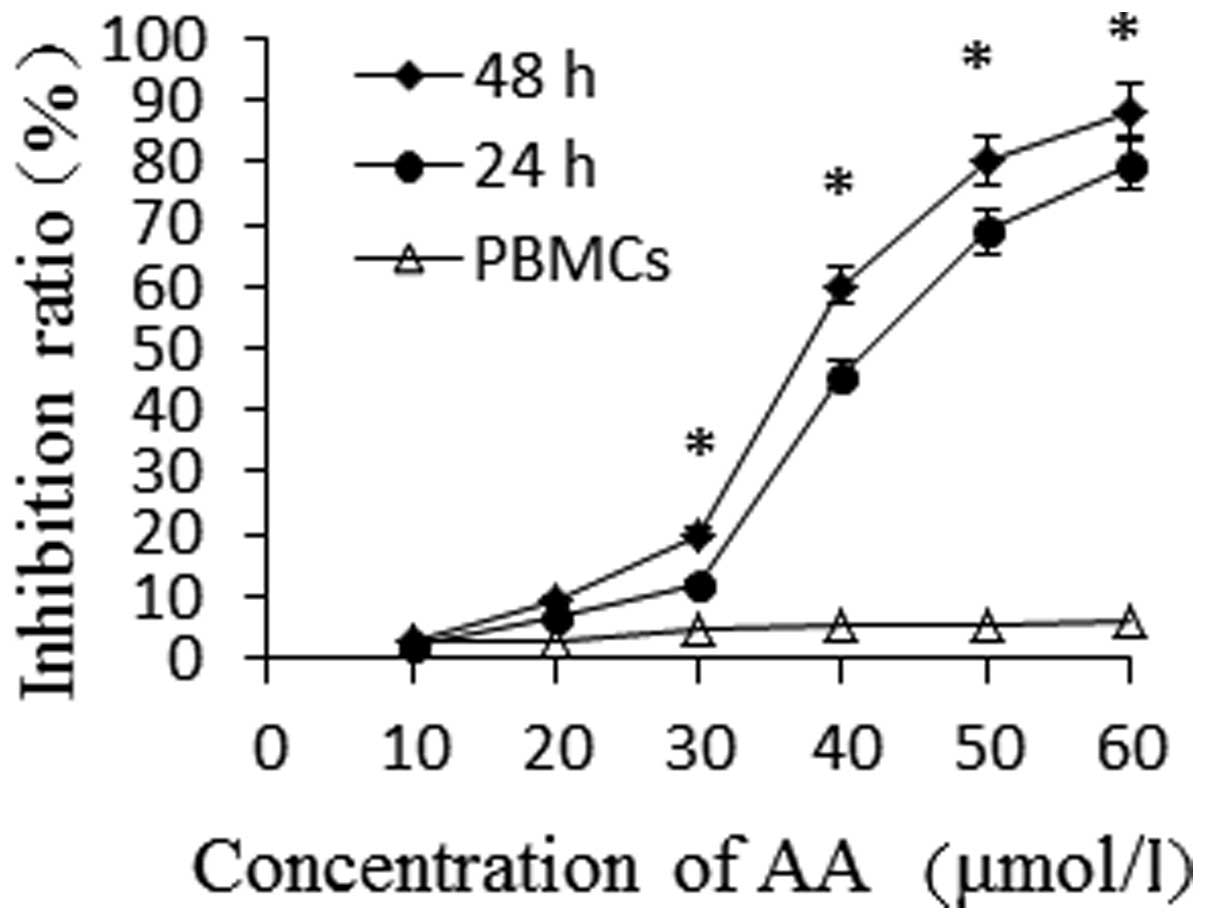
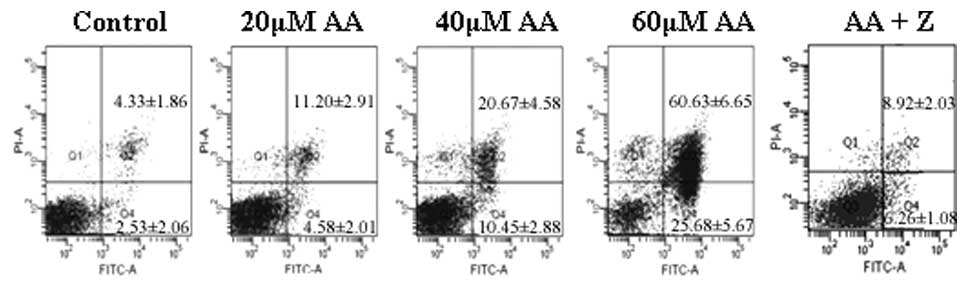
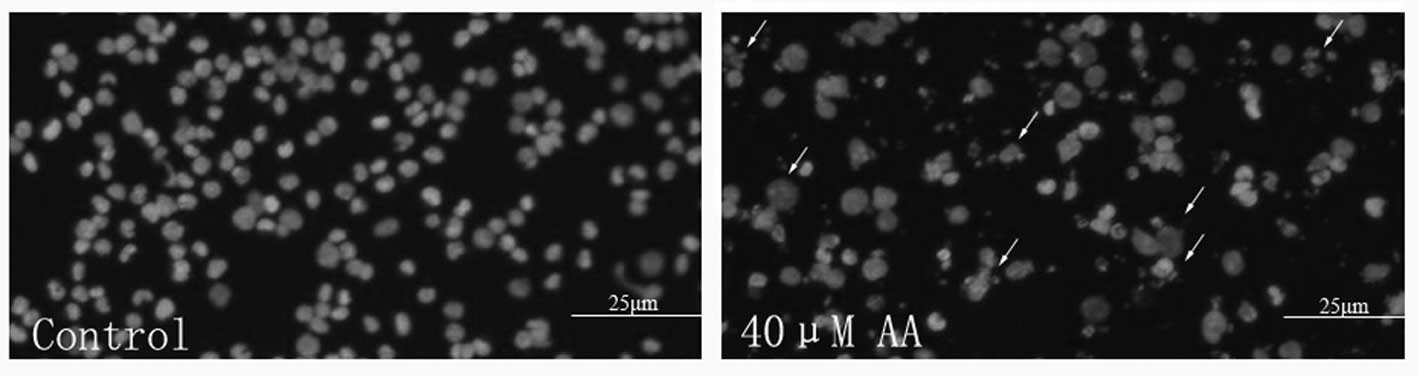
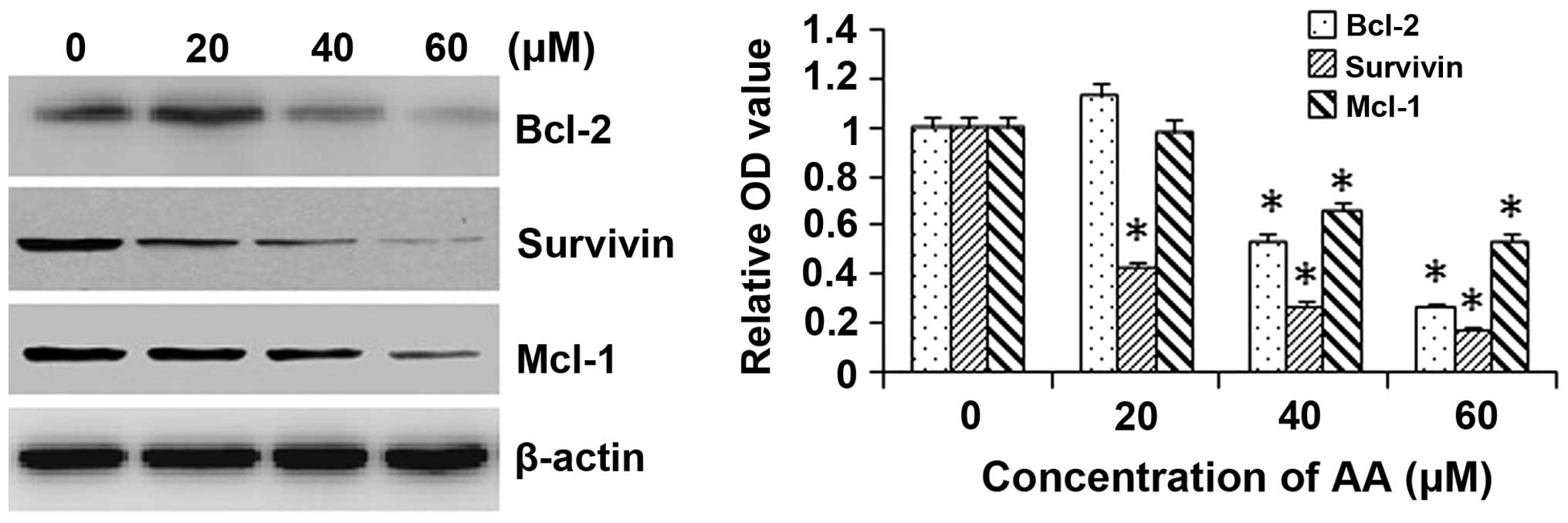
|
1
|
Ben-Ayre E, Attias S, Tadmor T and Schiff
E: Herbs in hemato-oncological care: An evidence-based review of
data on efficacy, safety, and drug interactions. Leuk Lymphoma.
51:1414–1423. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Wang N, Li DY, Niu HY, et al:
2-hydroxy-3-methylanthraquinone from Hedyotis diffusa Willd induces
apoptosis in human leukemic U937 cells through modulation of MAPK
pathways. Arch Pharm Res. 36:752–758. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li Q, Huai L, Zhang C, et al: Icaritin
induces AML cell apoptosis via the MAPK/ERK and PI3K/AKT signal
pathways. Int J Hematol. 97:617–623. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yu Z, Wang R, Xu L, Xie S, Dong J and Jing
Y: β-Elemene piperazine derivatives induce apoptosis in human
leukemia cells through down-regulation of c-FLIP and generation of
ROS. PLoS One. 6:e158432011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Shin SW and Park JW: Ursolic acid
sensitizes prostate cancer cells to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1833:723–730. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Liu L, Fu J, Li T, et al: NG, a novel
PABA/NO-based oleanolic acid derivative, induces human hepatoma
cell apoptosis via a ROS/MAPK-dependent mitochondrial pathway. Eur
J Pharmacol. 691:61–68. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang P, Li Q, Li K, et al: Betulinic acid
exerts immunoregulation and anti-tumor effect on cervical carcinoma
(U14) tumor-bearing mice. Pharmazie. 67:733–739. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tang LX, He RH, Yang G, et al: Asiatic
acid inhibits liver fibrosis by blocking TGF-beta/Smad signaling in
vivo and in vitro. PLoS One. 7:e313502012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu J, He T, Lu Q, Shang J, Sun H and
Zhang L: Asiatic acid preserves beta cell mass and mitigates
hyperglycemia in streptozocin-induced diabetic rats. Diabetes Metab
Res Rev. 26:448–454. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lee KY, Bae ON, Serfozo K, et al: Asiatic
acid attenuates infarct volume, mitochondrial dysfunction and
matrix metalloproteinase-9 induction after focal cerebral ischemia.
Stroke. 43:1632–1638. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Somboonwong J, Kankaisre M, Tantisira B
and Tantisira MH: Wound healing activities of different extracts of
Centella asiatica in incision and burn wound models: an
experimental animal study. BMC Complement Altern Med. 12:1032012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kavitha CV, Agarwal C, Agarwal R and Deep
G: Asiatic acid inhibits pro-angiogenic effects of VEGF and human
gliomas in endothelial cell culture models. PLoS One. 6:e227452011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lee YS, Jin DQ, Kwon EJ, et al: Asiatic
acid, a triterpene, induces apoptosis through intracellular Ca2+
release and enhanced expression of p53 in HepG2 human hepatoma
cells. Cancer Lett. 186:83–91. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tang XL, Yang XY, Jung HJ, et al: Asiatic
acid induces colon cancer cell growth inhibition and apoptosis
through mitochondrial death cascade. Biol Pharm Bull. 32:1399–1405.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Park BC, Bosire KO, Lee ES, Lee YS and Kim
JA: Asiatic acid induces apoptosis in SK-MEL-2 human melanoma
cells. Cancer Lett. 218:81–90. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yoshida M, Fuchigami M, Nagao T, et al:
Antiproliferative constituents from Umbelliferae plants VII Active
triterpenes and rosmarinic acid from Centella asiatica. Biol Pharm
Bull. 28:173–175. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Reed JC: Bcl-2-family proteins and
hematologic malignancies: history and future prospects. Blood.
111:3322–3330. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: the next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ni Chonghaile T, Sarosiek KA, Vo TT, et
al: Pretreatment mitochondrial priming correlates with clinical
response to cytotoxic chemotherapy. Science. 334:1129–1133. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Reed JC and Pellecchia M: Apoptosis-based
therapies for hematologic malignancies. Blood. 106:408–418. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Glaser SP, Lee EF, Trounson E, et al:
Anti-apoptotic Mcl-1 is essential for the development and sustained
growth of acute myeloid leukemia. Genes Dev. 26:120–125. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Perego P, Righetti SC, Supino R, et al:
Role of apoptosis and apoptosis-related proteins in the
cisplatin-resistant phenotype of human tumor cell lines. Apoptosis.
2:540–548. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Campbell KJ, Bath ML, Turner ML, et al:
Elevated Mcl-1 perturbs lymphopoiesis, promotes transformation of
hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells and enhances drug resistance.
Blood. 116:3197–3207. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Robinson BW, Behling KC, Gupta M, et al:
Abundant anti-apoptotic BCL-2 is a molecular target in leukaemias
with t (4;11) translocation. Br J Haematol. 141:827–839. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bunpo P, Kataoka K, Arimochi H, et al:
Inhibitory effects of asiatic acid and CPT-11 on growth of HT-29
cells. J Med Invest. 52:65–73. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hsu YL, Kuo PL, Lin LT and Lin CC: Asiatic
acid, a triterpene, induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest through
activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase and p38
mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways in human breast cancer
cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 313:333–344. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tamm I, Wang Y, Sausville E, et al:
IAP-family protein survivin inhibits caspase activity and apoptosis
induced by Fas (CD95), Bax, caspases and anticancer drugs. Cancer
Res. 58:5315–5320. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mita AC, Mita MM, Nawrocki ST and Giles
FJ: Survivin: key regulator of mitosis and apoptosis and novel
target for cancer therapeutics. Clin Cancer Res. 14:5000–5005.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ibrahim AM, Mansour IM, Wilson MM, Mokhtar
DA, Helal AM and Al Wakeel HM: Study of survivin and X-linked
inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP) genes in acute myeloid
leukemia (AML). Lab Hematol. 18:1–10. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Adida C, Berrebi D, Peuchmaur M,
Reyes-Mugica M and Altieri DC: Anti-apoptosis gene, survivin and
prognosis of neuroblastoma. Lancet. 351:882–883. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Smolewski P and Robak T: Inhibitors of
apoptosis proteins (IAPs) as potential molecular targets for
therapy of hematological malignancies. Curr Mol Med. 11:633–649.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhu Z, Li E, Liu Y, et al: Bufalin induces
the apoptosis of acute promyelocytic leukemia cells via the
downregulation of survivin expression. Acta Haematol. 128:144–150.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Johnson GL and Lapadat R:
Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways mediated by ERK, JNK and
p38 protein kinases. Science. 298:1911–1912. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Olson JM and Hallahan AR: p38 MAP kinase:
a convergence point in cancer therapy. Trends Mol Med. 10:125–129.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kim EK and Choi EJ: Pathological roles of
MAPK signaling pathways in human diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1802:396–405. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhu JF, Li ZJ, Zhang GS, et al: Icaritin
shows potent anti-leukemia activity on chronic myeloid leukemia in
vitro and in vivo by regulating MAPK/ERK/JNK and JAK2/STAT3/AKT
signalings. PLoS One. 6:e237202011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Huh JE, Kang KS, Chae C, Kim HM, Ahn KS
and Kim SH: Roles of p38 and JNK mitogen-activated protein kinase
pathways during cantharidin-induced apoptosis in U937 cells.
Biochem Pharmacol. 67:1811–1818. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hendrickx N, Volanti C, Moens U, et al:
Up-regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 and apoptosis resistance by p38
MAPK in hypericin-mediated photodynamic therapy of human cancer
cells. J Biol Chem. 278:52231–52239. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yu C, Minemoto Y, Zhang J, et al: JNK
suppresses apoptosis via phosphorylation of the proapoptotic Bcl-2
family protein BAD. Mol Cell. 13:329–340. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|