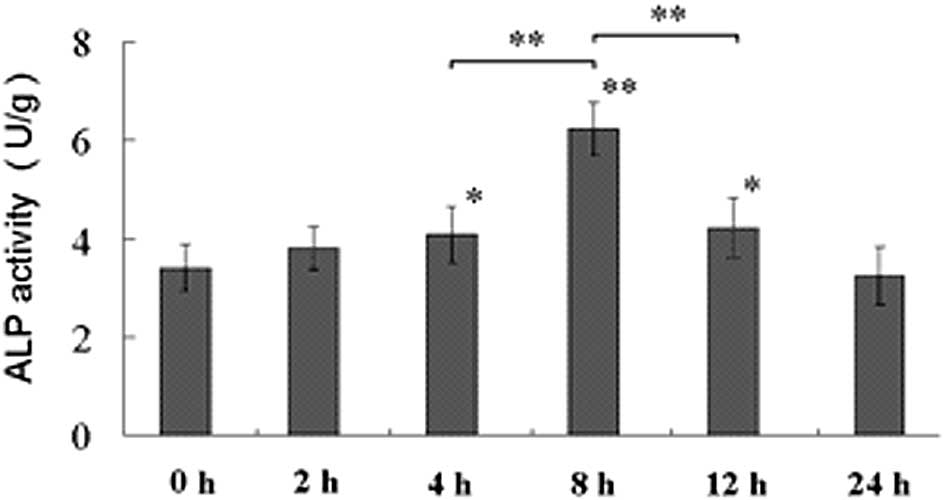
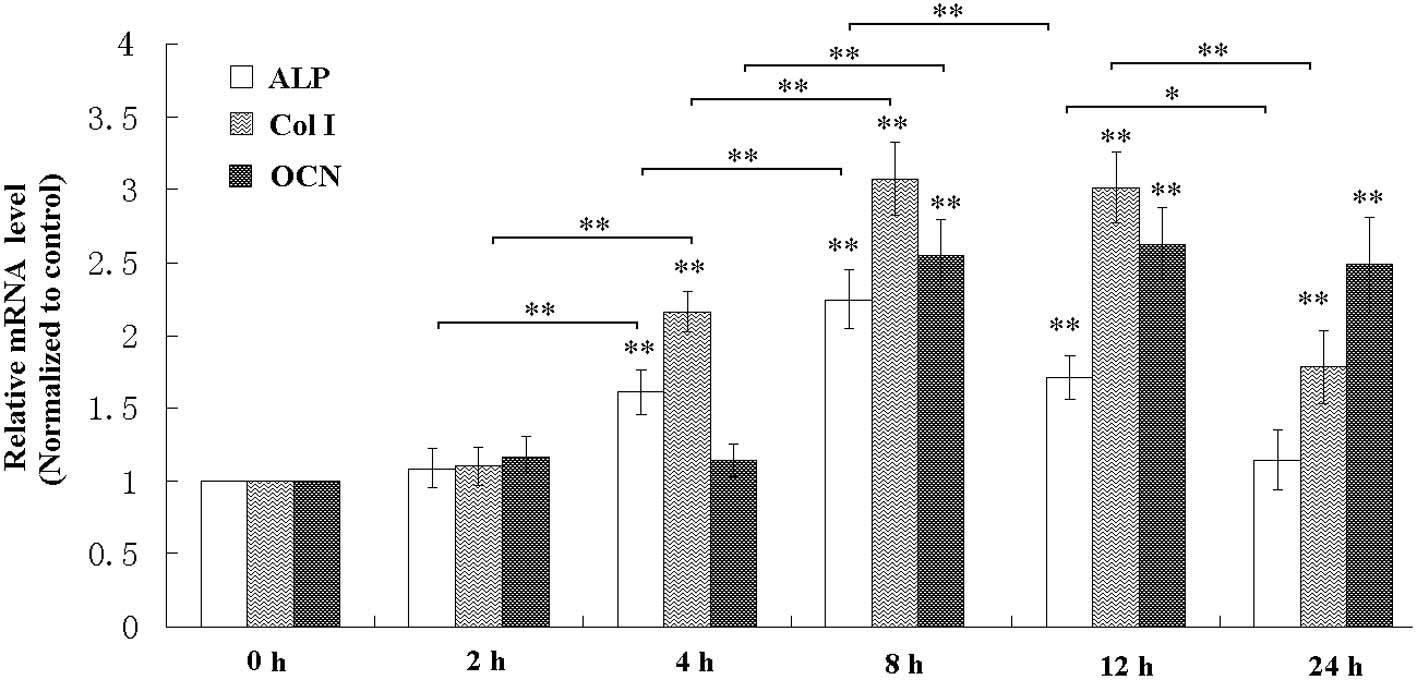
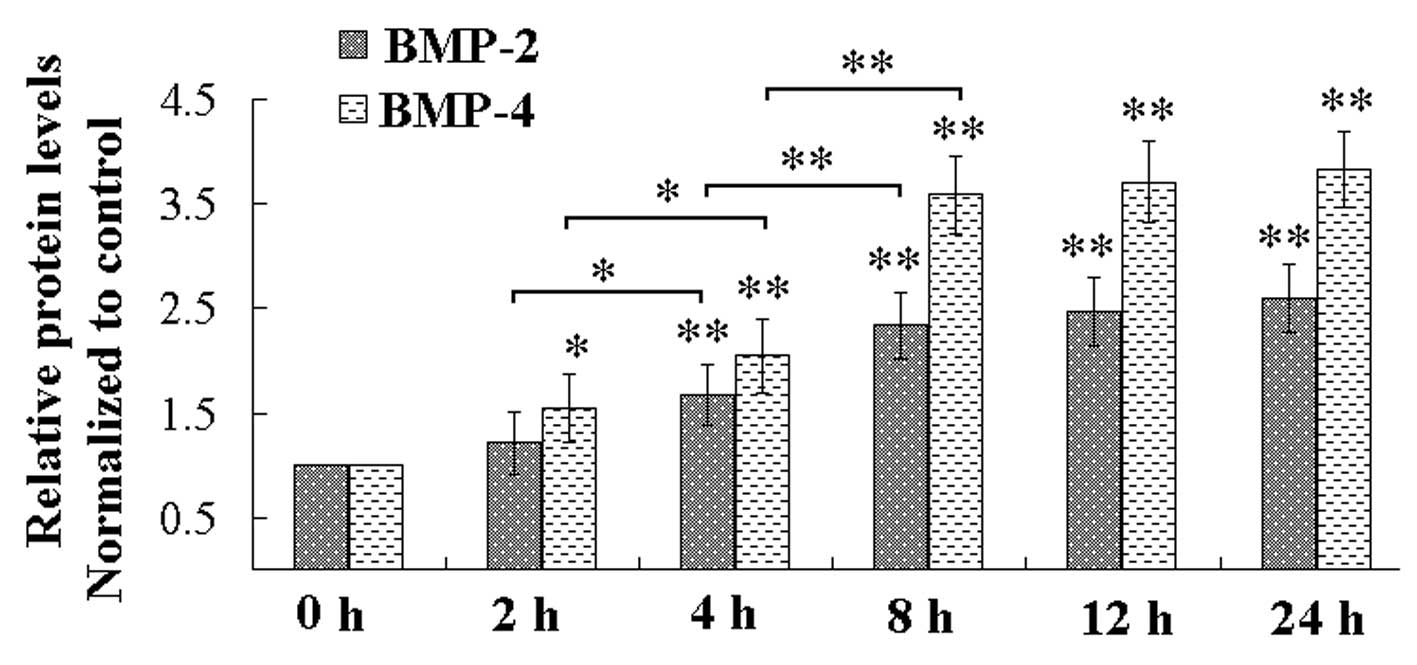
|
1
|
Schriefer JL, Warden SJ, Saxon LK, et al:
Cellular accommodation and the response of bone to mechanical
loading. J Biomech. 38:1838–1845. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Thompson WR, Rubin CT and Rubin J:
Mechanical regulation of signaling pathways in bone. Gene.
503:179–193. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wozniak M, Fausto A, Carron CP, Meyer DM
and Hruska KA: Mechanically strained cells of the osteoblast
lineageorganize their extracellular matrix through unique sites of
alphavbeta3-integrin expression. J Bone Miner Res. 15:1731–1745.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kaneuji T, Nogami S, Ariyoshi W, et al:
Regulatory effect on osteoclastogenesis of mechanical strain-loaded
osteoblasts. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 40:12152011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Rumney RM, Sunters A, Reilly GC and
Gartland A: Application of multiple forms of mechanical loading to
human osteoblasts reveals increased ATP release in response to
fluid flow in 3D cultures and differential regulation of immediate
early genes. J Biomech. 45:549–554. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
6
|
Zhao Y and Srivastava D: A developmental
view of microRNA function. Trends Biochem Sci. 32:189–197. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Stefani G and Slack FJ: Small non-coding
RNAs in animal development. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 9:219–230. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Taipaleenmäki H, Bjerre Hokland L, Chen L,
Kauppinen S and Kassem M: Mechanisms in endocrinology: micro-RNAs:
targets for enhancing osteoblast differentiation and bone
formation. Eur J Endocrinol. 166:359–371. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Vimalraj S and Selvamurugan N: MicroRNAs:
synthesis, gene regulation and osteoblast differentiation. Curr
Issues Mol Biol. 15:7–18. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ni CW, Qiu H and Jo H: MicroRNA-663
upregulated by oscillatory shear stress plays a role in
inflammatory response of endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 300:H1762–H1769. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Guan YJ, Yang X, Wei L and Chen Q:
MiR-365: a mechanosen-sitive microRNA stimulates chondrocyte
differentiation through targeting histone deacetylase 4. FASEB J.
25:4457–4466. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Song JT, Hu B, Qu HY, et al: Mechanical
stretch modulates microRNA-21 expression, participating in
proliferation and apoptosis in cultured human aortic smooth muscle
cells. PLoS One. 7:e476572012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Tang LL, Wang YL, Pan J and Cai SX: The
effect of step-wise increased stretching on rat calvarial
osteoblast collagen production. J Biomech. 37:157–161. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Jang WG, Kim EJ and Koh JT: Tunicamycin
negatively regulates BMP2-induced osteoblast differentiation
through CREBH expression in MC3T3E1 cells. BMB Rep. 44:735–740.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wan M and Cao X: BMP signaling in skeletal
development. Biochen Biophys Res Commun. 328:651–657. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Guo Y, Zhang CQ, Zeng QC, et al:
Mechanical strain promotes osteoblast ECM formation and improves
its osteoinductive potential. Biomed Eng Online. 11:802012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rubin CT and Lanyon LE: Regulation of bone
formation by applied dynamic loads. J Bone Joint Surg Am.
66:397–402. 1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lanyon LE and Rubin CT: Static versus
dynamic loads as an influence on bone remodelling. J Biomech.
17:897–905. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Hillam RA and Skerry TM: Inhibition of
bone resorption and stimulation offormulation by mechanical loading
of the modeling rat ulna in vivo. J Bone Miner Res. 10:683–689.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Turner CH and Pavalko FM:
Mechanotransduction and functional responseof the skeleton to
physical stress: the mechanisms and mechanics of bone adaptation. J
Orthop Sci. 3:346–355. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Wozniak M, Fausto A, Carron CP, Meyer DM
and Hruska KA: Mechanically strained cells of the osteoblast
lineage organize their extracellular matrix through unique sites of
alphavbeta3-integrin expression. J Bone Miner Res. 15:1731–1745.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bhatt KA, Chang EI, Warren SM, et al:
Uniaxial mechanical strain: an in vitro correlate to distraction
osteogenesis. J Surg Res. 143:329–336. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ducy P, Zhang R, Geoffroy V, Ridall AL and
Karsenty G: Osf2/Cbfa1: a transcriptional activator of osteoblast
differentiation. Cell. 89:747–754. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Olivares-Navarrete R, Hyzy S, Wieland M,
Boyan BD and Schwartz Z: The roles of Wnt signaling modulators
Dickkopf-1 (Dkk1) and Dickkopf-2 (Dkk2) and cell maturation state
in osteogenesis on microstructured titanium surfaces. Biomaterials.
31:2015–2024. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Lin TH, Yang RS, Tang CH, Wu MY and Fu WM:
Regulation of the maturation of osteoblasts and osteoclastogenesis
by glutamate. Eur J Pharmacol. 589:37–44. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Szczesniak AM, Gilbert RW, Mukhida M and
Anderson GI: Mechanical loading modulates glutamate receptor
subunit expression in bone. Bone. 37:63–73. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Danciu TE, Adam RM, Naruse K, Freeman MR
and Hauschka PV: Calcium regulates the PI3K-Akt pathway in
stretched osteoblasts. FEBS Lett. 536:193–197. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Futatsugi A, Nakamura T, Yamada MK, et al:
IP3 receptor types 2 and 3 mediate exocrine secretion underlying
energy metabolism. Science. 309:2232–2234. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lin GL and Hankenson KD: Integration of
BMP, Wnt and notch signaling pathways in osteoblast
differentiation. J Cell Biochem. 112:3491–501. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ito Y, Inoue D, Kido S and Matsumoto T:
c-Fos degradation by the ubiquitin-proteasome proteolytic pathway
in osteoclast progenitors. Bone. 37:842–849. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Xing L, Zhang M and Chen D: Smurf control
in bone cells. J Cell Biochem. 110:554–563. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hatakeyama N, Kojima T, Iba K, et al:
IGF-I regulates tight-junction protein claudin-1 during
differentiation of osteoblast-like MC3T3-E1 cells via a MAP-kinase
pathway. Cell Tissue Res. 334:243–254. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Greenblatt MB, Shim JH, Zou W, et al: The
p38 MAPK pathway is essential for skeletogenesis and bone
homeostasis in mice. J Clin Invest. 120:2457–2473. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Nakano Y, Forsprecher J and Kaartinen MT:
Regulation of ATPase activity of transglutaminase 2 by MT1-MMP:
implications for mineralization of MC3T3-E1 osteoblast cultures. J
Cell Physiol. 223:260–269. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sun D, Junger WG, Yuan C, et al:
Shockwaves induce osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal
stem cells through ATP release and activation of P2×7 receptors.
Stem Cells. 31:1170–80. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chen G, Deng C and Li YP: TGF-β and BMP
signaling in osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. Int J
Biol Sci. 8:272–288. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|