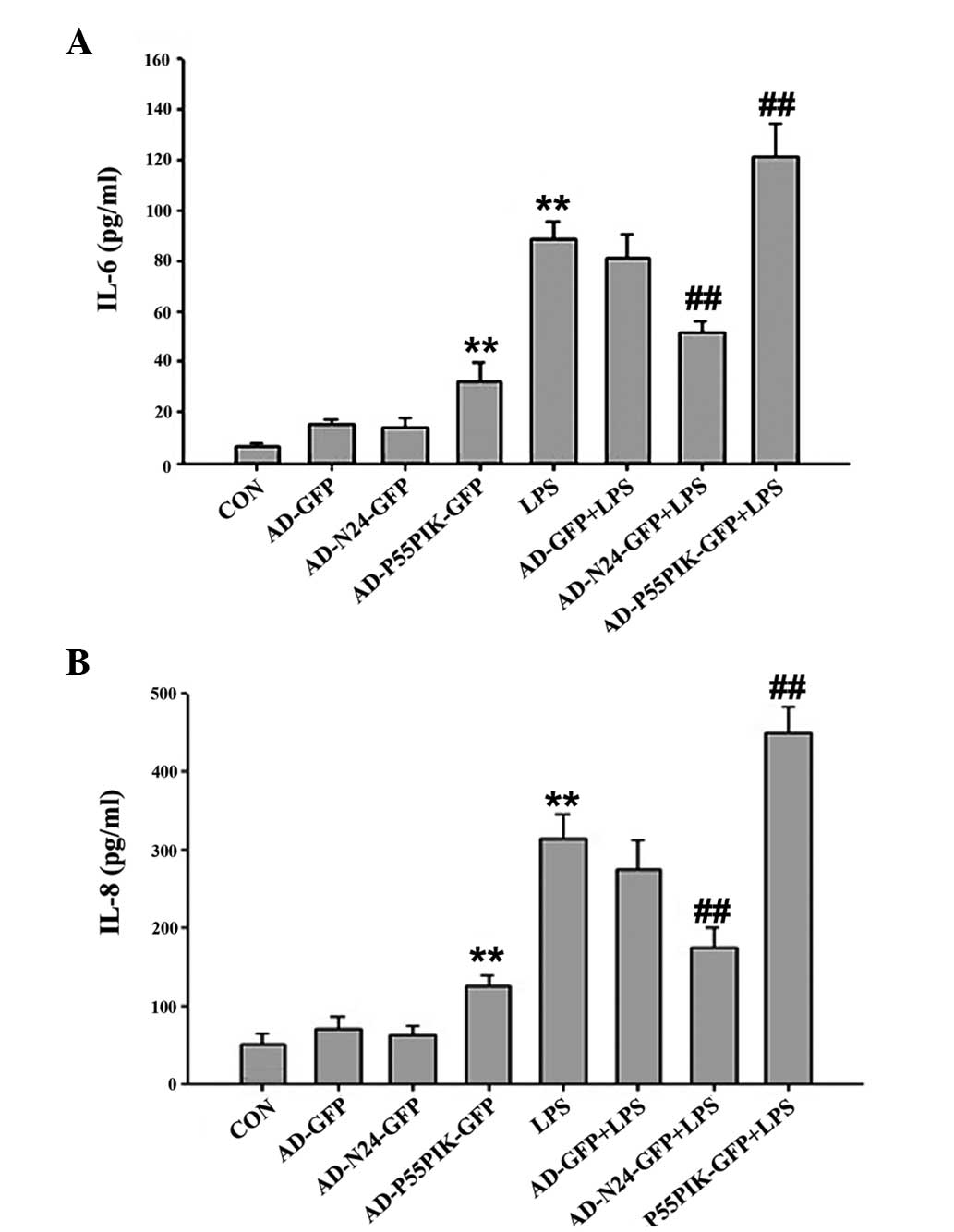
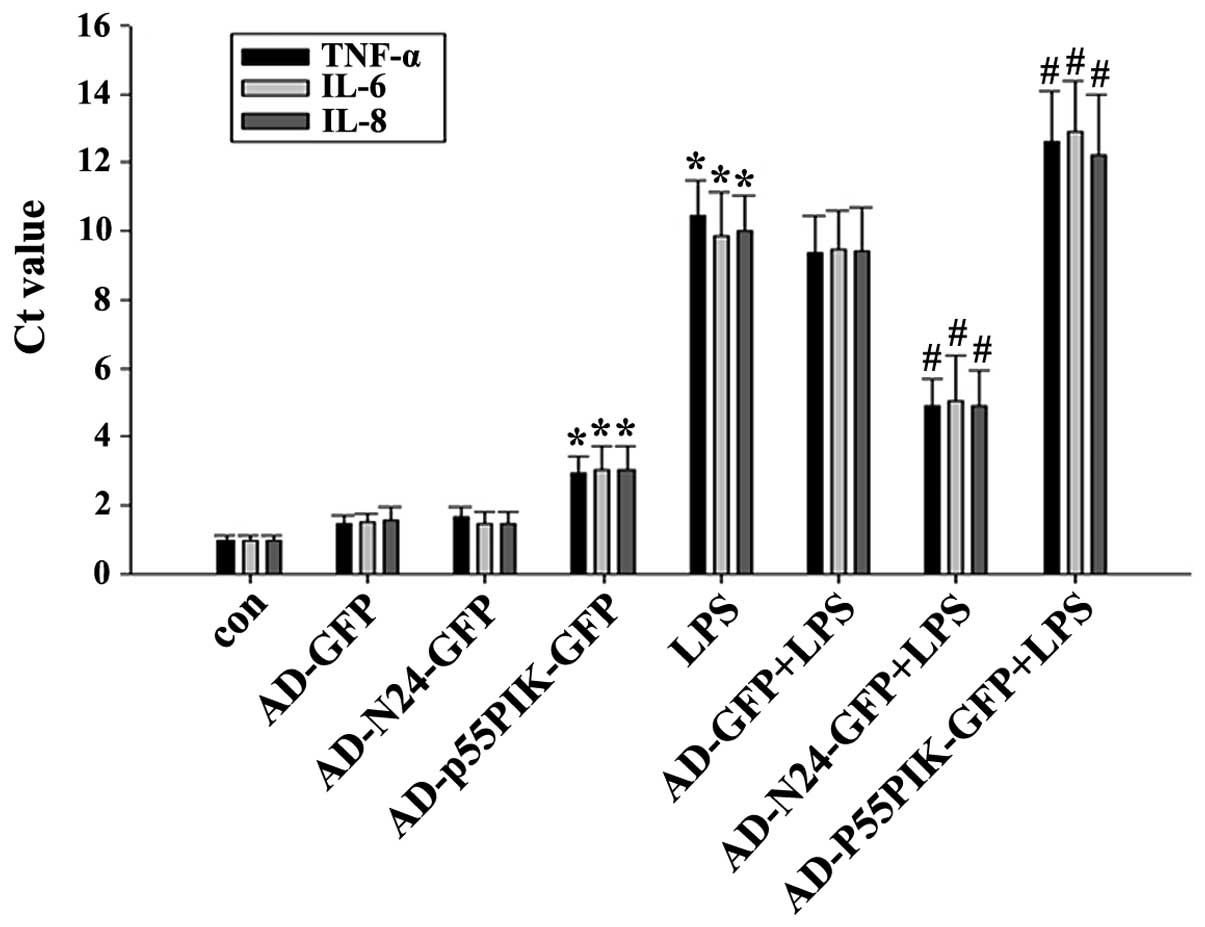
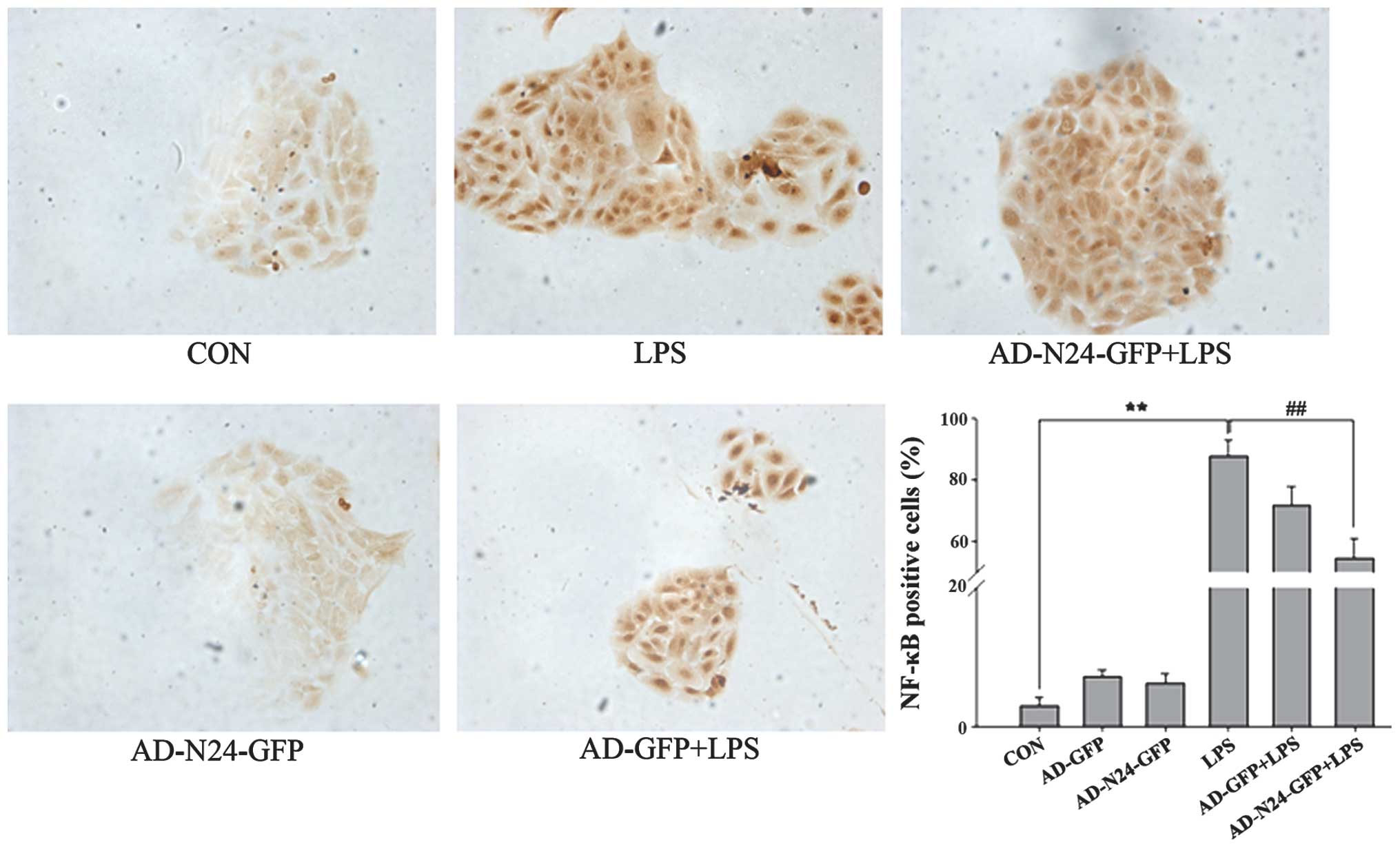
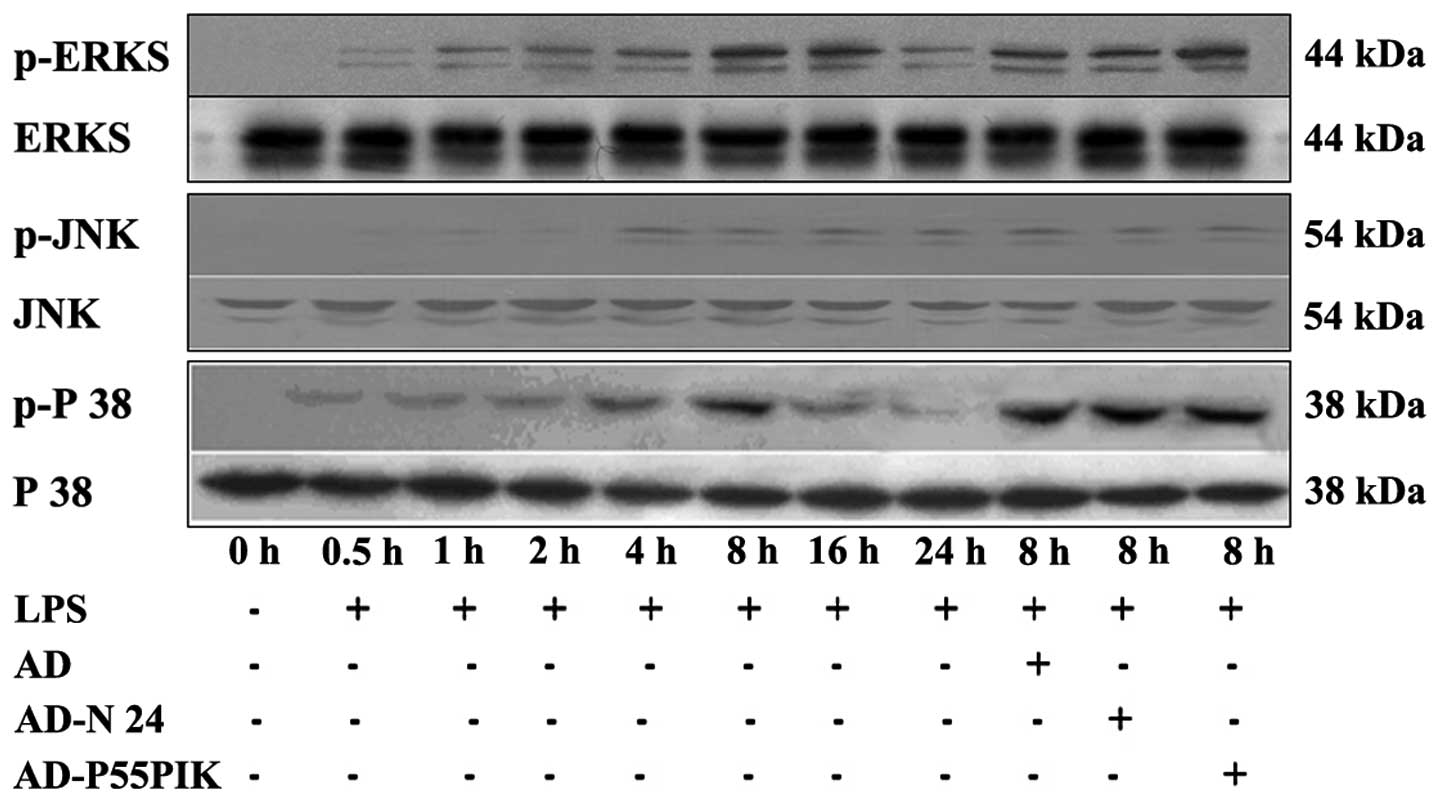
|
1
|
Cho JH and Gregersen PK: Genomics and the
multifactorial nature of human autoimmune disease. N Engl J Med.
365:1612–1623. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bogdanos DP, Smyk DS, Rigopoulou EI, et
al: Twin studies in autoimmune disease: genetics, gender and
environment. J Autoimmun. 38:J156–J169. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Bruce B1 and Fries JF: The Stanford Health
Assessment Questionnaire: a review of its history, issues,
progress, and documentation. J Rheumatol. 30:167–178.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bos JD and De Rie MA: The pathogenesis of
psoriasis: Immunological facts and speculations. Immunol Today.
20:40–46. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lowes MA, Kikuchi T, Fuentes-Duculan J, et
al: Psoriasis vulgaris lesions contain discrete populations of Th1
and Th17 T cells. J Invest Dermatol. 128:1207–1211. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cooper KD, Hammerberg C, Baadsgaard O,
Elder JT, Chan LS, Sauder DN, Voorhees JJ and Fisher G: IL-1
activity is reduced in psoriatic skin. Decreased IL-1 alpha and
increased nonfunctional IL-1 beta. J Immunol. 144:4593–4603.
1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gomi T, Shiohara T, Munakata T, Imanishi K
and Nagashima M: Interleukin 1 alpha, tumor necrosis factor alpha
and interferon gamma in psoriasis. Arch Dermatol. 127:827–830.
1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Neuner P, Urbanski A, Trautinger F, Moller
A, Kirnbauer R, Kapp A, Schopf E, Schwarz T and Luger TA: Increased
IL-6 production by monocytes and keratinocytes in patients with
psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol. 97:27–33. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Luger TA and Schwarz T: Evidence for an
epidermal cytokine network. J Invest Dermatol. 95:100S–104S. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gilhar A, Pillar T and Etzioni A: Possible
role of cytokines in cellular proliferation of the skin
transplanted onto nude mice. Arch Dermatol. 131:38–42. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Stein M, Bernd A, Ramirez-Bosca A,
Kippenberger S and Holzmann H: Measurement of anti-inflammatory
effects of glucocorticoids on human keratinocytes in vitro.
Comparison of normal human keratinocytes with the keratinocyte cell
line HaCaT. Arzneimittelforschung. 47:1266–1270. 1997.
|
|
12
|
Hu J, Xia X, Cheng A, Wang G, Luo X, Reed
MF, Fojo T, Oetting A, Gong J and Yen PM: A peptide inhibitor
derived from p55PIK phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulatory
subunit: a novel cancer therapy. Mol Cancer Ther. 7:3719–3728.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mutis T, De Bueger M, Bakker A and
Ottenhoff TH: HLA class II+ human keratinocytes present
Mycobacterium leprae antigens to CD4+ Th1-like cells. Scand J
Immunol. 37:43–51. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Barker JN, Mitra RS, Griffiths CE, Dixit
VM and Nickoloff BJ: Keratinocytes as initiators of inflammation.
Lancet. 337:211–214. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Akira S: Toll-like receptors and innate
immunity. Adv Immunol. 78:1–56. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Su SB, Silver PB, Grajewski RS, Agarwal
RK, Tang J, Chan CC and Caspi RR: Essential role of the MyD88
pathway, but nonessential roles of TLRs 2, 4, and 9, in the
adjuvant effect promoting Th1-mediated autoimmunity. J Immunol.
175:6303–6310. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Okkenhaug K, Bilancio A, Farjot G, Priddle
H, Sancho S, Peskett E, Pearce W, Meek SE, Salpekar A, Waterfield
MD, et al: Impaired B and T cell antigen receptor signaling in
p110delta PI 3-kinase mutant mice. Science. 297:1031–1034.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Iwasaki A and Medzhitov R: Toll-like
receptor control of the adaptive immune responses. Nat Immunol.
5:987–995. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li Z, Jiang H, Xie W, Zhang Z, Smrcka AV
and Wu D: Roles of PLC-beta2 and -beta3 and PI3Kgamma in
chemoattractant-mediated signal transduction. Science.
287:1046–1049. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Puri KD, Doggett TA, Huang CY, Douangpanya
J, Hayflick JS, Turner M, Penninger J and Diacovo TG: The role of
endothelial PI3Kgamma activity in neutrophil trafficking. Blood.
106:150–157. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Puri KD, Doggett TA, Douangpanya J, Hou Y,
Tino WT, Wilson T, Graf T, Clayton E, Turner M, Hayflick JS, et al:
Mechanisms and implications of phosphoinositide 3-kinase delta in
promoting neutrophil trafficking into inflamed tissue. Blood.
103:3448–3456. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|