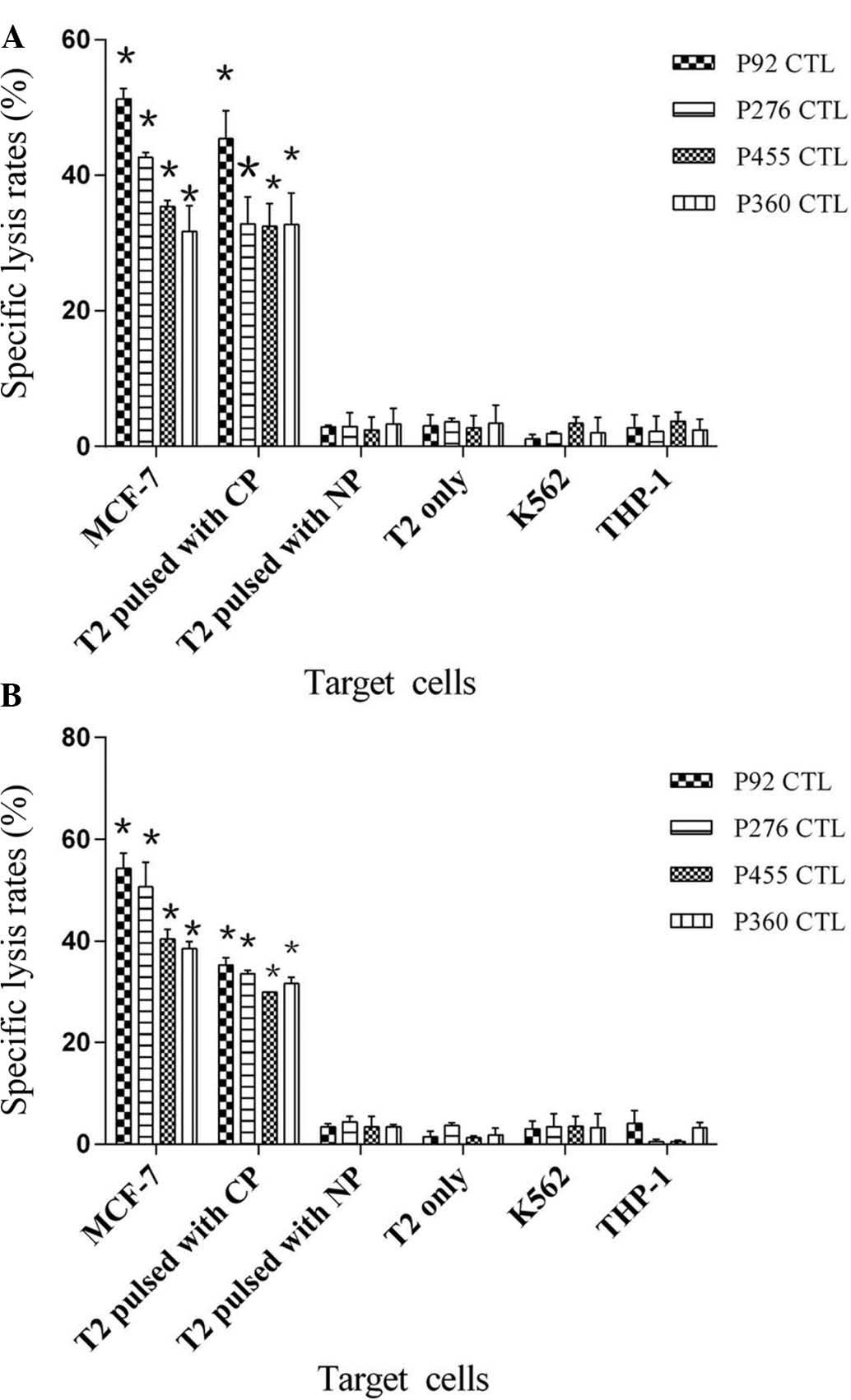
|
1
|
Zigler M, Shir A and Levitzki A: Targeted
cancer immunotherapy. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 13:504–510. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Casalegno-Garduño R, Schmitt A and Schmitt
M: Clinical peptide vaccination trials for leukemia patients.
Expert Rev Vaccines. 10:785–799. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Vaggi F, Disanza A, Milanesi F, Di Fiore
PP, Menna E, Matteoli M, Gov NS, Scita G and Ciliberto A: The
Eps8/IRSp53/VASP network differentially controls actin capping and
bundling in filopodia formation. PLOS Comput Biol. 7:e10020882011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Disanza A, Carlier MF, Stradal TE, Didry
D, Frittoli E, Confalonieri S, Croce A, Wehland J, Di Fiore PP and
Scita G: Eps8 controls actin-based motility by capping the barbed
ends of actin filaments. Nat cell Biol. 6:1180–1188. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Werner A, Disanza A, Reifenberger N,
Habeck G, Becker J, Calabrese M, Urlaub H, Lorenz H, Schulman B,
Scita G, et al: SCFFbxw5 mediates transient degradation of actin
remodeller Eps8 to allow proper mitotic progression. Nat cell Biol.
15:179–188. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yao J, Weremowicz S, Feng B, Gentleman RC,
Marks JR, Gelman R, Brennan C and Polyak K: Combined cDNA array
comparative genomic hybridization and serial analysis of gene
expression analysis of breast tumor progression. Cancer Res.
66:4065–4078. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Xu M, Shorts-Cary L, Knox AJ,
Kleinsmidt-DeMasters B, Lillehei K and Wierman ME: Epidermal growth
factor receptor pathway substrate 8 is overexpressed in human
pituitary tumors: Role in proliferation and survival.
Endocrinology. 150:2064–2071. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Welsch T, Endlich K, Giese T, Büchler MW
and Schmidt J: Eps8 is increased in pancreatic cancer and required
for dynamic actin-based cell protrusions and intercellular
cytoskeletal organization. Cancer Lett. 255:205–218. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen YJ, Shen MR, Chen YJ, Maa MC and Leu
TH: Eps8 decreases chemosensitivity and affects survival of
cervical cancer patients. Mol Cancer Ther. 7:1376–1385. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Maa MC, Lee JC, Chen YJ, Chen YJ, Lee YC,
Wang ST, Huang CC, Chow NH and Leu TH: Eps8 facilitates cellular
growth and motility of colon cancer cells by increasing the
expression and activity of focal adhesion kinase. J Biol Chem.
282:19399–19409. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang H, Patel V, Miyazaki H, Gutkind JS
and Yeudall WA: Role for EPS8 in squamous carcinogenesis.
Carcinogenesis. 30:165–174. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Bashir M, Kirmani D, Bhat HF, Baba RA,
Hamza R, Naqash S, Wani NA, Andrabi KI, Zargar MA and Khanday FA:
P66shc and its downstream Eps8 and Rac1 proteins are upregulated in
esophageal cancers. Cell Commun Signal. 8:132010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ding X, Zhou F, Wang F, Yang Z, Zhou C,
Zhou J, Zhang B, Yang J, Wang G, Wei Z, et al: Eps8 promotes
cellular growth of human malignant gliomas. Oncol Rep. 29:697–703.
2013.
|
|
14
|
Gorsic LK, Stark AL, Wheeler HE, Wong SS,
Im HK and Dolan ME: EPS8 inhibition increases cisplatin sensitivity
in lung cancer cells. PLoS One. 8:e822202013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang L, Cai SH, Xiong WY, He YJ, Deng L
and Li YH: Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction assay
for detecting the eps8 gene in acute myeloid leukemia. Clin Lab.
59:1261–1269. 2013.
|
|
16
|
He YJ, Zhou J, Zhao TF, Hu LS, Gan JY,
Deng L and Li Y: Eps8 vaccine exerts prophylactic antitumor effects
in a murine model: A novel vaccine for breast carcinoma. Mol Med
Rep. 8:662–668. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li S, Li H, Chen B, Lu D, Deng W, Jiang Y,
Zhou Z and Yang Z: Identification of novel HLA-A 0201-restricted
cytotoxic T lymphocyte epitopes from Zinc Transporter 8. Vaccine.
31:1610–1615. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Wang B, Chen H, Jiang X, Zhang M, Wan T,
Li N, Zhou X, Wu Y, Yang F, Yu Y, et al: Identification of an
HLA-A*0201-restricted CD8+ T-cell epitope SSp-1 of SARS-CoV spike
protein. Blood. 104:200–206. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Guo YJ, Wang KY and Sun SH: Identification
of an HLA-A*0201-restricted CD8(+) T-cell epitope encoded within
Leptospiral immunoglobulin like protein. A Microbes Infect.
12:364–373. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Dervillez X, Qureshi H, Chentoufi AA, Khan
AA, Kritzer E, Yu DC, Diaz OR, Gottimukkala C, Kalantari M,
Villacres MC, et al: Asymptomatic HLA-A*02:01-restricted epitopes
from herpes simplex virus glycoprotein B preferentially recall
polyfunctional CD8+ T-cells from seropositive asymptomatic
individuals and protect HLA transgenic mice against ocular herpes.
J Immunol. 191:5124–5138. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Saini SK, Ostermeir K, Ramnarayan VR,
Schuster H, Zacharias M and Springer S: Dipeptides promote folding
and peptide-binding of MHC class I molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 110:15383–15388. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Imai K, Hirata S, Irie A, Senju S, Ikuta
Y, Yokomine K, Harao M, Inoue M, Tomita Y, Tsunoda T, et al:
Identification of HLA-A2-restricted CTL epitopes of a novel
tumour-associated antigen, KIF20A, overexpressed in pancreatic
cancer. Br J Cancer. 104:300–307. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
23
|
Wu YH, Gao YF, He YJ, Shi RR, Zhai MX, Wu
ZY, Sun M, Zhai WJ, Chen X and Qi YM: A novel cytotoxic T
lymphocyte epitope analogue with enhanced activity derived from
cyclooxygenase-2. Scand J Immunol. 76:278–285. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhu B, Chen Z, Cheng X, Lin Z, Guo J, Jia
Z, Zou L, Wang Z, Hu Y, Wang D, et al: Identification of
HLA-A*0201-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocyte epitope from TRAG-3
antigen. Clin Cancer Res. 9:1850–1857. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Imahashi N, Nishida T, Ito Y, Kawada J,
Nakazawa Y, Toji S, Suzuki S, Terakura S, Kato T, Murata M, et al:
Identification of a novel HLA-A*24:02-restricted adenovirus
serotype 11-specific CD8+ T-cell epitope for adoptive
immunotherapy. Mol Immunol. 56:399–405. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Paul S, Weiskopf D, Angelo MA, Sidney J,
Peters B and Sette A: HLA class I alleles are associated with
peptide-binding repertoires of different size, affinity, and
immunogenicity. J Immunol. 191:5831–5839. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gajewski TF: Cancer immunotherapy. Mol
Oncol. 6:242–250. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Weber G, Gerdemann U, Caruana I, Savoldo
B, Hensel NF, Rabin KR, Shpall EJ, Melenhorst JJ, Leen AM, Barrett
AJ, et al: Generation of multi-leukemia antigen-specific T cells to
enhance the graft-versus-leukemia effect after allogeneic stem cell
transplant. Leukemia. 27:1538–1547. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Vesely MD and Schreiber RD: Cancer
immunoediting: Antigens, mechanisms, and implications to cancer
immunotherapy. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1284:1–5. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mishra S and Sinha S: Immunoinformatics
and modeling perspective of T cell epitope-based cancer
immunotherapy: A holistic picture. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 27:293–306.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Matoskova B, Wong WT, Salcini AE, Pelicci
PG and Di Fiore PP: Constitutive phosphorylation of eps8 in tumor
cell lines: Relevance to malignant transformation. Mol Cell Biol.
15:3805–3812. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li YH, Xue TY, He YZ and Du JW: Novel
oncoprotein EPS8: A new target for anticancer therapy. Future
Oncol. 9:1587–1594. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kessler JH and Melief CJ: Identification
of T-cell epitopes for cancer immunotherapy. Leukemia.
21:1859–1874. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Vigneron N and Van den Eynde BJ: Insights
into the processing of MHC class I ligands gained from the study of
human tumor epitopes. Cell Mol Life Sci. 68:1503–1520. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Dönnes P and Kohlbacher O: Integrated
modeling of the major events in the MHC class I antigen processing
pathway. Protein Sci. 14:2132–2140. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Castelli M, Cappelletti F, Diotti RA,
Sautto G, Criscuolo E, Dal Peraro M and Clementi N: Peptide-based
vaccinology: Experimental and computational approaches to target
hyper-variable viruses through the fine characterization of
protective epitopes recognized by monoclonal antibodies and the
identification of T-cell-activating peptides. Clin Dev Immunol.
2013:5212312013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Lundegaard C, Nielsen M and Lund O: The
validity of predicted T-cell epitopes. Trends Biotechnol.
24:537–538. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sieker F, May A and Zacharias M:
Predicting affinity and specificity of antigenic peptide binding to
major histocompatibility class I molecules. Curr Protein Pept Sci.
10:286–296. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lundegaard C, Lund O, Buus S and Nielsen
M: Major histocompatibility complex class I binding predictions as
a tool in epitope discovery. Immunology. 130:309–318. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Viatte S, Alves PM and Romero P: Reverse
immunology approach for the identification of CD8 T-cell-defined
antigens: Advantages and hurdles. Immunol Cell Biol. 84:318–330.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kessler JH, Mommaas B, Mutis T, Huijbers
I, Vissers D, Benckhuijsen WE, Schreuder GM, Offringa R, Goulmy E,
Melief CJ, et al: Competition-based cellular peptide binding assays
for 13 prevalent HLA class I alleles using fluorescein-labeled
synthetic peptides. Hum Immunol. 64:245–255. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Cole DK, Edwards ES, Wynn KK, et al:
Modification of MHC anchor residues generates heteroclitic peptides
that alter TCR binding and T cell recognition. J Immunol.
185:2600–2610. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Assarsson E, Sidney J, Oseroff C, et al: A
quantitative analysis of the variables affecting the repertoire of
T cell specificities recognized after vaccinia virus infection. J
Immunol. 178:7890–7901. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Jørgensen KW, Rasmussen M, Buus S and
Nielsen M: NetMHCstab-predicting stability of peptide-MHC-I
complexes; impacts for cytotoxic T lymphocyte epitope discovery.
Immunology. 141:18–26. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Harndahl M, Rasmussen M, Roder G, Dalgaard
Pedersen I, Sørensen M, Nielsen M and Buus S: Peptide-MHC class I
stability is a better predictor than peptide affinity of CTL
immunogenicity. Eur J Immunol. 42:1405–1416. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Strous GJ, van Kerkhof P, van Meer G,
Rijnboutt S and Stoorvogel W: Differential effects of brefeldin A
on transport of secretory and lysosomal proteins. J Biol Chem.
268:2341–2347. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Misumi Y, Misumi Y, Miki K, Takatsuki A,
Tamura G and Ikehara Y: Novel blockade by brefeldin A of
intracellular transport of secretory proteins in cultured rat
hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 261:11398–11403. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Okuyama R, Aruga A, Hatori T, Takeda K and
Yamamoto M: Immunological responses to a multi-peptide vaccine
targeting cancer-testis antigens and VEGFRs in advanced pancreatic
cancer patients. OncoImmunology. 2:e270102013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Laugel B, van den Berg HA, Gostick E, Cole
DK, Wooldridge L, Boulter J, Milicic A, Price DA and Sewell AK:
Different T cell receptor affinity thresholds and CD8 coreceptor
dependence govern cytotoxic T lymphocyte activation and tetramer
binding properties. J Biol Chem. 282:23799–23810. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhong S, Malecek K, Johnson LA, Yu Z,
Vega-Saenz de Miera E, Darvishian F, McGary K, Huang K, Boyer J,
Corse E, et al: T-cell receptor affinity and avidity defines
antitumor response and autoimmunity in T-cell immunotherapy. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:6973–6978. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Corse E, Gottschalk RA, Krogsgaard M and
Allison JP: Attenuated T cell responses to a high-potency ligand in
vivo. PLoS Biol. 8:e10004812010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Slansky JE and Jordan KR: The Goldilocks
model for TCR-too much attraction might not be best for vaccine
design. PLoS Biol. 8:e10004822010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Hebeisen M, Baitsch L, Presotto D,
Baumgaertner P, Romero P, Michielin O, Speiser DE and Rufer N:
SHP-1 phosphatase activity counteracts increased T cell receptor
affinity. J Clin Invest. 123:1044–1056. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Alexander Miller MA, Leggatt GR and
Berzofsky JA: Selective expansion of high- or low-avidity cytotoxic
T lymphocytes and efficacy for adoptive immunotherapy. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 93:4102–4107. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Zeh HJ 3rd, Perry-Lalley D, Dudley ME,
Rosenberg SA and Yang JC: High avidity CTLs for two self antigens
demonstrate superior in vitro and in vivo antitumor efficacy. J
Immunol. 162:989–994. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Brentville VA, Metheringham RL, Gunn B and
Durrant LG: High avidity cytotoxic T lymphocytes can be selected
into the memory pool but they are exquisitely sensitive to
functional impairment. PLoS One. 7:e411122012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Ho WY, Nguyen HN, Wolfl M, Kuball J and
Greenberg PD: In vitro methods for generating CD8+ T-cell clones
for immunotherapy from the naïve repertoire. J Immunol Methods.
310:40–52. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Kang YJ, Zeng W, Song W, Reinhold B, Choi
J, Brusic V, Yamashita T, Munshi A, Li C, Minvielle S, et al:
Identification of human leucocyte antigen (HLA)-A*0201-restricted
cytotoxic T lymphocyte epitopes derived from HLA-DOβ as a novel
target for multiple myeloma. Br J Haematol. 163:343–351. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|