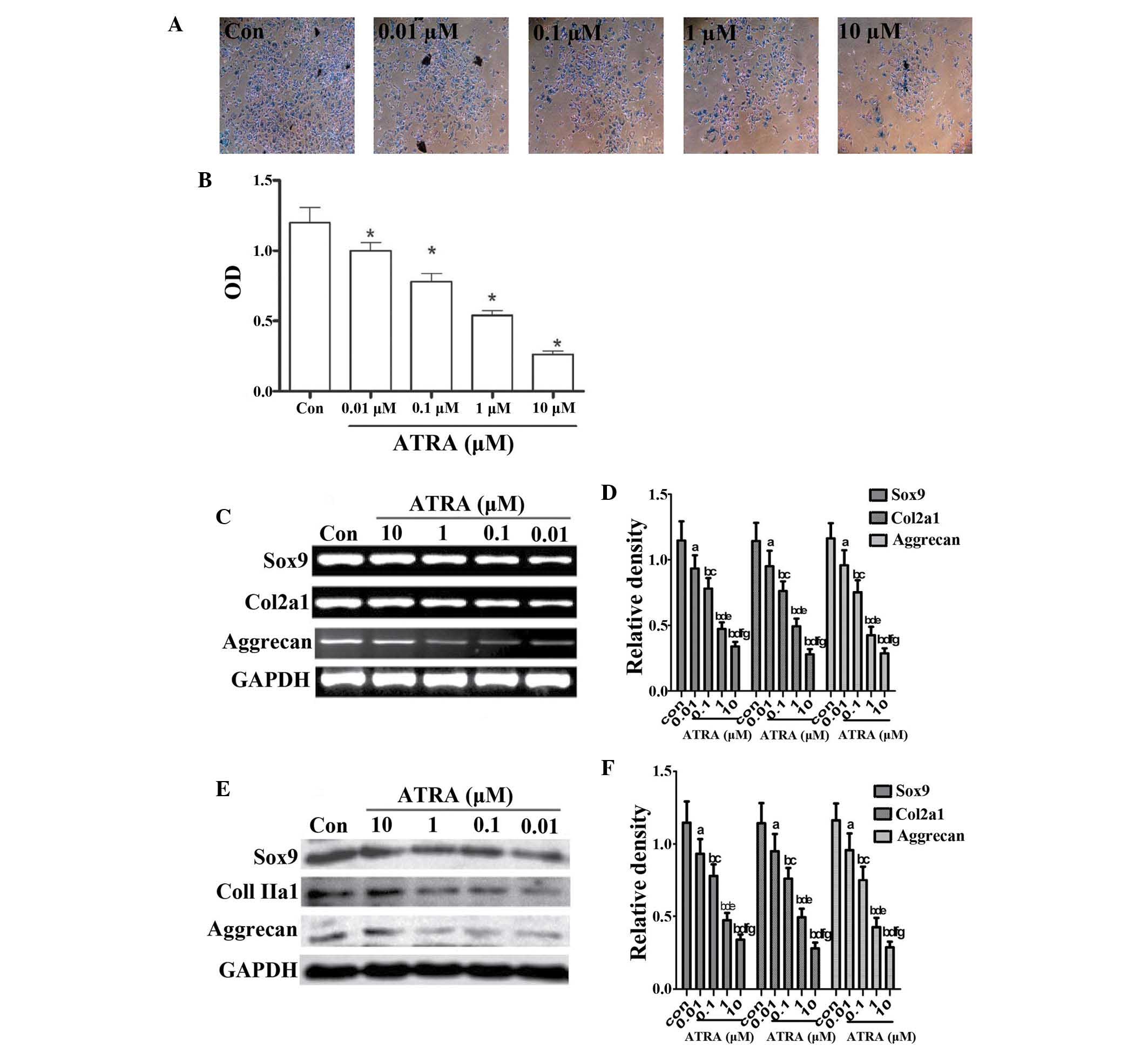
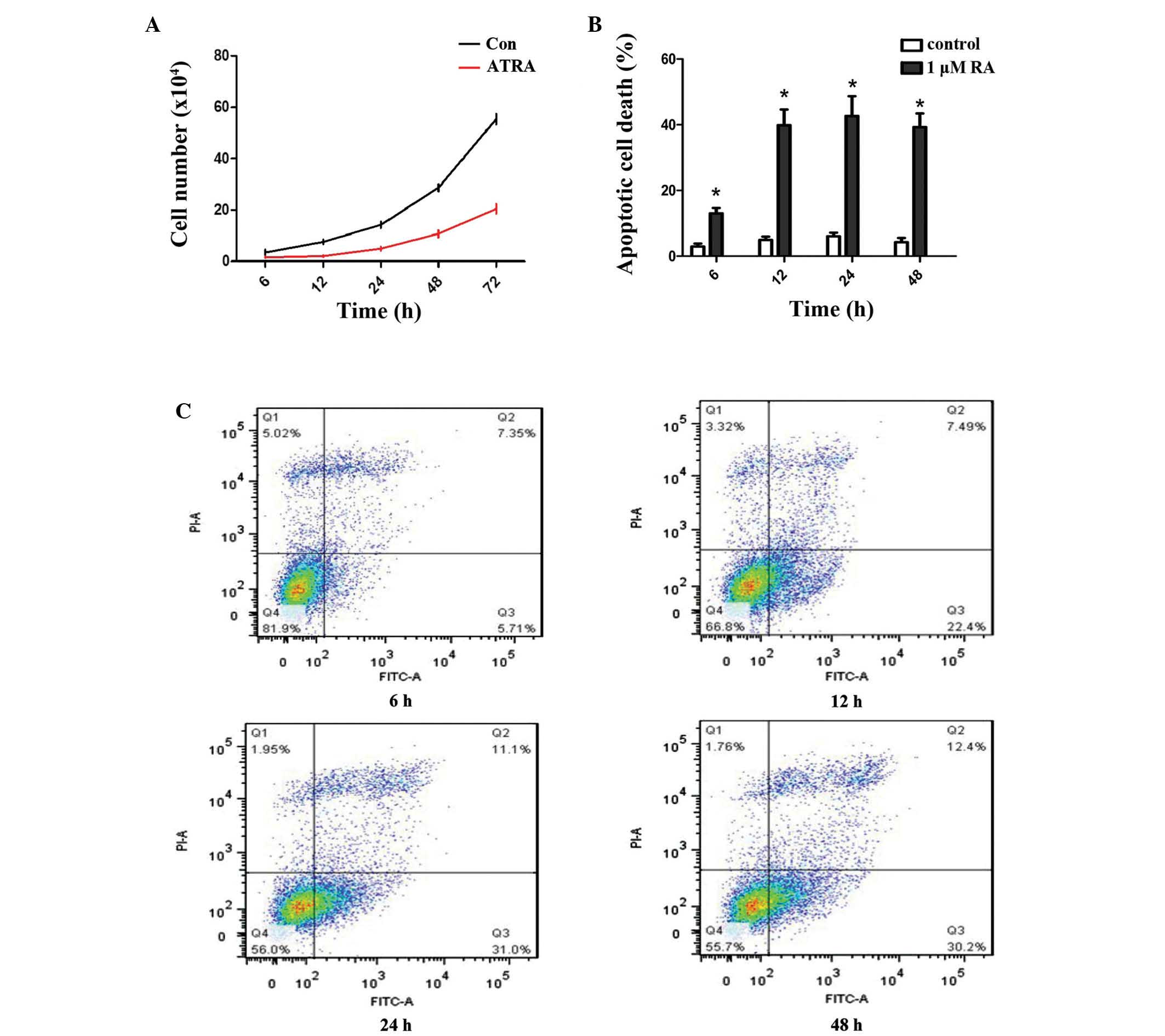
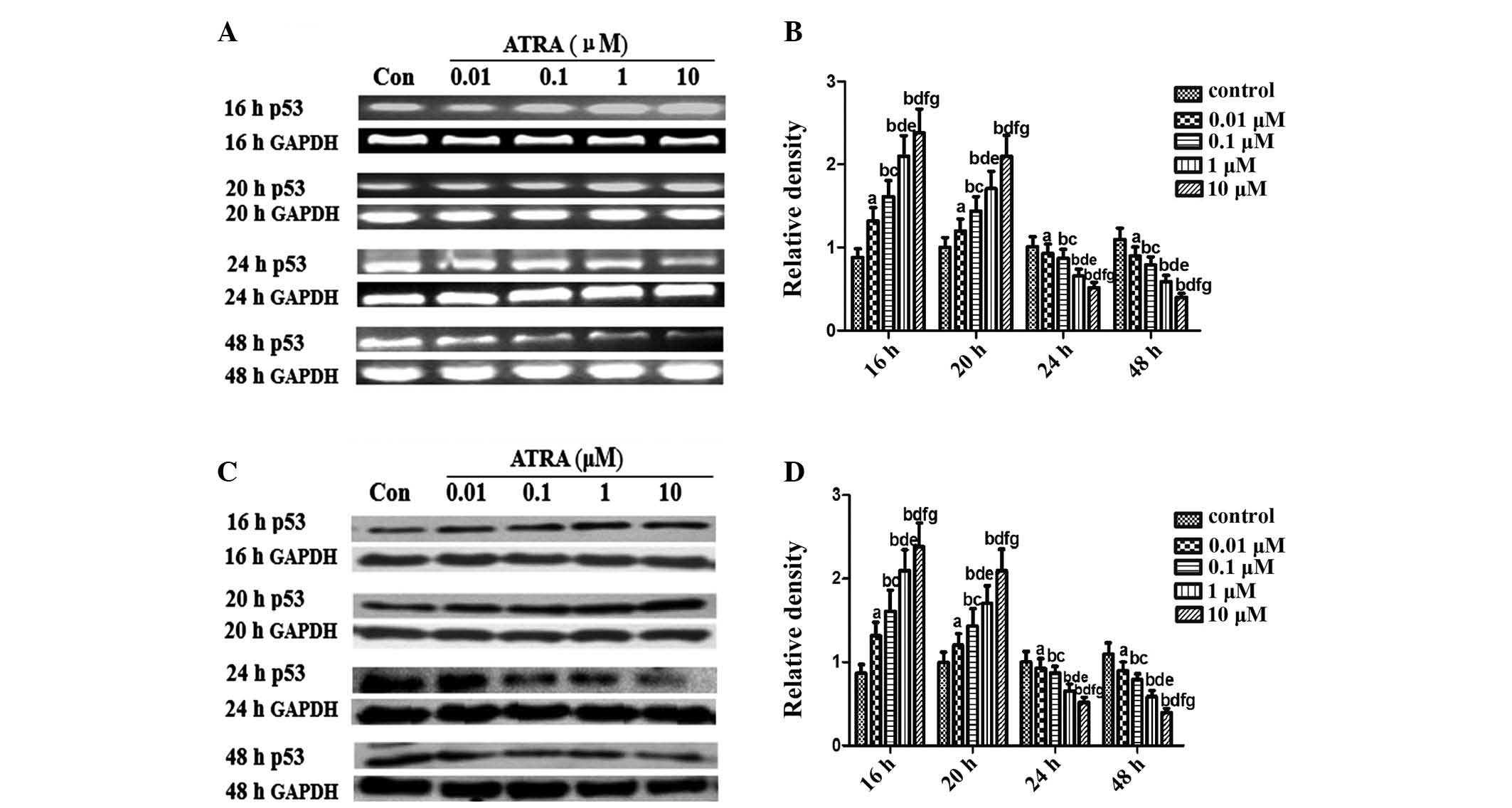
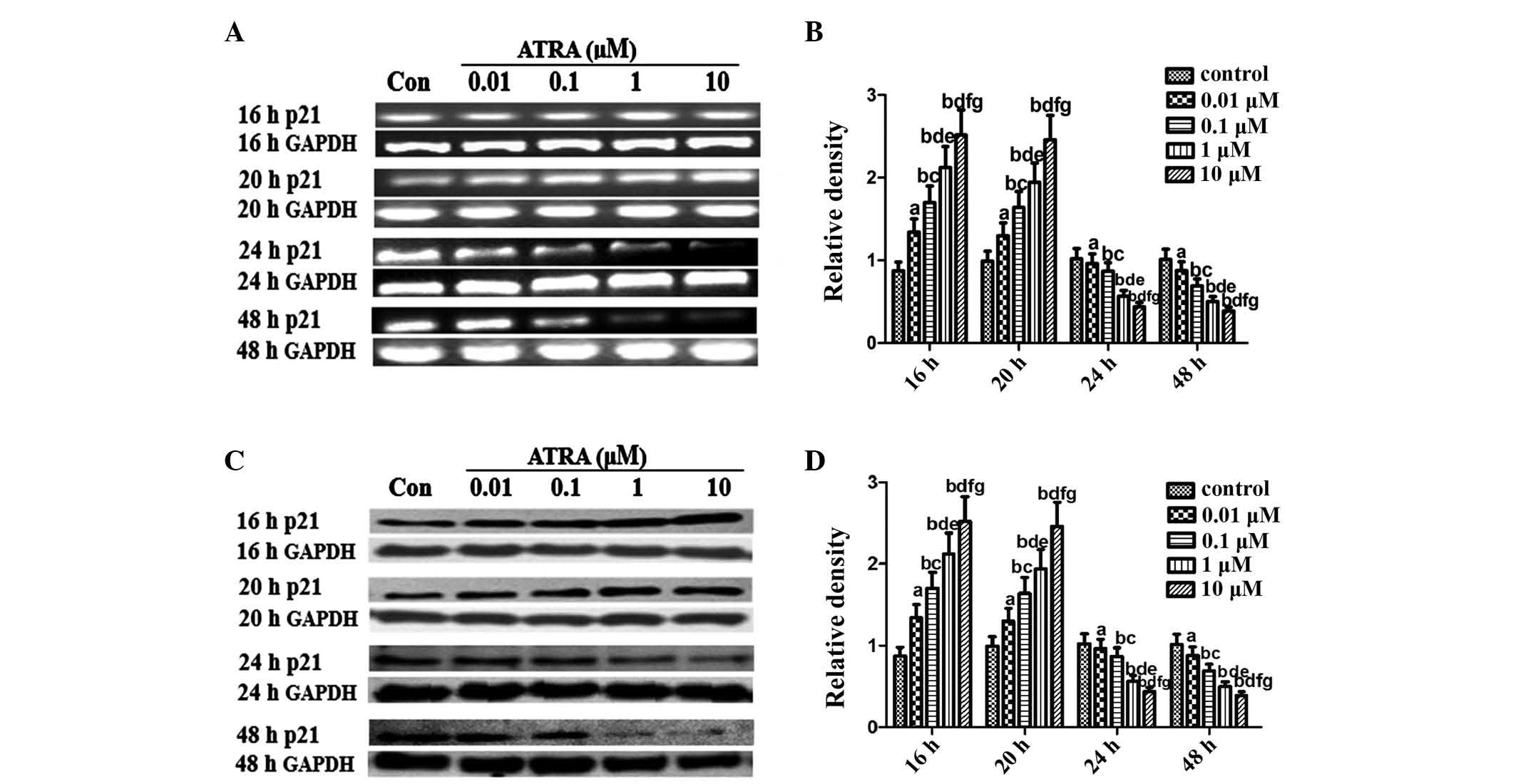
|
1
|
Lee GS, Kochhar DM and Collins MD:
Retinoid-induced limb malformations. Curr Pharm Design.
10:2657–2699. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Delgado-Baeza E, Santos-Alvarez I and
Martos-Rodriguez A: Retinoic acid-induced clubfoot-like deformity:
pathoanatomy in rat fetuses. J Pediatr Orthoped B. 8:12–18.
1999.
|
|
3
|
Zhong YS, Zheng C, Jia Y, et al:
Quantitative evaluation in vivo of the degree of differentiation of
hindlimb cartilage in a rat clubfoot model. Toxicol Mech Methods.
19:292–297. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liu ZY, Li XD, Chen B, et al: Retinoic
acid retards fetal and hindlimb skeletal development asymmetrically
in a retinoic acid-induced clubfoot model. Exp Toxicol Pathol.
62:663–670. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zelzer E and Olsen BR: The genetic basis
for skeletal diseases. Nature. 423:343–348. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tickle C: Patterning systems - from one
end of the limb to the other. Dev Cel. 4:449–458. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Kastan MB, Zhan Q, El-Deiry WS, et al: A
mammalian cell cycle checkpoint pathway utilizing p53 and GADD45 is
defective in ataxia-telangiectasia. Cell. 71:587–597. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sarkar SA and Sharma RP:
All-trans-retinoic acid-mediated modulation of p53 during neural
differentiation in murine embryonic stem cells. Cell Biol Toxicol.
18:243–257. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Beier F, Leask TA, Haque S, et al: Cell
cycle genes in chondrocyte proliferation and differentiation.
Matrix Biol. 18:109–120. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Beier F, Taylor AC and LuValle P: The
Raf-1/MEK/ERK pathway regulates the expression of the p21Cip1/Waf1
gene in chondrocytes. J Biol Chem. 274:30273–30279. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wade J, Adami GR, Wei N, Keyomarsi K and
Elledge SJ: The p21 Cdk-interacting protein Cip1 is a potent
inhibitor of G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Cell. 75:805–816. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
El-Deiry WS, Tokino T, Velculescu VE, et
al: WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression. Cell.
75:817–825. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gartel AL and Tyner AL: Transcriptional
regulation of the p21 [(WAF1/CIP1)] gene. Exp Cell Res.
246:280–289. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
de Oca Luna RM, Wagner DS and Lozano G:
Rescue of early embryonic lethality in mdm2-deficient mice by
deletion of p53. Nature. 378:203–206. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Uren AG and Vaux DL: Molecular and
clinical aspects of apoptosis. Pharmacol Ther. 72:37–50. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nomoto S, Ootsuyama A, Shioyama Y, Katsuki
M, Kondo S and Norimura T: The high susceptibility of heterozygous
p53(+/−) mice to malformation after foetal irradiation is related
to sub-competent apoptosis. Int J Radiat Biol. 74:419–429. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Westphal CH, Hoyes KP, Canman CE, et al:
Loss of atm radiosensitizes multiple p53 null tissues. Cancer Res.
58:5637–5639. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Armstrong JF, Kaufman MH, Harrison DJ and
Clarke AR: High-frequency developmental abnormalities in
p53-deficient mice. Curr Biol. 5:931–936. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cordenonsi M, Dupont S, Maretto S, Insinga
A, Imbriano C and Piccolo S: Links between tumor suppressors: p53
is required for TGF-β gene responses by cooperating with Smads.
Cell. 113:301–314. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Danilova N, Sakamoto KM and Lin S: p53
family in development. Mech Dev. 125:919–931. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Campbell WA, Yang H, Zetterberg H, et al:
Zebrafish lacking Alzheimer presenilin enhancer 2 (Pen-2)
demonstrate excessive p53-dependent apoptosis and neuronal loss. J
Neurochem. 96:1423–1440. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Villiard É, Brinkmann H, Moiseeva O,
Mallette FA, Ferbeyre G and Roy S: Urodele p53 tolerates amino acid
changes found in p53 variants linked to human cancer. BMC Evol
Biol. 7:1802007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Schmid P, Lorenz A, Hameister H and
Montenarh M: Expression of p53 during mouse embryogenesis.
Development. 113:857–865. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Flint O and Orton T: An in vitro assay for
teratogens with cultures of rat embryo midbrain and limb bud cells.
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 76:383–395. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lev R and Spicer S: Specific staining of
sulphate groups with alcian blue at low pH. J Histochem Cytochem.
12:309. 1964. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li Y, Jiang Y, Wan Y, et al:
Medroxyprogestogen enhances apoptosis of SKOV-3 cells via
inhibition of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. J Biomed Res.
27:43–50. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Solursh M: Differentiation of cartilage
and bone. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1:989–994. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ruberte E, Dolle P, Chambon P and
Morriss-Kay G: Retinoic acid receptors and cellular retinoid
binding proteins. II. Their differential pattern of transcription
during early morphogenesis in mouse embryos. Development.
111:45–60. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Thorogood P and Hinchliffe J: An analysis
of the condensation process during chondrogenesis in the embryonic
chick hindlimb. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 33:581–606. 1975.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ahrens PB, Solursh M and Reiter RS:
Stage-related capacity for limb chondrogenesis in cell culture. Dev
Biol. 60:69–82. 1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Duester G: Retinoic acid synthesis and
signaling during early organogenesis. Cell. 134:921–931. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Galdones E and Hales BF: Retinoic acid
receptor gamma-induced misregulation of chondrogenesis in the
murine limb bud in vitro. Toxicol Sci. 106:223–232. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kochlar D: Cellular basis of congenital
limb deformity induced in mice by vitamin A. Birth Defects Orig
Artic Ser. 13:111–154. 1977.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Paulsen DF, Chen WD, Pang L, Johnson B and
Okello D: Stage- and region-dependent chondrogenesis and growth of
chick wing-bud mesenchyme in serum-containing and defined tissue
culture media. Dev Dyn. 200:39–52. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Jia YL, Zhong YS, Chen B, et al: The
primary research of posterior buds in quantificated congenital
clubfoot at pathological and molecule levels. Chin J Exp Surg.
6:726–728. 2009.
|
|
36
|
Hall BK and Miyake T: All for one and one
for all: condensations and the initiation of skeletal development.
Bioessays. 22:138–147. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hall B and Miyake T: The membranous
skeleton: the role of cell condensations in vertebrate
skeletogenesis. Anat Embryol (Berl). 186:107–124. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Bi W, Deng JM, Zhang Z, Behringer RR and
de Crombrugghe B: Sox9 is required for cartilage formation. Nat
Genet. 22:85–89. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bi W, Huang W, Whitworth DJ, et al:
Haploinsufficiency of Sox9 results in defective cartilage primordia
and premature skeletal mineralization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
98:6698–6703. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Goldring MB, Tsuchimochi K and Ijiri K:
The control of chondrogenesis. J Cell Biochem. 97:33–44. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Stewart M, Farnum C and MacLeod J:
Expression of p21CIP1/WAF1 in chondrocytes. Calcif Tissue Int.
61:199–204. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
de Crombrugghe B, Lefebvre V and Nakashima
K: Regulatory mechanisms in the pathways of cartilage and bone
formation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 13:721–727. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Almog N and Rotter V: Involvement of p53
in cell differentiation and development. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1333:F1–F27. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ng LJ, Wheatley S, Muscat GE, et al: SOX9
binds DNA, activates transcription and coexpresses with type II
collagen during chondrogenesis in the mouse. Dev Biol. 183:108–121.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Meletis K, Wirta V, Hede S-M, Nistér M,
Lundeberg J and Frisén J: p53 suppresses the self-renewal of adult
neural stem cells. Development. 133:363–369. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Qin H, Yu T, Qing T, et al: Regulation of
apoptosis and differentiation by p53 in human embryonic stem cells.
J Biol Chem. 282:5842–5852. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Ikeda T, Kawaguchi H, Saito T, et al: p63
plays a central role in cartilage development by directly
regulating key genes for chondrogenesis. J Bone Miner Res.
22:s52–s101. 2007.
|