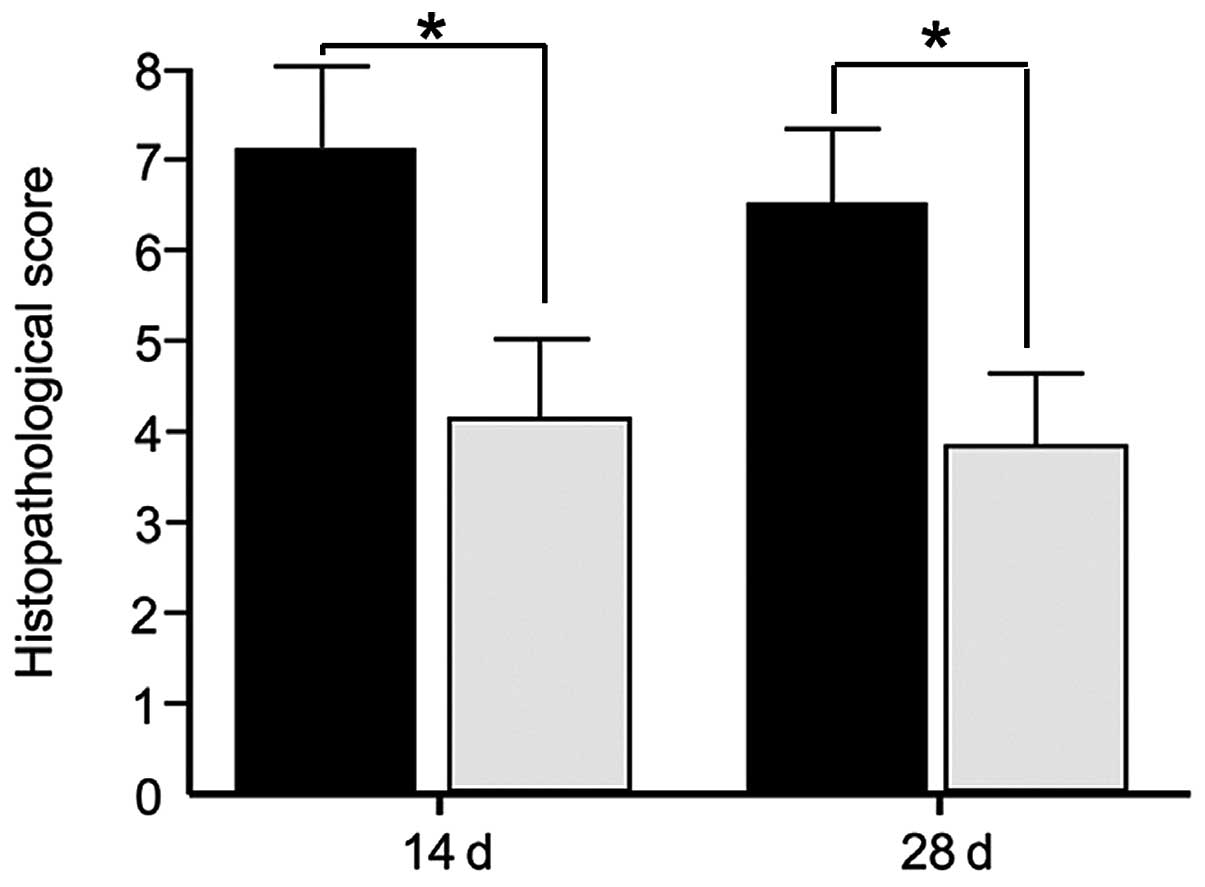
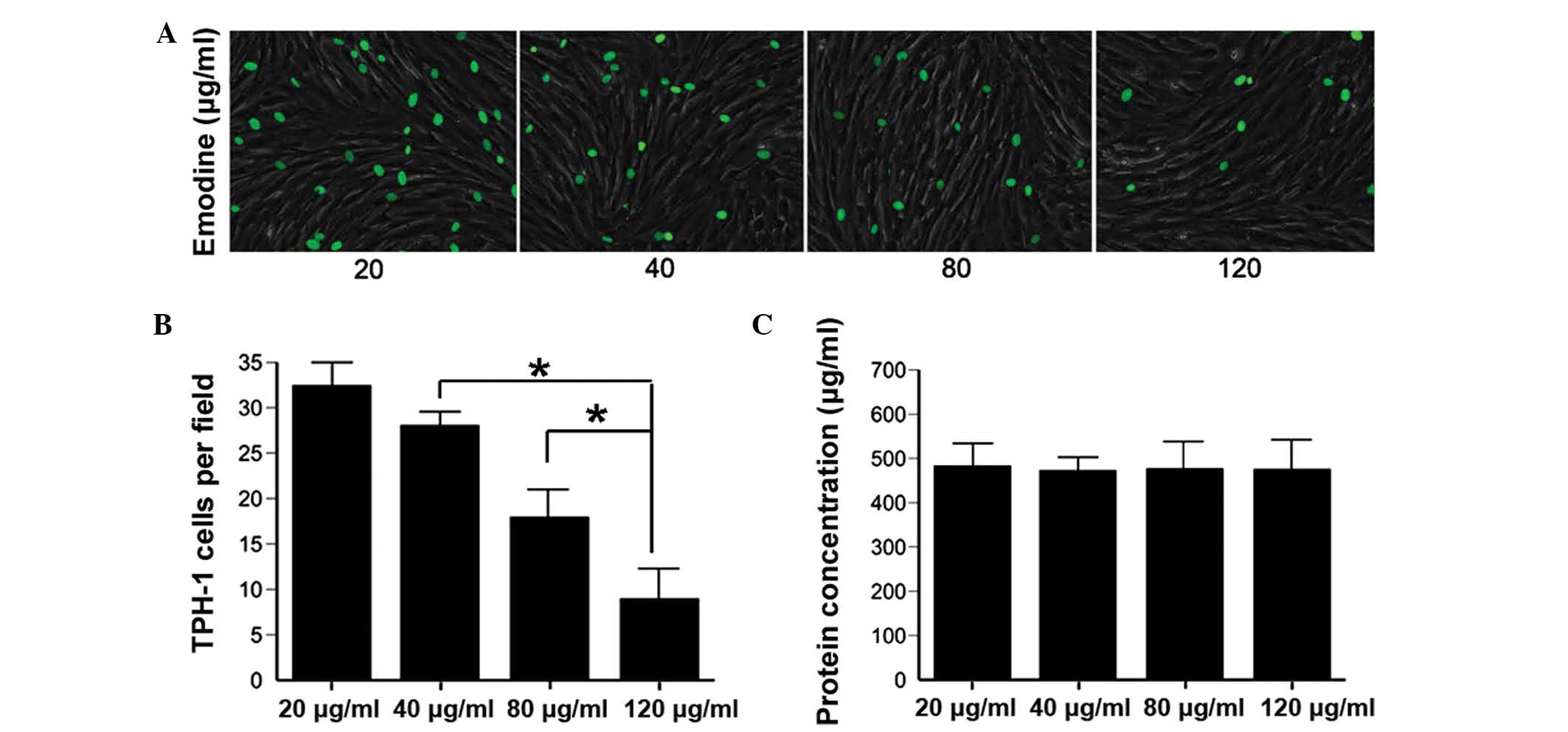
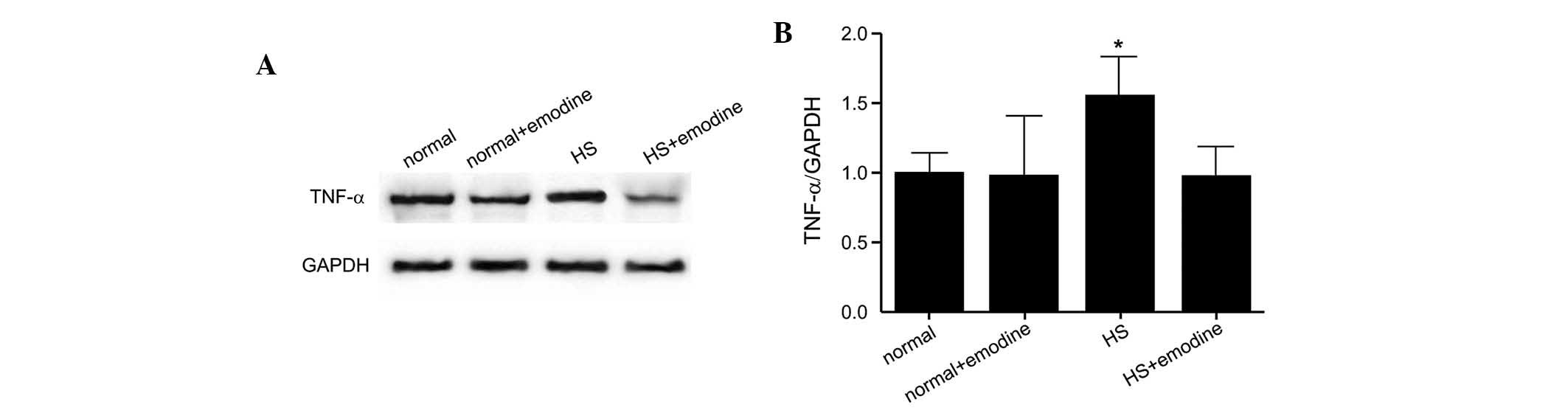
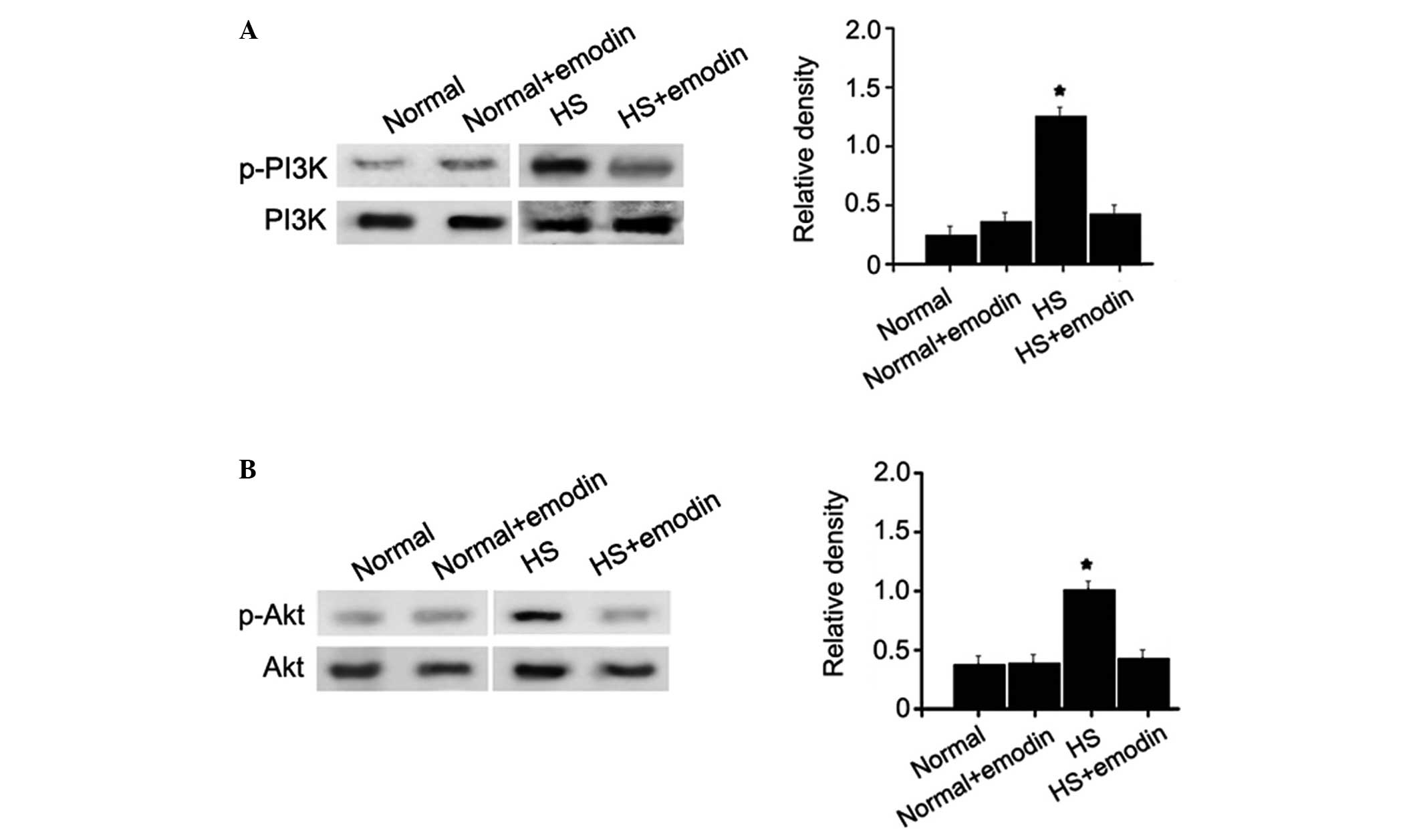
|
1
|
Wolfram D, Tzankov A, Pülzl P and
Piza-Katzer H: Hypertrophic scars and keloids - a review of their
pathophysiology, risk factors, and therapeutic management. Dermatol
Surg. 35:171–181. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rahmani-Neishaboor E, Yau FM, Jalili R,
Kilani RT and Ghahary A: Improvement of hypertrophic scarring by
using topical anti-fibrogenic/anti-inflammatory factors in a rabbit
ear model. Wound Repair Regen. 18:401–408. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Huang C, Akaishi S, Hyakusoku H and Ogawa
R: Are keloid and hypertrophic scar different forms of the same
disorder? A fibroproliferative skin disorder hypothesis based on
keloid findings. Int Wound J. 11:517–522. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Eming SA, Krieg T and Davidson JM:
Inflammation in wound repair: molecular and cellular mechanisms. J
Invest Dermatol. 127:514–525. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gauglitz GG, Korting HC, Pavicic T, et al:
Hypertrophic scarring and keloids: pathomechanisms and current and
emerging treatment strategies. Mol Med. 17:113–125. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
6
|
Wynn TA: Cellular and molecular mechanisms
of fibrosis. J Pathol. 214:199–210. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
van der Veer WM, Bloemen MC, Ulrich MM, et
al: Potential cellular and molecular causes of hypertrophic scar
formation. Burns. 35:15–29. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Wong VW, Paterno J, Sorkin M, et al:
Mechanical force prolongs acute inflammation via T-cell-dependent
pathways during scar formation. FASEB J. 25:4498–4510. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wong VW, Rustad KC, Akaishi S, et al:
Focal adhesion kinase links mechanical force to skin fibrosis via
inflammatory signaling. Nat Med. 18:148–152. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Krötzsch-Gómez FE, Furuzawa-Carballeda J,
Reyes-Márquez R, Quiróz-Hernández E and Díaz de León L: Cytokine
expression is downregulated by collagen-polyvinylpyrrolidone in
hypertrophic scars. J Invest Dermatol. 111:828–834. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Polo M, Ko F, Busillo F, Cruse CW, Krizek
TJ and Robson MC: The 1997 Moyer Award. Cytokine production in
patients with hypertrophic burn scars. J Burn Care Rehabil.
18:477–482. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wei WT, Lin SZ, Liu DL and Wang ZH: The
distinct mechanisms of the antitumor activity of emodin in
different types of cancer (Review). Oncol Rep. 30:2555–2562.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shrimali D, Shanmugam MK, Kumar AP, et al:
Targeted abrogation of diverse signal transduction cascades by
emodin for the treatment of inflammatory disorders and cancer.
Cancer Lett. 341:139–149. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hu Q, Noor M, Wong YF, et al: In vitro
anti-fibrotic activities of herbal compounds and herbs. Nephrol
Dial Transplant. 24:3033–3041. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lin YL, Wu CF and Huang YT: Phenols from
the roots of Rheum palmatum attenuate chemotaxis in rat hepatic
stellate cells. Planta Med. 74:1246–1252. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Aarabi S, Bhatt KA, Shi Y, et al:
Mechanical load initiates hypertrophic scar formation through
decreased cellular apoptosis. FASEB J. 21:3250–3261. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu XJ, Xu MJ, Fan ST, et al: Xiamenmycin
attenuates hypertrophic scars by suppressing local inflammation and
the effects of mechanical stress. J Invest Dermatol. 133:1351–1360.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Pfaff AW, Georges S and Candolfi E:
Different effect of Toxoplasma gondii infection on adhesion
capacity of fibroblasts and monocytes. Parasite Immunol.
30:487–490. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ha MK, Song YH, Jeong SJ, et al: Emodin
inhibits proinflammatory responses and inactivates histone
deacetylase 1 in hypoxic rheumatoid synoviocytes. Biol Pharm Bull.
34:1432–1437. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang L, Li Y, Liang C and Yang W: CCN5
overexpression inhibits profibrotic phenotypes via the PI3K/Akt
signaling pathway in lung fibroblasts isolated from patients with
idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and in an in vivo model of lung
fibrosis. Int J Mol Med. 33:478–486. 2014.
|
|
21
|
Son G, Hines IN, Lindquist J, Schrum LW
and Rippe RA: Inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling
in hepatic stellate cells blocks the progression of hepatic
fibrosis. Hepatology. 50:1512–1523. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Le Cras TD, Korfhagen TR, Davidson C, et
al: Inhibition of PI3K by PX-866 prevents transforming growth
factor-alpha-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Pathol. 176:679–686.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Son MK, Ryu YL, Jung KH, et al: HS-173, a
novel PI3K inhibitor, attenuates the activation of hepatic stellate
cells in liver fibrosis. Sci Rep. 3:34702013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yoon HE, Kim SJ, Kim SJ, Chung S and Shin
SJ: Tempol attenuates renal fibrosis in mice with unilateral
ureteral obstruction: the role of PI3K-Akt-FoxO3a signaling. J
Korean Med Sci. 29:230–237. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
van der Veer WM, Ferreira JA, de Jong EH,
Molema G and Niessen FB: Perioperative conditions affect long-term
hypertrophic scar formation. Ann Plast Surg. 65:321–325. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kitano A, Saika S, Yamanaka O, et al:
Emodin suppression of ocular surface inflammatory reaction. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 48:5013–5022. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Salgado RM, Alcántara L, Mendoza-Rodríguez
CA, et al: Post-burn hypertrophic scars are characterized by high
levels of IL-1β mRNA and protein and TNF-α type I receptors. Burns.
38:668–676. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Reno F, Sabbatini M, Lombardi F, et al: In
vitro mechanical compression induces apoptosis and regulates
cytokines release in hypertrophic scars. Wound Repair Regen.
11:331–336. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Dasu MR, Hawkins HK, Barrow RE, Xue H and
Herndon DN: Gene expression profiles from hypertrophic scar
fibroblasts before and after IL-6 stimulation. J Pathol.
202:476–485. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Song J, Xu H, Lu Q, Xu Z, Bian D, Xia Y,
Wei Z, Gong Z and Dai Y: Madecassoside suppresses migration of
fibroblasts from keloids: involvement of p38 kinase and PI3K
signaling pathways. Burns. 38:677–684. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lee SU, Shin HK, Min YK and Kim SH: Emodin
accelerates osteoblast differentiation through phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase activation and bone morphogenetic protein-2 gene
expression. Int Immunopharmacol. 8:741–747. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wei WT, Chen H, Ni ZL, et al: Antitumor
and apoptosis-promoting properties of emodin, an anthraquinone
derivative from rheum officinale Baill, against pancreatic cancer
in mice via inhibition of Akt activation. Int J Oncol.
39:1381–1390. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|