Diabetes, growth
hormone-insulin-like growth factor pathways and association to
benign prostatic hyperplasia. Differentiation. 82:261–271. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Descazeaud A, Weinbreck N, Robert G, et
al: Transforming growth factor β-receptor II protein expression in
benign prostatic hyperplasia is associated with prostate volume and
inflammation. BJU Int. 108:E23–E28. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Voss M, Trojan L, Steidler A, et al: Serum
vascular endothelial growth factor C level in patients with
prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia. Anal Quant Cytol
Histol. 30:199–202. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ma Z, Tsuchiya N, Yuasa T, et al:
Polymorphisms of fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 have
association with the development of prostate cancer and benign
prostatic hyperplasia and the progression of prostate cancer in a
Japanese population. Int J Cancer. 123:2574–2579. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang W, Zhang X, Mize GJ and Takayama TK:
Protease-activated receptor-1 upregulates fibroblast growth factor
7 in stroma of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Prostate.
68:1064–1075. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Haura EB, Turkson J and Jove R: Mechanisms
of disease: Insights into the emerging role of signal transducers
and activators of transcription in cancer. Nat Clin Pract Oncol.
2:315–324. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Siejka A, Schally AV, Block NL and
Barabutis N: Antagonists of growth hormone-releasing hormone
inhibit the proliferation of human benign prostatic hyperplasia
cells. Prostate. 70:1087–1093. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Siejka A, Schally AV, Block NL and
Barabutis N: Mechanisms of inhibition of human benign prostatic
hyperplasia in vitro by the luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone
antagonist cetrorelix. BJU Int. 106:1382–1388. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lin JM, Zhou JH, Xu W, et al: Qianliening
capsule treats benign prostatic hyperplasia via suppression of the
EGF/STAT3 signaling pathway. Exp Ther Med. 5:1293–1300.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lin J, Hong Z, Zhou H, et al: Expression
of the growth factor related to angiogenesis on the prostatic
hyperplasia in rats. J Fujian Univ Tradit Chin Med. 18:63–65.
2008.(In Chinese).
|
|
18
|
bin Jia, Hong Tang, Weimin Li and Wenqing
Cai: The effects of epidermal growth factor on the expression of
Bcl-2, Bax and c-myc in mice prostate cells. Chin J Gerontol.
27:251–252. 2007.(In Chinese).
|
|
19
|
Park OK, Schaefer TS and Nathans D: In
vitro activation of STAT3 by epidermal growth factor receptor
kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 93:13704–13708. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhong Z, Wen Z and Darnell JE Jr: Stat3: a
STAT family member activated by tyrosine phosphorylation in
response to epidermal growth factor and interleukin-6. Science.
264:95–98. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Catlett-Falcone R, Landowski TH, Oshiro
MM, et al: Constitutive activation of Stat3 signaling confers
resistance to apoptosis in human U266 myeloma cells. Immunity.
10:105–115. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Karni R, Jove R and Levitzki A: Inhibition
of pp60c-Src reduces Bcl-XL expression and reverses the transformed
phenotype of cells overexpressing EGF and HER-2 receptors.
Oncogene. 18:4654–4662. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Coqueret O and Gascan H: Functional
interaction of STAT3 transcription factor with the cell cycle
inhibitor p21WAF1/CIP1/SDI1. J Biol Chem. 275:18794–18800. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bienvenu F, Gascan H and Coqueret O:
Cyclin D1 represses STAT3 activation through a Cdk4-independent
mechanism. J Biol Chem. 276:16840–16847. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Huang YP, Du J, Hong ZF, et al: Effects of
Kangquan recipe on sex steroids and cell proliferation in rats with
benign prostatic hyperplasia. Chin J Integr Med. 15:289–292. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Boyle P, Robertson C, Lowe F and Roehrborn
C: Meta-analysis of clinical trials of Permixon in the treatment of
symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia. Urology. 55:533–539.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Vacherot F, Azzouz M, Gil-Diez-De-Medina
S, et al: Induction of apoptosis and inhibition of cell
proliferation by the lipido-sterolic extract of Serenoa repens
(LSESr, Permixon) in benign prostatic hyperplasia. Prostate.
45:259–266. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Quiles MT, Arbós MA, Fraga A, et al:
Antiproliferative and apoptotic effects of the herbal agent Pygeum
africanum on cultured prostate stromal cells from patients with
benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). Prostate. 70:1044–1053. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lin JM, Huang YP, Zhou Jh and Hong ZF:
Therapeutic efficacy of Qianliening capsules in the treatment of
benign prostatic hyperplasia. Asia-Pacific Traditional Medicine.
9:140–143. 2013.(In Chinese).
|
|
30
|
Zhou J, Lin J, Xu W, et al: Qianliening
capsule treats benign prostatic hyperplasia through regulating the
expression of sex hormones, estrogen receptor and androgen
receptor. Afr J Pharm and Pharmacol. 6:173–180. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Zhong X, Lin J, Zhou J, et al: Qianliening
capsule treats benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) by
down-regulating the expression of PCNA, CyclinD1 and CDK4. Afr J
Biotechnol. 11:7731–7737. 2012.
|
|
32
|
Zheng HY, Xu W, Lin JM, Peng J and Hong
ZF: Qianliening capsule treats benign prostatic hyperplasia via
induction of prostatic cell apoptosis. Mol Med Rep. 7:848–854.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hong ZF, Lin JM, Zhong XY, et al:
Qianliening capsule inhibits human prostate cell growth via
induction of the mitochondrion-dependent cell apoptosis. Chin J
Integr Med. 18:824–830. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lin JM, Chen YQ, Cai QY, et al:
Scutellaria barbata D Don inhibits colorectal cancer growth via
suppression of multiple signaling pathways. Integr Cancer Ther.
13:240–248. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Lin JM, Chen YQ, Wei LH, et al: Ursolic
acid promotes colorectal cancer cell apoptosis and inhibits cell
proliferation via modulation of multiple signaling pathways. Inter
J Oncol. 43:1235–1243. 2013.
|
|
36
|
Roehrborn CG, Nuckolls JG, Wei JT, et al:
The benign prostatic hyperplasia registry and patient survey: study
design, methods and patient baseline characteristics. BJU Int.
100:813–819. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Black L, Naslund MJ, Gilbert TD Jr, Davis
EA and Ollendorf DA: An examination of treatment patterns and costs
of care among patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Am J
Manag Care. 12:S99–S110. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Roehrborn C, Boyle P, Nickel JC, Hoefner K
and Andriole G: ARIA3001 ARIA3002 and ARIA3003 Study Investigators:
Efficacy and safety of a dual inhibitor of 5-alpha-reductase types
1 and 2 (dutasteride) in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia.
Urology. 60:434–441. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Roderick MacDonald and Wilt Timothy J:
Alfuzosin for treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms compatible
with benign prostatic hyperplasia: A systematic review of efficacy
and adverse effects. Urology. 66:780–788. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Youle RJ and Strasser A: The BCL-2 protein
family: opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 9:47–59. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Verma V, Sharma V, Singh V, et al:
Labda-8(17),12,14-trien-19-oic acid contained in fruits of
Cupressus sempervirens suppresses benign prostatic hyperplasia in
rat and in vitro human models through inhibition of androgen and
STAT-3 signaling. Phytother Res. 28:1196–203. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|