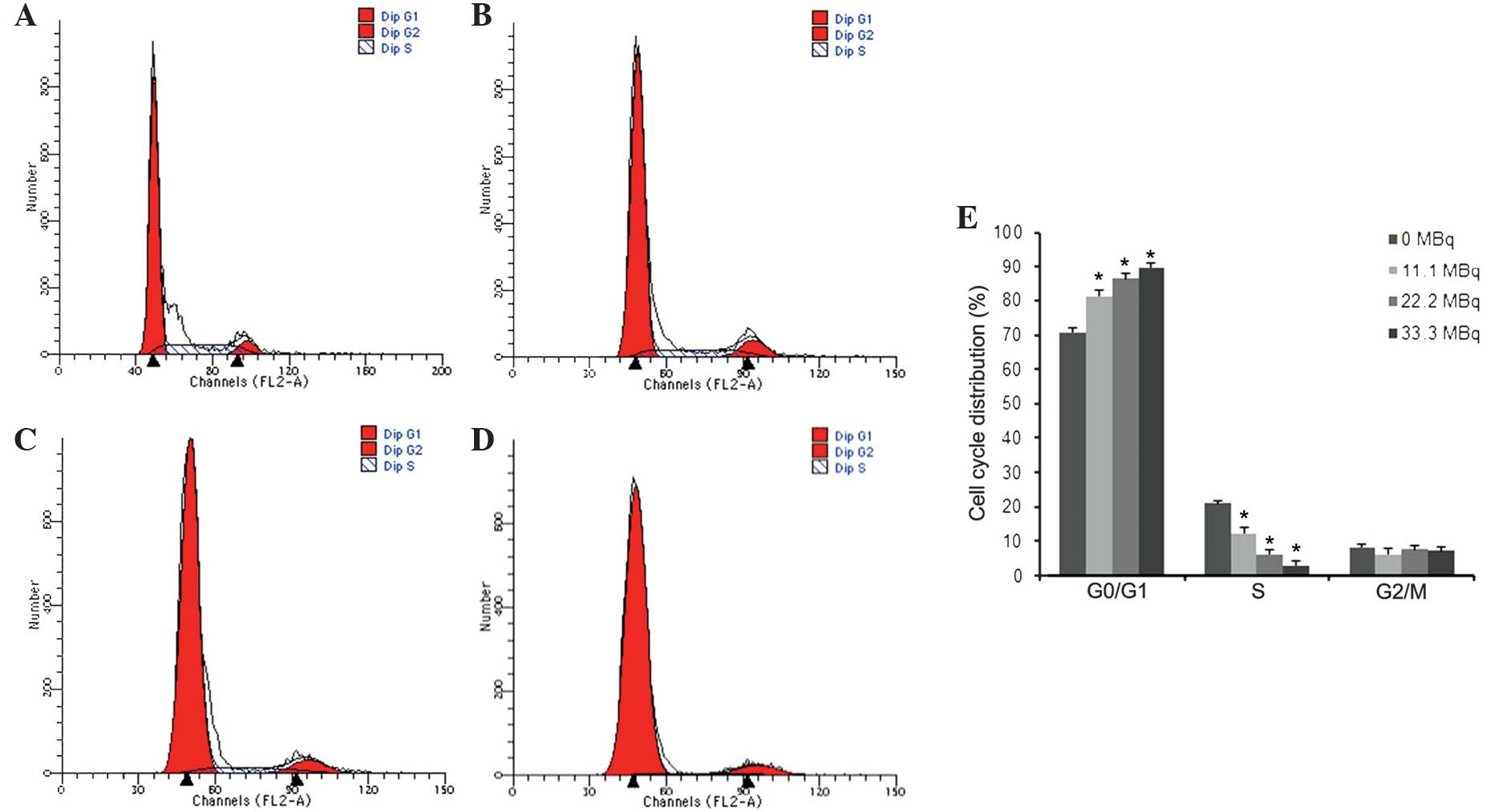
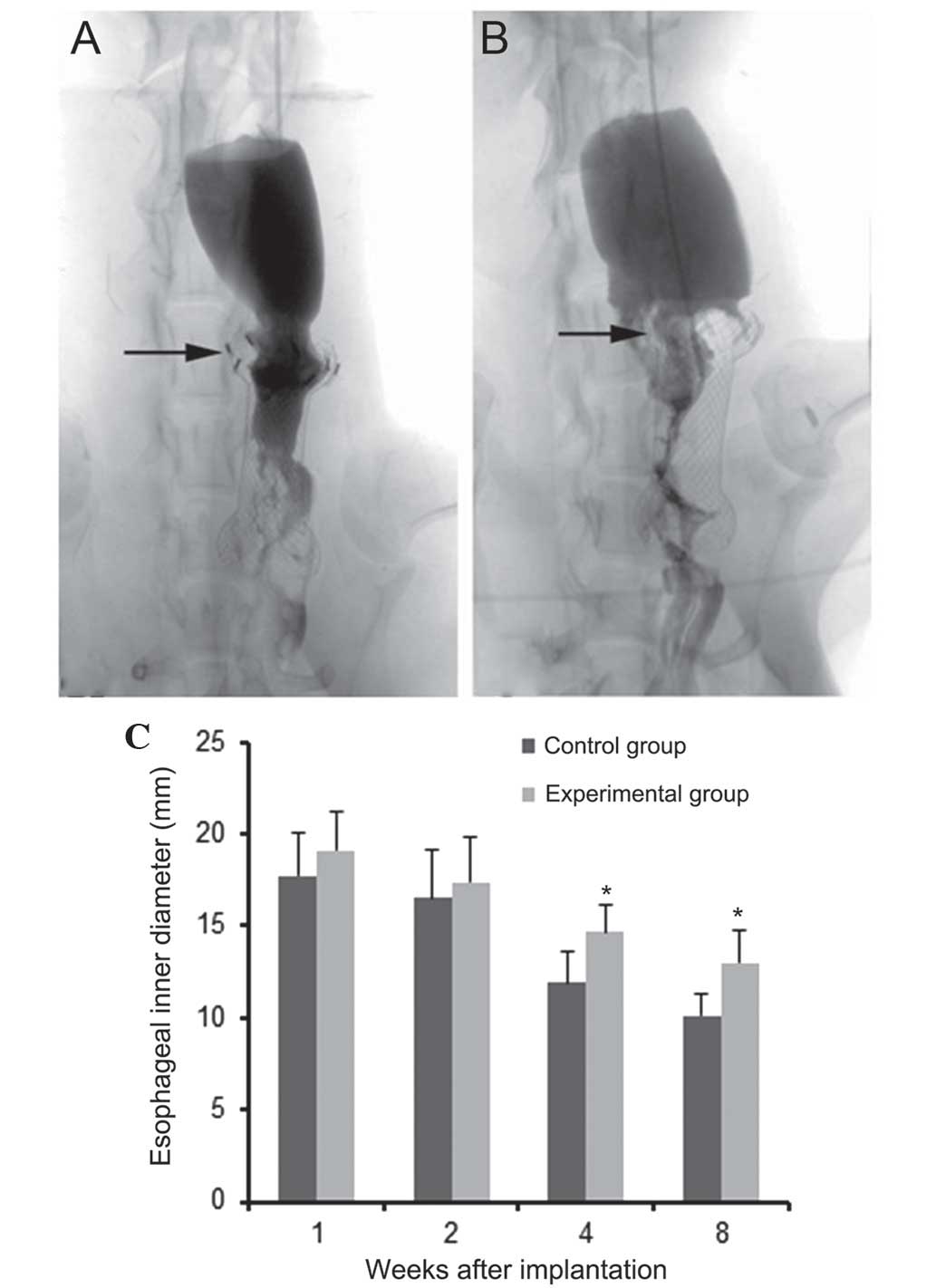
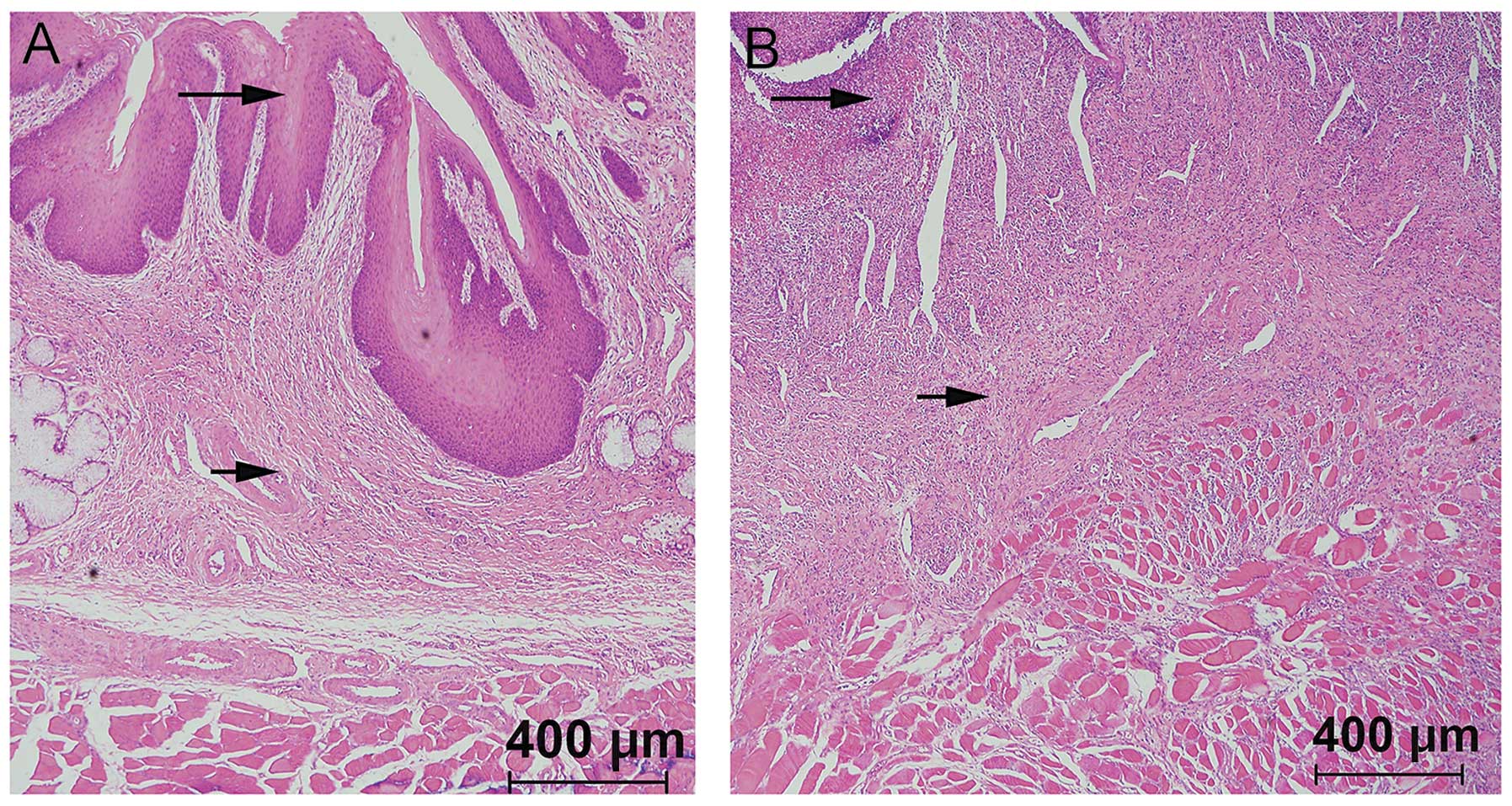
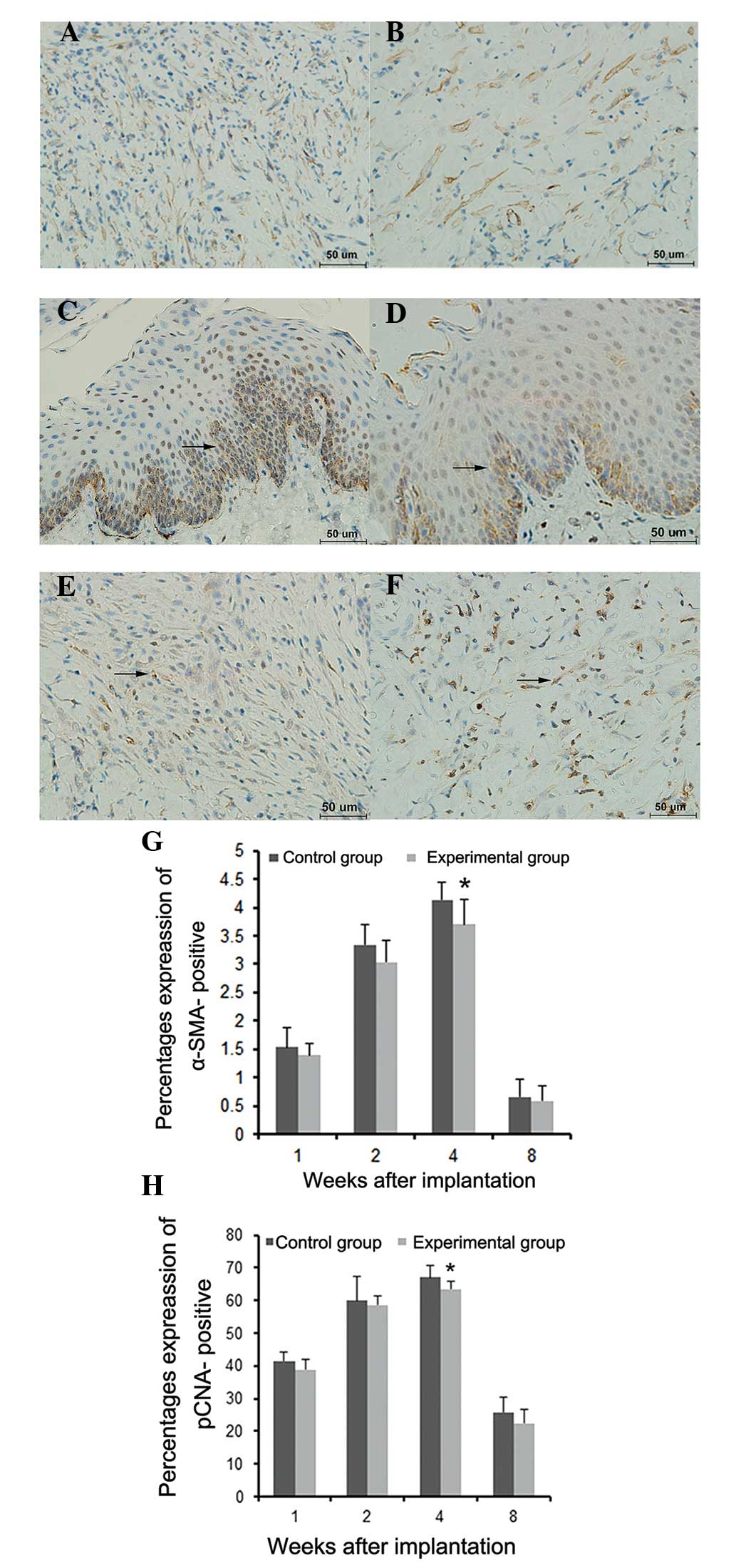
|
1
|
Sharma V, Mahantshetty U, Dinshaw KA,
Deshpande R and Sharma S: Palliation of advanced/recurrent
esophageal carcinoma with high-dose-rate brachytherapy. Int J
Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 52:310–315. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ghosh S, Sau S, Mitra S, Manna A and Ghosh
K: Palliation of dysphagia in advanced, metastatic or recurrent
carcinoma oesophagus with high dose rate intraluminal
brachytherapy-an eastern Indian experience of 35 cases. J Indian
Med Assoc. 110:449–452. 2012.
|
|
3
|
Bhatt L, Tirmazy S and Sothi S:
Intraluminal high-dose-rate brachytherapy for palliation of
dysphagia in cancer of the esophagus: initial experience at a
single UK center. Dis Esophagus. 26:57–60. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Song HY, Do YS, Han YM, et al: Covered,
expandable esophageal metallic stent tubes: experiences in 119
patients. Radiology. 193:689–695. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dua KS, Vleggaar FP, Santharam R and
Siersema PD: Removable self-expanding plastic esophageal stent as a
continuous, non-permanent dilator in treating refractory benign
esophageal strictures: a prospective two-center study. Am J
Gastroenterol. 103:2988–2994. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sreedharan A, Harris K, Crellin A, Forman
D and Everett SM: Interventions for dysphagia in oesophageal
cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. CD0050482009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ernst A, Feller-Kopman D, Becker HD and
Mehta AC: Central airway obstruction. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
169:1278–1297. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Krueger KD, Mitra AK, DelCore MG, Hunter
WJ III and Agrawal DK: A comparison of stent-induced stenosis in
coronary and peripheral arteries. J Clin Pathol. 59:575–579. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bauriedel G, Skowasch D, Jabs A, et al:
Insights into vascular pathology after intracoronary brachytherapy.
Z Kardiol. 91(Suppl 3): 1–9. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Guo JH, Teng GJ, Zhu GY, et al:
Self-expandable esophageal stent loaded with 125I seeds: initial
experience in patients with advanced esophageal cancer. Radiology.
247:574–581. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Guo JH, Teng GJ, Zhu GY, He SC, Deng G and
He J: Self-expandable stent loaded with 125I seeds: feasibility and
safety in a rabbit model. Eur J Radiol. 61:356–361. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Mayoral W, Fleischer D, Salcedo J, Roy P,
Al-Kawas F and Benjamin S: Nonmalignant obstruction is a common
problem with metal stents in the treatment of esophageal cancer.
Gastrointest Endosc. 51:556–559. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kim JH, Song HY, Choi EK, Kim KR, Shin JH
and Lim JO: Temporary metallic stent placement in the treatment of
refractory benign esophageal strictures: results and factors
associated with outcome in 55 patients. Eur Radiol. 19:384–390.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Albiero R, Adamian M, Kobayashi N, et al:
Short- and intermediate-term results of (32) P radioactive
beta-emitting stent implantation in patients with coronary artery
disease: The Milan Dose-Response Study. Circulation. 101:18–26.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fareh J, Martel R, Kermani P and Leclerc
G: Cellular effects of beta-particle delivery on vascular smooth
muscle cells and endothelial cells: a dose-response study.
Circulation. 99:1477–1484. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
John M, Shroff S, Farb A and Virmani R:
Local arterial responses to 32P beta-emitting stents. Cardiovasc
Radiat Med. 2:143–150. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Teirstein PS: Prevention of vascular
restenosis with radiation. Tex Heart Inst J. 25:30–33.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Williams DO: Radiation vascular therapy: a
novel approach to preventing restenosis. Am J Cardiol. 81:18E–20E.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ishiwata S, Robinson K, Chronos N, Crocker
IR and King SB III: Irradiation and postangioplasty restenosis: a
recent overview. Jpn Heart J. 41:541–570. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Marzocchi A, Marrozzini C, Piovaccari G,
et al: Restenosis after coronary angioplasty: its pathogenesis and
prevention. Cardiologia. 36(12 Suppl 1): 309–320. 1991.(In
Italian). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen H, Bao Y, Yu L, Jia R, Cheng W and
Shao C: Comparison of cellular damage response to low-dose-rate
125I seed irradiation and high-dose-rate gamma irradiation in human
lung cancer cells. Brachytherapy. 11:149–156. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Zhuang HQ, Wang JJ, Liao AY, Wang JD and
Zhao Y: The biological effect of 125I seed continuous low dose rate
irradiation in CL187 cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 28:122009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liao A, Wang J, Wang J, Zhuang H and Zhao
Y: Relative biological effectiveness and cell-killing efficacy of
continuous low-dose-rate 125I seeds on prostate carcinoma cells in
vitro. Integr Cancer Ther. 9:59–65. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zamorano L, Yakar D, Dujovny M, Sheehan M
and Kim J: Permanent iodine-125 implant and external beam radiation
therapy for the treatment of malignant brain tumors. Stereotact
Funct Neurosurg. 59:183–192. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ma ZH, Yang Y, Zou L and Luo KY: 125I seed
irradiation induces up-regulation of the genes associated with
apoptosis and cell cycle arrest and inhibits growth of gastric
cancer xenografts. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 31:612012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Goodpaster T, Legesse-Miller A, Hameed MR,
Aisner SC, Randolph-Habecker J and Coller HA: An
immunohistochemical method for identifying fibroblasts in
formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue. J Histochem Cytochem.
56:347–358. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Aird EG, Folkard M, Mayes CR, Bownes PJ,
Lawson JM and Joiner MC: A purpose-built iodine-125 irradiation
plaque for low dose rate low energy irradiation of cell lines in
vitro. Br J Radiol. 74:56–61. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Macheboeuf M, Basset J, Barbu E, Le Saget
M and Nunez G: Effect of pressure on the hydrolysis of proteins by
acids or alkalis. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 144:962–964. 1950.(In
French). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Meredith WJ: Radium dosage-The Marchester
system. E&S Livingstone Ltd; Edinburgh: 1947
|
|
30
|
He QM and Wu XT: Experimental study on
apoptosis of gastric cancer cell line MKN45 induced by continuous
irradiation from iodine-125seeds. J Sichuan Univ Med Sci Ed.
40:454–458. 2009.(In Chinese).
|
|
31
|
Wang J, Zhang H, Zhuang H, Zhao Y and Liao
A: Development and validation of radioactive iodine-125 irradiator
in vitro. Chin J Radiol Med Protect. 27:267–271. 2007.
|
|
32
|
Vávrová J, Rezácová M, Vokurková D and
Psutka J: Cell cycle alteration, apoptosis and response of leukemic
cell lines to gamma radiation with high- and low-dose rate. Physiol
Res. 53:335–342. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mirzaie-Joniani H, Eriksson D, Johansson
A, et al: Apoptosis in HeLa Hep2 cells is induced by low-dose,
low-dose-rate radiation. Radiat Res. 158:634–640. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang YE, Xu ZD and Wang XH: Dynamic
changes in extracellular matrix and related interstitial calls in
experimental organ sclerosis. Chin J Pathol. 23:111–114. 1994.(In
Chinese).
|
|
35
|
Kovacs EJ and DiPietro LA: Fibrogenic
cytokines and connective tissue production. FASEB J. 8:854–861.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|