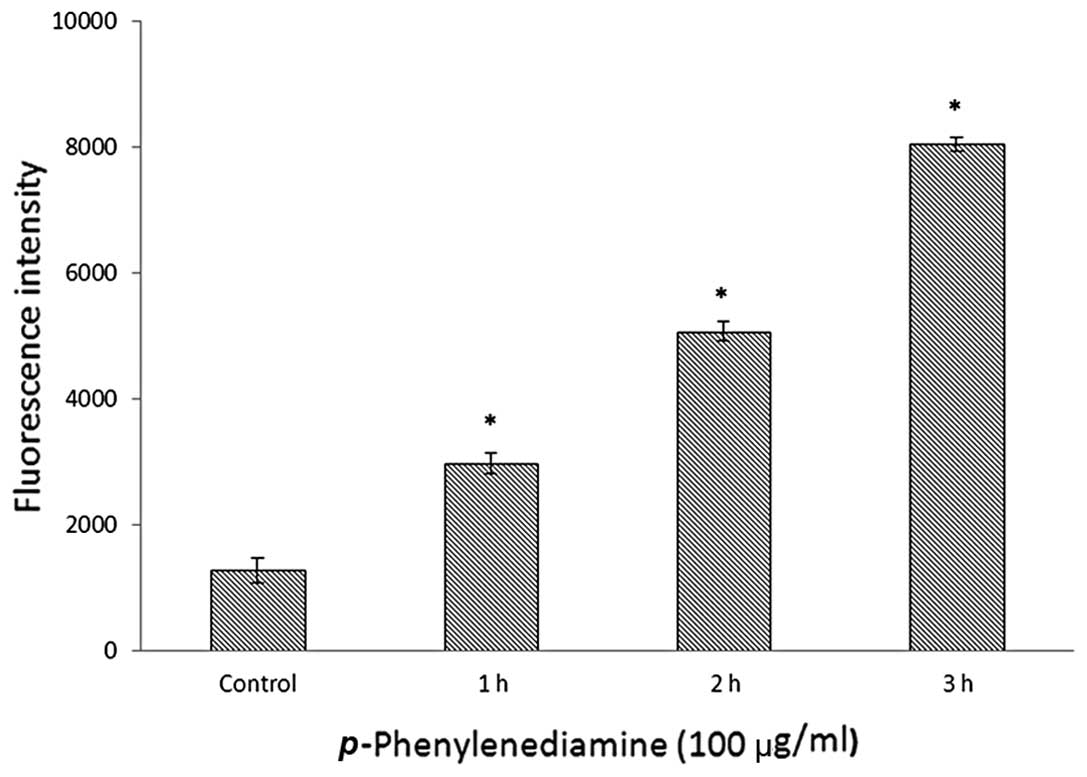
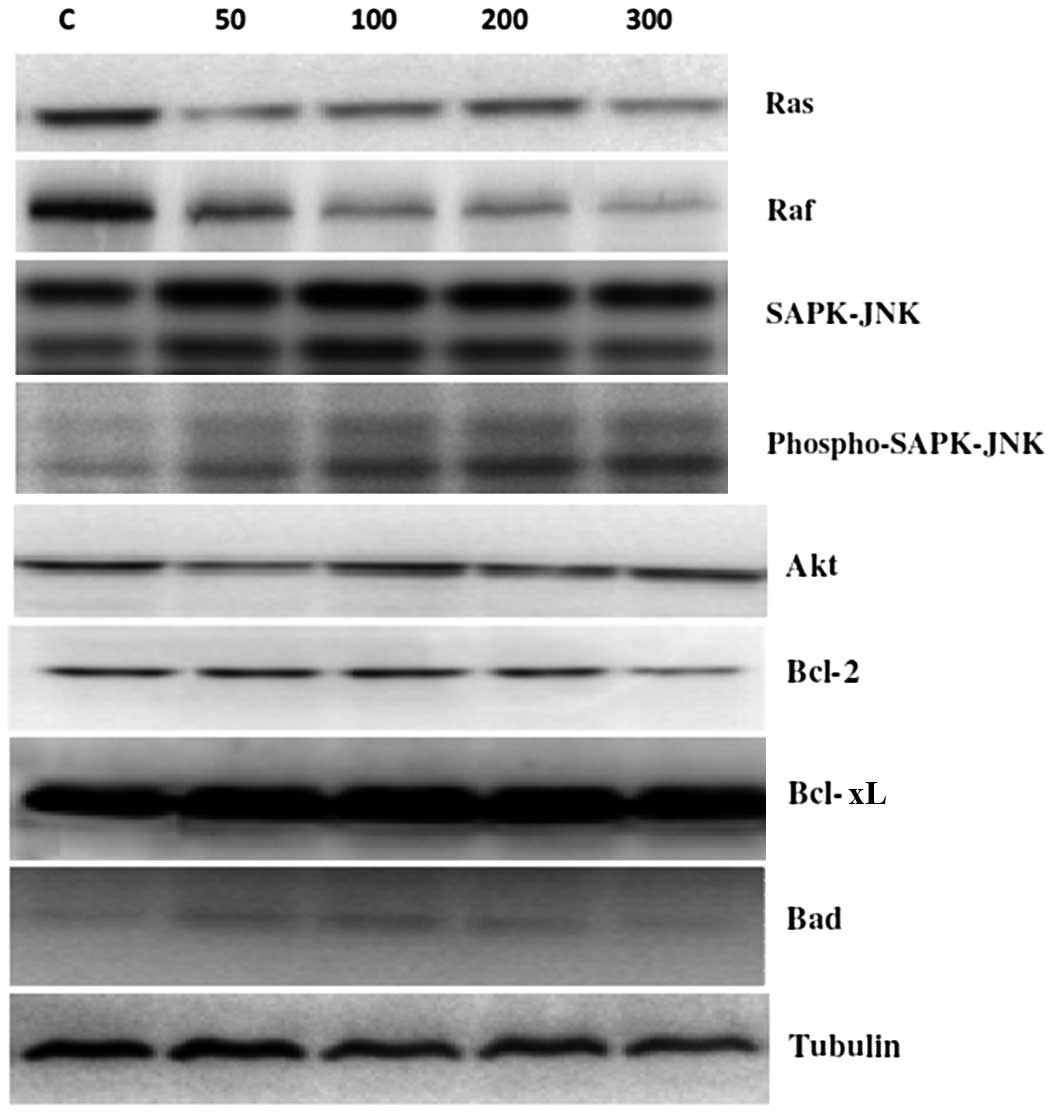
|
1
|
Gago-Dominguez M, Castelao JE, Yuan JM, Yu
MC and Ross RK: Use of permanent hair dyes and bladder-cancer risk.
Int J Cancer. 91:575–579. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chung KT and Stevens SE Jr: Degradation of
azo dyes by environmental microorganisms and helminths. Environ
Toxicol Chem. 12:2121–2132. 1993.
|
|
3
|
Chung KT, Stevens SE Jr and Cerniglia CE:
The reduction of azo dyes by the intestinal microflora. Crit Rev
Microbiol. 18:175–190. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Thun MJ, Altekruse SF, Namboodiri MM,
Calle EE, Myers DG and Heath CW Jr: Hair dye use and risk of fatal
cancers in US women. J Natl Cancer Inst. 86:210–215. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rauscher GH, Shore D and Sandler DP: Hair
dye use and risk of adult acute leukemia. Am J Epidemiol.
160:19–25. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sontag JM: Carcinogenicity of
substituted-benzenediamines (phenylenediamines) in rats and mice. J
Natl Cancer Inst. 66:591–602. 1981.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ding X, Zhu F, Li T, Zhou Q, Hou FF and
Nie J: Numb protects renal proximal tubular cells from puromycin
aminonucleoside-induced apoptosis through inhibiting Notch
signaling pathway. Int J Biol Sci. 7:269–278. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wu CT, Sheu ML, Tsai KS, Weng TI, Chiang
CK and Liu SH: The role of endoplasmic reticulum stress-related
unfolded protein response in the radiocontrast medium-induced renal
tubular cell injury. Toxicol Sci. 114:295–301. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Stupack DG and Cheresh DA: Get a ligand,
get a life: integrins, signaling and cell survival. J Cell Sci.
115:3729–3738. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Guan JL and Shalloway D: Regulation of
focal adhesion-associated protein tyrosine kinase by both cellular
adhesion and oncogenic transformation. Nature. 358:690–692. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Frisch SM, Vuori K, Ruoslahti E and
Chan-Hui PY: Control of adhesion-dependent cell survival by focal
adhesion kinase. J Cell Biol. 134:793–799. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gilmore AP, Metcalfe AD, Romer LH and
Streuli CH: Integrin-mediated survival signals regulate the
apoptotic function of Bax through its conformation and subcellular
localization. J Cell Biol. 149:431–446. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhao JH, Reiske H and Guan JL: Regulation
of the cell cycle by focal adhesion kinase. J Cell Biol.
143:1997–2008. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kurenova E, Xu LH, Yang X, Baldwin AS Jr,
et al: Focal adhesion kinase suppresses apoptosis by binding to the
death domain of receptor-interacting protein. Mol Cell Biol.
24:4361–4371. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Leverrier Y, Thomas J, Mathieu AL, Low W,
Blanquier B and Marvel J: Role of PI3-kinase in Bcl-X induction and
apoptosis inhibition mediated by IL-3 or IGF-1 in Baf-3 cells. Cell
Death Differ. 6:290–296. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lee BH and Ruoslahti E: Alpha5beta1
integrin stimulates Bcl-2 expression and cell survival through Akt,
focal adhesion kinase, and Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent
protein kinase IV. J Cell Biochem. 95:1214–1223. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shaw RJ and Cantley LC: Ras, PI(3)K and
mTOR signalling controls tumour cell growth. Nature. 441:424–430.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Abe M, Suzuki K, Inagaki O, Sassa S and
Shikama H: A novel MPL point mutation resulting in
thrombopoietin-independent activation. Leukemia. 16:1500–1506.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang J, Wu LJ, Tashino S, Onodera S and
Ikejima T: Protein tyrosine kinase pathway-derived ROS/NO
productions contribute to G2/M cell cycle arrest in
evodiamine-treated human cervix carcinoma HeLa cells. Free Radic
Res. 44:792–802. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cheng Y, Qiu F, Ye YC, Tashiro S, Onodera
S and Ikejima T: Oridonin induces G2/M arrest and apoptosis via
activating ERK-p53 apoptotic pathway and inhibiting PTK-Ras-Raf-JNK
survival pathway in murine fibrosarcoma L929 cells. Arch Biochem
Biophys. 490:70–75. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen SC, Chen CH, Chern CL, Hsu LS, Huang
YC, Chung KT and Chye SM: p-Phenylenediamine induces p53-mediated
apoptosis in Mardin-Darby canine kidney cells. Toxicol In Vitro.
20:801–807. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen SC, Chen CH, Tioh YL, Zhong PY, Lin
YS and Chye SM: Para-phenylenediamine induced DNA damage and
apoptosis through oxidative stress and enhanced caspase-8 and -9
activities in Mardin-Darby canine kidney cells. Toxicol In Vitro.
24:1197–1202. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Huang YC, Hung WC, Kang WY, Chen WT and
Chai CY: p-Phenylenediamine induced DNA damage in SV-40
immortalized human uroepithelial cells and expression of mutant p53
and COX-2 proteins. Toxicol Lett. 170:116–123. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pettit GR, Hoard MS, Doubek DL, Schmidt
JM, Pettit RK, Tackett LP and Chapuis JC: Antineoplastic agents
338: The cancer cell growth inhibitory. Constituents of Terminalia
arjuna (Combretaceae). J Ethnopharmacol. 53:57–63. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhu HJ, Wang JS, Guo QL, Jiang Y and Liu
GQ: Reversal of P-glycoprotein mediated multidrug resistance in
K562 cell line by a novel synthetic calmodulin inhibitor, E6. Biol
Pharm Bull. 28:1974–1978. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Haendeler J, Zeiher AM and Dimmeler S:
Vitamin C and E prevent lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis in
human endothelial cells by modulation of Bcl-2 and Bax. Eur J
Pharmacol. 317:407–411. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ernst O and Zor T: Linearization of the
bradford protein assay. J Vis Exp. 38(Pt II): 19182010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Balmain A, Gray J and Ponder B: The
genetics and genomics of cancer. Nat Genet. 33(Suppl): 238–244.
2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: The hallmarks
of cancer. Cell. 100:57–70. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hahn WC and Weinberg RA: Modelling the
molecular circuitry of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:331–341. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sun SY, Hail N Jr and Lotan R: Apoptosis
as a novel target for cancer chemoprevention. J Natl Cancer Inst.
96:662–672. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen S, Xu Y, Xu B, Guo M, Zhang Z, Liu L,
et al: CaMKII is involved in cadmium activation of MAPK and mTOR
pathways leading to neuronal cell death. J Neurochem.
119:1108–1118. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Arbon KS, Christensen CM, Harvey WA and
Heggland SJ: Cadmium exposure activates the ERK signaling pathway
leading to altered osteoblast gene expression and apoptotic death
in Saos-2 cells. Food Chem Toxicol. 50:198–205. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
34
|
Habib GM: Arsenite causes down-regulation
of Akt and c-Fos, cell cycle dysfunction and apoptosis in
glutathione-deficient cells. J Cell Biochem. 110:363–371.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kelsh MA, Alexander DD, Kalmes RM and
Buffler PA: Personal use of hair dyes and risk of bladder cancer: a
meta-analysis of epidemiologic data. Cancer Causes Control.
19:549–558. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
McFadden JP, White IR, Frosch PJ, Sosted
H, Johansen JD and Menne T: Allergy to hair dye. BMJ. 334:2202007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Atukeren P, Yavuz B, Soydinc HO, Purisa S,
Camlica H, Gumustas MK and Balcioglu I: Variations in systemic
biomarkers of oxidative/nitrosative stress and DNA damage before
and during the consequent two cycles of chemotherapy in breast
cancer patients. Clin Chem Lab Med. 48:1487–1495. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zeraatpishe A, Oryan S, Bagheri MH,
Pilevarian AA, et al: Effects of Melissa officinalis L. on
oxidative status and DNA damage in subjects exposed to long-term
low-dose ionizing radiation. Toxicol Ind Health. 27:205–212. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Reddy PH: Amyloid precursor
protein-mediated free radicals and oxidative damage: implications
for the development and progression of Alzheimer’s disease. J
Neurochem. 96:1–13. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Curtin JF, Donovan M and Cotter TG:
Regulation and measurement of oxidative stress in apoptosis. J
Immunol Methods. 265:49–72. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chan PH: Reactive oxygen radicals in
signaling and damage in the ischemic brain. J Cereb Blood Flow
Metab. 21:2–14. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ling YH, Liebes L, Zou Y and Perez-Soler
R: Reactive oxygen species generation and mitochondrial dysfunction
in the apoptotic response to Bortezomib, a novel proteasome
inhibitor, in human H460 non-small cell lung cancer cells. J Biol
Chem. 278:33714–33723. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Qiu JH, Asai A, Chi S, Saito N, Hamada H
and Kirino T: Proteasome inhibitors induce cytochrome
c-caspase-3-like protease-mediated apoptosis in cultured cortical
neurons. J Neurosci. 20:259–265. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Chiarugi P and Cirri P: Redox regulation
of protein tyrosine phosphatases during receptor tyrosine kinase
signal transduction. Trends Biochem Sci. 28:509–514. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Baselga J and Arteaga CL: Critical update
and emerging trends in epidermal growth factor receptor targeting
in cancer. J Clin Oncol. 23:2445–2459. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Khosravi-Far R, Solski PA, Clark GJ, Kinch
MS and Der CJ: Activation of Rac1, RhoA, and mitogen-activated
protein kinases is required for Ras transformation. Mol Cell Biol.
15:6443–6453. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Chen YR, Wang W, Kong AN and Tan TH:
Molecular mechanism of c-Jun N-terminal kinase-mediated apoptosis
induced by anticarcinogenic isothiocyanates. J Biol Chem.
273:1769–1775. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wu K, Zhao Y, Li GC and Yu WP: c-Jun
N-terminal kinase is required for vitamin E succinate-induced
apoptosis in human gastric cancer cells. World J Gastroenterol.
10:1110–1114. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wang TH, Wang HS and Soong YK:
Paclitaxel-induced cell death: where the cell cycle and apoptosis
come together. Cancer. 88:2619–2628. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Sánchez-Pérez I, Martínez-Gomariz M,
Williams D, Keyse SM and Perona R: CL100/MKP-1 modulates JNK
activation and apoptosis in response to cisplatin. Oncogene.
19:5142–5152. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Matsui T and Rosenzweig A: Convergent
signal transduction pathways controlling cardiomyocyte survival and
function: the role of PI3-kinase and Akt. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
38:63–71. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
She QB, Solit DB, Ye Q, O’Reilly KE, Lobo
J and Rosen N: The BAD protein integrates survival signaling by
EGFR/MAPK and PI3K/Akt kinase pathways in PTEN-deficient tumor
cells. Cancer Cell. 8:287–297. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Finucane DM, Bossy-Wetzel E, Waterhouse
NJ, Cotter TG and Green DR: Bax induced caspase activation and
apoptosis via cytochrome c release from mitochondria is inhibitable
by Bcl-xL. J Biol Chem. 274:2225–2233. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Budihardjo I, Oliver H, Lutter M, Luo X
and Wang X: Biochemical pathways of caspase activation during
apoptosis. Ann Rev Cell Dev Biol. 15:269–290. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Desagher S and Martinou JC: Mitochondria
as the central control point of apoptosis. Trends Cell Biol.
10:369–377. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|