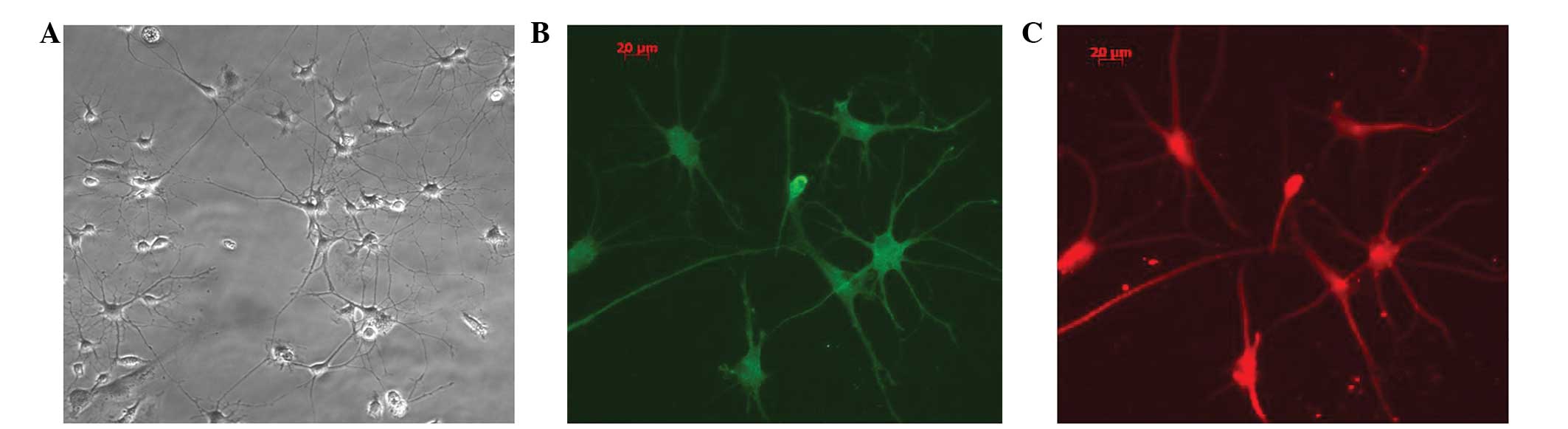
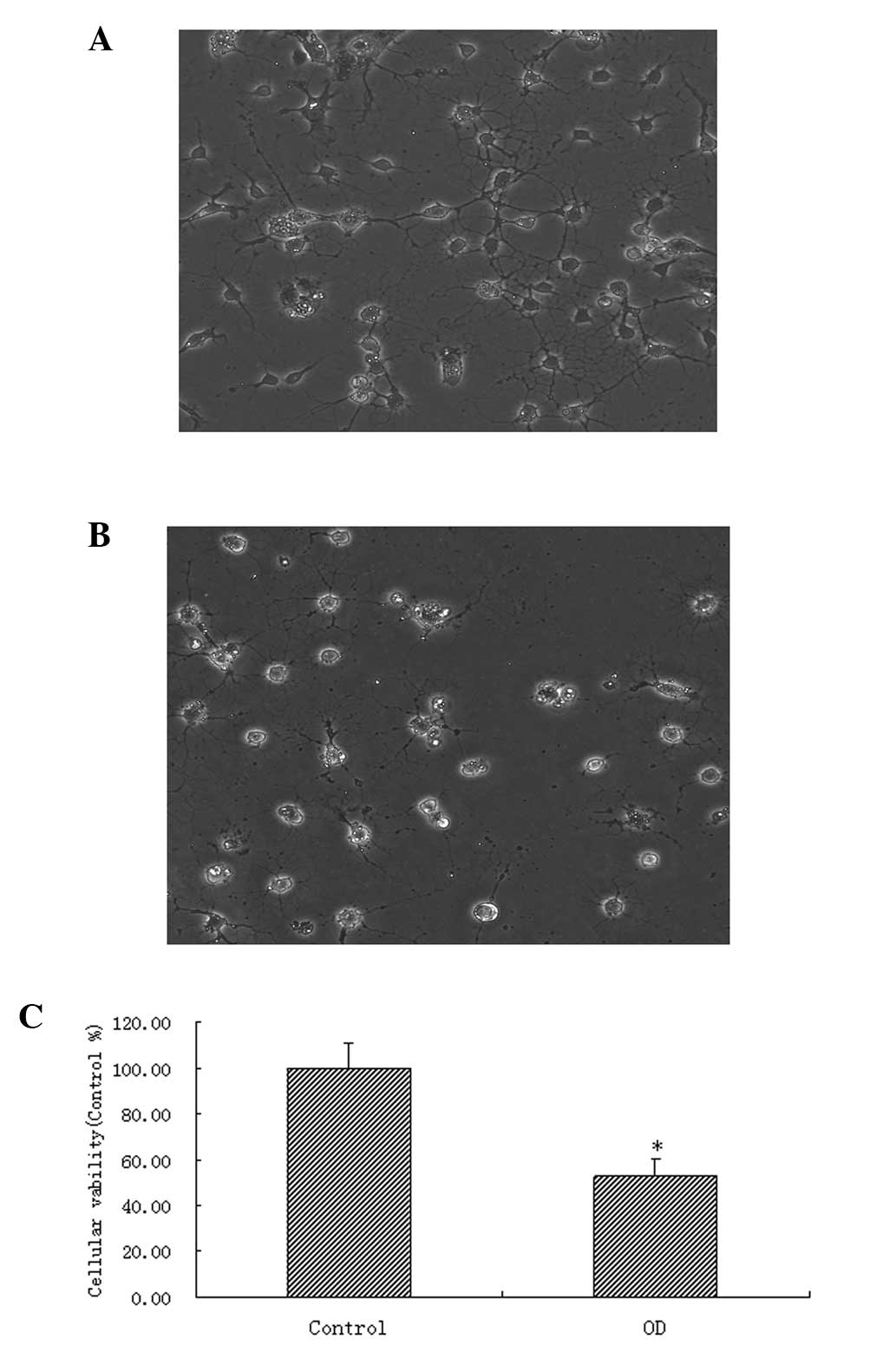
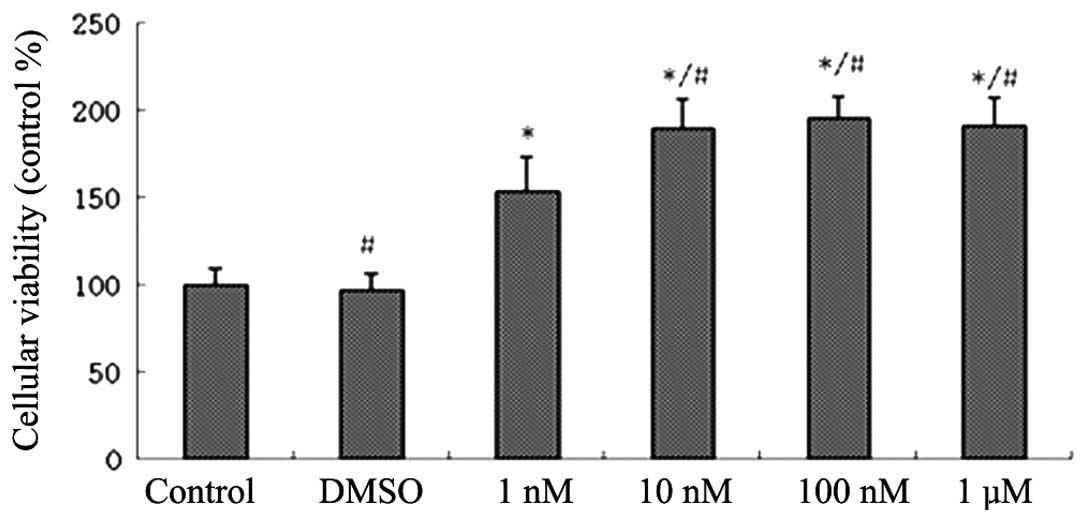
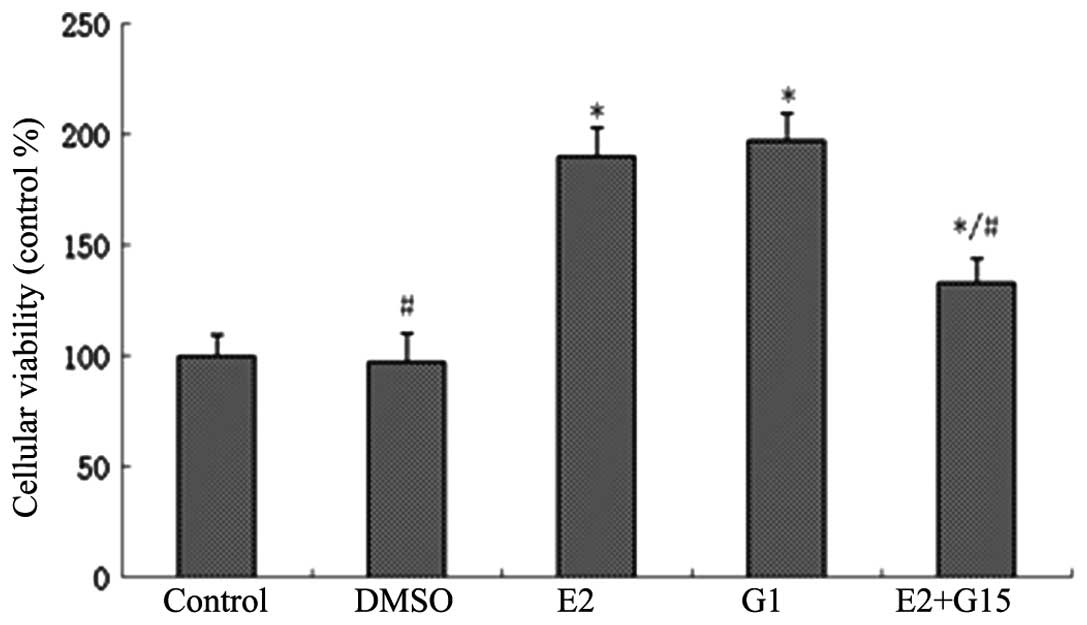
|
1
|
Thuret S, Moon LD and Gage FH: Therapeutic
interventions after spinal cord injury. Nat Rev Neurosci.
7:628–643. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fehlings MG and Hawryluk GW: Scarring
after spinal cord injury. J Neurosurg Spine. 13:165–167. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Crowe MJ, Bresnahan JC, Shuman SL, et al:
Apoptosis and delayed degeneration after spinal cord injury in rats
and monkeys. Nat Med. 3:73–76. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liu XZ, Xu XM, Hu R, et al: Neuronal and
glial apoptosis after traumatic spinal cord injury. J Neurosci.
17:5395–5406. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Grossman SD, Rosenberg LJ and Wrathall JR:
Temporal-spatial pattern of acute neuronal and glial loss after
spinal cord contusion. Exp Neurol. 168:273–282. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hu R, Zhou J, Luo C, et al: Glial scar and
neuroregeneration: Histological, functional, and magnetic resonance
imaging analysis in chronic spinal cord injury. J Neurosurg Spine.
13:169–180. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Macias CA, Rosengart MR, Puyana JC, et al:
The effects of trauma center care, admission volume, and surgical
volume on paralysis after traumatic spinal cord injury. Ann Surg.
249:10–17. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Samantaray S, Sribnick EA, Das A, et al:
Neuroprotective efficacy of estrogen in experimental spinal cord
injury in rats. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1199:90–94. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fu ES and Tummala RP: Neuroprotection in
brain and spinal cord trauma. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 18:181–187.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Elloso MM, Phiel K, Henderson RA, et al:
Suppression of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis using
estrogen receptor-selective ligands. J Endocrinol. 185:243–252.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cho T and Chaban VV: Interaction between
P2X3 and ERα/ERβ in ATP-mediated calcium signaling in mice sensory
neurons. J Neuroendocrinology. 24:789–797. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Sribnick EA, Ray SK and Banik NL: Estrogen
prevents glutamate-induced apoptosis in C6 glioma cells by a
receptor-mediated mechanism. Neuroscience. 137:197–209. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Furlan JC, Krassioukov AV and Fehlings MG:
The effects of gender on clinical and neurological outcomes after
acute cervical spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma. 22:368–381. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Webb AA, Chan CB, Brown A and Saleh TM:
Estrogen reduces the severity of autonomic dysfunction in spinal
cord-injured male mice. Behav Brain Res. 171:338–349. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Vanderhorst VG, Gustafsson JA and Ulfhake
B: Estrogen receptor-alpha and -beta immunoreactive neurons in the
brainstem and spinal cord of male and female mice: Relationships to
monoaminergic, cholinergic, and spinal projection systems. J Comp
Neurol. 488:152–179. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Vanderhorst VG, Terasawa E and Ralston HJ
III: Estrogen receptor-alpha immunoreactive neurons in the
brainstem and spinal cord of the female rhesus monkey:
Species-specific characteristics. Neuroscience. 158:798–810. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Platania P, Seminara G, Aronica E, et al:
17B-estradiol rescues spinal motoneurons from AMPA-induced
toxicity: A role for glial cells. Neurobiol Dis. 20:461–470. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
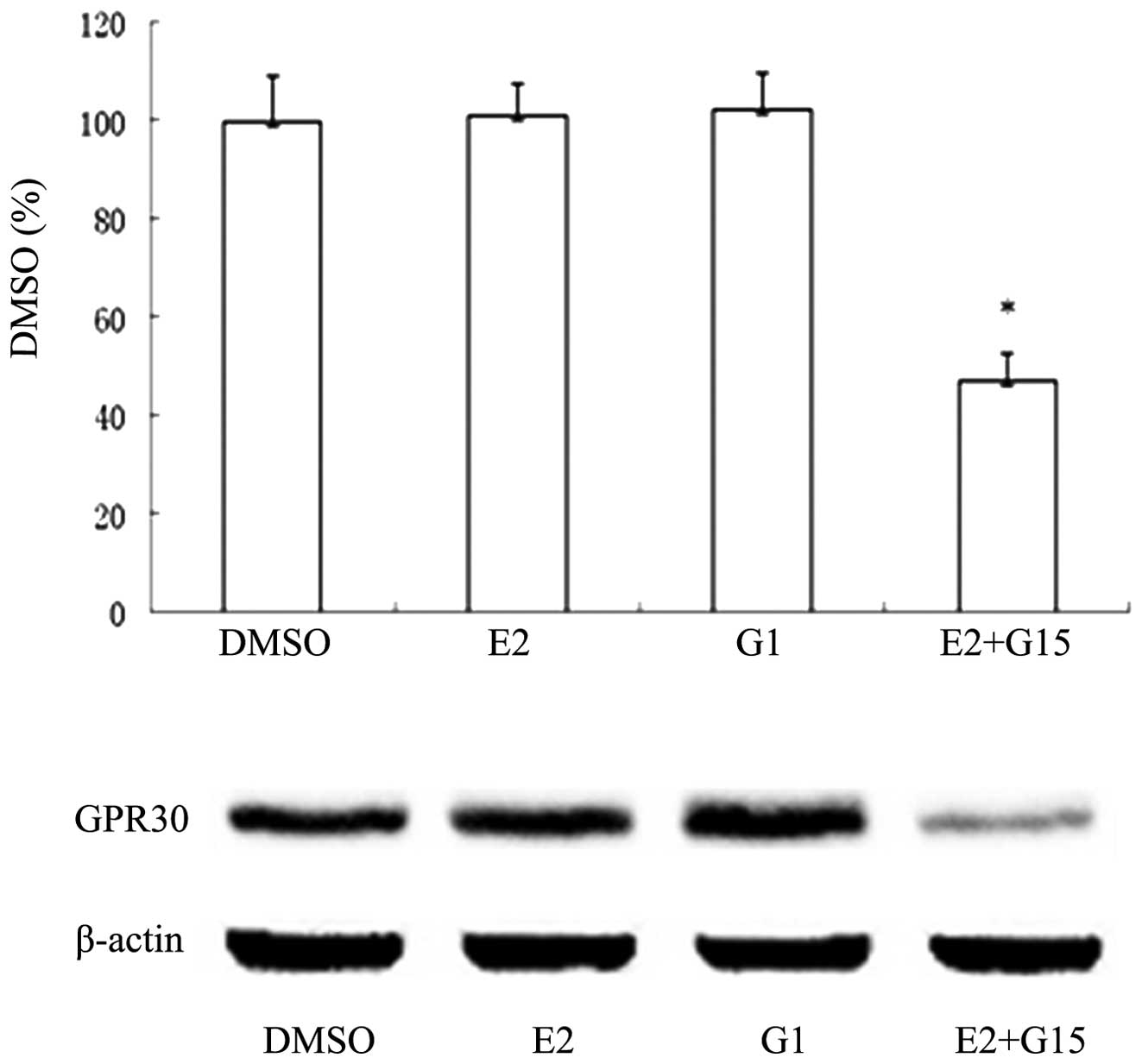
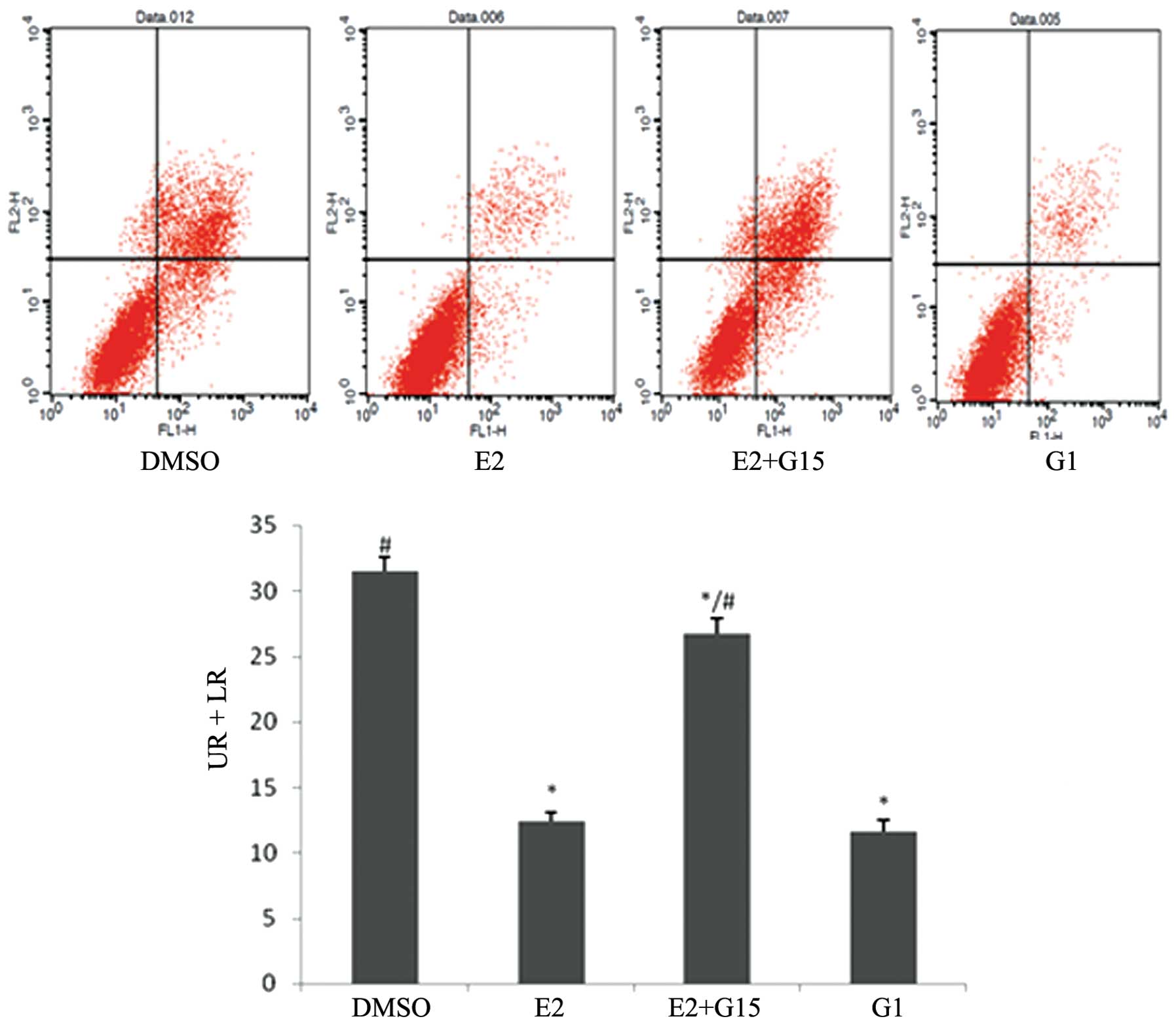
Hu R, Sun HD, Zhang Q, et al: G-protein
coupled estrogen receptor 1 mediated estrogenic neuroprotection
against spinal cord injury. Crit Care Med. 40:3230–3237. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
McEwen BS: Invited review: Estrogens
effects on the brain: Multiple sites and molecular mechanisms. J
Appl Physiol. 91:2785–2801. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yang X, Tomita T, Wines-Samuelson M,
Beglopoulos V, Tansey MG, Kopan R and Shen J: Notch1 signaling
influences v2 interneuron and motor neuron development in the
spinal cord. Dev Neurosci. 28:102–117. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yune TY, Kim SJ, Lee SM, et al: Systemic
administration of 17beta-estradiol reduces apoptotic cell death and
improves functional recovery following traumatic spinal cord injury
in rats. J Neurotrauma. 21:293–306. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lu CL, Hsieh JC, Dun NJ, et al: Estrogen
rapidly modulates 5-hydroxytrytophan-induced visceral
hypersensitivity via GPR30 in rats. Gastroenterology.
137:1040–1050. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dennis MK, Burai R, Ramesh C, et al: In
vivo effects of a GPR30 antagonist. Nature ChemBiol. 5:421–427.
2009.
|
|
24
|
Du DS, Ma XB, Zhang JF, et al: The
protective effect of capsaicin receptor-mediated genistein
postconditioning on gastric ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats.
Dig Dis Sci. 55:3070–3077. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Basso DM, Beattie MS and Bresnahan JC: A
sensitive and reliable locomotor rating scale for open field
testing in rats. J Neurotrauma. 12:1–21. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
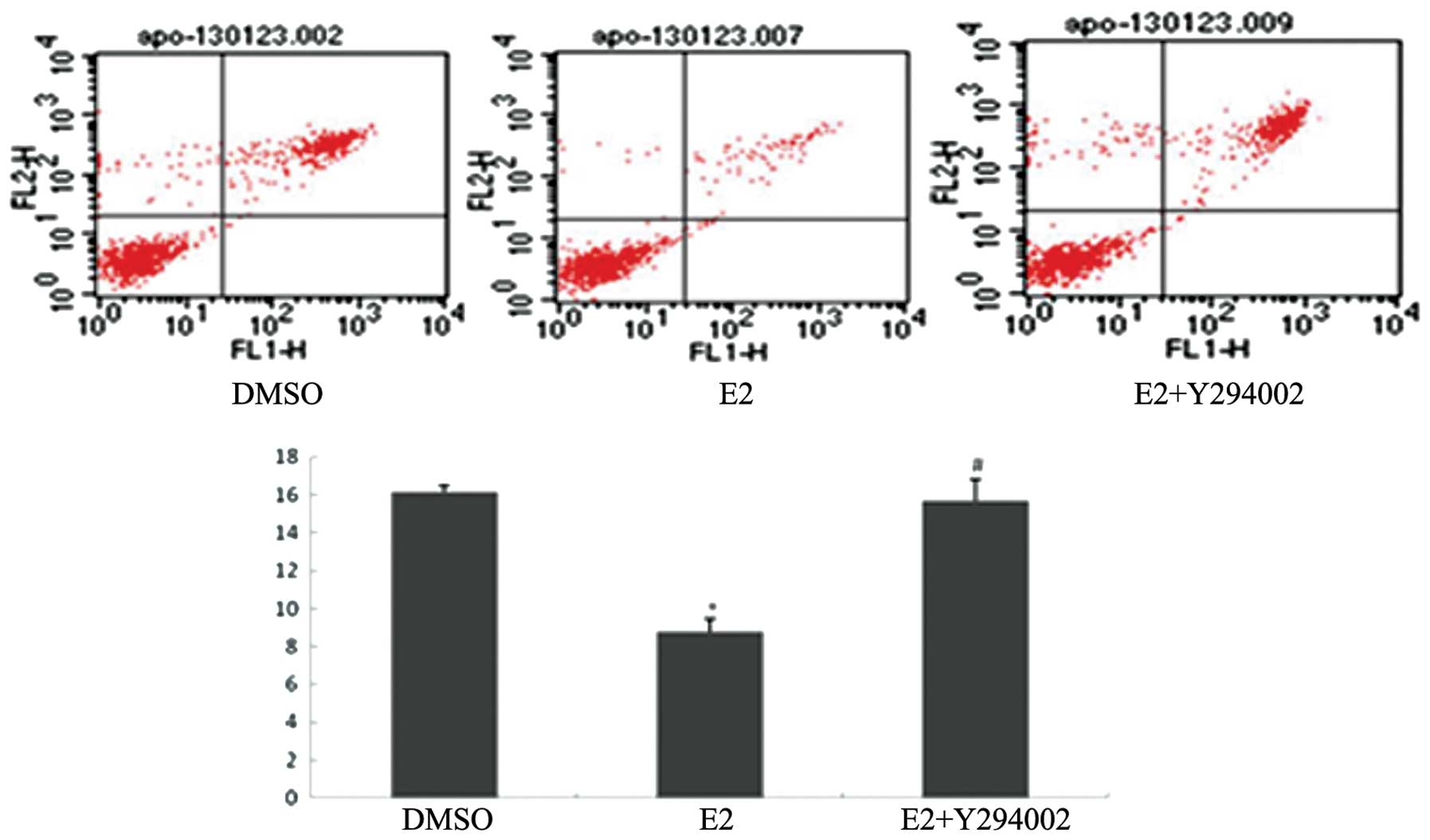
Yu HP, Hsieh YC, Suzuki T, et al: The
PI3K/Akt pathway mediates the nongenomic cardioprotective effects
of estrogen following trauma-hemorrhage. Ann Surg. 245:971–977.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tator CH: Upadate on the pathophysiology
and pathology of acute spinal cord injury. Brain Pathol. 5:407–413.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ambrozaitis E, Spakauskas B and Vaitkaitis
D: Pathophysiology of acute spinal cord injury. Medicina (Kaunas).
255–261. 2006.In Lithuanian.
|
|
29
|
Fiford RJ, Bilston LE, Waite P and Lu J: A
vertebral dislocation model cord injury in rats. J Neurotrauma.
21:451–458. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Akdemir H, Paşaoğlu A, Oztürk F, et al:
Histopathology of experiment spinal cord trauma. Comparison of
treatment with TRH, naloxone, and dexamethasone. Res Exp Med
(Berl). 92:177–183. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Nguyen TV, Jayaraman A, Quaglino A and
Pike CJ: Androgens selectively protect against apoptosis in
hippocampal neurones. J Neuroendocrinol. 22:1013–1022. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Meda C, Vegeto E, Pollio G, et al:
Oestrogen prevention of neural cell death correlates with decreased
expression of mRNA for the pro-apoptotic protein nip-2. J
Neuroendocrinol. 12:1051–1059. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Revankar CM, Cimino DF, Sklar LA, et al: A
transmembrane intracellular estrogen receptor mediates rapid cell
signaling. Science. 307:1625–1630. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dennis MK, Burai R, Ramesh C, et al: In
vivo effects of a GPR30 antagonist. Nat Chem Biol. 5:421–427. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
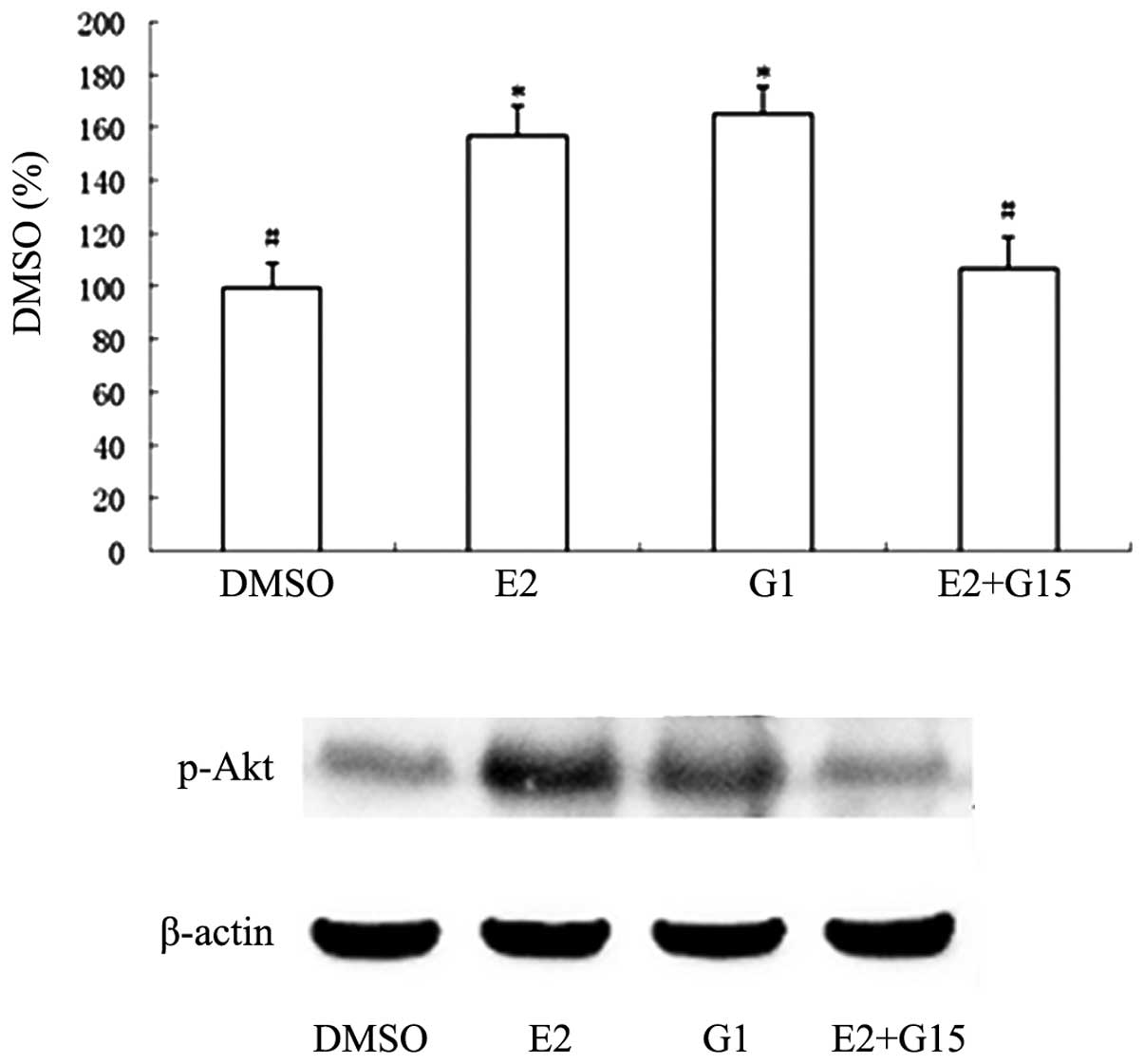
Yune TY, Park HG, Lee JY and Oh TH:
Estrogen-induced Bcl-2 expression after spinal cord injury is
mediated through phosphoinositide- 3-kinase/Akt-dependent CREB
activation. J Neurotrauma. 25:1121–1131. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sribnick EA, Matzelle DD, Ray SK and Banik
NL: Estrogen treatment of spinal cord injury attenuates calpain
activation and apoptosis. J Neurosci Res. 84:1064–1075. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Das A, Smith JA, Gibson C, et al: Estrogen
receptor agonists and estrogen attenuate TNF-α-induced apoptosis in
VSC4.1 motoneurons. J Endocrinol. 208:171–182. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Danial NN and Korsmeyer SJ: Cell death:
Critical control points. Cel. 116:205–219. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Ferrington DA, Tran TN, Lew KL, et al:
Different death stimuli evoke apoptosis via multiple pathways in
retinal pigment epithelial cells. Exp Eye Res. 83:638–650. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhang J, Yang Y, Zhang Z, et al: Gankyrin
plays an essential role in estrogen-driven and GPR30-mediated
endometrial carcinoma cell proliferation via the PTEN/PI3K/AKT
signaling pathway. Cancer Lett. 339:279–287. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Revankar CM, Mitchell HD, Field AS, Burai
R, Corona C, Ramesh C, Sklar LA, Arterburn JB and Prossnitz ER:
Synthetic estrogen derivatives demonstrate the functionality of
intracellular GPR30. ACS Chem Biol. 2:536–544. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lin BC, Suzawa M, Blind RD, et al:
Stimulating the GPR30 estrogen receptor with a novel tamoxifen
analogue activates SF-1 and promotes endometrial cell
proliferation. Cancer Res. 69:5415–5423. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|