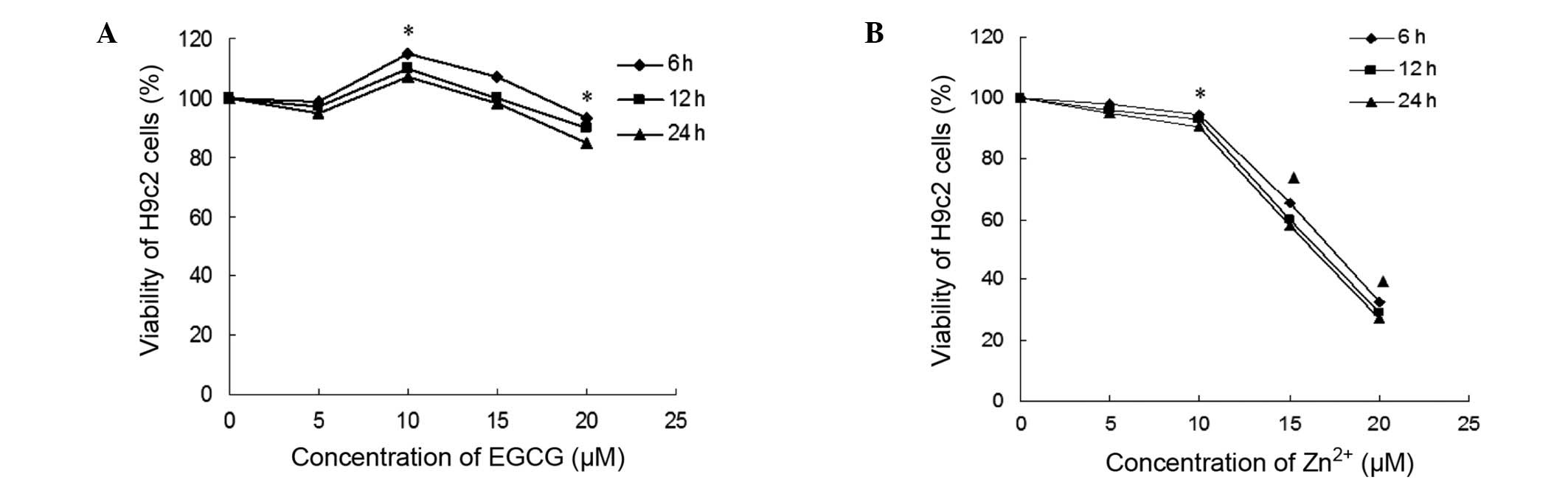
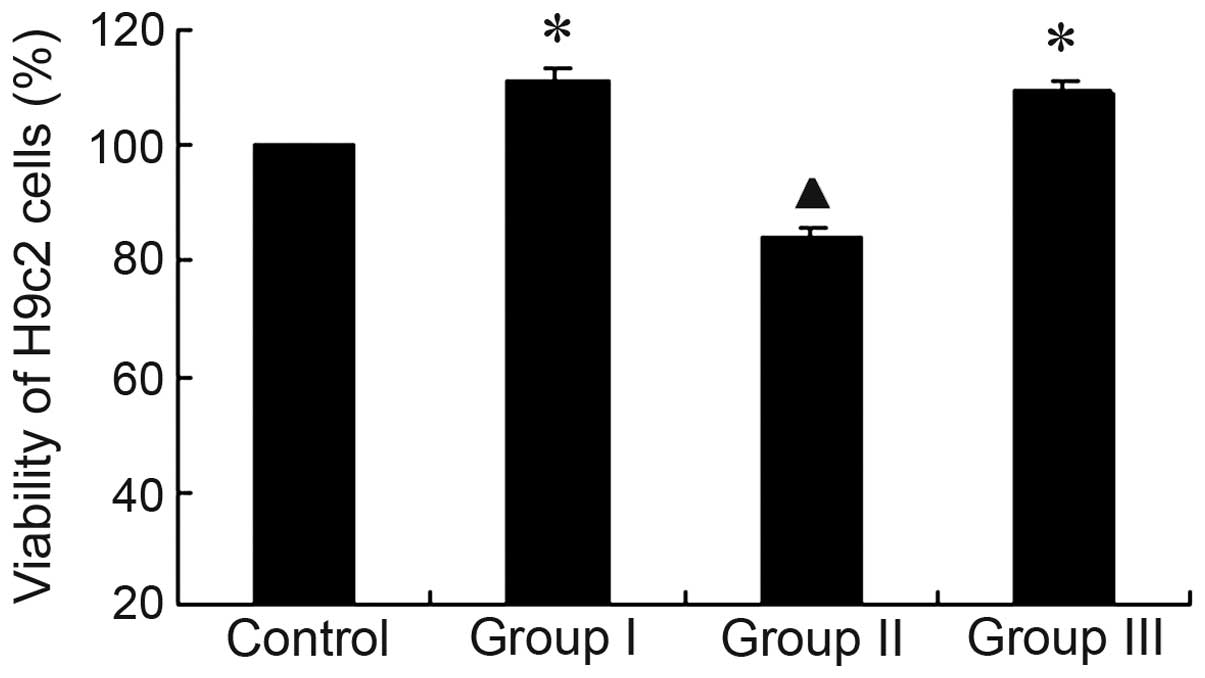
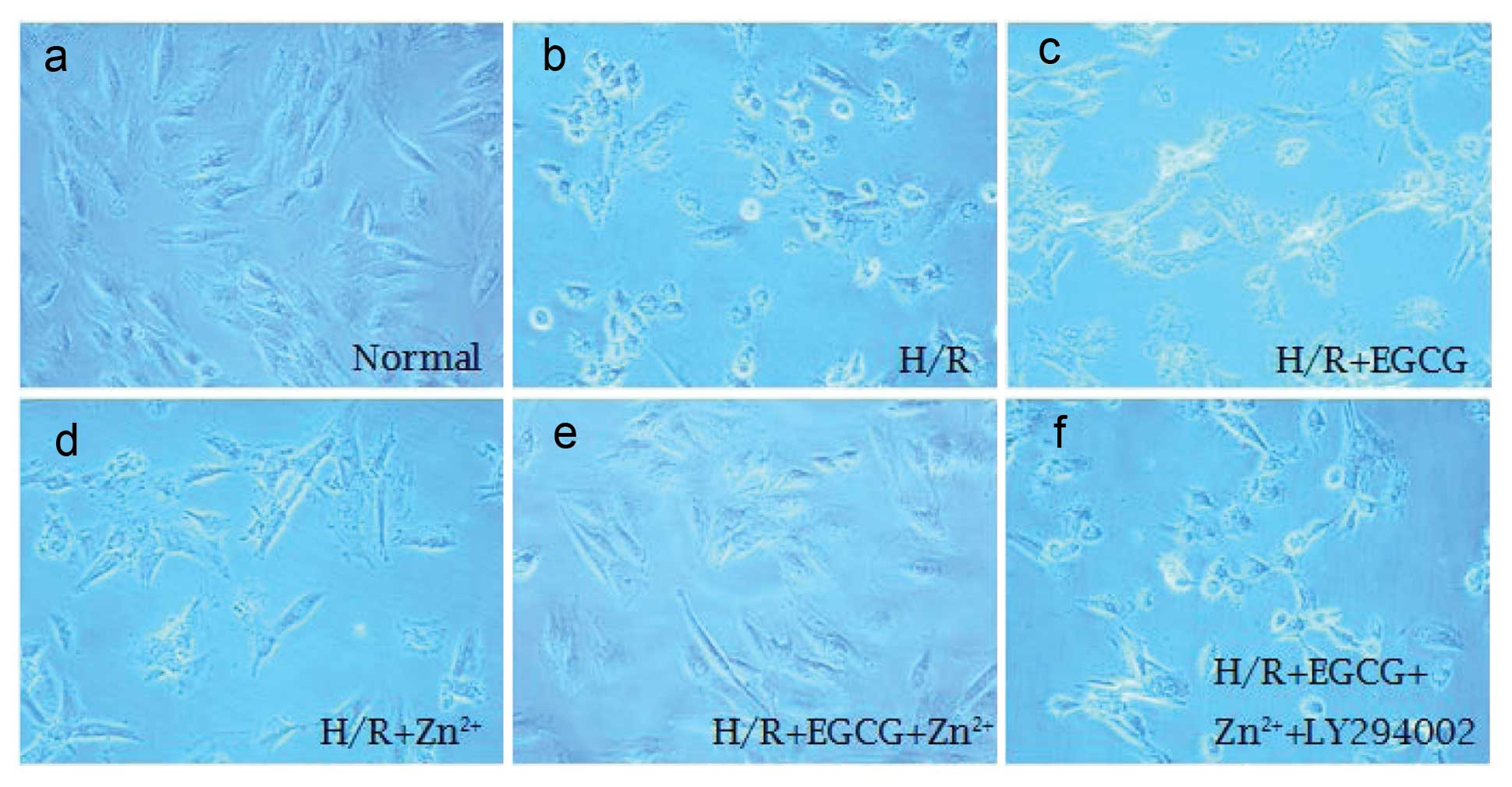
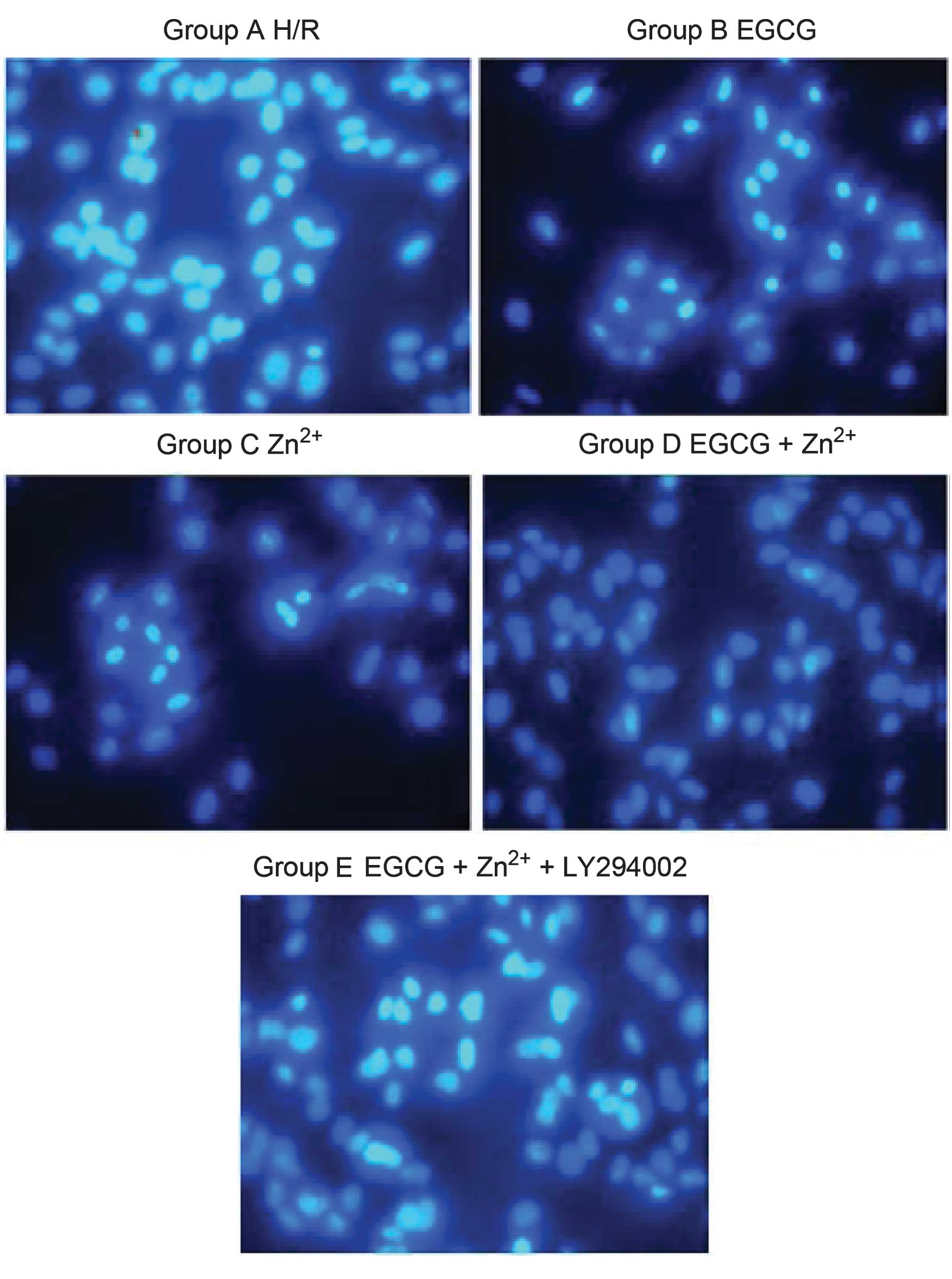
|
1
|
Cannon RO III: Mechanisms, management and
future directions for reperfusion injury after acute myocardial
infarction. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med. 2:88–94. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Aversano T, Aversano LT, Passamani E, et
al: Thrombolytic therapy vs. primary percutaneous coronary
intervention for myocardial infarction in patients presenting to
hospitals without on-site cardiac surgery: a randomized controlled
trial. JAMA. 287:1943–1951. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fröhlich GM, Meier P, White SK, Yellon DM
and Hausenloy DJ: Myocardial reperfusion injury: looking beyond
primary PCI. Eur Heart J. 34:1714–1722. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang GW, Zhou Z, Klein JB and Kang YJ:
Inhibition of hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced apoptosis in
metallothionein-overexpressing cardio-myocytes. Am J Physiol Heart
Circ Physiol. 280:H2292–H2299. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Moens AL, Claeys MJ, Timmermans JP and
Vrints CJ: Myocardial ischemia/reperfusion-injury, a clinical view
on a complex patho-physiological process. Int J Cardiol.
100:179–190. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Stephanou A, Brar B, Liao Z, et al:
Distinct initiator caspases are required for the induction of
apoptosis in cardiac myocytes during ischaemia versus reperfusion
injury. Cell Death Differ. 8:434–435. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Scarabelli TM, Stephanou A, Pasini E, et
al: Different signaling pathways induce apoptosis in endothelial
cells and cardiac myocytes during ischemia/reperfusion injury. Circ
Res. 90:745–748. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Buja LM and Entman ML: Modes of myocardial
cell injury and cell death in ischemic heart disease. Circulation.
98:1355–1357. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Geleijnse JM, Launer LJ, Hofman A, Pols HA
and Witteman JC: Tea flavonoids may protect against
atherosclerosis: the Rotterdam Study. Arch Intern Med.
159:2170–2174. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sano J, Inami S, Seimiya K, et al: Effects
of green tea intake on the development of coronary artery disease.
Circ J. 68:665–670. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Aneja R, Hake PW, Burroughs TJ, et al:
Epigallocatechin, a green tea polyphenol, attenuates myocardial
ischemia reperfusion injury in rats. Mol Med. 10:55–62. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Townsend PA, Scarabelli TM, Pasini E, et
al: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits STAT-1 activation and
protects cardiac myocytes from ischemia/reperfusion-induced
apoptosis. FASEB J. 18:1621–1623. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Piao CS, Kim DS, Ha KC, et al: The
protective effect of epigallocatechin-3 gallate on
ischemia/reperfusion injury in isolated rat hearts: An ex vivo
approach. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 15:259–266. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sheng R, Gu ZL and Xie ML:
Epigallocatechin gallate, the major component of polyphenols in
green tea, inhibits telomere attrition mediated cardiomyocyte
apoptosis in cardiac hypertrophy. Int J Cardiol. 162:199–209. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Hayakawa F, Ishizu Y, Hoshino N, et al:
Prooxidative activities of tea catechins in the presence of
Cu2+. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 68:1825–1830. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yu HN, Shen SR and Xiong YK: Cytotoxicity
of epigallo-catechin-3-gallate to LNCaP cells in the presence of
Cu2+. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 6:125–131. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen X, Yu H, Shen S and Yin J: Role of
Zn2+ in epigallocatechin gallate affecting the growth of
PC-3 cells. J Trace Elem Med. 21:125–131. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Viswanath K, Bodiga S, Balogun V, Zhang A
and Bodiga VL: Cardioprotective effect of zinc requires ErbB2 and
Akt during hypoxia/reoxygenation. Biometals. 24:171–180. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Lee S, Chanoit G, McIntosh R, et al:
Molecular mechanism underlying Akt activation in zinc-induced
cardioprotection. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 297:H569–H575.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Vinten-Johansen J, Zhao ZQ, Jiang R, Zatta
AJ and Dobson GP: Preconditioning and postconditioning: innate
cardioprotection from ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Appl Physiol
(1985). 103:1441–1448. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Hausenloy DJ and Yellon DM: Survival
kinases in ischemic preconditioning and postconditioning.
Cardiovasc Res. 70:240–253. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang T, Yang D, Fan Y, et al:
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate enhances ischemia/reperfusion-induced
apoptosis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells via AKT and
MAPK pathways. Apoptosis. 14:1245–1254. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yaoita H, Ogawa K, Maehara K and Maruyama
Y: Attenuation of ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats by a caspase
inhibitor. Circulation. 97:276–281. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mocanu MM, Baxter GF and Yellon DM:
Caspase inhibition and limitation of myocardial infarct size:
Protection against lethal reperfusion injury. Br J Pharmacol.
130:197–200. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ross R: Atherosclerosis is an inflammatory
disease. Am Heart J. 138:S419–S420. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bayes-Genis A, Conover CA and Schwartz RS:
The insulin-like growth factor axis: a review of atherosclerosis
and restenosis. Circ Res. 86:125–130. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zeng X, Li Q, Zhang M, et al: Green tea
may be benefit to the therapy of atrial fibrillation. J Cell
Biochem. 112:1709–1712. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sesso HD, Gaziano JM, Buring JE and
Hennekens CH: Coffee and tea intake and the risk of myocardial
infarction. Am J Epidemiol. 149:162–167. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cheng TO: Tea is good for the heart. Arch
Intern Med. 160:23972000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kagaya N, Kawase M, Maeda H, Tagawa Y,
Nagashima H, Ohmori H and Yagi K: Enhancing effect of zinc on
hepatoprotectivity of epigallocatechin gallate in isolated rat
hepatocytes. Biol Pharm Bull. 25:1156–1160. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kim MK, Jung HS, Yoon CS, et al: EGCG and
quercetin protected INS-1 cells in oxidative stress via different
mechanisms. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2:810–817. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Brewer GJ, Johnson VD, Dick RD, et al:
Treatment of Wilson’s disease with zinc. XVII: treatment during
pregnancy. Hepatology. 31:364–370. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|