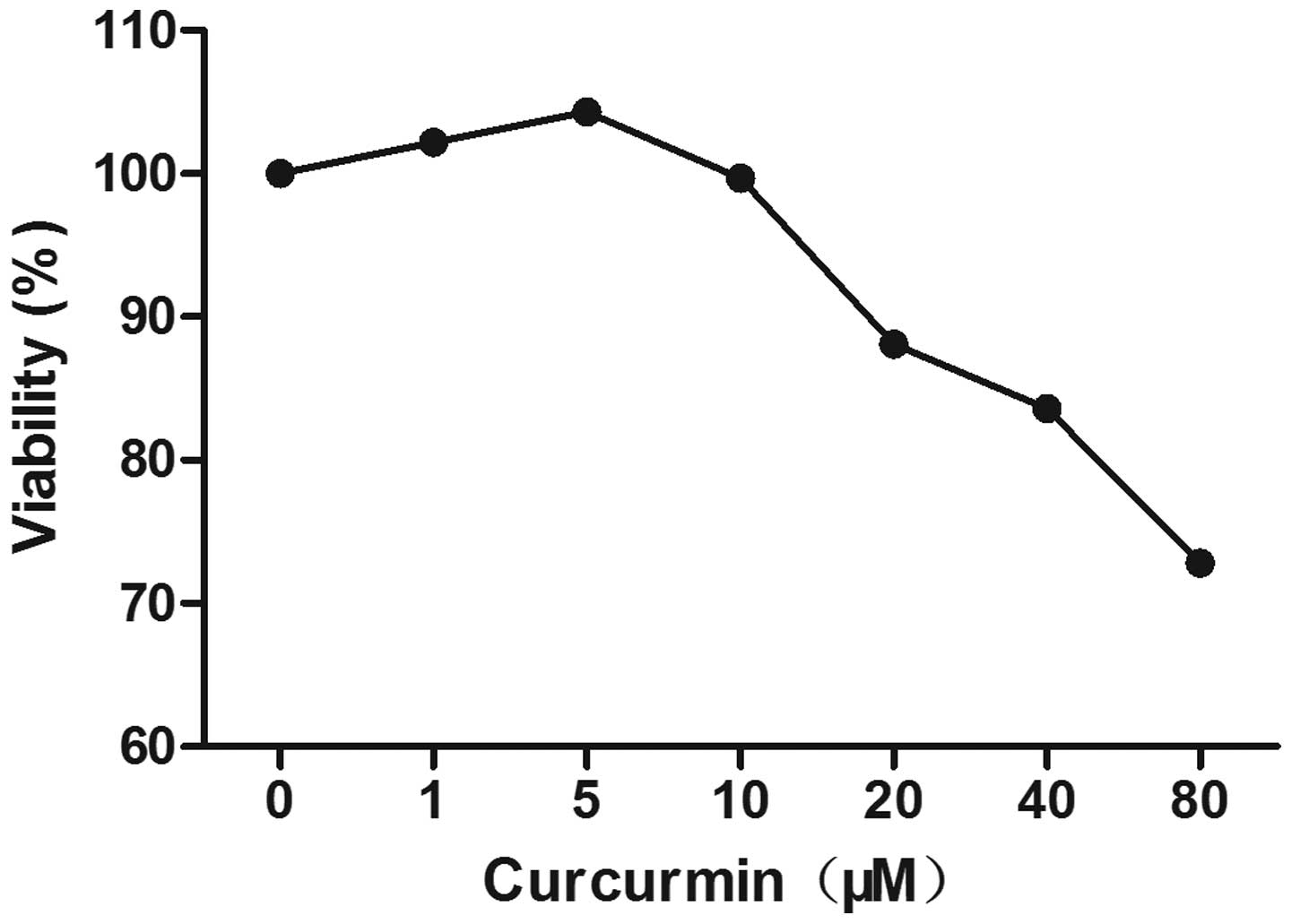
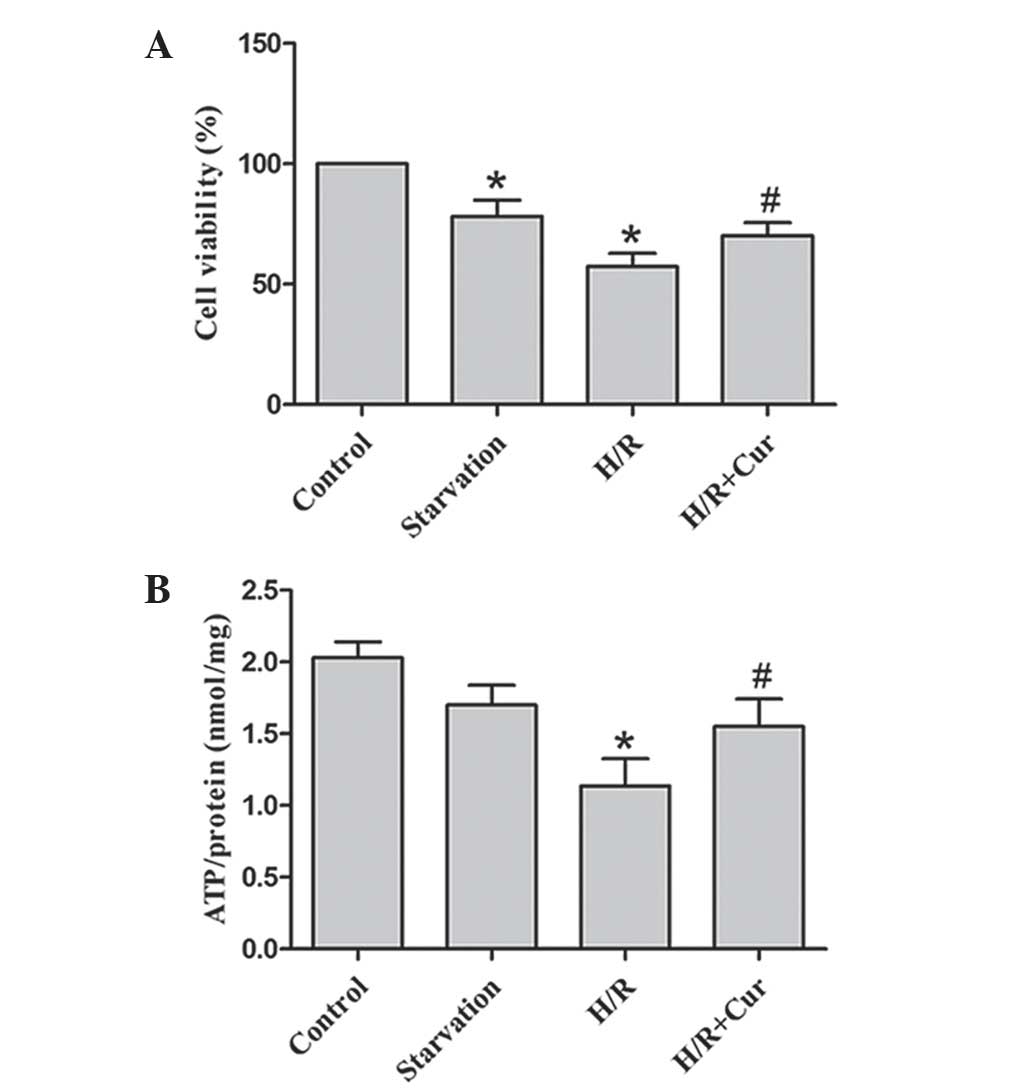
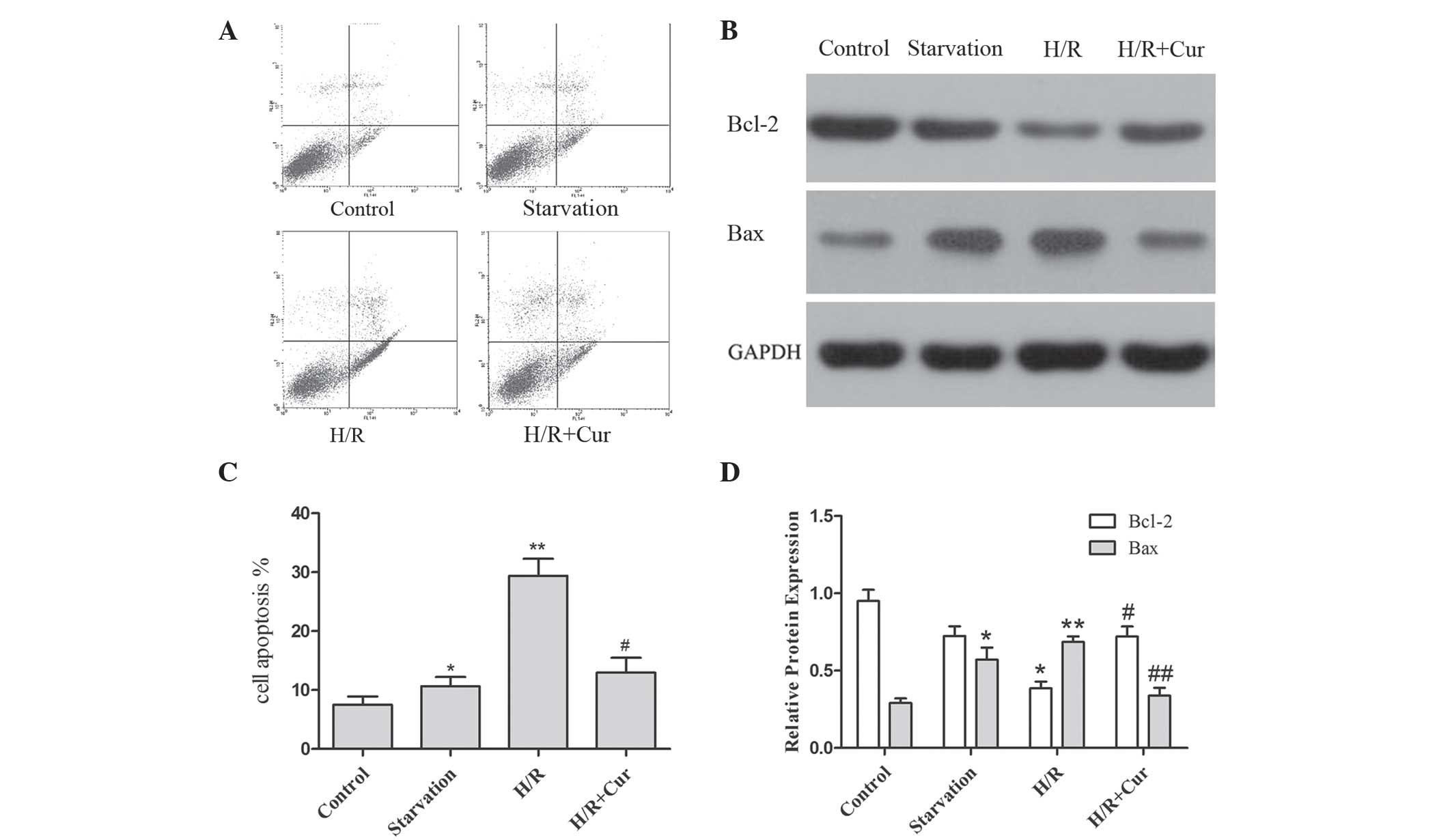
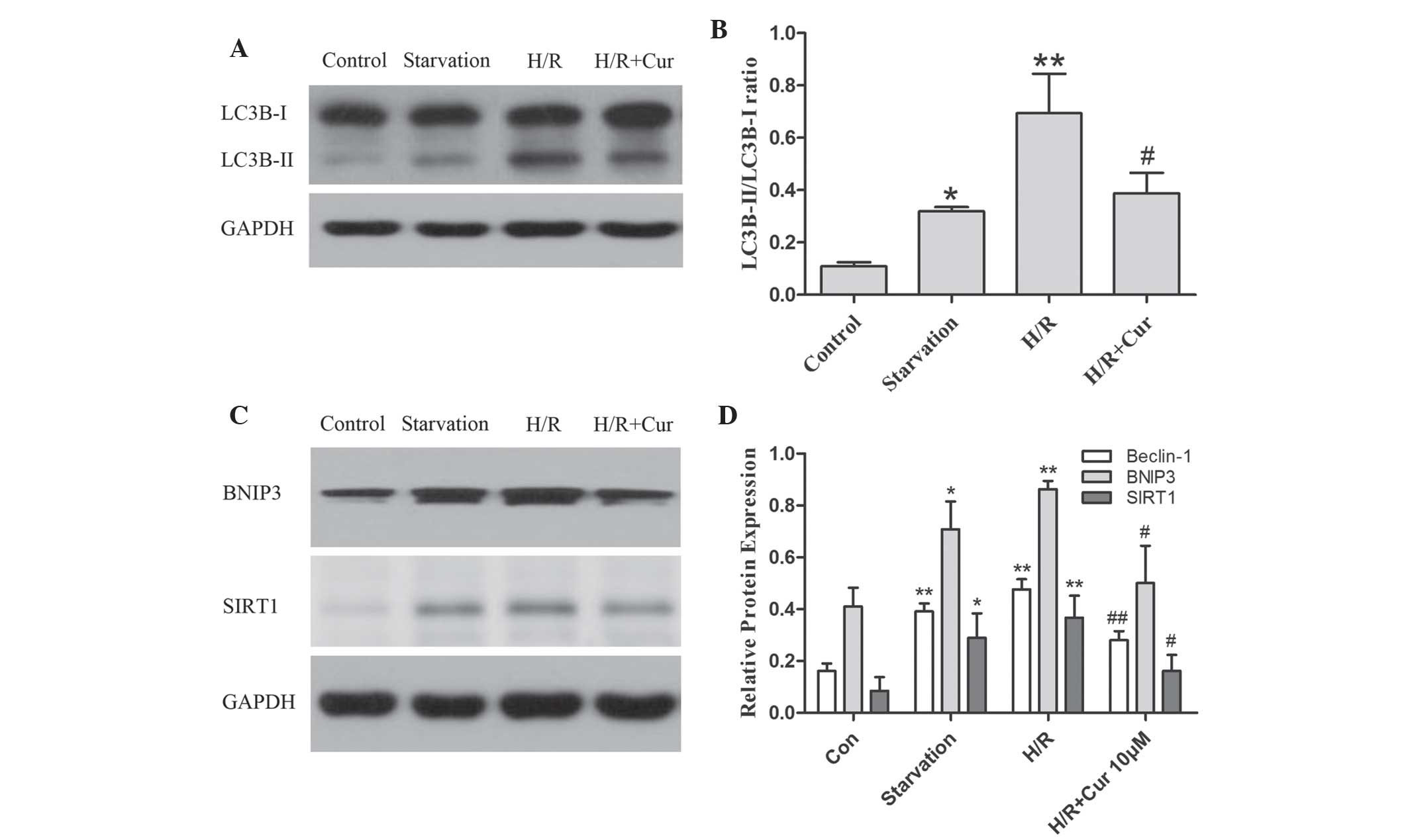
|
1
|
Keeley EC, Boura JA and Grines CL: Primary
angioplasty versus intravenous thrombolytic therapy for acute
myocardial infarction: a quantitative review of 23 randomised
trials. Lancet. 361:13–20. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hausenloy DJ and Yellon DM: Myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury: A neglected therapeutic target. J Clin
Invest. 123:92–100. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yellon DM and Hausenloy DJ: Myocardial
reperfusion injury. N Engl J Med. 357:1121–1135. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ong SB and Gustafsson AB: New roles for
mitochondria in cell death in the reperfused myocardium. Cardiovasc
Res. 94:190–196. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
5
|
Zeng M, Wei X, Wu Z, et al: NF-κB-mediated
induction of autophagy in cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 436:180–185. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wagner C, Tillack D, Simonis G, Strasser
RH and Weinbrenner C: Ischemic post-conditioning reduces infarct
size of the in vivo rat heart: role of PI3-K, mTOR, GSK-3beta, and
apoptosis. Mol Cell Biochem. 339:135–147. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ma X, Liu H, Foyil SR, Godar RJ,
Weinheimer CJ and Diwan A: Autophagy is impaired in cardiac
ischemia-reperfusion injury. Autophagy. 8:1394–1396. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yin Y, Guan Y, Duan J, et al:
Cardioprotective effect of Danshensu against myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury and inhibits apoptosis of H9c2
cardiomyocytes via Akt and ERK1/2 phosphorylation. Eur J Pharmacol.
699:219–226. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Hadi NR, Yusif FG, Yousif M and Jaen KK:
Both castration and goserelin acetate ameliorate myocardial
ischemia reperfusion injury and apoptosis in male rats. ISRN
Pharmacol. 2014:2069512014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hadi NR, Al-Amran F, Yousif M and Zamil
ST: Antiapoptotic effect of simvastatin ameliorates myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury. ISRN Pharmacol. 2013:8150942013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Levine B and Klionsky DJ: Development by
self-digestion: molecular mechanisms and biological functions of
autophagy. Dev cell. 6:463–477. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Loos B, Genade S, Ellis B, et al: At the
core of survival: autophagy delays the onset of both apoptotic and
necrotic cell death in a model of ischemic cell injury. Exp Cell
Res. 317:1437–1453. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Levine B and Yuan J: Autophagy in cell
death: An innocent convict? J Clin Invest. 115:2679–2688. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Matsui Y, Takagi H, Qu X, et al: Distinct
roles of autophagy in the heart during ischemia and reperfusion:
roles of AMP-activated protein kinase and Beclin 1 in mediating
autophagy. Circ Res. 100:914–922. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kang M, Kim JH, Cho C, et al: Effect of
Acori graminei Rhizoma on contractile dysfunction of ischemic and
reperfused rat heart. Biol Pharm Bull. 29:483–488. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kang M, Kim JH, Cho C, et al:
Anti-ischemic effect of Aurantii Fructus on contractile dysfunction
of ischemic and reperfused rat heart. J Ethnopharmacol.
111:584–591. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Abe Y, Hashimoto S and Horie T: Curcumin
inhibition of inflammatory cytokine production by human peripheral
blood monocytes and alveolar macrophages. Pharmacol Res. 39:41–47.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dhandapani KM, Mahesh VB and Brann DW:
Curcumin suppresses growth and chemoresistance of human
glioblastoma cells via AP-1 and NF-kappaB transcription factors. J
Neurochem. 102:522–538. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kapakos G, Youreva V and Srivastava AK:
Cardiovascular protection by curcumin: molecular aspects. Indian J
Biochem Biophys. 49:306–315. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yucel AF, Kanter M, Pergel A, Erboga M and
Guzel A: The role of curcumin on intestinal oxidative stress, cell
proliferation and apoptosis after ischemia/reperfusion injury in
rats. J Mol Histol. 42:579–587. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shen SQ, Zhang Y, Xiang JJ and Xiong CL:
Protective effect of curcumin against liver warm
ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat model is associated with
regulation of heat shock protein and antioxidant enzymes. World J
Gastroenterol. 13:1953–1961. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Awad AS and El-Sharif AA: Curcumin
immune-mediated and anti-apoptotic mechanisms protect against renal
ischemia/reperfusion and distant organ induced injuries. Int
Immunopharmacol. 11:992–996. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang L, Li C, Guo H, Kern TS, Huang K and
Zheng L: Curcumin inhibits neuronal and vascular degeneration in
retina after ischemia and reperfusion injury. PloS One.
6:e231942011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gonzalez-Salazar A, Molina-Jijon E, Correa
F, et al: Curcumin protects from cardiac reperfusion damage by
attenuation of oxidant stress and mitochondrial dysfunction.
Cardiovasc Toxicol. 11:357–364. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Huang Z, Wang C, Wei L, et al: Resveratrol
inhibits EMMPRIN expression via P38 and ERK1/2 pathways in
PMA-induced THP-1 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 374:517–521.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Levine B, Sinha S and Kroemer G: Bcl-2
family members: Dual regulators of apoptosis and autophagy.
Autophagy. 4:600–606. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tanida I, Ueno T and Kominami E: LC3
conjugation system in mammalian autophagy. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
36:2503–2518. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kroemer G, Galluzzi L, Vandenabeele P, et
al: Classification of cell death: Recommendations of the
nomenclature committee on cell death. Cell Death Differ. 16:3–11.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
29
|
Wagener FA, Dekker D, Berden JH, et al:
The role of reactive oxygen species in apoptosis of the diabetic
kidney. Apoptosis. 14:1451–1458. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tian Y, Zhang W, Xia D, et al:
Postconditioning inhibits myocardial apoptosis during prolonged
reperfusion via a JAK2-STAT3-Bcl-2 pathway. J Biomed Sci.
18:532011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fletcher JI, Meusburger S, Hawkins CJ, et
al: Apoptosis is triggered when prosurvival Bcl-2 proteins cannot
restrain Bax. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:18081–18087. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kim H, Rafiuddin-Shah M, Tu HC, et al:
Hierarchical regulation of mitochondrion-dependent apoptosis by
BCL-2 subfamilies. Nat Cell Biol. 8:1348–1358. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Takagi H, Matsui Y and Sadoshima J: The
role of autophagy in mediating cell survival and death during
ischemia and reperfusion in the heart. Antioxid Redox Signal.
9:1373–1381. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Takagi H, Matsui Y, Hirotani S, et al:
AMPK mediates autophagy during myocardial ischemia in vivo.
Autophagy. 3:405–407. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Fu LL, Cheng Y and Liu B: Beclin-1:
autophagic regulator and therapeutic target in cancer. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 45:921–924. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang J and Ney PA: Role of BNIP3 and NIX
in cell death, autophagy, and mitophagy. Cell Death Differ.
16:939–946. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Shin BH, Lim Y, Oh HJ, et al:
Pharmacological activation of Sirt1 ameliorates
polyglutamine-induced toxicity through the regulation of autophagy.
PloS One. 8:e649532013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sinha S and Levine B: The autophagy
effector Beclin 1: A novel BH3-only protein. Oncogene. 27:S137–148.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Przyklenk K, Dong Y, Undyala VV and
Whittaker P: Autophagy as a therapeutic target for
ischaemia/reperfusion injury? Concepts, controversies, and
challenges. Cardiovasc Res. 94:197–205. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Valentim L, Laurence KM, Townsend PA, et
al: Urocortin inhibits Beclin1-mediated autophagic cell death in
cardiac myocytes exposed to ischaemia/reperfusion injury. J Mol
Cell Cardiol. 40:846–852. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Marquez RT and Xu L: Bcl-2:Beclin 1
complex: Multiple, mechanisms regulating autophagy/apoptosis toggle
switch. Am J Cancer Res. 2:214–221. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Pattingre S, Tassa A, Qu X, et al: Bcl-2
antiapoptotic proteins inhibit Beclin 1-dependent autophagy. Cell.
122:927–939. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Liang XH, Kleeman LK, Jiang HH, et al:
Protection against fatal Sindbis virus encephalitis by beclin, a
novel Bcl-2-interacting protein. J Virol. 72:8586–8596.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Akar U, Chaves-Reyez A, Barria M, et al:
Silencing of Bcl-2 expression by small interfering RNA induces
autophagic cell death in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Autophagy.
4:669–679. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Hamacher-Brady A, Brady NR, Logue SE, et
al: Response to myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury involves
Bnip3 and autophagy. Cell Death Differ. 14:146–157. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Bellot G, Garcia-Medina R, Gounon P, et
al: Hypoxia-induced autophagy is mediated through hypoxia-inducible
factor induction of BNIP3 and BNIP3L via their BH3 domains. Mol
Cell Biol. 29:2570–2581. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Yasuda M, Theodorakis P, Subramanian T and
Chinnadurai G: Adenovirus E1B-19K/BCL-2 interacting protein BNIP3
contains a BH3 domain and a mitochondrial targeting sequence. J
Biol Chem. 273:12415–12421. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Chen G, Ray R, Dubik D, et al: The E1B
19K/Bcl-2-binding protein Nip3 is a dimeric mitochondrial protein
that activates apoptosis. J Exp Med. 186:1975–1983. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Hariharan N, Maejima Y, Nakae J, Paik J,
Depinho RA and Sadoshima J: Deacetylation of FoxO by Sirt1 plays an
essential role in mediating starvation-induced autophagy in cardiac
myocytes. Circ res. 107:1470–1482. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Lee IH, Cao L, Mostoslavsky R, et al: A
role for the NAD-dependent deacetylase Sirt1 in the regulation of
autophagy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:3374–3379. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Ou X, Lee MR, Huang X, Messina-Graham S
and Broxmeyer HE: SIRT1 positively regulates autophagy and
mitochondria function in embryonic stem cells under oxidative
stress. Stem Cells. 32:1183–1194. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Lee Y, Lee HY, Hanna RA and Gustafsson AB:
Mitochondrial autophagy by Bnip3 involves Drp1-mediated
mitochondrial fission and recruitment of Parkin in cardiac
myocytes. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 301:H1924–1931. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|