Introduction
The potassium ion (K+) is an important
ion, which is involved in the metabolism of sugar and protein in a
variety of cell types, and maintains the balance between the pH and
osmolarity of cells. It is essential in the formation of resting
potential, neuromuscular excitability and the maintenance of normal
myocardial diastolic movement coordination (1). Hypokalemia is a common disease in
which abnormal concentrations of K+ in the blood cause
severe pathological changes, including muscle weakness, intestinal
paralysis, sinus tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation and other
arrhythmias (2). Hypokalemia is
caused by various factors, including insufficient food, vomiting,
severe diarrhea, kidney disease, digitalism and long-term use of
glucocorticoids (3). The major
treatment for hypokalemia is K+ supplementation.
L-aspartic acid potassium salt (K-asp) is commonly used in the
clinical treatment of hypokalemia (4,5), in
which L-aspartic acid is used as the carrier to transport
K+ into the cells (6).
However, the protective effect of K-asp in nerve cells surrounded
by a low potassium environment remains to be elucidated.
Several neurodegenerative diseases, including
Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, amyotrophic lateral
sclerosis, ischemia and excitotoxicity are associated with
oxidative injury (7). Previous
findings have indicated that oxidative damage may be associated
with reactive oxygen species (ROS) and manifested by cell lysis,
oxidative bursting or excessive quantities of free transition
metals (8,9). H2O2 is one type
of ROS, which has been used as an important reagent to establish an
in vitro model of oxidative stress injury (10). Ouabain is an Na+ and
K+-adenosine triphosphate (ATP)ase inhibitor, which can
induce concentration-dependent neuronal cell death. Neuronal cell
swelling is followed by cell shrinkage, which is accompanied by an
increase in intracellular Na+ and decrease in
K+ (11). In the
present study, the anti-apoptotic effect of K-asp was investigated
in ouabain-treated and H2O2-treated human
SH-SY5Y cells.
Materials and methods
Cells and drugs
Human SH-SY5Y cells were obtained from American Type
Culture Collection (Rockville, MD, USA) and were cultured in
Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (Invitrogen Life Technologies,
Carlsbad, CA, USA), supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (Gibco
Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA) and 100 U/ml
penicillin/streptomycin (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA). The
cells were incubated in a humidified incubator at 37°C with 5%
CO2, and the medium was replaced every 2 days. Ouabain
(Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA), H2O2
(Sigma-Aldrich), 25 mM KCl, 2 μM MK801 (Sigma-Aldrich) and
15, 25, 50 or 75 mM K-asp (Liaoning Union Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.,
Liaoning, China) were dissolved in distilled water. KCl, MK801 and
K-asp were added 4 h prior to treatment with either ouabain or
H2O2. The present study was approved by the
ethics committee of China Medical University (Shenyang, China).
Analysis of cell death using a
3-(4,5-dimethylthi-azol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT)
assay
The human SH-SY5Y cells were plated into 96-well
plates at a concentration of 5×103 cells/well and were
incubated with KCl (25 mM), MK801 (2 μM) or K-asp (15 mM, 25
mM, 50 mM or 75 mM), at 37°C for 4 h, prior to the addition of
ouabain (100 μM). Following treatment, the cells were
incubated for 24 and 48 h. The cells were treated with MTT (0.5
mg/ml/well) for 4 h, prior to the MTT being replaced with 150
μl dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and the absorption was
determined at 570 nm using a spectrophotometric plate reader (680;
Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., Hercules, CA, USA).
Nissl staining
The human SH-SY5Y cells (5×104) were
plated into 24-well plates and incubated, as described above.
Following incubation with 100 μM ouabain for 6, 24 or 48 h,
the cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde (Sinopharm Chemical
Reagent Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) and subsequently incubated in
Nissl solution (1%) at room temperature for 12 min. The stained
cells were observed under a light microscope (CK X41; Olympus,
Tokyo, Japan).
Analysis of apoptosis using
4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) staining
The human SH-SY5Y cells (5×104) were
plated onto a cover slip and incubated as described above.
Following incubation with 100 μM ouabain for 24 or 48 h, the
cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde and incubated in DAPI
solution (100 ng/ml) for 1 min in the dark. The stained cells were
observed under a fluorescence microscope (BX61/DP71; Olympus).
Transmission electron microscopy
The cells were incubated as described above.
Following incubation with 100 μM ouabain for 24 and 48 h,
the cells were fixed using 4% gluteraldehyde (Sinopharm Chemical
Reagent Co., Ltd.) in 0.1 M phosphate buffer (pH 7.4; Sinopharm
Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd.), and postfixed with 1% osmioum
tetroxide (Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd.) in 0.1 M
cacodylate (Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd.) buffer for 1 h at
4°C. The cells (5×104) were subsequently dehydrated
using ethanol (50, 70 and 90%), infiltrated using acetone and epoxy
resin (Structure Probe, Inc., West Chester, PA, USA), and finally
embedded in capsules (Agar Scientific, Essex, UK). Polymerization
was performed at 60°C for 48 h. Thin sections were cut with a
diamond knife on an ultramicrotome and mounted onto slot grids (Ted
Pella, Inc., Redding, CA, USA). The unstained sections were
observed under a Hitachi H-600 transmission electron microscope
(Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan).
Flow cytometry
The cells (1×106) were incubated, as
described above. Following incubation with 100 μM
H2O2 for 48 h, the cells were collected into
tubes and washed twice with 10 ml phosphate-buffered saline (PBS;
Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd.). The cells (1×106
cells/sample) were stained with annexin V-fluorescein
isothiocyanate (FITC)/propidium iodide (PI; BD Biosciences, San
Jose, CA, USA), according to the manufacturer’s instructions (BD
Biosciences, San Jose, CA, USA), and subsequently analyzed on a
fluorescence-activated cell sorting instrument (FACSAsia; Becton
Dickinson, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA). The PI- and annexin V-negative
cells (lower left quadrant) were considered to be normal,
PI-negative and annexin V-positive cells (lower right quadrant)
were considered early apoptotic cells, PI- and annexin V-positive
cells (upper right quadrant) were considered late apoptotic cells,
and the PI-positive and annexin V-negative cells (upper left
quadrant) were considered mechanically injured. All experiments
were performed in triplicate and representative figures
produced.
Statistical analysis
The results were analyzed using SPSS 13.0 software
(SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). The data are expressed as the mean
± standard deviation. Two groups of mean values were compared using
Student’s t-test. P<0.05 was considered to indicate a
statistically significant difference.
Results
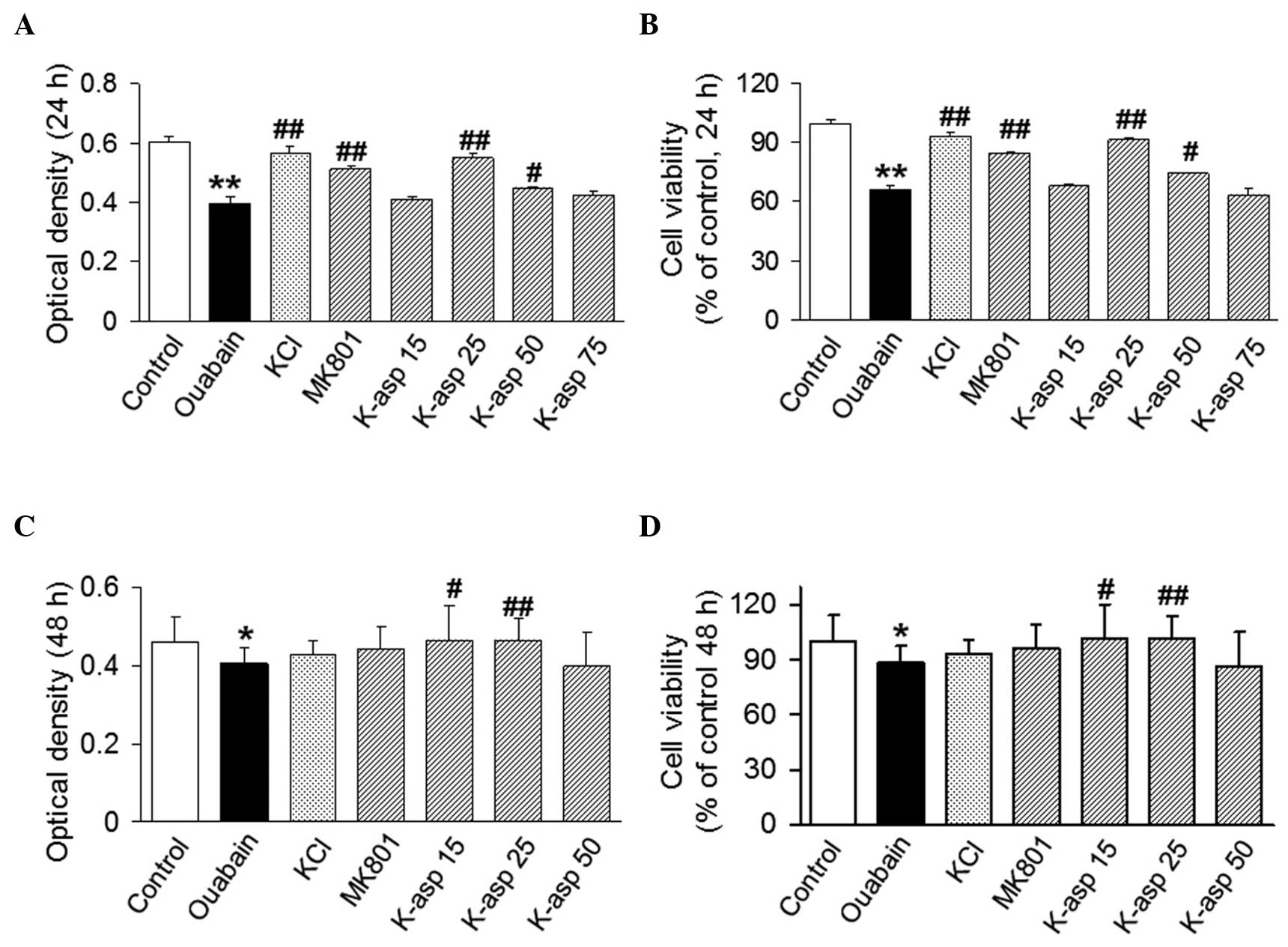
K-asp attenuates the cytotoxicity of
ouabain on SH-SY5Y cells in a dose-dependent manner
To investigate the effect of K-asp on
ouabain-induced cell death, an MTT assay was performed. The
viability of the SH-SY5Y cells exposed to ouabain for 24 h was
65.89±3.41% of that in the control group. The viabilities of the
cells treated with KCl, MK801, K-asp (25 mM) and K-asp (50 mM) were
93.21±3.67 (P<0.01), 84.49±1.89 (P<0.01), 91.32±1.75
(P<0.01) and 74.19±0.82% (P<0.05), respectively (Fig. 1A). The cells exposed to ouabain for
48 h was 88.37±9.08% of that of the control group. The viabilities
of the cells treated with K-asp (15 and 25 mM) were 101.20±19.07
(P<0.05) and 101.40±12.54% (P<0.01), respectively (Fig. 1B). The data suggested that K-asp
attenuated the ouabain-induced cytotoxicity of the SH-SY5Y cells in
a dose-dependent manner.
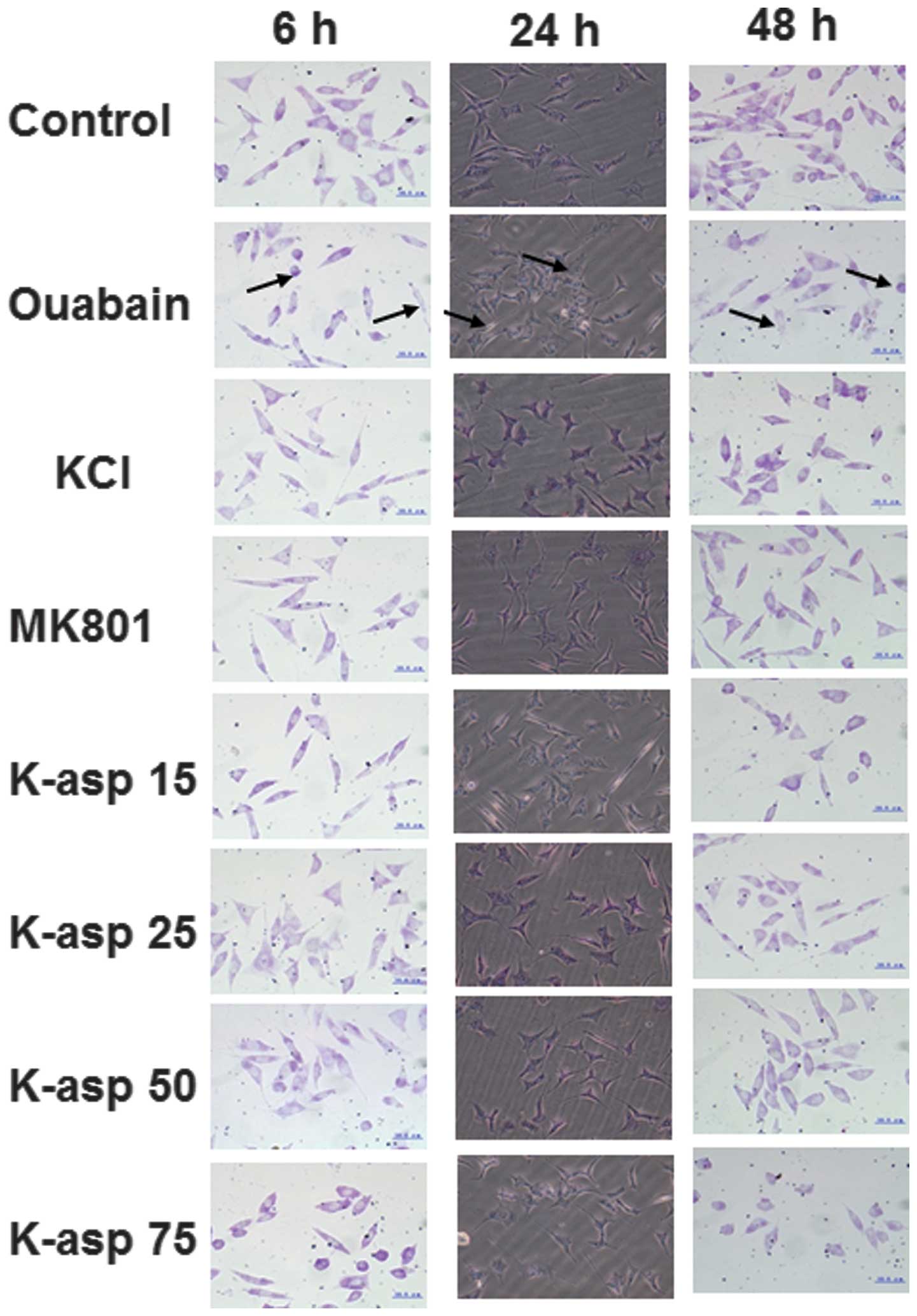
K-asp decreases the severity of
ouabain-induced necrosis in the SH-SY5Y cells, in a dose-dependent
manner
To observe the morphological changes of the SH-SY5Y
cells, Nissl staining was performed. Following incubation with
ouabain for 6, 24 and 48 h, the control group exhibited few injured
cells, and the visual field was predominantly clear and intact
cells without cell necrosis. However, a significant proportion of
the cells in the ouabain group were damaged, exhibiting extensive
degenerative changes, including sparse cell arrangements, loss of
integrity, a shrunken cytoplasm and swollen cell bodies (Fig. 2). The cells of the 48 h incubation
group exhibited more severe injury compared with those in the 6 and
24 h incubation groups. By contrast, the severity of cell necrosis
in the KCl, MK801, K-asp (15 mM) and K-asp (25 mM) groups was
alleviated, whereas cell necrosis in K-asp (50 mM) and K-asp (75
mM) groups was not. These results suggested that K-asp alleviated
the severity of ouabain-induced necrosis in the SH-SY5Y cells, in a
dose-dependent manner.
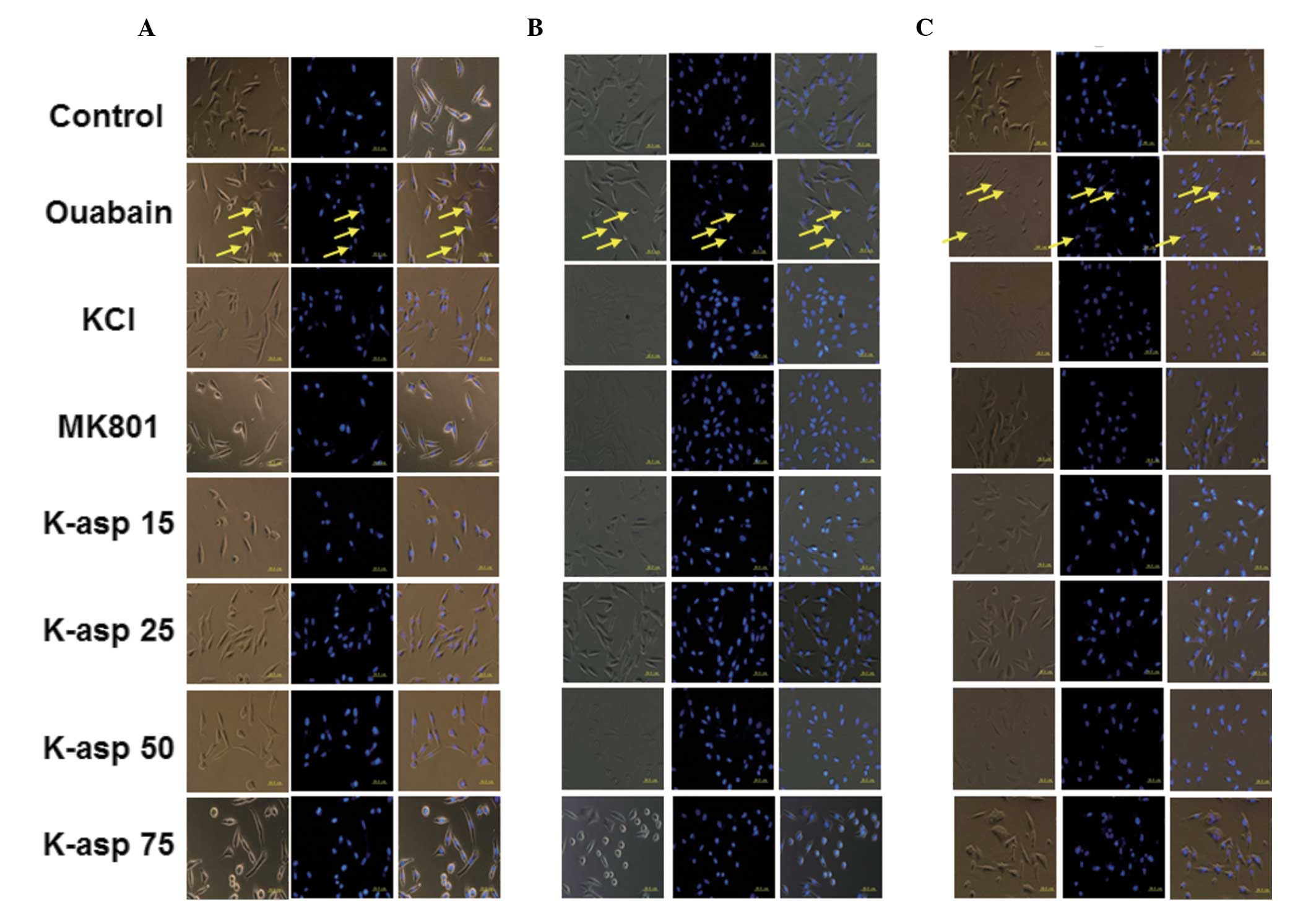
K-asp ameliorates ouabain-induced
apoptosis of SH-SY5Y cells, and 25 mM K-asp is the most effective
concentration
To examine the apoptotic response of the SH-SY5Y
cells incubated with ouabain for 6, 24 or 48 h, light microscopy
and DAPI staining were performed. In the control group, the cell
structures were clear, synapses were complete and large quantities
of the stained nuclei were uniform and oval in shape. In the
ouabain-treated group, the cell structures were unclear and the
number of viable cells were reduced, with a large quantity of cell
fragments. The nuclei were unevenly stained, their shape and size
were irregular, and their number was significantly reduced. The
number of cells in the ouabain-treated group, following incubation
for 24 and 48 h, was significantly reduced compared with the
control group. In the KCl group, light microscopy revealed that the
cell structures were clear and few cells were round, and the
results of the DAPI staining demonstrated that the number of the
cells was increased. In the MK801 group, light microscopy revealed
that the cell structures were clear and only a few cell fragments
were observed, with the DAPI staining demonstrating few cell shape
abnormalities. In the K-asp (25 mM) group, light microscopy
revealed higher numbers of cells and fewer cell fragments, compared
with the KCl, MK801, K-asp (15 mM) and K-asp (50 mM) groups
(Fig. 3). These data demonstrated
that K-asp ameliorated the ouabain-induced apoptosis of the SH-SY5Y
cells, with K-asp (25 mM) being the most effective.
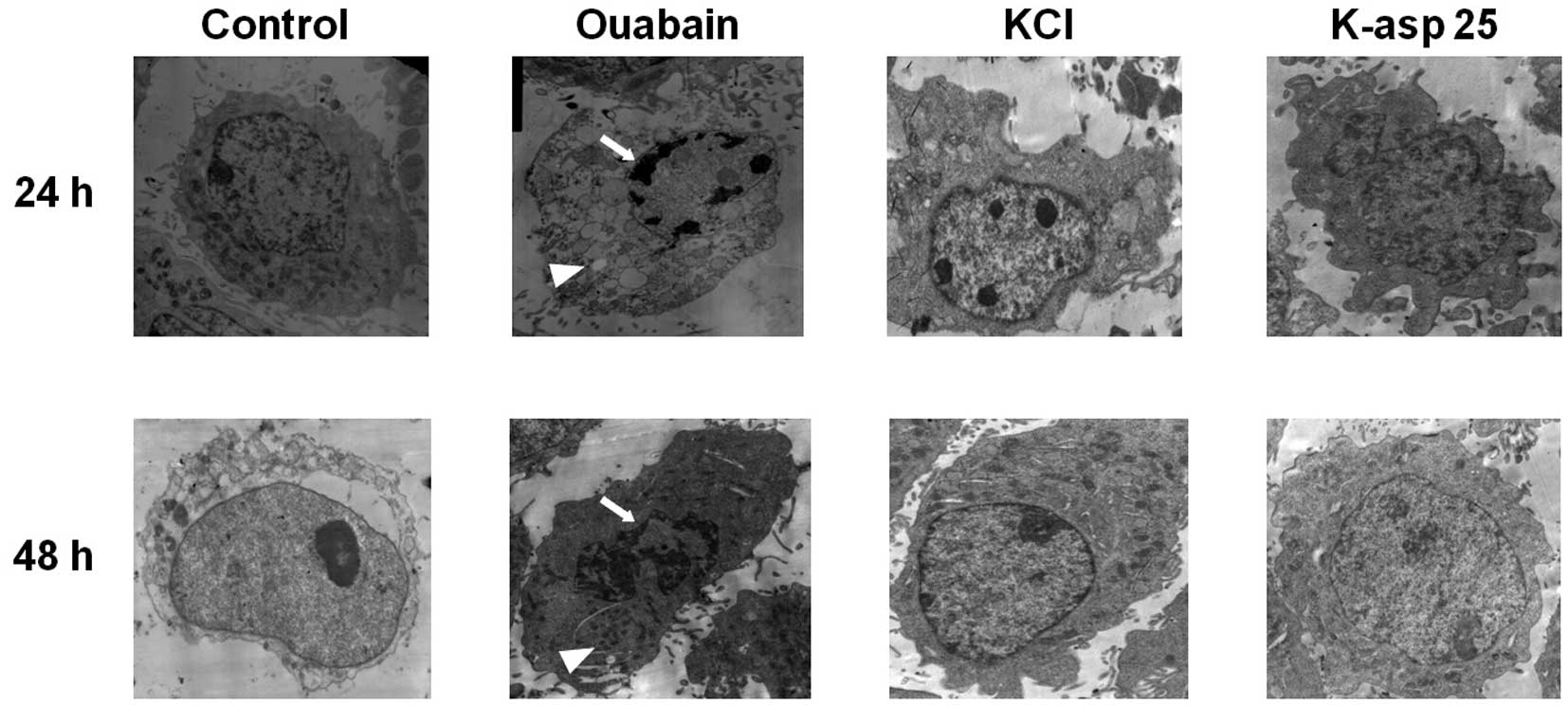
K-asp (25 mM) reduces cellular
ultrastructure changes, induced by ouabain
To determine the effect of K-asp on ultrastructure
changes of the SH-SY5Y cells following incubation with ouabain for
24 and 48 h, the cells were visualized using transmission electron
microscopy. In the control group, the cell membrane and nuclear
membrane were intact, and the structures of the mitochondria and
endoplasmic reticulum were clear. The ouabain group exhibited
incomplete cell membranes, cell shrinkage, nuclear cleavage
fragments, sparse necrotic cell chromatin, irregular granular
distribution, cell swelling and damage to the organelle structures.
By contrast, the KCl group and K-asp (25 mM) group exhibited
nuclear chromatin condensation, crescent- or ring-shaped nuclear
membrane bodies and clear organelle structures (Fig. 4). These data suggested that KCl and
K-asp (25 mM) alleviated the cellular ultrastructure changes, which
were induced following treatment with ouabain.
K-asp (25 mM) ameliorates the apoptosis
of SH-SY5Y cells induced by H2O2
To determine how K-asp affected
H2O2-induced cell apoptosis, an annexin
V-FITC/PI binding assay and flow cytometry were performed to detect
cell apoptosis. In the double parameter dot plots (Fig. 5), an increased number of cells in
the LR area were indicative of early apoptotic cells and those in
the UR area were indicative late apoptotic cells (Fig. 5A). In the control group, the early
apoptotic population of the SH-SY5Y cells was 1.38±0.50% and the
late apoptotic population was 3.69±0.98%, combining to a total
apoptotic population 5.07±0.87%. In the H2O2
group, the early apoptotic population of cells was 10.29±3.96% and
the late apoptotic population was 10.09±0.85%, combining to a total
apoptotic population 20.38±3.89%. The total number of apoptotic
population of the cells in H2O2 group was
significantly higher than that in the control group (P<0.001).
In the K-asp (25 mM) group, the early apoptotic population of cells
was 0.77±0.45% and the late apoptotic population was 4.89±1.56%,
combining to a total apoptotic population of 5.66±1.98%. The total
apoptotic population of the cells in K-asp (25 mM) group was
significantly decreased, compared with the
H2O2 group (P<0.001; Fig. 5E). These data demonstrated that
K-asp (25 mM) ameliorated the apoptotic response of
the-H2O2-induced SH-SY5Y cells.
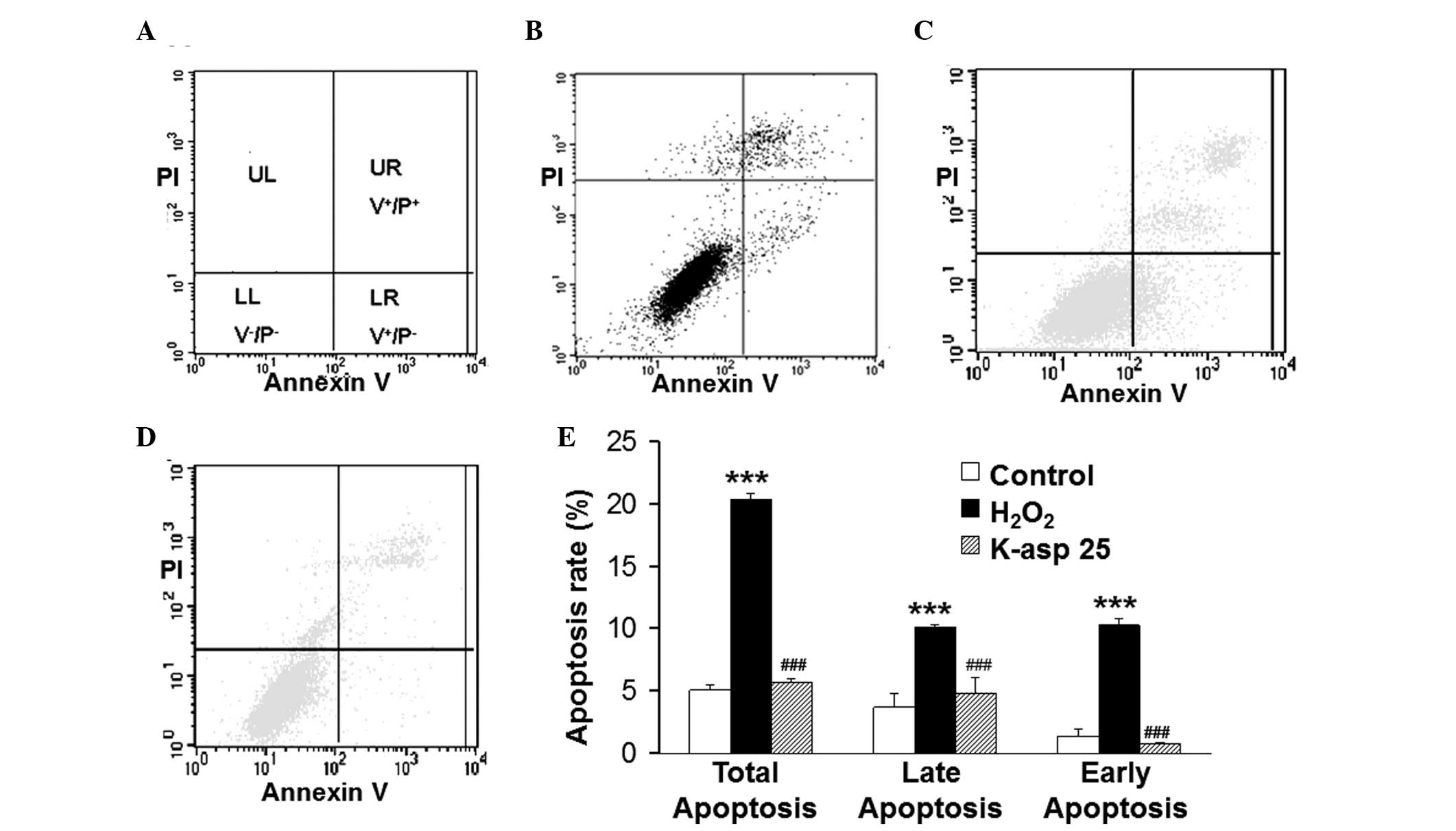 | Figure 5Effect of K-asp on the apoptosis of
SH-SY5Y cells following incubation with H2O2 for 48 h. Apoptosis
was determined using an annexin-V fluorescein
isothiocyanate/propidium iodide binding assay and flow cytometry.
K-asp (25 mM) was added 4 h prior to treatment of the cells with
H2O2 (100 μM). (A) Normal cells
(V−/PI−) were indicated in the LL quadrant of
the dot plot, early apoptotic cells (V+/P+)
were indicated in the UR dot quadrant and late apoptotic cells
(V+/P−) were indicated in the LR quadrant.
(B) Dot plot of cells in the control group. (C) Dot plot of cells
in the H2O2 group. (D) Dot plot of cells in
the K-asp group. (E) Histograms of the percentages of apoptosis,
based on the accumulation of annexin-V FITC positive cells in UR
and LR quadrants. The data are expressed as the mean ± standard
error of the mean (***P<0.001, compared with the
control group; ###P<0.001, compared with the
H2O2 group). K-asp, potassium aspartate; V,
annexin-V fluorescein isothiocyanate; P, propidium iodide,
+, positive; −, negative; UL, upper left; UR,
upper right; LL, lower left; LR, lower right. |
Discussion
Ouabain is a Na+-K+-ATP enzyme
inhibitor, which increases the levels of Na+ and
Ca2+ and decreases the levels of K+ under
intracellular conditions (11). In
the early period of ouabain treatment (2–6 h), SH-SY5Y cells swell
and the cell volume decreases gradually, resulting in cell
apoptosis and necrosis (11).
Previous studies have demonstrated that intracellular K+
concentrations are reduced to 80% in neurons treated with ouabain
for 12 h (12–14). The present study demonstrated that,
following treatment with ouabain for 24 h, the number of cells was
significantly decreased and the cell survival rate was
significantly increased in the KCl, MK801 and K-asp (25 mM) groups.
No difference in cell survival rate was observed between the KCl
and K-asp (25 mM) groups, and the cell survival rates in these two
groups were higher compared with that in the MK801 group. The cell
survival rates following incubation for 48 h in the K-asp (15 mM)
and K-asp (25 mM) groups were higher compared with the KCl and
MK801 groups. These results indicated that KCl had a short-term
protective effect against cellular damage caused by low potassium,
however, K-asp exhibited a longer duration of protective effects
compared with KCl.
Nissl bodies indicate nerve cell functions (12). The results of the Nissl staining in
the present study demonstrated that the cells in the KCl, MK801 and
K-asp (25 mM) groups exhibited darker staining, compared with those
in the ouabain group, with the number of cells being increased.
This observation indicated that K-asp and KCl protected against
ouabain-induced cell damage.
As a well-established model of in vitro
SH-SY5Y cell oxidative stress, H2O2 can
readily pass through the cell membrane and cause cell damage,
resulting in the disturbance of ion homeostasis (15,16).
H2O2 inhibits
Na+-K+-pump activity and decreases
intracellular levels of K+. A previous study
demonstrated that apoptotic cell dehydration was caused by the loss
of K+ (17). In
cancerous tissues, fewer KV1.1 and KV1.3
potassium channels are expressed and the cell apoptosis is
abnormal, indicating that potassium channels may contribute to
apoptosis (18). Another previous
study demonstrated cerebellar granule neuron apoptosis following
the transfer of cells from different extracellular potassium
concentrations (19). In the
present study, K-asp (25 mM) protected the SH-SY5Y cells from the
induction of apoptosis following incubation with
H2O2 48 h. The total apoptotic population of
the cells in the H2O2 group was significantly
increased compared with the control group, however, this effect was
suppressed following treatment with K-asp (25 mM). Subsequent
analysis revealed that the protective effect of K-asp (25 mM) was
persistent in the early and late periods of apoptosis. These
results demonstrated that K-asp (25 mM) significantly reduced the
apoptotic rate of the cells, however, excessively high
K+ concentrations (≥50 mM) resulted in apoptosis. These
results were consistent with those reported in previous studies
(20,21).
It has been reported that ouabain inhibits the
reduction in Bcl-2 and the increases the phosphorylation of the
pro-apoptotic factor, p53, in SH-SY5Y cells (13). Ouabain, a
Na+-K+-ATP enzyme inhibitor, increases levels
of intracellular Na+ and promotes
Na+-Ca2+ exchange, which causes intracellular
calcium overload and activates caspase-3 and endogenous nucleases,
leading to apoptosis and irreversible damage (11). In the present study, analysis using
DAPI staining and transmission electron microscopy revealed that
KCl and K-asp (25 mM) reduced the level of apoptosis induced by
ouabain. The annexin V-FITC/PI binding assay indicated that K-asp
(25 mM) also reduced apoptosis, which was induced by
H2O2. In the present study, MK801, a NMDA
receptor antagonist, reduced ouabain-induced cell damage
caused.
Decreased intracellular ions lead to decreased
intracellular osmotic crystals and the outflow of water molecules,
causing a reduction in cell volume (19). This is partly consistent with the
results of the present study. K-asp, a novel energy type potassium
agent, has a high affinity towards cells. Aspartic acid contributes
to the citric acid cycle to provide ATP for the body and to assist
in Na+-K+-ATP enzyme recovery (22). In the present study, K-asp (15 mM
and 25 mM) had a better protective effect compared with KCl,
whereas the cells in the K-asp (75 mM) group exhibited severe
damage, caused by the high concentration of K+ (23,24).
In conclusion, the present study demonstrated that
K-asp (25 mM) had protective effects on the SH-SY5Y cells, with
superior effects compared with KCl, following incubation for 48 h.
This suggested that K-asp supplemented the levels of intracellular
K+ and inhibited the apoptosis of the SH-SY5Y cells.
References
|
1
|
Abe K and Saito H: Involvement of
Na+-K+ pump in L-glutamate clearance by
cultured rat cortical astrocytes. Biol Pharm Bull. 23:1051–1054.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ueno Y, Ogino Y and Kinouchi T: Sodium,
potassium. Nihon Rinsho. 12:250–256. 2004.In Chinese.
|
|
3
|
Willard MD: Disorders of potassium
homeostasis. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract. 19:241–263. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shiino A, Nishida Y, Yasuda H, Suzuki M,
Matsuda M and Inubushi T: Magnetic resonance spectroscopic
determination of a neuronal and axonal marker in white matter
predicts reversibility of deficits in secondary normal pressure
hydrocephalus. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 75:1141–1148. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Suleiman MS, Dihmis WC, Caputo M, Angelini
GD and Bryan AJ: Changes in myocardial concentration of glutamate
and aspartate during coronary artery surgery. Am J Physiol.
272:H1063–H1069. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Saunders EC, Ng WW, Chambers JM, et al:
Isotopomer profiling of Leishmania mexicana promastigotes reveals
important roles for succinate fermentation and aspartate uptake in
tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA) anaplerosis, glutamate synthesis and
growth. J Biol Chem. 286:27706–27717. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Olanow CW and Tatton WG: Etiology and
pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Annu Rev Neurosci. 22:123–144.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Bellavite P: The superoxide-forming
enzymatic system of phagocytes. Free Radic Biol Med. 4:225–261.
1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Halliwell B and Gutteridge JM: Lipid
peroxidation in brain homogenates: the role of iron and hydroxyl
radicals. J Neurochem. 69:1330–1331. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gardner AM, Xu FH, Fady C, Jacoby FJ,
Duffey DC, Tu Y and Lichtenstein A: Apoptotic vs. nonapoptotic
cytotoxicity induced by hydrogen peroxide. Free Radic Biol Med.
22:73–83. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xiao AY, Wei L, Xia S, Rothman S and Yu
SP: Ionic mechanism of ouabain induced concurrent apoptosis and
necrosis in individual cultured cortical neurons. Neuroscience.
22:1350–1362. 2002.
|
|
12
|
Huang X, Moir RD, Tanzi RE, Bush AI and
Rogers JT: Redox-active metals, oxidative stress and Alzheimer’s
disease pathology. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1012:153–163. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kulikov A, Eva A, Kirch U, Boldyrev A and
Scheiner-Bobis G: Ouabain activates signaling pathways associated
with cell death in human neuroblastoma. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1768:1691–1702. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yu SP, Yeh C, Strasser U, Tian M and Choi
DW: NMDA receptor mediated K+ efflux and neuronal apoptosis.
Science. 284:336–339. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang XQ, Xiao AY, Sheline C, et al:
Apoptotic insults impair Na+-K+-ATPase
activity as a mechanism of neuronal death mediated by concurrent
ATP deficiency and oxidant stress. J Cell Sci. 116:2099–2110. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xiao AY, Wang XQ, Yang A and Yu SP: Slight
impairment of Na+-K+-ATPase synergistically aggravates ceramide-
and beta-amyloid-induced apoptosis in cortical neurons. Brain Res.
955:253–259. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yurinskaya VE, Rubashkin AA and Vereninov
AA: Balance of unidirectional monovalent ion fluxes in cells
undergoing apoptosis: why does Na+-K+ pump suppression not cause
cell swelling? J Physiol. 589:2197–2211. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Brevet M, Ahidouch A, Sevestre H, Merviel
P, El Hiani Y, Robbe M and Ouadid-Ahidouch H: Expression of K+
channels in normal and cancerous human breast. Histol Histopathol.
23:965–972. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hernández-Enríquez B, Arellano RO and
Morán J: Role for ionic fluxes on cell death and apoptotic volume
decrease in cultured cerebellar granule neurons. Neuroscience.
167:298–311. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Huang XP, Tan H, Chen BY and Deng CQ:
Astragalus extract alleviates nerve injury after cerebral ischemia
by improving energy metabolism and inhibiting apoptosis. Biol Pharm
Bull. 35:449–454. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang M, Qiu J, Mi W, Wang F and Qu J: In
vitro effect of altering potassium concentration in artificial
endolymph on apoptosis and ultrastructure features of olfactory
bulb neural precursor cells. Neurosci Lett. 487:383–388. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Jorgensen PL and Pedersen PA:
Structure-function relationships of Na+, K+, ATP, or Mg2+ binding
and energy transduction in Na, K-ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1505:57–74. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gugliotta T, De Luca G, Romano P, Rigano
C, Scuteri A and Romano L: Effects of lead chloride on human
erythrocyte membranes and on kinetic anion sulphate and glutathione
concentrations. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 17:586–597. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Noguchi T, Kamiyama N and Kashiwayanagi M:
Modulation of voltage-gated ion channels on SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma
by non-ionic surfactant, Cremophor EL. Biol Pharm Bull.
33:2013–2017. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|