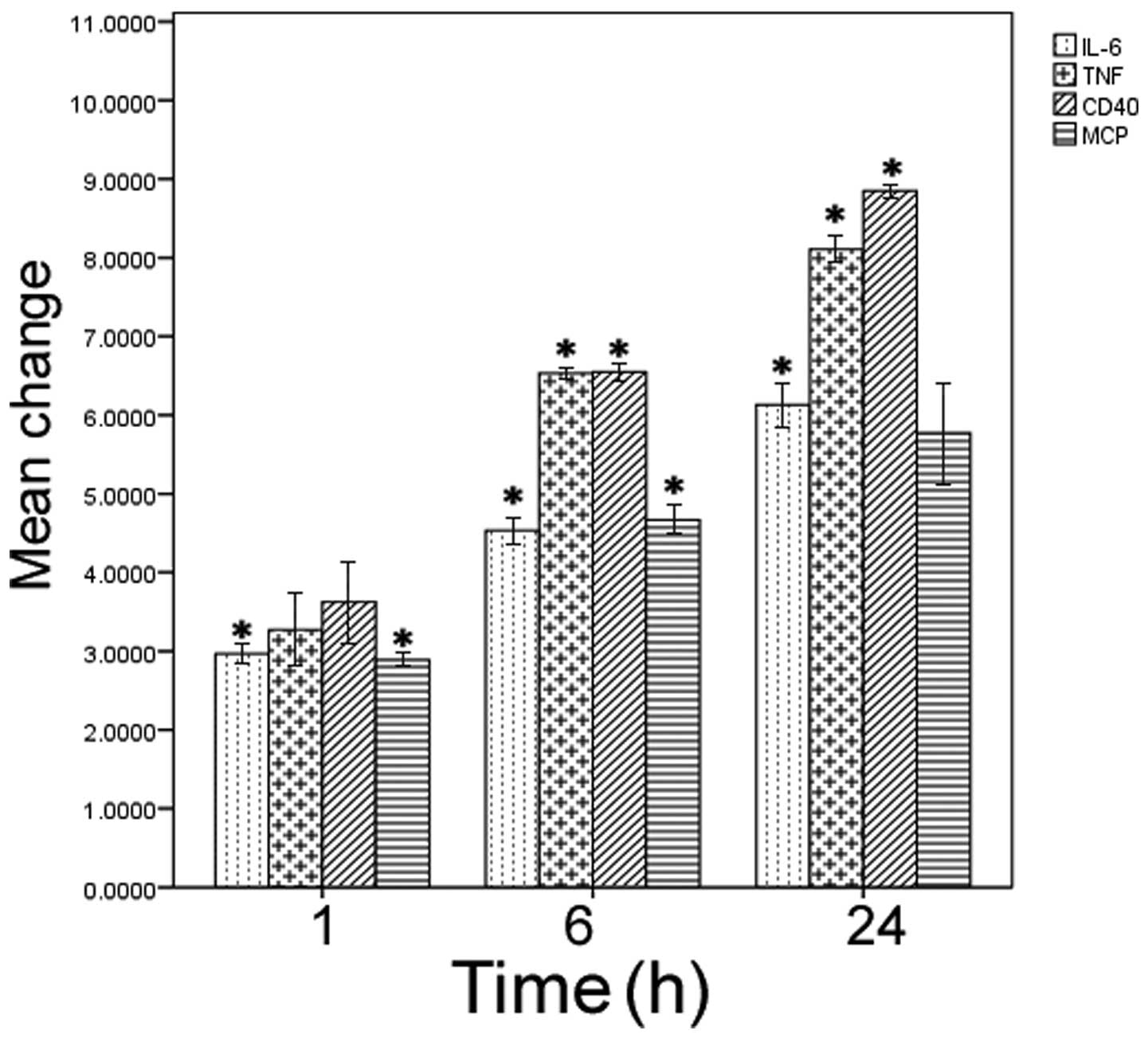
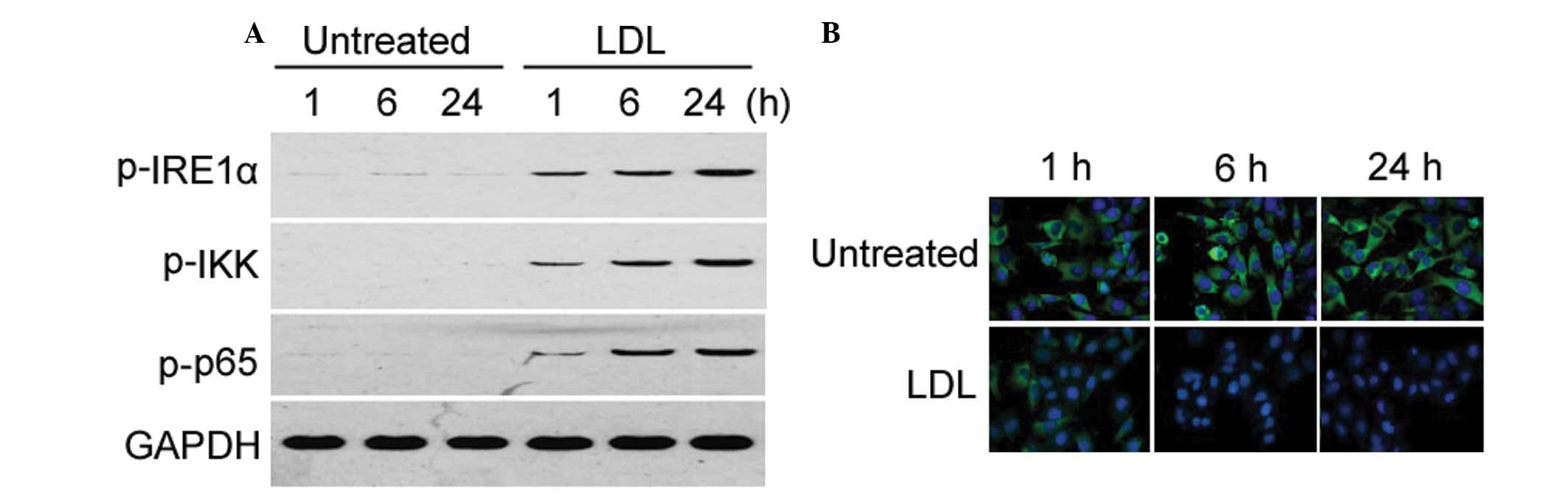
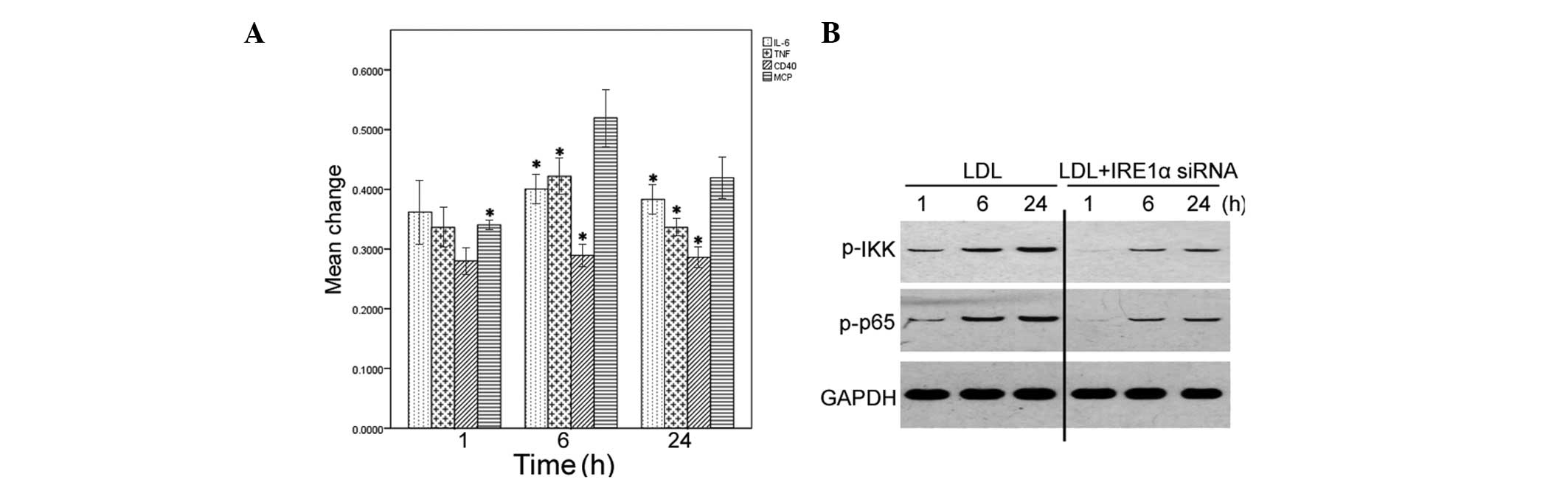
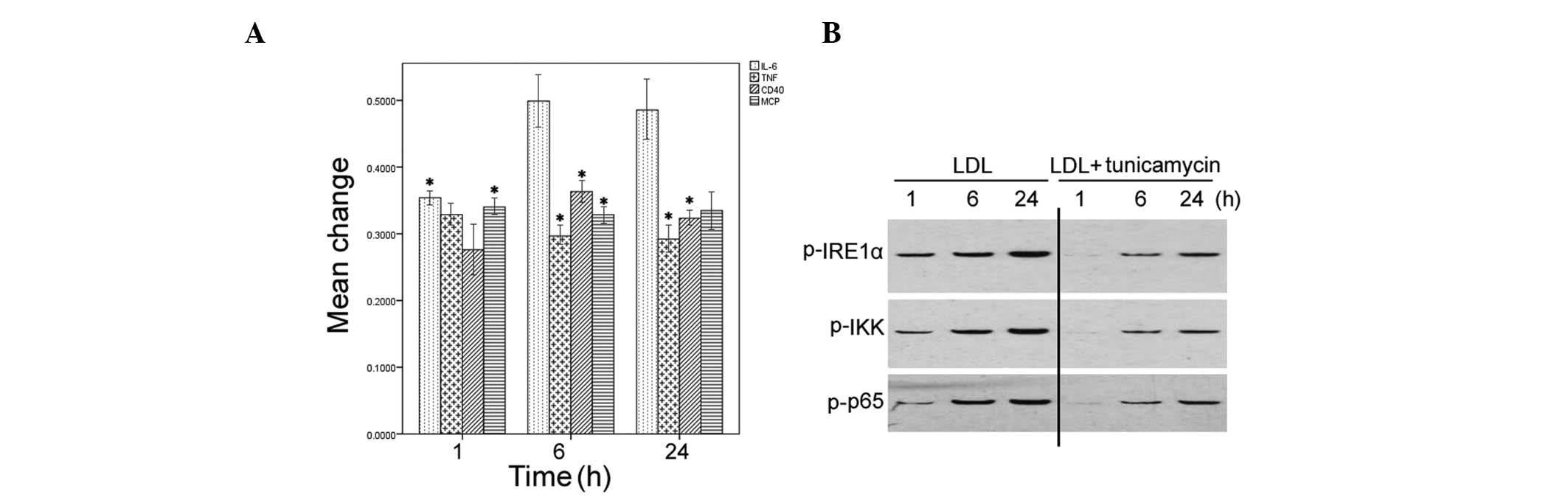
|
1
|
Wakasugi M, Kazama JJ and Narita I:
Differences in the local and national prevalences of chronic kidney
disease based on annual health check program data. Clin Exp
Nephrol. 16:749–754. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Nitta K: Clinical assessment and
management of dyslipidemia in patients with chronic kidney disease.
Clin Exp Nephrol. 16:522–529. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Vaziri ND and Norris K: Lipid disorders
and their relevance to outcomes in chronic kidney disease. Blood
Purif. 31:189–196. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Podrez EA: Anti-oxidant properties of
high-density lipoprotein and atherosclerosis. Clin Exp Pharmacol
Physiol. 37:719–725. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pirillo A, Norata GD and Catapano AL:
LOX-1, OxLDL, and atherosclerosis. Mediators Inflamm.
2013:1527862013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xu C, Bailly-Maitre B and Reed JC:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress: cell life and death decisions. J Clin
Invest. 115:2656–2664. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Inagi R: Endoplasmic reticulum stress as a
progression factor for kidney injury. Curr Opin Pharmacol.
10:156–165. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Dickhout JG and Krepinsky JC: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress and renal disease. Antioxid Redox Signal.
11:2341–2352. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chiang CK, Hsu SP, Wu CT, et al:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress implicated in the development of renal
fibrosis. Mol Med. 17:1295–1305. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li J, Wang JJ and Zhang SX:
Preconditioning with endoplasmic reticulum stress mitigates retinal
endothelial inflammation via activation of X-box binding protein 1.
J Biol Chem. 286:4912–4921. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
11
|
Aminzadeh MA, Sato T and Vaziri ND:
Participation of endoplasmic reticulum stress in the pathogenesis
of spontaneous glomerulosclerosis - role of intra-renal angiotensin
system. Transl Res. 160:309–318. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Inagi R, Kumagai T, Nishi H, et al:
Preconditioning with endoplasmic reticulum stress ameliorates
mesangioproliferative glomerulonephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol.
19:915–922. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cottone S, Lorito MC, Riccobene R, et al:
Oxidative stress, inflammation and cardiovascular disease in
chronic renal failure. J Nephrol. 21:175–179. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Santini E, Lupi R, Baldi S, et al: Effects
of different LDL particles on inflammatory molecules in human
mesangial cells. Diabetologia. 51:2117–2125. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Livak MJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Meng Z, Yan C, Deng Q, et al: Oxidized
low-density lipoprotein induces inflammatory responses in cultured
human mast cells via Toll-like receptor 4. Cell Physiol Biochem.
31:842–853. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
van Tits LJ, Stienstra R, van Lent PL, et
al: Oxidized LDL enhances pro-inflammatory responses of
alternatively activated M2 macrophages: a crucial role for
Krüppel-like factor 2. Atherosclerosis. 214:345–349. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Massy ZA, Kim Y, Guijarro C, et al:
Low-density lipoprotein-induced expression of interleukin-6, a
marker of human mesangial cell inflammation: effects of oxidation
and modulation by lovastatin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
267:536–540. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Antoniades C, Bakogiannis C, Tousoulis D,
Antonopoulos AS and Stefanadis C: The CD40/CD40 ligand system:
linking inflammation with atherothrombosis. J Am Coll Cardiol.
54:669–677. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yellin MJ, D’Agati V, Parkinson G, et al:
Immunohistologic analysis of renal CD40 and CD40L expression in
lupus nephritis and other glomerulonephritides. Arthritis Rheum.
40:124–134. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kuroiwa T, Schlimgen R, Illei GG, McInnes
IB and Boumpas DT: Distinct T cell/renal tubular epithelial cell
interactions define differential chemokine production: implications
for tubulointerstitial injury in chronic glomerulonephritides. J
Immunol. 164:3323–3329. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tanaka T, Kuroiwa T, Ikeuchi H, et al:
Human platelets stimulate mesangial cells to produce monocyte
chemoattractant protein-1 via the CD40/CD40 ligand pathway and may
amplify glomerular injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. 13:2488–2496. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Deambrosis I, Scalabrino E, Deregibus MC,
Camussi G and Bussolati B: CD40-dependent activation of
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT pathway inhibits apoptosis of
human cultured mesangial cells induced by oxidized LDL. Int J
Immunopathol Pharmacol. 18:327–337. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Su J, Zhou L, Kong X, et al: Endoplasmic
reticulum is at the crossroads of autophagy, inflammation, and
apoptosis signaling pathways and participates in the pathogenesis
of diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Res. 2013:1934612013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li J, Wang JJ, Yu Q, Wang M and Zhang SX:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress is implicated in retinal inflammation
and diabetic retinopathy. FEBS Lett. 583:1521–1527. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hayakawa K, Hiramatsu N, Okamura M, et al:
Acquisition of anergy to proinflammatory cytokines in nonimmune
cells through endoplasmic reticulum stress response: a mechanism
for subsidence of inflammation. J Immunol. 182:1182–1191. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gora S, Maouche S, Atout R, et al:
Phospholipolyzed LDL induces an inflammatory response in
endothelial cells through endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling.
FASEB J. 24:3284–3297. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hung CC, Ichimura T, Stevens JL and
Bonventre JV: Protection of renal epithelial cells against
oxidative injury by endoplasmic reticulum stress preconditioning is
mediated by ERK1/2 activation. J Biol Chem. 278:29317–29326. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
So JS, Hur KY, Tarrio M, et al: Silencing
of lipid metabolism genes through IRE1α-mediated mRNA decay lowers
plasma lipids in mice. Cell Metab. 16:487–499. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lee AH, Heidtman K, Hotamisligil GS and
Glimcher LH: Dual and opposing roles of the unfolded protein
response regulated by IRE1alpha and XBP1 in proinsulin processing
and insulin secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:8885–8890. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|