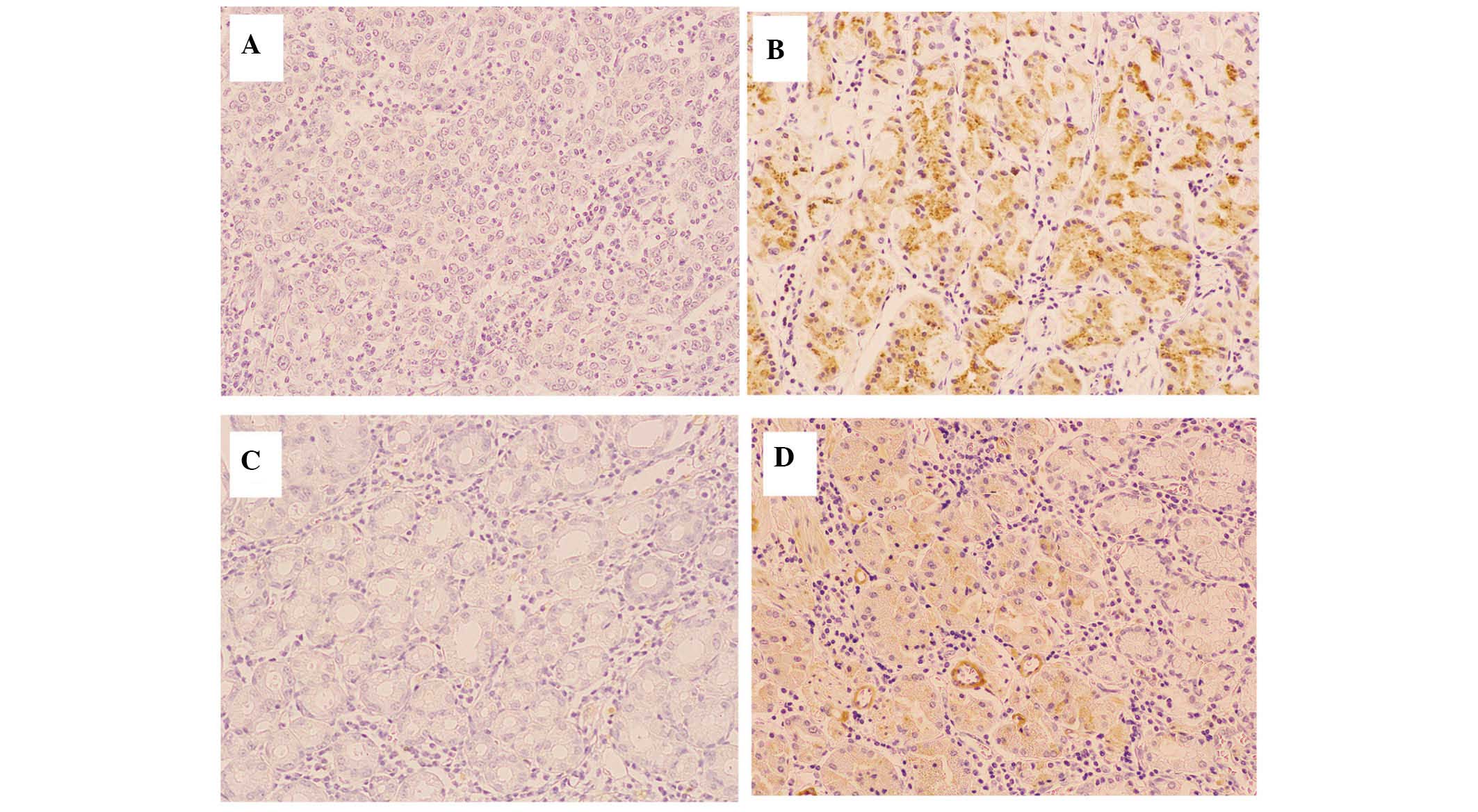
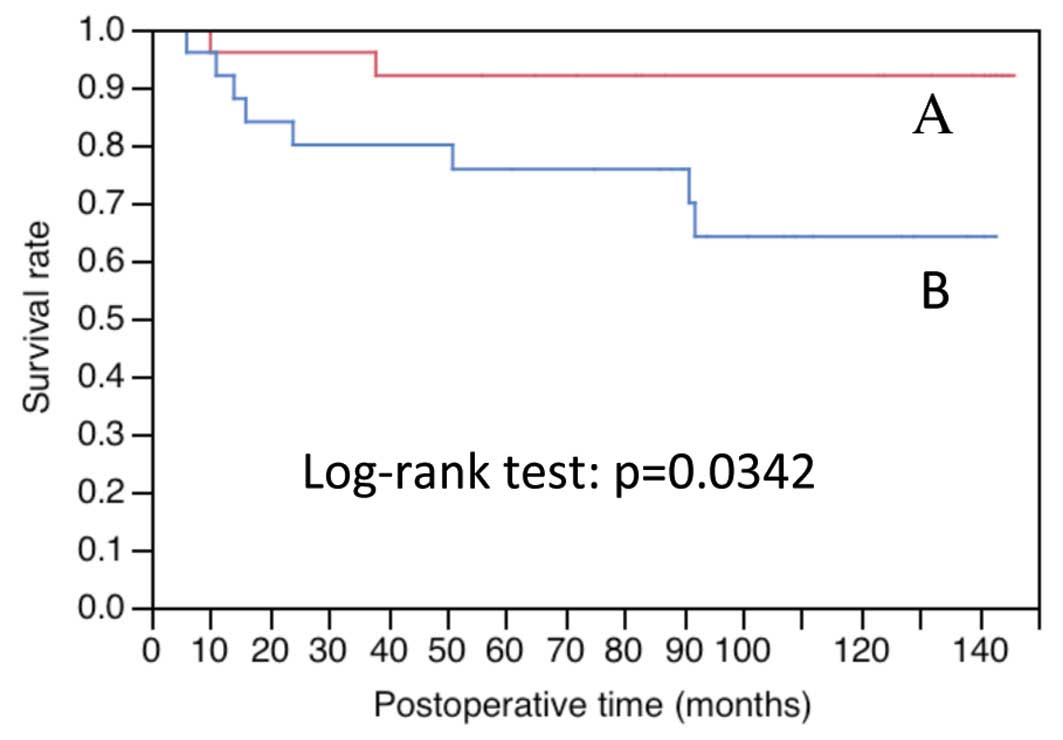
|
1
|
Yamada A, Saito N, Kameoka S and Kobayashi
M: Clinical significance of epidermal growth factor (EGF)
expression in gastric cancer. Hepatogastroenterology. 54:1049–1052.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hirosawa T, Saito N, Kameoka S and
Kobayashi M: Clinical significance of epidermal growth factor (EGF)
expression for assessing the spreading of human colon cancer.
Nippon Daicho Komonbyo Gakkai Zasshi. 55:402–412. 2002.(In
Japanese). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Soyama K, Saito N and Kameoka S: Study on
adhesion molecule beta1 integrin in colorectal
cancer-quantification of blood levels and immunohistological
staining. Nippon Daicho Komonbyo Gakkai Zasshi. 52:119–127.
1999.(In Japanese). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Saito N, Nishimura H and Kameoka S:
Clinical significance of fibronectin expression in colorectal
cancer. Mol Med Rep. 1:77–81. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tani H, Saito N, Kobayashi M and Kameoka
S: Clinical significance of keratinocyte growth factor and K-sam
gene expression in gastric cancer. Mol Med Rep. 7:1381–1386.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Suda A, Saito N, Seshimo A, Kameoka S and
Kobayashi M: Examination of transforming growth factor beta1
expression in the serum and tumor tissue of gastric cancer. Int
Surg. 94:182–188. 2009.
|
|
7
|
Daiko W, Saito N and Kameoka S: Clinical
significance of TGF-beta1 expression in evaluation of the
malignancy of colorectal cancer. Nippon Daicho Komonbyo Gakkai
Zasshi. 58:377–382. 2005.(In Japanese). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Hashimoto T, Saito N, Kameoka S, Shibata N
and Kobayashi M: Clinical significance of hepatocyte growth factor
and its specific receptor c-Met expression in colorectal cancer
progression. Acta Histochem Cytochem. 37:139–146. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Nakamura T, Nawa K and Ichihara A: Partial
purification and characterization of hepatocyte growth factor from
serum of hepatectomized rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
122:1450–1459. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nakamura T, Teramoto H and Ichihara A:
Purification and characterization of a growth factor from rat
platelets for mature parenchymal hepatocytes in primary cultures.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 83:6489–6493. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nakamura T, Nawa K, Ichihara A, Kaise N
and Nishino T: Purification and subunit structure of hepatocyte
growth factor from rat platelets. FEBS Lett. 224:311–316. 1987.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Nakamura T, Nishizawa T, Hagiya M, et al:
Molecular cloning and expression of human hepatocyte growth factor.
Nature. 342:440–443. 1989. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Higashio K, Shima N, Goto M, et al:
Identity of a tumor cytotoxic factor from human fibroblasts and
hepatocyte growth factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 170:397–404.
1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Stoker M and Gherardi E: Regulation of
cell movement: the motogenic cytokines. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1072:81–102. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nakamura T: Structure and function of
hepatocyte growth factor. Prog Growth Factor Res. 3:67–85. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Botraro DP, Rubin JS, Faletro DL, et al:
Identification of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor as the
c-met proto-oncogene product. Science. 251:802–804. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Naldini L, Weidner KM, Vigna E, et al:
Scatter factor and hepatocyte growth factor are indistinguishable
ligands for the MET receptor. EMBO J. 10:2867–2878. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Conrotto P, Valdembri D, Corso S, et al:
Sema4D induces angiogenesis through Met recruitment by Plexin B1.
Blood. 105:4321–4329. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yi S and Tsao MS: Activation of hepatocyte
growth factor-met autocrine loop enhances tumorigenicity in a human
lung adenocarcinoma cell line. Neoplasia. 2:226–234. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Schmidt L, Duh FM, Chen F, et al: Germline
and somatic mutations in the tyrosine kinase domain of the MET
proto-oncogene in papillary renal carcinomas. Nat Genet. 16:68–73.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Schmidt L, Junker K, Weirich G, et al: Two
North American families with hereditary papillary renal carcinoma
and identical novel mutations in the MET proto-oncogene. Cancer
Res. 58:1719–1722. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Park WS, Dong SM, Kim SY, et al: Somatic
mutations in the kinase domain of the Met/hepatocyte growth factor
receptor gene in childhood hepatocellular carcinomas. Cancer Res.
59:307–310. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lee JH, Han SU, Cho H, et al: A novel germ
line juxtamembrane Met mutation in human gastric cancer. Oncogene.
19:4947–4953. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ma PC, Kijima T, Maulik G, et al: c-MET
mutational analysis in small cell lung cancer: novel juxtamembrane
domain mutations regulating cytoskeletal functions. Cancer Res.
63:6272–6281. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ma PC, Jagdeesh S, Jagadeeswaran R, et al:
c-MET expression/activation, functions and mutations in non-small
cell lung cancer. Proc Am Assoc Cancer Res. 44:18752004.
|
|
26
|
Christensen JG, Burrows J and Salgia R:
c-Met as a target for human cancer and characterization of
inhibitors for therapeutic intervention. Cancer Lett. 225:1–26.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nakamura T, Sakai K, Nakamura T and
Matsumoto K: Hepatocyte growth factor twenty years on: Much more
than a growth factor. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 26:188–202. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Japanese Gastric Cancer Association.
Gastric cancer. 1. Japanese Classification of Gastric Carcinoma.
2nd English Edition. June. 1998, pp. 10–24
|
|
29
|
Hattori Y, Itoh H, Uchino S, et al:
Immunohistochemical detection of K-sam protein in stomach cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 2:1373–1381. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Maeda K, Chung YS, Ogawa Y, et al:
Prognostic value of vascular endothelial growth factor expression
in gastric carcinoma. Cancer. 77:858–863. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nishimoto N: Identification of
clinicopathological and molecular prognostic factors in patients of
gastric cancer by multivariate analyses. Hiroshima J Med Sci.
49:171–181. 2001.(In Japanese).
|
|
32
|
Wu CW, Chi CW, Su TL, Liu TY, Lui WY and
P’eng FK: Serum hepatocyte growth factor level associate with
gastric cancer progression. Anticancer Res. 18:3657–3659.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Han SU, Lee JH, Kim WH, Cho YK and Kim MW:
Significant correlation between serum level of hepatocyte growth
factor and progression of gastric carcinoma. World J Surg.
23:1176–1180. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Taniguchi T, Kitamura M, Arai K, Iwasaki
Y, Yamamoto Y, Igari A and Toi M: Increase in the circulating level
of hepatocyte growth factor in gastric cancer patients. Br J
Cancer. 75:673–677. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Niki M, Okajima K, Isozaki H, et al:
Clinical evaluation of preoperative measurement of the serum human
hepatocyte growth factor levels in patients of gastric cancer. Jpn
J Gastroenterol Surg. 28:2139–2144. 1995.(In Japanese). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Ide T, Kitajima Y, Miyoshi A, et al:
Tumor-stromal cell interaction under hypoxia increases the
invasiveness of pancreatic cancer cells through the hepatocyte
growth factor/c-Met pathway. Int J Cancer. 119:2750–2759. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Jiang WG, Martin TA, Parr C, Davies G,
Matsumoto K and Nakamura T: Hepatocyte growth factor, its receptor,
and their potential value in cancer therapies. Crit Rev Oncol
Hematol. 53:35–69. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Catenacci DV, Cervantes G, Yala S, et al:
RON (MST1R) is a novel prognostic marker and therapeutic target for
gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Biol Ther. 12:9–46. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Li Y, Chen CQ, He YL, Cai SR, Yang DJ, et
al: Abnormal expression of e-cadherin in tumor cells is associated
with poor prognosis of gastric carcinoma. J Surg Oncol.
106:304–310. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Taniguchi K, Yonemura Y, Nojima N, et al:
The relation between the growth patterns of gastric carcinoma and
the expression of hepatocyte growth factor receptor (c-met),
autocrine motility factor receptor, and urokinase-type plasminogen
activator receptor. Cancer. 82:2112–2122. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Nakajima M, Sawada H, Yamada Y, et al: The
prognostic significance of amplification and overexpression of
c-met and c-erb B-2 in human gastric carcinomas. Cancer.
85:1894–1902. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Huang TJ, Wang JY, Lin SR, Lian ST and
Hsieh JS: Overexpression of the c-met protooncogene in human
gastric carcinoma: Correlation to clinical features. Acta Oncol.
40:638–643. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Kubicka S, Claas C, Staab S, et al: p53
mutation pattern and expression of c-erbB2 and c-met in gastric
cancer: relation to histological subtypes, Helicobacter pylori
infection, and prognosis. Dig Dis Sci. 47:114–121. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Han SU, Lee HY, Lee JH, et al: Modulation
of E-cadherin by hepatocyte growth factor induces aggressiveness of
gastric carcinoma. Ann Surg. 242:676–683. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Drebber U, Baldus SE, Nolden B, et al: The
overexpression of c-met as a prognostic indicator for gastric
carcinoma compared to p53 and p21 nuclear accumulation. Oncol Rep.
19:1477–1483. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhao J, Zhang X and Xin Y: Up-regulated
expression of Ezrin and c-Met proteins are related to the
metastasis and prognosis of gastric carcinomas. Histol Histopathol.
26:1111–1120. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Iveson T, Donehower RC, Davidenko I, et
al: Rilotumumab in combination with epirubicin, cisplatin, and
capecitabine as first-line treatment for gastric or
oesophagogastric junction adenocarcinoma: an open-label, dose
de-escalation phase 1b study and a double-blind, randomised phase 2
study. Lancet Oncol. 15:1007–1018. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Davidenko I, Iveson T, Donehower RC, et
al: Updated efficacy, biomarker, and exposure-response data form a
phase 2 study of rilotumumab (R) plus epirubicin, cisplatin, and
capecitabine (ECX) in gastric (G) or esophagogastric junction (EGJ)
cancer. In: European Society for Medical Oncology Congress; Vienna.
pp. 687P2012
|
|
49
|
Yamada Yasuhide: Molecular therapy for
gastric cancer. Chin Clin Oncol. 2:52013.
|