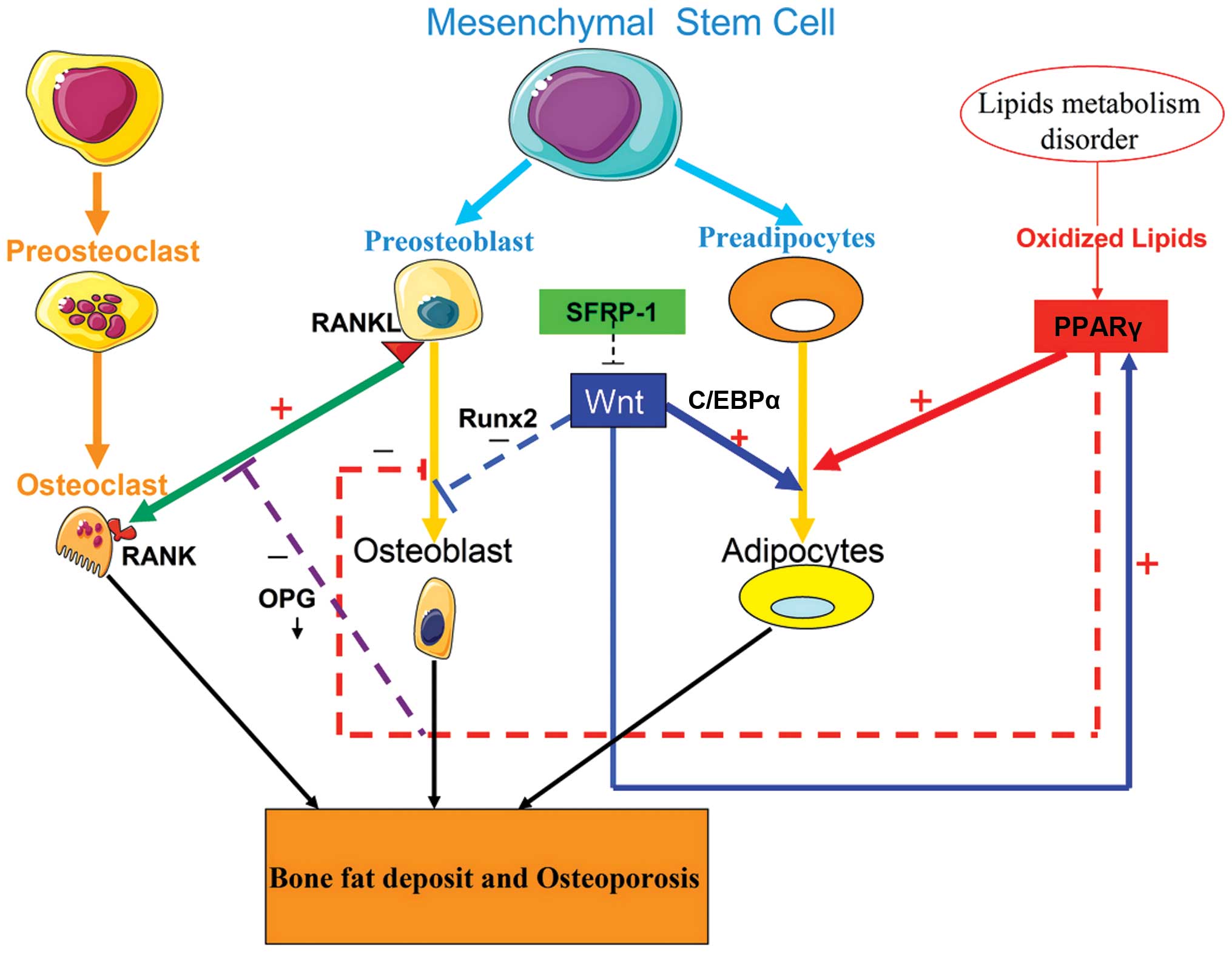
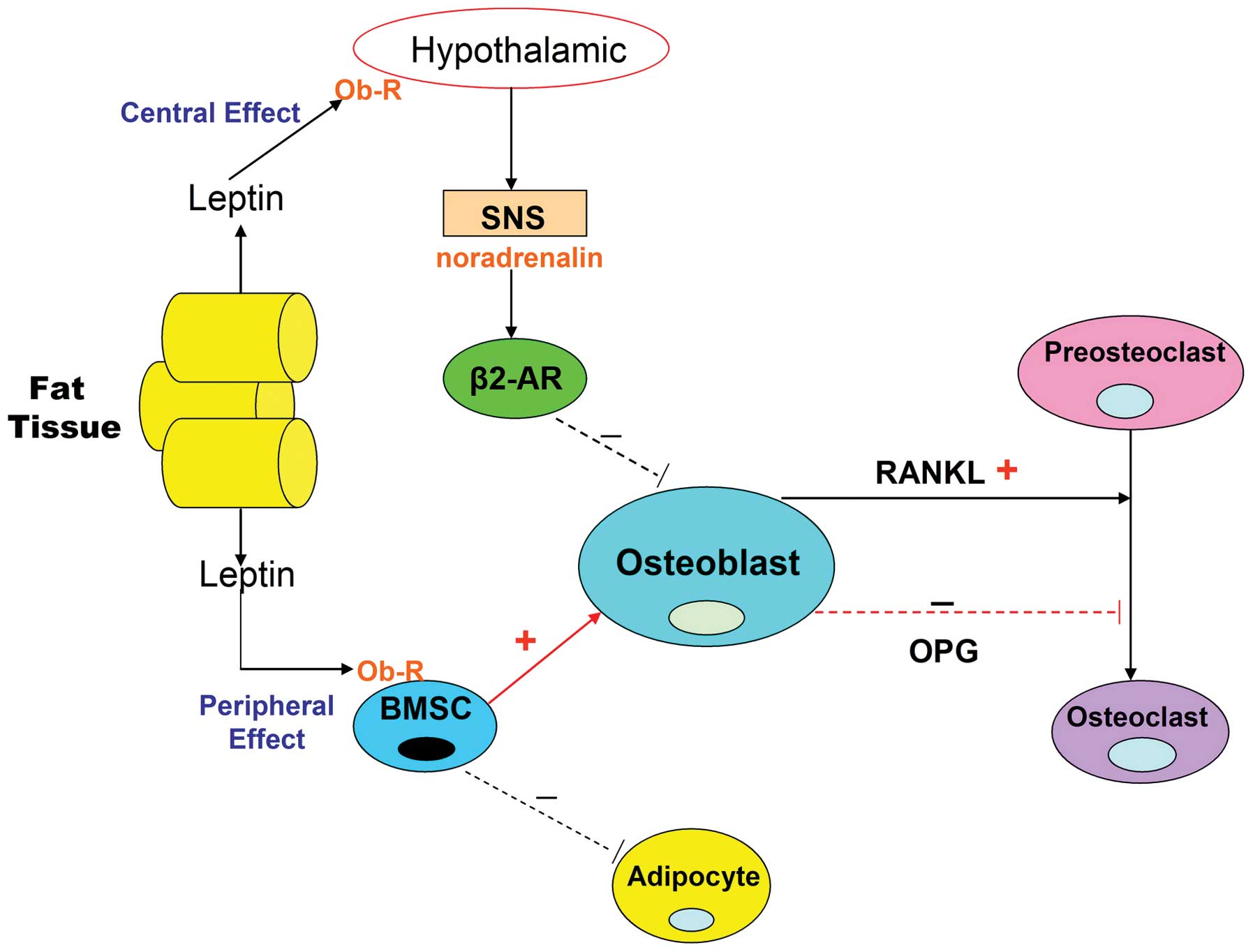
|
1
|
Bagger YZ, Tankó LB, Alexandersen P, Qin G
and Christiansen C: Prospective epidemiological risk factors study
group: radiographic measure of aorta calcification is a
site-specific predictor of bone loss and fracture risk at the hip.
J Intern Med. 259:598–605. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sinnott B, Syed I, Sevrukov A and
Barengolts E: Coronary calcification and osteoporosis in men and
postmenopausal females are independent processes associated with
aging. Calcif Tissue Int. 78:195–202. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yao W, Cheng Z, Busse C, Pham A, Nakamura
MC and Lane NE: Glucocorticoid excess in mice results in early
activation of osteoclastogenesis and adipogenesis and prolonged
suppression of osteogenesis: a longitudinal study of gene
expression in bone tissue from glucocorticoid-treated mice.
Arthritis and Rheum. 58:1674–1686. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Edwards CJ, Hart DJ and Spector TD: Oral
statins and increased bone-mineral density in postmenopausal
females. Lancet. 355:2218–2219. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Barengolts EI, Berman M, Kukreja SC,
Kouznetsova T, Lin C and Chomka EV: Osteoporosis and coronary
atherosclerosis in asymptomatic postmenopausal females. Calcif
Tissue Int. 62:209–213. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Consensus development conference:
diagnosis, prophylaxis and, treatment of osteoporosis. Am J Med.
94:646–650. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Bonjour JP, Ammann P and Rizzoli R:
Importance of preclinical studies in the development of drugs for
treatment of osteoporosis: a review related to the 1998. WHO
guielelines. 9:379–393. 1999.
|
|
8
|
Mundy G, Garrett R, Harris S, et al:
Stimulation of bone formation in vitro and in rodents by statins.
Science. 286:1946–1949. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yamaguchi T, Sugimoto T, Yano S, Yamauchi
M, Sowa H, Chen Q and Chihara K: Plasma lipids and osteoporosis in
postmenopausal females. Endocr J. 49:211–217. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Orozco P: Atherogenic lipid profile and
elevated lipoprotein (a) are associated with lower bone mineral
density in early postmenopausal overweight females. Eur J
Epidemiol. 19:1105–1112. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Dennison EM, Syddall HE, Aihie Sayer A,
Martin HJ and Cooper C: Lipid profile, obesity and bone mineral
density: the Hertfordshire Cohort Study. QJM. 100:297–303. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Broulik PD and Kapitola J: Interrelations
between body weight, cigarette smoking and spine bone mineral
density in osteoporotic Czech females. Endocr Regul. 27:57–60.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tang YJ, Sheu WH, Liu PH, Lee WJ and Chen
YT: Positive associations of bone mineral density with body mass
index, physical activity and blood triglyceride level in men over
70 years old: a TCVGHAGE study. J Bone Miner Metab. 25:54–59. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Sivas F, Alemdaroǧlu E, Elverici E, Kuluǧ
and Ozoran K: Serum lipid profile: its relationship with
osteoporotic vertebrae fractures and bone mineral density in
Turkish postmenopausal females. Rheumatol Int. 29:885–890. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Szulc P, Varennes A, Delmas PD, Goudable J
and Chapurlat R: Men with metabolic syndrome have lower bone
mineral density but lower fracture risk-the MINOS study. J Bone
Miner Res. 25:1446–1454. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Samelson EJ, Cupples LA, Hannan MT, et al:
Long-term effects of serum cholesterol on bone mineral density in
females and men: the Framingham Osteoporosis Study. Bone.
34:557–561. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tankó LB, Bagger YZ, Nielsen SB and
Christiansen C: Does serum cholesterol contribute to vertebral bone
loss in postmenopausal females? Bone. 32:8–14. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Hsu YH, Venners SA, Terwedow HA, et al:
Relation of body composition, fat mass and serum lipids to
osteoporotic fractures and bone mineral density in Chinese men and
females. Am J Clin Nutr. 83:146–154. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Czerny B, Pawlik A, Juzyszyn Z and
Myśliwiec Z: Effect of tamoxifen on bone mineral density and blood
lipids in ovariectomized rats. Pol J pharmacol. 55:1137–1142.
2003.
|
|
20
|
Liu KJ, Wang WJ, Li DJ, Jin HF and Zhou
WJ: Effect of Gengnianchun Recipe on bone mineral density, bone
biomechanical parameters and serum lipid level in ovariectomized
rats. Chin J Integr Med. 12:132–136. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Parhami F, Tintut Y, Beamer WG, Gharavi N,
Goodman W and Demer LL: Atherogenic high-fat diet reduces bone
mineralization in mice. J Bone Miner Res. 16:182–188. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pelton K, Krieder J, Joiner D, Freeman MR,
Goldstein SA and Solomon KR: Hypercholesterolemia promotes an
osteoporotic phenotype. Am J Pathol. 181:928–936. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Parhami F, Mody N, Gharavi N, Ballard AJ,
Tintut Y and Demer LL: Role of cholesterol biosynthetic pathway in
osteoblastic differentiation of marrow stromal cells. J Miner Res.
17:1997–2003. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Xu S and Yu JJ: Beneath the minerals, a
layer of round lipid particles was identified to mediate collagen
calcification in compact bone formation. Biophys J. 91:4221–4229.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang Y, Tao Y, Hyman ME, Li J and Chen Y:
Osteoporosis in China. Osteoporosis Int. 20:1651–1662. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Gimble JM, Robinson CE, Wu X, et al:
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptorgamma activation by
thiazolidinediones induces adipogenesis in bone marrow stromal
cells. Mol Pharmacol. 50:1087–1094. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lecka-Czernik B, Moerman EJ, Grant DF,
Lehman JM, Manolagas SC and Jilka RL: Divergent effects of
selective peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor-gamma2
ligands on adipocyte versus osteoblast differentiation.
Endocrinology. 143:2376–2384. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Huang JT, Welch JS, Ricote M, et al:
Interleukin-4-dependent production of PPAR gamma ligands in
macrophages by 12/15-lipoxygenase. Nature. 400:378–382. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kirkland JL, Tchkonia T, Pirtskhalava T,
Han J and Karagiannides I: Adipogenesis and aging: does aging make
fat go MAD? Exp Gerontol. 37:757–767. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Simonet WS, Lacey DL, Dunstan CR, et al:
Osteoprotegerin: a novel secreted protein involved in the
regulation of bone density. Cell. 89:309–319. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Schoppet M, Preissner KT and Hofbauer LC:
RANK ligand and osteoprotegerin: paracrine regulators of bone
metabolism and vascularfunction. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
22:549–553. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jabbar S, Drury J, Fordham JN, Datta HK,
Francis RM and Tuck SP: Osteoprotegerin, RANKL and bone turnover in
postmenopausal osteoporosis. J Clin Pathol. 64:354–357. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bekker PJ, Holloway D, Nakanishi A,
Arrighi M, Leese PT and Dunstan CR: The effect of a single dose of
osteoprotegerin in postmenopausal females. J Bone Miner Res.
16:348–360. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mezquita-Raya P, de la Hiquera M, García
DF, et al: The contribution of serum osteoprotegerin to bone mass
and vertebral fractures in postmenopausal females. Osteoporos Int.
16:1368–1374. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Indridason OS, Franzson L and Sigurdsson
G: Serum osteoprotegerin and its relationship with bone mineral
density and markers of bone turnover. Osteoporos Int. 16:417–423.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cummings SR, Martin JS, McClung MR, et al:
Denosumab for prevention of fractures in postmenopausal females
with osteoporosis. N Engl J Med. 361:756–765. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Qiu W, Andersen TE, Bollerslev J, Mandrup
S, Abdallah BM and Kassem M: Patients with high bone mass phenotype
exhibit enhanced osteoblast differentiation and inhibition of
adipogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells. J Bone and Mineral
Res. 22:1720–1731. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Abdallah BM and Kassem M: New factors
controlling the balance between osteoblastogenesis and
adipogenesis. Bone. 50:540–545. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Tamai K, Semenov M, Kato Y, et al:
LDL-receptor related proteins in Wnt signal transduction. Nature.
407:530–535. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bienz M: TCF: transcriptional activator or
repressor? Curr Opin Cell Biol. 10:366–372. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Taipaleenmäki H, Abdallah BM, AlDahmash A,
Säämänen AM and Kassem M: Wnt signaling mediates the cross-talk
between bone marrow derived pre-adipocytic and pre-osteoblastic
cell populations. Exp Cell Res. 317:745–756. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Kang S, Bennett CN, Gerin I, Rapp LA,
Hankenson KD and Macdougald OA: Wnt signaling stimulates
osteolastogenesis of mesenchymal precursors by suppressing
CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha and peroxisome
proliferators-activated receptor gamma. J Biol Chem.
282:14515–14524. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Jones SE and Jomary C: Secreted
frizzled-related proteins: searching for relationships and
patterns. Bioessays. 24:811–820. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Gaur T, Rich L, Lengner CJ, et al:
Secreted frizzled related protein 1 regulates Wnt signaling for
BMP2 induced chondrocyte differentiation. J Cell Physiol.
208:87–96. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yao W, Cheng Z, Shahnazari M, Dai W,
Johnson ML and Lane NE: Overexpression of secreted frizzled-related
protein 1 inhibits bone formation and attenuates parathyroid
hormone bone anabolic effects. J Bone Miner Res. 25:190–199. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Lagathu C, Christodoulides C, Tan CY, et
al: Secreted frizzled-related protein 1 regulates adipose tissue
expansion and is dysregulated in severe obesity. Int J Obes.
34:1695–1705. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Denver RJ, Bonett RM and Boorse GC:
Evolution of leptin structure and function. Neuroendocrinology.
94:21–38. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Thomas T: The complex effects of leptin on
bone metabolism through multiple pathways. Curr Opin Pharmacol.
4:295–300. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Turner RT, Kalra SP, Wong CP, Philbrick
KA, Lindenmaier LB, Boghossian S and Iwaniec UT: Peripheral leptin
regulates bone formation. J Bone Mineral Res. 28:22–34. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Cornish J, Callon KE, Bava U, et al:
Leptin directly regulates bone cell function in vitro and reduces
bone fragility in vivo. J Endocrinol. 175:405–415. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Hamrick MW, Pennington C, Newton D, Xie D
and Isales C: Leptin deficiency produces contrasting phenotypes in
bones of the limb and spine. Bone. 34:376–383. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Iwaniec UT, Boghossian S, Lapke PD, Turner
RT and Kalra SP: Central leptin gene therapy corrects skeletal
abnormalities in leptin-deficient ob/ob mice. Peptides.
28:1012–1019. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Kalra SP, Dube MG and Iwaniec UT: Leptin
increases osteoblast-specific osteocalcin release through a
hypothalamic relay. Peptides. 30:967–973. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Bartell SM, Rayalam S, Ambati S, et al:
Central (ICV) leptin injection increases bone formation, bone
mineral density, muscle mass, serum IGF-1, and the expression of
osteogenic genes in leptin-deficient ob/ob mice. J Bone Miner Res.
26:1710–1720. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Ducy P, Amling M, Takeda S, et al: Leptin
inhibits bone formation through a hypothalamic relay: a central
control of bone mass. Cell. 100:197–207. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Holloway WR, Collier FM, Aitken CJ, et al:
Leptin inhibits osteoclast generation. J Bone Miner Res.
17:200–209. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Thomas T, Gori F, Khosla S, Jensen MD,
Burguera B and Riggs BL: Leptin acts on human marrow stromal cells
to enhance differentiation to osteoblasts and to inhibit
differentiation to adipocytes. Endocrinology. 140:1630–1638.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Kim GS, Hong JS, Kim SW, Koh JM, An CS,
Choi JY and Cheng SL: Leptin induces apoptosis via
ERK/cPLA2/cytochrome pathway in human bone marrow stromal cells. J
Biol Chem. 278:21920–21929. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Hamrick MW and Ferrari SL: Leptin and the
sympathetic connection of fat to bone. Osteoporos Int. 19:905–912.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Hamrick MW, Della-Fera MA, Hartzell D,
Pennington C and Baile CA: Intrahypothalamic injections of leptin
increase adipocyte apoptosis in peripheral fat pad and in bone
marrow. Cell Tissue Res. 327:133–141. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Idelevich A, Sato K and Baron R: What are
the effects of leptin on bone and where are they exerted? J Bone
Miner Res. 28:18–21. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Farooqi IS, Jebb SA, Langmack G, et al:
Effects of recombinant leptin therapy in a child with congenital
leptin deficiency. N Engl J Med. 341:879–884. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Paz-Filho G, Mastronardi C, Delibasi T,
Wong ML and Licinio J: Congenital leptin deficiency: diagnosis and
effects of leption replacement therapy. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metab.
54:690–697. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Arita Y, Kihara S, Ouchi N, et al:
Paradoxical decrease of an adipose-specific protein, adiponectin,
in obesity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 257:79–83. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Kumada M, Kihara S, Dumitsuji S, et al:
Association of hypoadiponectinemia with coronary artery disease in
men. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 23:85–89. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Hara K, Horikoshi M, Yamauchi T, et al:
Measurement of the high-molecular weight form of adiponectin in
plasma is useful for the prediction of insulin resistance and
metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Care. 29:1357–1362. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Oshima K, Nampei A, Matsuda M, et al:
Adiponectin increases bone mass by suppressing osteoclast and
activating osteoblast. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 331:520–526.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Yamaguchi N, Kukita T, Li YJ, Marinez
Argueta JG, Saito T, Hanazawa S and Yamashita Y: Adiponectin
inhibits osteoclast formation stimulated by lipoplysaccharide from
Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol.
49:28–34. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Kajimura D, Lee WH, Riley JK, et al:
Adiponectin regulates bone mass via opposite central and peripheral
mechanisms through FoxO1. Cell Metab. 17:901–915. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Luo XH, Guo LJ, Xie H, Yuan LQ, Wu XP,
Zhou HD and Liao EY: Adiponectin stimulates RANKL and inhibits OPG
expression in human osteoblasts through the MAPK signaling pathway.
J Bone Miner Res. 21:1648–1656. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Tu QS, Zhang J, Dong LQ, Saunders E, Luo
E, Tang J and Chen J: Adiponectin inhibits osteoclastogenesis and
bone resorption via APPL1-mediated suppression of Akt1. J Bio Chem.
286:12542–12553. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Yamaguchi N, Kukita T, Li YJ, et al:
Adiponectin inhibits induction of TNF-alpha/RANKL-stimulated NFATc1
via the AMPK signaling. FEBS Letters. 582:451–456. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Luo XH, Guo LJ, Yuan LQ, Xie H, Zhou HD,
Wu XP and Liao EY: Adiponectin stimulates human osteobalsts
proliferation and differentiation via the MAPK signaling pathway.
Exp Cell Res. 309:99–109. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Lee HW, Kim SY, Kim AY, Lee EJ, Choi JY
and Kim JB: Adiponection stimulates osteoblast differentiation
through induction of COX2 in mesenchymal progenitor cells. Stem
Cells. 27:2254–2262. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Mitsui Y, Gotoh M, Fukushima N, et al:
Hyperadiponectinemia enhances bone formation in mice. BMC
Musculoskelet Disord. 12:182011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Ealey KN, Kaludjerovic J, Archer M and
Ward WE: Adiponectin is a negative regulator of bone mineral and
bone strength in growing mice. Exp Biol Med (Maywood).
233:1546–1553. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Hotta K, Funahashi T, Bodkin NL, et al:
Circulating concentrations of the adipocyte protein adiponetin are
decreased in parallel with reduced insulin sensitivity during the
progression to type 2 diabetes in rhesus monkeys. Diabetes.
50:1126–1133. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Bauche IB, E1 Mkadem SA, Pottier AM, et
al: Overexpression of adiponectin targeted to adipose tissue in
transgenic mice: impaired adipocyte differentiation. Endocrinology.
148:1539–1549. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Otabe S, Yuan X, Fukutani T, et al:
Overexpression of human adiponectin in transgenic mice results in
suppression of fat accumulation and prevention of premature death
by high-calorie diet. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 293:E210–E218.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Williams GA, Wang Y, Callon KE, et al: In
vitro and in vivo effects of adiponectin on bone. Endocrinology.
150:3603–3610. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Yano W, Kubota N, Itoh S, et al: Molecular
mechanism of moderate insulin resistance in adiponectin-knockout
mice. Endocr J. 55:515–522. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Nawrocki AR, Rajala MW, Tomas E, et al:
Mice lacking adiponectin show decreased hepatic insulin sensitivity
and reduced responsiveness to peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor gamma agonists. J Biol Chem. 281:2654–2660. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Kubota N, Terauchi Y, Yamauchi T, et al:
Disruption of adiponectin causes insulin resistance and neointimal
formation. J Biol Chem. 277:25863–25866. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Maeda N, Shimomura I, Kishida K, et al:
Diet-induced insulin resistance in mice lacking adiponectin/ACRP30.
Nat Med. 8:731–737. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Kanazawa I: Does adiponectin have adverse
effects on bone mass and fracture. Internal Med. View Article : Google Scholar : 2011.
|
|
86
|
Mohiti-Ardekani J, Soleymani-Salehabadi H,
Owlia MB and Mohiti A: Relationships between serum adipocyte
hormones (adiponectin, leptin, resistin), bone mineral density and
bone metabolic markers in osteoporosis patients. J Bone Miner
Metab. 32:400–404. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Wu N, Wang QP, Li H, Wu XP, Sun ZQ and Luo
XH: Relationships between serum adiponectin, leptin concentrations
and bone mineral density and bone biochemical markers in Chinese
females. Clin Chim Acta. 411:771–775. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Tenta R, Kontogianni MD and Yiannakouris
N: Association between circulating levels of adiponectin and
indices of bone mass and bone metabolism in middle-aged
post-menopausal females. J Endocrinol Invest. 35:306–311. 2012.
|
|
89
|
Schwartz AV, Sigurdsson S, Hue TF, et al:
Vertebral bone marrow fat associated with lower trabecular BMD and
prevalent vertebral fracture in older adults. J Clin Endocrinol
Metab. 98:2294–2300. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Widlansky ME, Gokce N, Keaney JF and Vita
JA: The clinical implications of endothelial dysfunction. J Am Coll
Cardiol. 42:1149–1160. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Wang GJ, Maga DB, Richemer WG, Sweet DE,
Reger SI and Thompson RC: Cortisone induced bone changes and its
response to lipid clearing agents. Clin Orthop. 130:81–85.
1978.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Miyanishi K, Yamamoto T, Irisa T,
Yamashita A, Jingushi S, Noguchi Y and Iwamoto Y: Bone marrow fat
cell enlargement and a rise in intraosseous pressure in
steroid-treated rabbits with osteonecrosis. Bone. 30:185–190. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Zhou Q, Li Q, Yang L and Liu F: Changes of
blood vessels in glucocorticoid-induced avascular necrosis of
femoral head in rabbits. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 38:212–215.
2000.In Chinese.
|
|
94
|
Kitajima M, Shigematsu I, Ogawa K,
Sugihara H and Hotokebuchi T: Effects of glucocorticoid on
adipocyte size in human bone marrow. Med Mol Morphol. 40:150–156.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Kerachian MA, Séguin C and Harvey EJ:
Glucocorticoids in osteonecrosis of the femoral head: a new
understanding of the mechanisms of action. J Steroid Biochem Mol
Biol. 114:121–128. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Savopoulos CH, Dokos CH, Kaiafa G and
Hatzitolios A: Adipogenesis and osteoblastogenesis:
trans-differentiation in the pathophysiology of bone disorders.
Hippokratia. 15:18–21. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Tsartsalis AN, Dokos C, Kaiafa GD,
Tsartsalis DN, Kattamis A, Hatzitolios AI and Savopoulos CG:
Statins, bone formation and osteoporosis: hope or hype? Hormones
(Athens). 11:126–139. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Esposito K, Capuano A, Sportiello L,
Giustina A and Giugliano D: Should we abandon statins in the
prevention of bone fractures? Endocrine. 44:326–333. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Borton AJ, Frederick JP, Datto MB, Wang XF
and Weinstein RS: The loss of Smad3 results in a lower rate of bone
formation and osteopenia through dysregulation of osteoblast
differentiation and apoptosis. J Bone Miner Res. 16:1754–1764.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Kaji H, Kanatani M, Sugimoto T and Chihara
K: Stains modulate the levels of osteoprotegerin/receptor activator
of NF kappaB ligand mRNA in mouse bone-cell cultures. Horm Metab
Res. 37:589–592. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Garrett IR and Mundy GR: The role of
statins as potential targets for bone formation. Arthritis Res.
4:237–240. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Sugiyama M, Kodama T, Konishi K, Abe K,
Asami S and Oikawa S: Compactin and simvastatin, but not
pravastatin, induce bone morphogenetic protein-2 in human
osteosarcoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 271:688–692. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Maeda T, Matsunuma A, Kawane T and
Horiuchi N: Simvastatin promotes osteoblast differentiation and
mineralization in MC3T3-E1 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
280:874–877. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Oxlund H, Dalstra M and Andreassen TT:
Statin given perorally to adult rats increases cancellous bone mass
and compressive strength. Calcif Tissue Int. 69:299–304. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Uzzan B, Cohen R, Nicolas P, Cucherat M
and Perret GY: Effects of statins on bone mineral density: a
meta-analysis of clinical studies. Bone. 40:1581–1587. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Anagnostis P, Karagiannis A, Kakafika AI,
Tziomalos K, Athyros VG and Mikhailidis DP: Atherosclerosis and
osteoporosis: age-dependent degenerative processes or related
entities? Osteoporos Int. 20:197–207. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
de Nijs RN, Jacobs JW, Lems WF, et al:
Alendronate or alfacalcidol in glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis.
N Engl J Med. 355:675–684. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Reid DM, Devogelaer JP, Saag K, et al:
Zoledronic acid and risedronate in the prevention and treatment of
glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis (HORIZON): a multicentre,
double-blind, double-dummy, randomized controlled trial. Lancet.
373:1253–1263. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Saag KG, Shane E, Boonen S, et al:
Teriparatide or alendronate in glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis.
N Engl J Med. 357:2028–2039. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Wallach S, Cohen S, Reid DM, et al:
Effects of risedronate treatment on bone density and vertebral
fracture in patients on corticosteroid therapy. Calcif Tissue Int.
67:277–285. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Riggs BL, Khosla S and Melton LJ III: A
unitary model for involutional osteoporosis: Estrogen deficiency
causes both type I and type II osteoporosis in postmenopausal
females and contributes to bone loss in aging men. J Bone Miner
Res. 13:763–773. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Heaney RP, Recker RR and Saville PD:
Menopausal changes in bone remodeling. J Lab Clin Med. 92:964–970.
1978.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Manolagas SC and Jilka RL: Bone marrow,
cytokines, and bone remodeling. Emerging insights into the
pathophysiology of osteoporosis. N Engl J Med. 332:305–311. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Khosla S, Atkinson EJ, Melton LJ III and
Riggs BL: Effects of age and estrogen status on serum parathyroid
hormone levels and biochemical markers of bone turnover in females:
a population based study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 82:1522–1527.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
D’Amelio P, Grimaldi A, Di Bella S, et al:
Estrogen deficiency increases osteoclastogenesis up-regulating T
cells activity: a key mechanism in osteoporosis. Bone. 43:92–100.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
116
|
Wells G, Tugwell P, Shea B, et al:
Meta-analysis of the efficacy of hormone replacement therapy in
treating and preventing osteoporosis in postmenopausal females.
Endocr Rev. 23:529–539. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Bonnet N, Gadois C, McCloskey E, Lemineur
G, Lespessailles E, Courteix D and Benhamou CL: Protective effect
of beta blockers in postmenopausal females: influence on fractures,
bone density, micro and macroarchitecture. Bone. 40:1209–1216.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Bonnet N, Benhamou CL, Brunet-lmbault B,
et al: Severe bone alterations under beta2 agonist treatment: bone
mass, microarchitecture and strength analyses in female rats. Bone.
37:622–633. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Bonnet N, Benhamou CL, Malaval L, et al:
Low dose beta-blocker prevents ovariectomy-induced bone loss in
rats without affecting heart functions. J Cell Physiol.
217:819–827. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Pasco JA, Henry MJ, Sanders KM, Kotowicz
MA, Seeman E and Nicholson GC: beta-adrenergic blockers reduce the
risk of fracture partly by increasing bone mineral density: Geelong
Osteoporosis Study. J Bone Miner Res. 19:19–24. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Schlienger RG, Kraenzlin ME, Jick SS and
Meier CR: Use of beta-blockers and risk of fractures. JAMA.
292:1326–1332. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Ferrari SL, Demissie S, Karasik D, Cupples
LA, Imamovic A, Dupuis J and Kiel DP: Beta 2 adrenergic receptor,
beta-blockers and their influence on bone mass in humans: the
Framingham osteoporosis study. J Bone Miner Res. 20(Suppl 1):
11–12. 2005.
|
|
123
|
Rejnmark L, Vestergaard P, Kassem M,
Christoffersen BR, Kolthoff N, Brixen K and Mosekilde L: Fracture
risk in perimenopausal females treated with beta-blockers. Calcif
Tissue Int. 75:365–372. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|