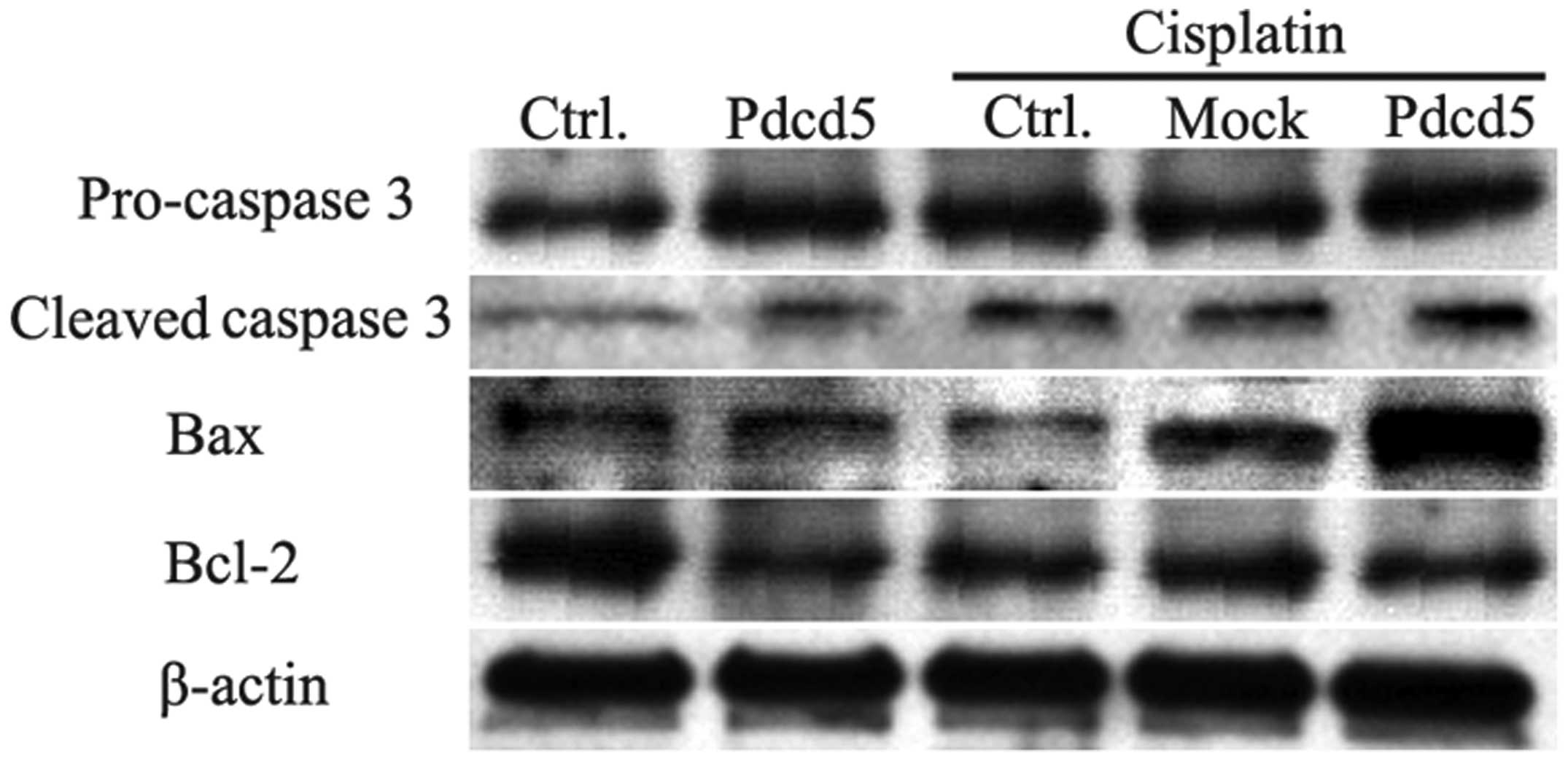
|
1
|
Wallner LP and Jacobsen SJ:
Prostate-specific antigen and prostate cancer mortality: a
systematic review. Am J Prev Med. 45:318–326. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Thomsen FB, Brasso K, Klotz LH, Røder MA,
Berg KD and Iversen P: Active surveillance for clinically localized
prostate cancer - a systematic review. J Surg Oncol. 109:830–835.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
van den Bergh RC, Albertsen PC, Bangma CH,
et al: Timing of curative treatment for prostate cancer: a
systematic review. Eur Urol. 64:204–215. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Punnen S, Cooperberg MR, D’Amico AV, et
al: Management of biochemical recurrence after primary treatment of
prostate cancer: a systematic review of the literature. Eur Urol.
64:905–915. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang Y, Sun G, Pan JG, Guo ZJ and Li T:
Performance of tPSA and f/tPSA for prostate cancer in Chinese. A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis.
9:374–378. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wilkinson S and Chodak GW: Critical review
of complementary therapies for prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol.
21:2199–2210. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Parekh A, Graham PL and Nguyen PL: Cancer
control and complications of salvage local therapy after failure of
radiotherapy for prostate cancer: a systematic review. Semin Radiat
Oncol. 23:222–234. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Murray L, Henry A, Hoskin P, Siebert FA
and Venselaar J; BRAPHYQS/PROBATE group of the GEC ESTRO: Second
primary cancers after radiation for prostate cancer: a review of
data from planning studies. Radiat Oncol. 8:1722013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Matos CS, de Carvalho AL, Lopes RP and
Marques MP: New strategies against prostate cancer - Pt(II)-based
chemotherapy. Curr Med Chem. 19:4678–4687. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Dhar S, Kolishetti N, Lippard SJ and
Farokhzad OC: Targeted delivery of a cisplatin prodrug for safer
and more effective prostate cancer therapy in vivo. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 108:1850–1855. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Menen R, Zhao M, Zhang L, et al:
Comparative chemosensitivity of circulating human prostate cancer
cells and primary cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 32:2881–2884.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Seifert M and Reichrath J: The role of the
human DNA mismatch repair gene hMSH2 in DNA repair, cell cycle
control and apoptosis: implications for pathogenesis, progression
and therapy of cancer. J Mol Histol. 37:301–307. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu H, Wang Y, Zhang Y, et al: TFAR19, a
novel apoptosis-related gene cloned from human leukemia cell line
TF-1, could enhance apoptosis of some tumor cells induced by growth
factor withdrawal. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 254:203–210. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hedenfalk I, Duggan D, Chen Y, et al:
Gene-expression profiles in hereditary breast cancer. N Engl J Med.
344:539–548. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu ZH, Zhang D, Li KM and Liao QP:
Expression of Pdcd5 in tissues of normal cervix, CIN I–III and
cervical cancer. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao. 36:407–410. 2004.In
Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xu XR, Huang J, Xu ZG, et al: Insight into
hepatocellular carcinogenesis at transcriptome level by comparing
gene expression profiles of hepatocellular carcinoma with those of
corresponding noncancerous liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
98:15089–15094. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yang YH, Zhao M, Li WM, et al: Expression
of programmed cell death 5 gene involves in regulation of apoptosis
in gastric tumor cells. Apoptosis. 11:993–1001. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Spinola M, Meyer P, Kammerer S, et al:
Association of the Pdcd5 locus with lung cancer risk and prognosis
in smokers. J Clin Oncol. 24:1672–1678. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Du YJ, Xiong L, Lou Y, Tan WL and Zheng
SB: Reduced expression of programmed cell death 5 protein in tissue
of human prostate cancer. Chin Med Sci J. 24:241–245. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Zhang X, Wang X, Song X, et al: Clinical
and prognostic significance of lost or decreased PDCD5 expression
in human epithelial ovarian carcinomas. Oncol Rep. 25:353–358.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Chen Y, Zou Z, Xu A, Liu Y, Pan H and Jin
L: Serum programmed cell death protein 5 (PDCD5) levels is
upregulated in liver diseases. J Immunoassay Immunochem.
34:294–304. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang Y, Wang GH and Zhang QY:
Determination of Pdcd5 in peripheral blood serum of cancer
patients. Chin J Cancer Res. 23:224–228. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shiota M, Izumi H, Tanimoto A, et al:
Programmed cell death protein 4 down-regulates Y-box binding
protein-1 expression via a direct interaction with Twist1 to
suppress cancer cell growth. Cancer Res. 69:3148–3156. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jansen AP, Camalier CE, Stark C and
Colburn NH: Characterization of programmed cell death 4 in multiple
human cancers reveals a novel enhancer of drug sensitivity. Mol
Cancer Ther. 3:103–110. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bernas T and Dobrucki J: Mitochondrial and
nonmitochondrial reduction of MTT: interaction of MTT with TMRE,
JC-1, and NAO mitochondrial fuorescent probes. Cytometry.
47:236–242. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sylvester PW: Optimization of the
tetrazolium dye (MTT) colorimetric assay for cellular growth and
viability. Methods Mol Biol. 716:157–168. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nishitani H, Sugimoto N, Roukos V, et al:
Two E3 ubiquitin ligases, SCF-Skp2 and DDB1-Cul4, target human Cdt1
for proteolysis. EMBO J. 25:1126–1136. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Peng L, Xu Z, Zhou Y, et al: Effect of
rosiglitazone on cells cycle, apoptosis and expression of Skp2 and
p27Kip1 in hepatocellular carcinoma cell line. Zhonghua Gan Zang
Bing Za Zhi. 18:148–149. 2010.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Schulman BA, Carrano AC, Jeffrey PD, et
al: Insights into SCF ubiquitin ligases from the structure of the
Skp1-Skp2 complex. Nature. 408:381–386. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Amantana A, London CA, Iversen PL and Devi
GR: X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein inhibition induces
apoptosis and enhances chemotherapy sensitivity in human prostate
cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 3:699–707. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li Y, Chen HQ, Chen MF, et al:
Neuroendocrine differentiation is involved in chemoresistance
induced by EGF in prostate cancer cells. Life Sci. 84:882–887.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Larkin D, Lopez V and Aromataris E:
Managing cancer-related fatigue in men with prostate cancer: A
systematic review of non-pharmacological interventions. Int J Nurs
Pract. Nov 15–2013.Epub ahead of print. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kao CJ, Wurz GT, Monjazeb AM, et al:
Antitumor effects of cisplatin combined with tecemotide
immunotherapy in a human MUC1 transgenic lung cancer mouse model.
Cancer Immunol Res. 2:581–589. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
de Biasi AR, Villena-Vargas J and
Adusumilli PS: Cisplatin-Induced Antitumor Immunomodulation: A
Review of Preclinical and Clinical Evidence. Clin Cancer Res.
20:5384–5391. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sun S, Tang L, Zhang J, et al: Cisplatin
improves antitumor activity of weekly nab-paclitaxel in patients
with metastatic breast cancer. Int J Nanomedicine. 9:1443–1452.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Itoh T, Terazawa R, Kojima K, et al:
Cisplatin induces production of reactive oxygen species via NADPH
oxidase activation in human prostate cancer cells. Free Radic Res.
45:1033–1039. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Murshed F, Farhana L, Dawson MI and
Fontana JA: NF-κB p65 recruited SHP regulates Pdcd5-mediated
apoptosis in cancer cells. Apoptosis. 19:506–517. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Xu HY, Chen ZW, Pan YM, et al:
Transfection of Pdcd5 effect on the biological behavior of tumor
cells and sensitized gastric cancer cells to cisplatin-induced
apoptosis. Dig Dis Sci. 57:1847–1856. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kaeidi A, Rasoulian B, Hajializadeh Z,
Pourkhodadad S and Rezaei M: Cisplatin toxicity reduced in human
cultured renal tubular cells by oxygen pretreatment. Ren Fail.
35:1382–1386. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Motawi TK, Abd-Elgawad HM and Shahin NN:
Effect of protein malnutrition on the metabolism and toxicity of
cisplatin, 5-fluorouracil and mitomycin C in rat stomach. Food Chem
Toxicol. 56:467–482. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wang L, Wang C, Su B, et al: Recombinant
human Pdcd5 protein enhances chemosensitivity of breast cancer in
vitro and in vivo. Biochem Cell Biol. 91:526–531. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Li SJ, Yu J, Zhao XF, et al: Pdcd5 induces
the apoptosis of human prostate cancer cells PC-3M-1E8. Zhonghua
Nan Ke Xue. 13:979–982. 2007.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yin A, Jiang Y, Zhang X, Zhao J and Luo H:
Transfection of Pdcd5 sensitizes colorectal cancer cells to
cisplatin-induced apoptosis in vitro and in vivo. Eur J Pharmacol.
649:120–126. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|