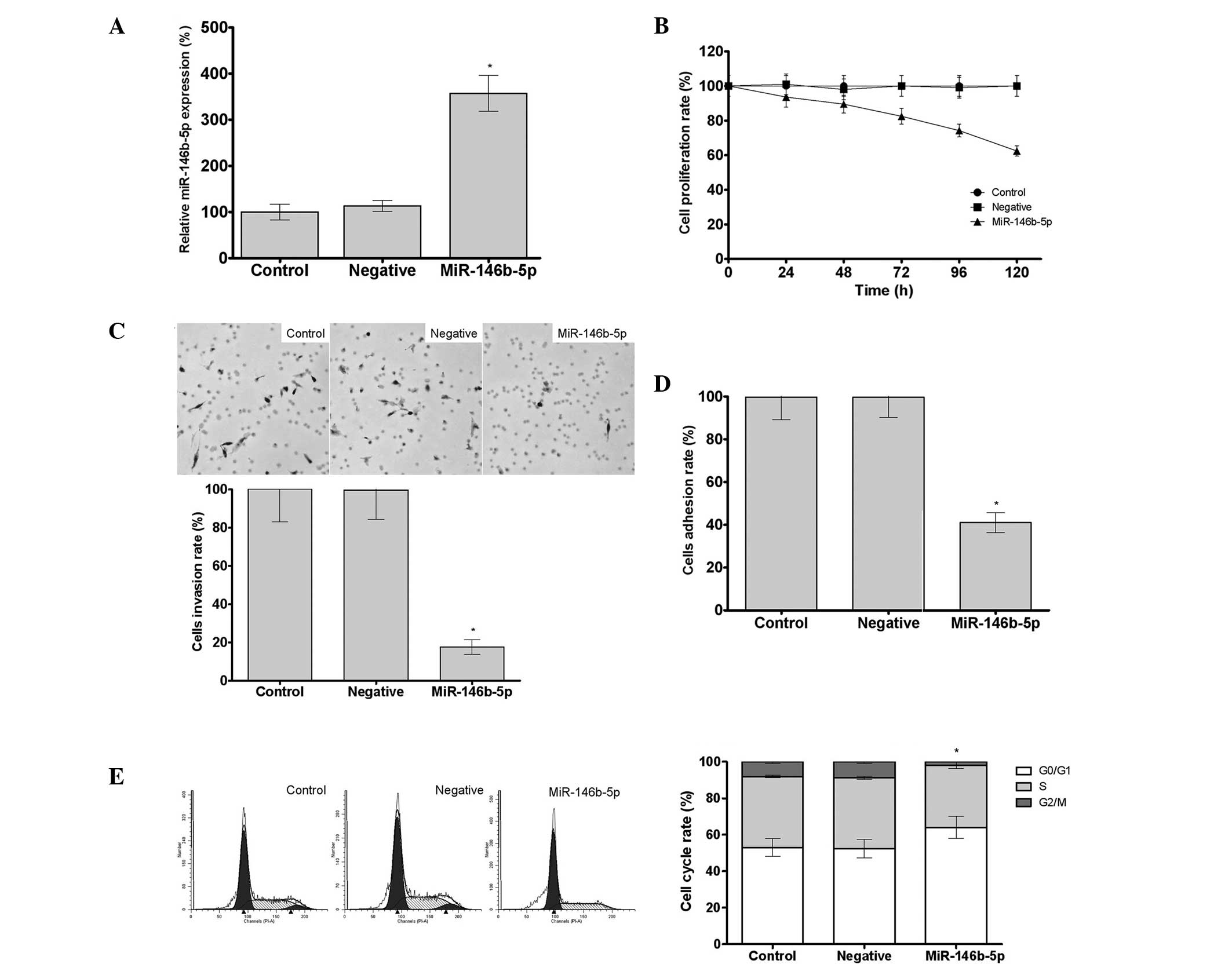
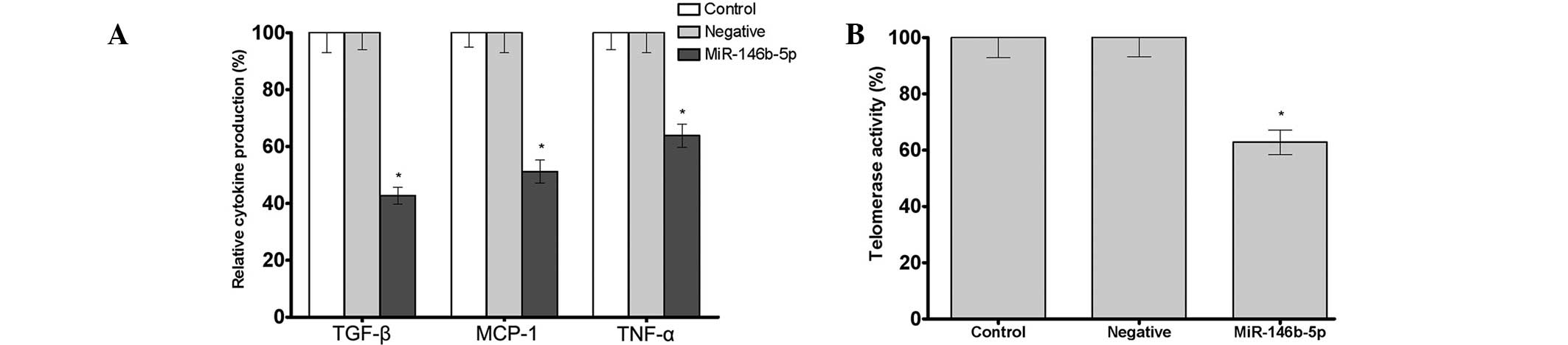
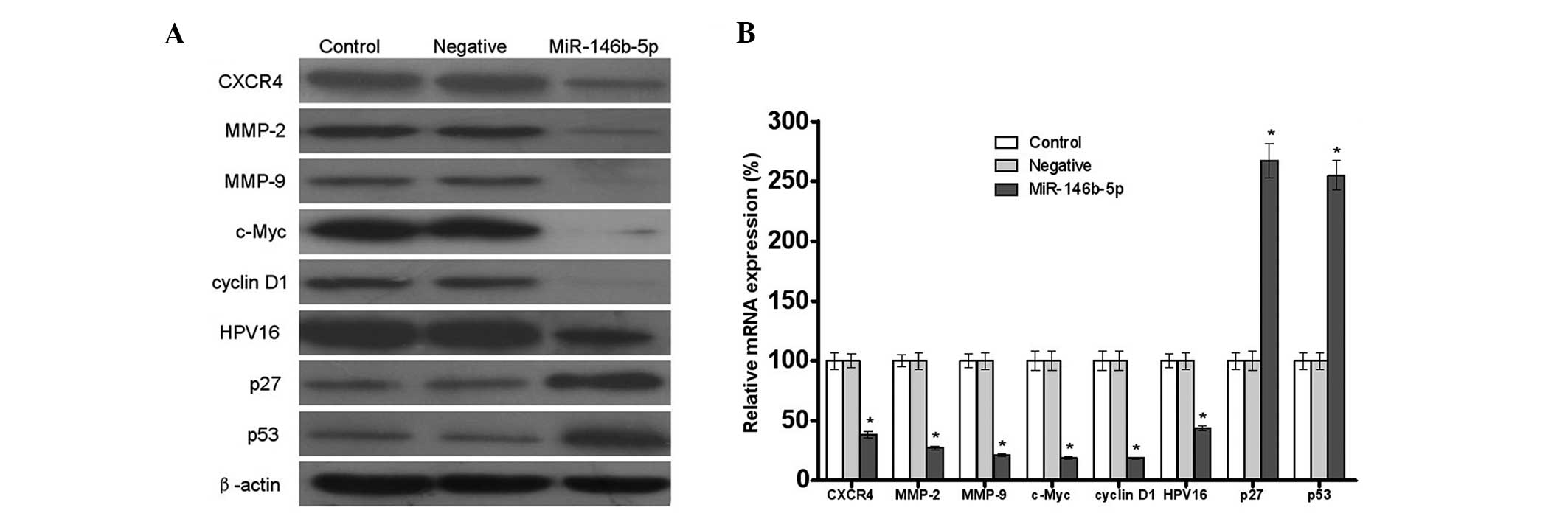
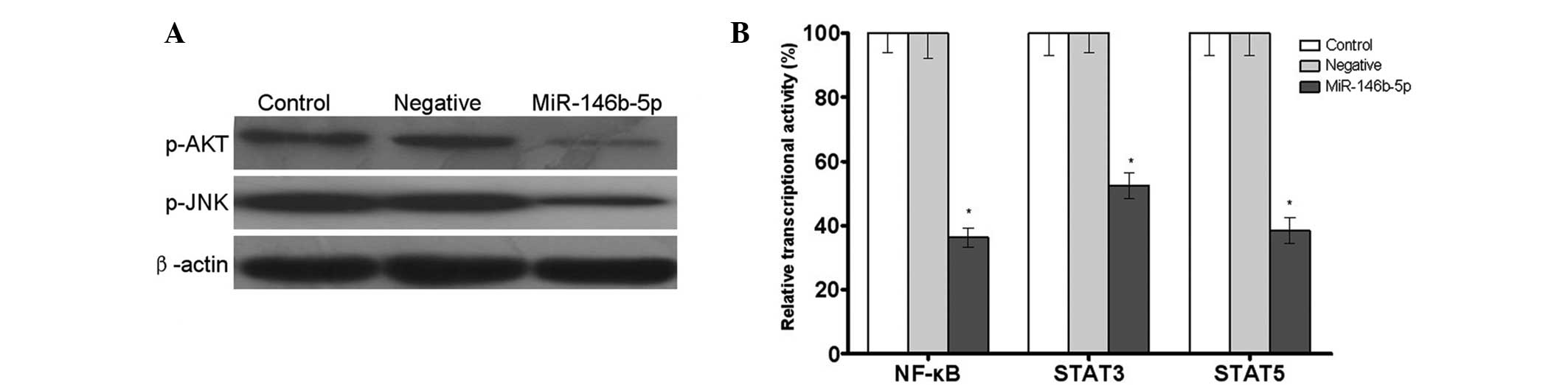
|
1
|
Sriplung H, Singkham P, Iamsirithaworn S,
Jiraphongsa C and Bilheem S: Success of a cervical cancer screening
program: trends in incidence in songkhla, southern Thailand,
1989–2010, and prediction of future incidences to 2030. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 15:10003–10008. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Üreyen I, Aksoy Ü, Dündar B, Tapisiz ÖL,
Karalök MA, Turan AT, Boran N and Tulunay HG: Does lymph node
involvement affect the patterns of recurrence in stage IB cervical
cancer? Turk J Med Sci. 44:844–852. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chawla N, Breen N, Liu B, Lee R and
Kagawa-Singer M: Asian American Women in California: a pooled
analysis of predictors for breast and cervical cancer screening. Am
J Public Health. 18:e1–e12. 2014.
|
|
4
|
Li C, Ma C, Zhang W and Wang J: The immune
function differences and high-risk human papillomavirus infection
in the progress of cervical cancer. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol.
5:557–561. 2014.
|
|
5
|
Bai LX, Wang JT, Ding L, Jiang SW, Kang
HJ, Gao CF, Chen X, Chen C and Zhou Q: Folate deficiency and FHIT
hypermethylation and HPV 16 infection promote cervical
cancerization. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 21:9313–9317. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
García-Zepeda SP, García-Villa E,
Díaz-Chávez J, Hernández-Pando R and Gariglio P: Resveratrol
induces cell death in cervical cancer cells through apoptosis and
autophagy. Eur J Cancer Prev. 22:577–584. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gocze K, Gombos K, Kovacs K, Juhasz K,
Gocze P and Kiss I: MicroRNA expressions in HPV-induced cervical
dysplasia and cancer. Anticancer Res. 1:523–530. 2015.
|
|
8
|
Shishodia G, Verma G, Srivastava Y,
Mehrotra R, Das BC and Bharti AC: Deregulation of microRNAs Let-7a
and miR-21 mediate aberrant STAT3 signaling during human
papillomavirus-induced cervical carcinogenesis: role of E6
oncoprotein. BMC Cancer. 14:9962014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ribeiro J and Sousa H: MicroRNAs as
biomarkers of cervical cancer development: a literature review on
miR-125b and miR-34a. Mol Biol Rep. 3:1525–1531. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Wang X, Wang HK, Li Y, Hafner M, Banerjee
NS, Tang S, Briskin D, Meyers C, Chow LT, et al: MicroRNAs are
biomarkers of oncogenic human papillomavirus infections. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 11:4262–4267. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Kutty RK, Nagineni CN, Samuel W,
Vijayasarathy C, Jaworski C, Duncan T, Cameron JE, Flemington EK,
Hooks JJ and Redmond TM: Differential regulation of microRNA-146a
and microRNA-146b-5p in human retinal pigment epithelial cells by
interleukin-1β, tumor necrosis factor-α, and interferon-γ. Mol Vis.
19:737–750. 2013.
|
|
12
|
Li Y, Wang Y, Yu L, Sun C, Cheng D, Yu S,
Wang Q, Yan Y, Kang C, Jin S, An T, Shi C, Xu J, Wei C, Liu J, Sun
J, Wen Y, Zhao S and Kong Y: miR-146b-5p inhibits glioma migration
and invasion by targeting MMP16. Cancer Lett. 339:260–269. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bergot AS, Ford N, Leggatt GR, Wells JW,
Frazer IH and Grimbaldeston MA: HPV16-E7 expression in squamous
epithelium creates a local immune suppressive environment via CCL2-
and CCL5- mediated recruitment of mast cells. PLoS Pathog.
10:e10044662014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yu Y, Zhang Y and Zhang S: MicroRNA-92
regulates cervical tumorigenesis and its expression is upregulated
by human papilloma virus-16 E6 in cervical cancer cells. Oncol
Lett. 6:468–474. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhu Y, Zhang L, Zhang GD, Wang HO, Liu MY,
Jiang Y, Qi LS, Li Q and Yang P: Potential mechanisms of benzyl
isothiocyanate suppression of invasion and angiogenesis by the
U87MG human glioma cell line. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
19:8225–8228. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Li J, Jiang K, Qiu X, Li M, Hao Q, Wei L,
Zhang W, Chen B and Xin X: Overexpression of CXCR4 is significantly
associated with cisplatin-based chemotherapy resistance and can be
a prognostic factor in epithelial ovarian cancer. BMB Rep.
47:33–38. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
17
|
Nowak E, Galilejczyk A, Sypniewski D and
Bednarek I: MMP-9 directed shRNAs as relevant inhibitors of matrix
metalloproteinase 9 activity and signaling. Postepy Hig Med Dosw
(Online). 67:742–749. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Gutschalk CM, Yanamandra AK, Linde N,
Meides A, Depner S and Mueller MM: GM-CSF enhances tumor invasion
by elevated MMP-2, -9, and -26 expression. Cancer Med. 2:117–129.
2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fan X, Wu W, Shi H and Han J: RNA
interference targeting CD147 inhibits the invasion of human
cervical squamous carcinoma cells by downregulating MMP-9. Cell
Biol Int. 37:737–741. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhu Y, Zhu L, Lu L, Zhang L, Zhang G, Wang
Q and Yang P: Role and mechanism of the alkylglycerone phosphate
synthase in suppressing the invasion potential of human glioma and
hepatic carcinoma cells in vitro. Oncol Rep. 1:431–436. 2014.
|
|
21
|
Kuroda H, Jomen W, Miura S, Arihara Y,
Yamada M, Hirako T, Abe T, Sakurai T, Fujii S, Maeda M, et al:
Bendamustine-rituximab therapy is effective for transformed
follicular lymphoma with significant expression of p53. Gan To
Kagaku Ryoho. 40:1055–1058. 2013.(In Japanese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang M, Li J, Wang L, Tian Z, Zhang P, Xu
Q, Zhang C, Wei F and Chen W: Prognostic significance of p21, p27
and survivin protein expression in patients with oral squamous cell
carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 6:381–386. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Portari EA, Russomano FB, de Camargo MJ,
Machado Gayer CR, da Rocha Guillobel HC, Santos-Rebouças CB and
Brito Macedo JM: Immunohistochemical expression of cyclin D1,
p16Ink4a, p21WAF1, and Ki-67 correlates with the severity of
cervical neoplasia. Int J Gynecol Pathol. 32:501–508. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sui X, Kong N, Wang Z and Pan H:
Epigenetic regulation of the human telomerase reverse transciptase
gene: A potential therapeutic target for the treatment of leukemia
(Review). Oncol Lett. 6:317–322. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kim MS, Bak Y, Park YS, Lee DH, Kim JH,
Kang JW, Song HH, Oh SR and Yoon do Y: Wogonin induces apoptosis by
suppressing E6 and E7 expressions and activating intrinsic
signaling pathways in HPV-16 cervical cancer cells. Cell Biol
Toxicol. 29:259–272. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Almajhdi FN, Senger T, Amer HM, Gissmann L
and Ohlschläger P: Design of a highly effective therapeutic HPV16
E6/E7-Specific DNA vaccine: Optimization by different ways of
sequence rearrangements (shuffling). PLoS One. 9:e1134612014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Masuda S, Kumano K, Shimizu K, Imai Y,
Kurokawa M, Ogawa S, Miyagishi M, Taira K, Hirai H and Chiba S:
Notch1 oncoprotein antagonizes TGF-beta/Smad-mediated cell growth
suppression via sequestration of coactivator p300. Cancer Sci.
96:274–282. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bhaumik D, Scott GK, Schokrpur S, Patil
CK, Campisi J and Benz CC: Expression of microRNA-146 suppresses
NF-kappaB activity with reduction of metastatic potential in breast
cancer cells. Oncogene. 27:5643–5647. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Geraldo MV, Yamashita AS and Kimura ET:
MicroRNA miR-146b-5p regulates signal transduction of TGF-β by
repressing SMAD4 in thyroid cancer. Oncogene. 31:1910–1922. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|