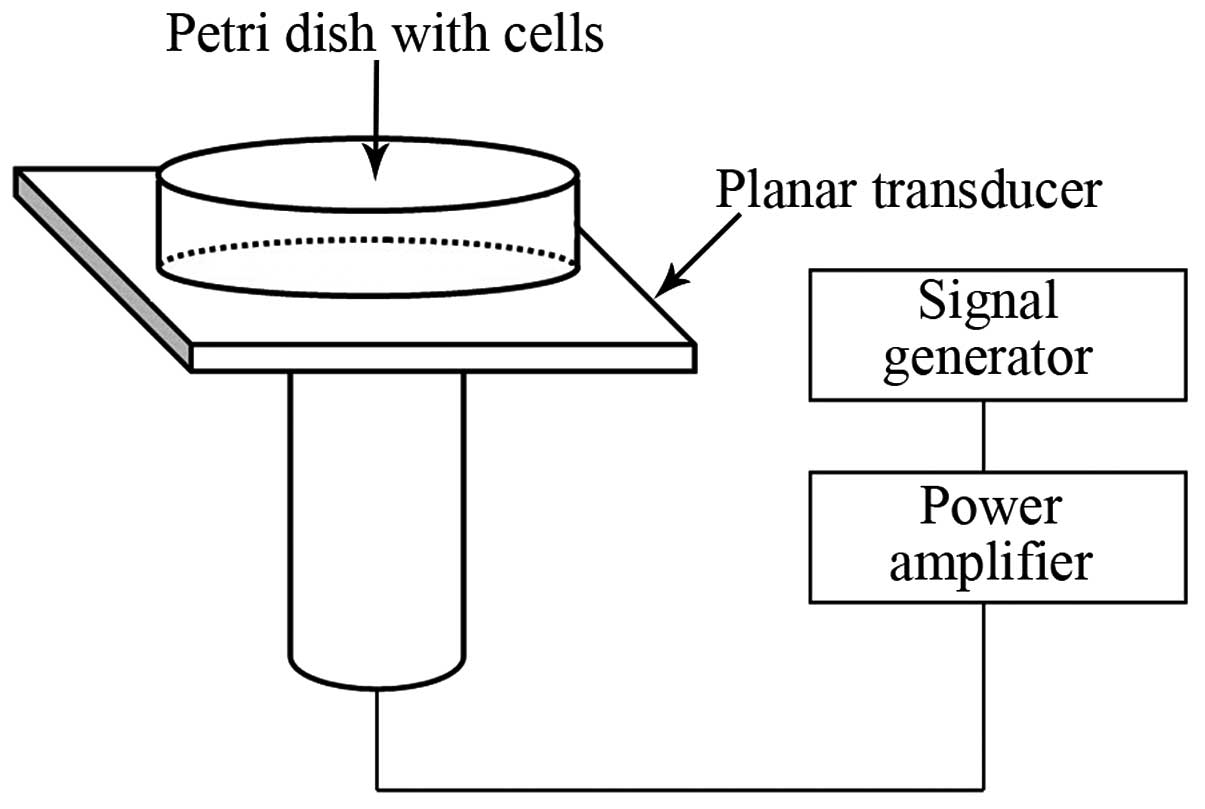
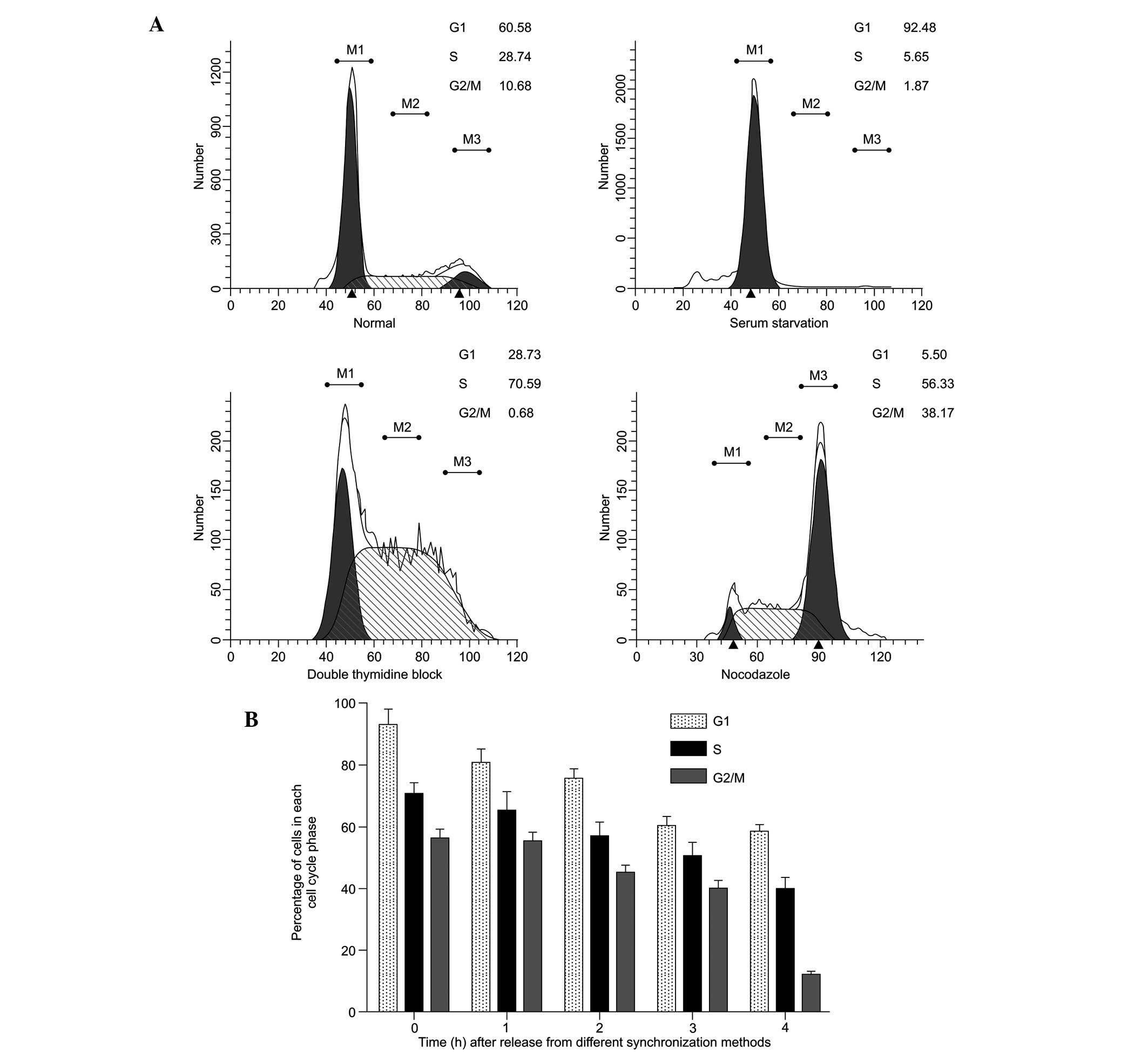
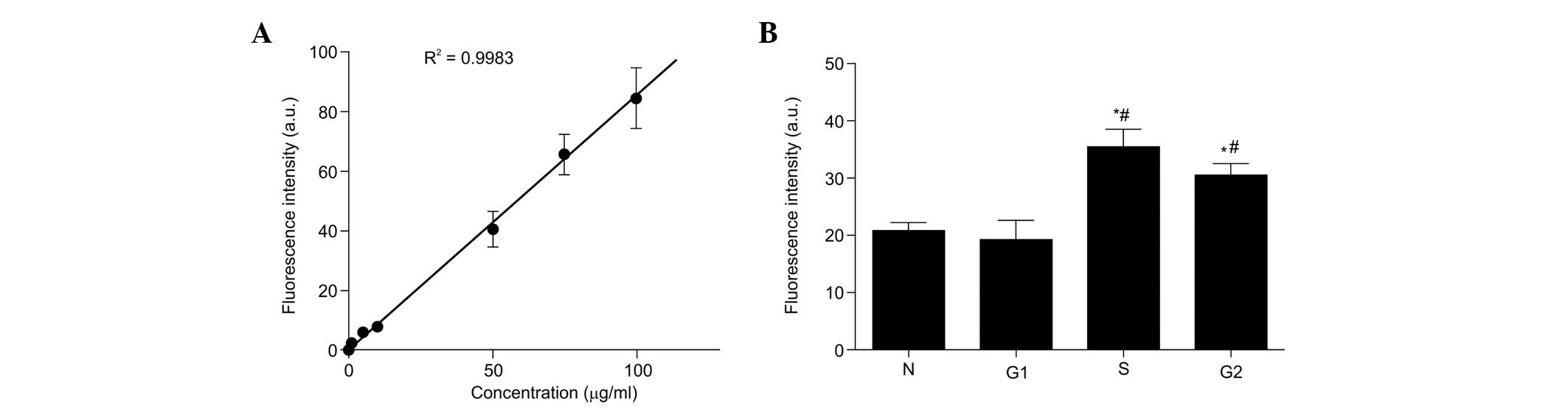
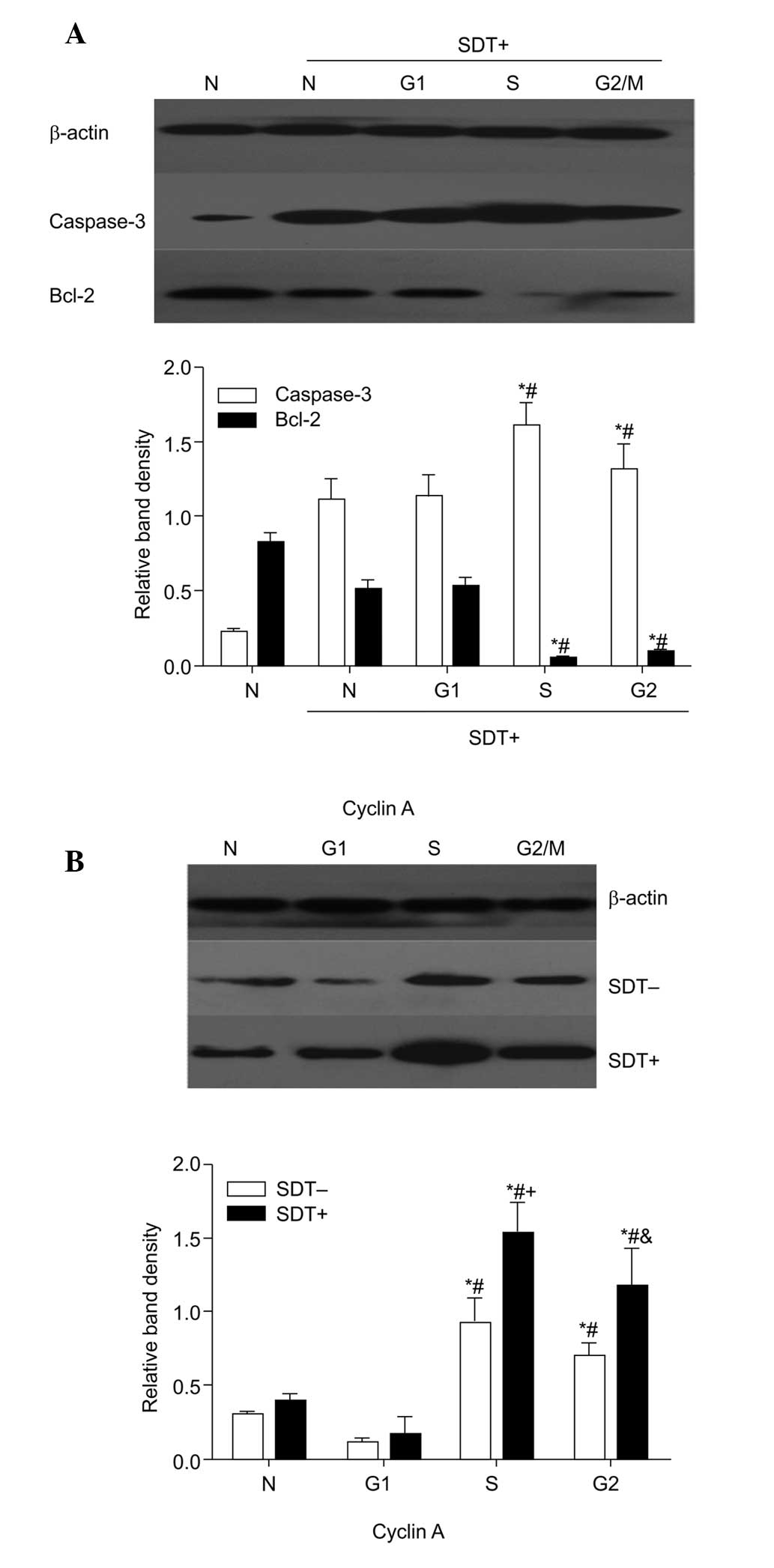
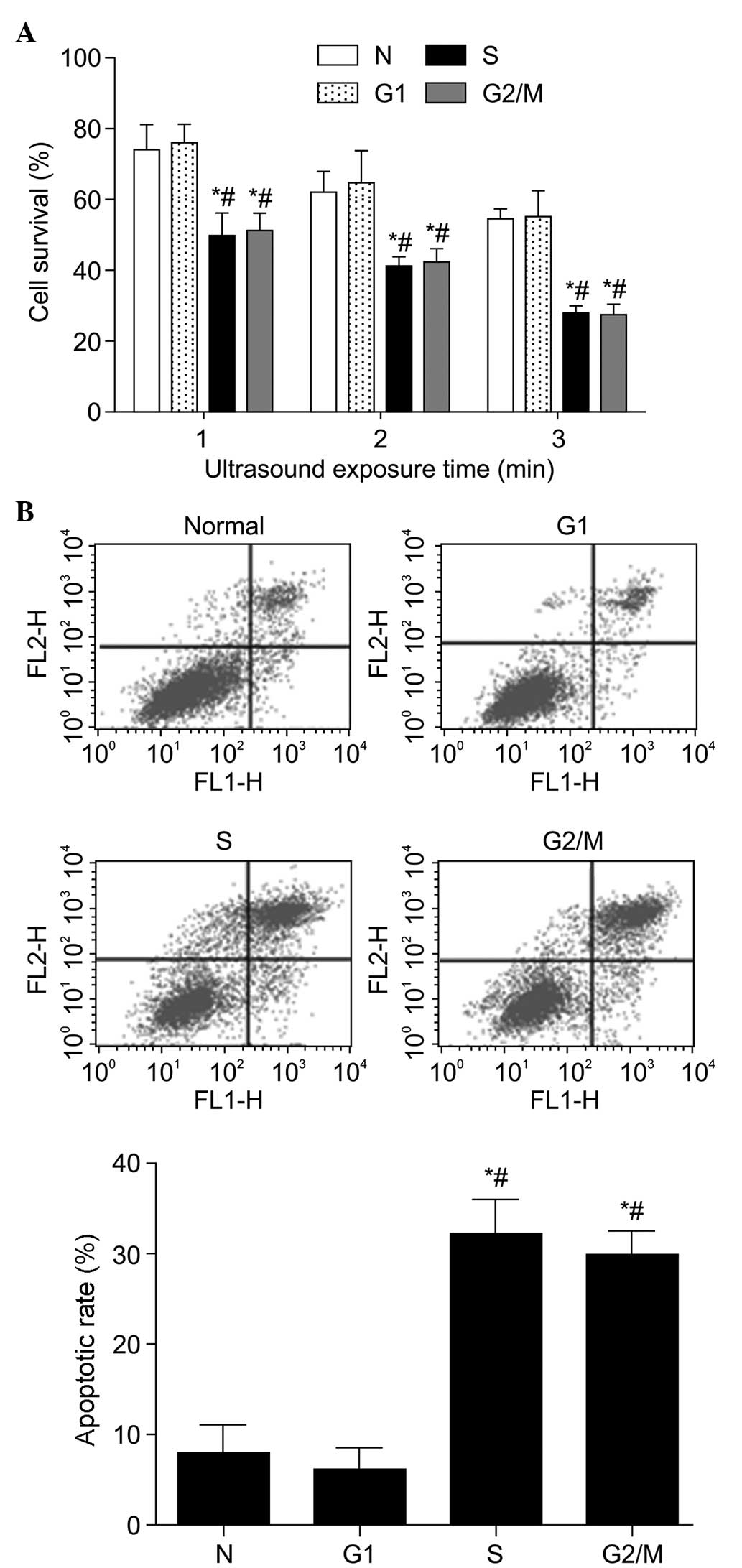
|
1
|
Shibaguchi H, Tsuru H and Kuroki M:
Sonodynamic cancer therapy: a non-invasive and repeatable approach
using low-intensity ultrasound with a sonosensitizer. Anticancer
Res. 31:2425–2429. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rosenthal I, Sostaric JZ and Riesz P:
Sonodynamic therapy-a review of the synergistic effects of drugs
and ultrasound. Ultrason Sonochem. 11:349–363. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tsuru H, Shibaguchi H, Kuroki M and
Yamashita Y: Tumor growth inhibition by sonodynamic therapy using a
novel sonosensitizer. Free Radic Biol Med. 53:464–472. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yumita N, Okuyama N, Sasaki K and Umemura
S: Sonodynamic therapy on chemically induced mammary tumor:
pharmacokinetics, tissue distribution and sonody-namically induced
antitumor effect of gallium-porphyrin complex ATX-70. Cancer
Chemother Pharmacol. 60:891–897. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Komori C, Okada K, Kawamura K, Chida S and
Suzuki T: The sonodynamic antitumor effect of methylene blue on
sarcoma180 cells in vitro. Anticancer Res. 29:2411–2415.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liu Q, Li X, Xiao L, Wang P, Wang X and
Tang W: Sonodynamically induced antitumor effect of hematoporphyrin
on Hepatoma 22. Ultrason Sonochem. 15:943–948. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ohmura T, Fukushima T, Shibaguchi H, et
al: Sonodynamic therapy with 5-aminolevulinic acid and focused
ultrasound for deep-seated intracranial glioma in rat. Anticancer
Res. 31:2527–2533. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Peng Q, Berg K, Moan J, Kongshaug M and
Nesland JM: 5-Aminolevulinic acid-based photodynamic therapy:
principles and experimental research. Photochem Photobiol.
65:235–251. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zenzen V and Zankl H: Protoporphyrin
IX-accumulation in human tumor cells following topical ALA- and
h-ALA-application in vivo. Cancer Lett. 202:35–42. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wu SM, Ren QG, Zhou MO, Peng Q and Chen
JY: Protoporphyrin IX production and its photodynamic effects on
glioma cells, neuroblastoma cells and normal cerebellar granule
cells in vitro with 5-aminolevulinic acid and its hexylester.
Cancer Lett. 200:123–131. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Schick E, Kaufmann R, Ruck A, Hainzl A and
Boehncke WH: Influence of activation and differentiation of cells
on the effectiveness of photodynamic therapy. Acta Derm Venereol.
75:276–279. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wyld L, Burn JL, Reed MW and Brown NJ:
Factors affecting aminolaevulinic acid-induced generation of
protoporphyrin IX. Br J Cancer. 76:705–712. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wyld L, Smith O, Lawry J, Reed MW and
Brown NJ: Cell cycle phase influences tumour cell sensitivity to
aminolaevulinic acid-induced photodynamic therapy in vitro. Br J
Cancer. 78:50–55. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sano M, Furuta T, Takahira K, et al:
Cell-cycle-dependent efficacy of photodynamic therapy with
ATX-S10(Na). Lasers Med Sci. 20:1–5. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Heinemann L, Simpson GR, Annels NE, et al:
The effect of cell cycle synchronization on tumor sensitivity to
reovirus oncolysis. Mol Ther. 18:2085–2093. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Huang X, Di Liberto M, Jayabalan D, et al:
Prolonged early G(1) arrest by selective CDK4/CDK6 inhibition
sensitizes myeloma cells to cytotoxic killing through cell
cycle-coupled loss of IRF4. Blood. 120:1095–1106. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hassan MAIA, Braam SR and Kruyt FAE:
Paclitaxel and vincristine potentiate adenoviral oncolysis that is
associated with cell cycle and apoptosis modulation, whereas they
differentially affect the viral life cycle in non-small-cell lung
cancer cells. Cancer Gene Ther. 13:1105–1114. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Connell CM, Wheatley SP and McNeish IA:
Nuclear survivin abrogates multiple cell cycle checkpoints and
enhances viral oncolysis. Cancer Res. 68:7923–7931. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lv Y, Fang M, Zheng J, et al:
Low-intensity ultrasound combined with 5-aminolevulinic acid
administration in the treatment of human tongue squamous carcinoma.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 30:321–333. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Song W, Cui H, Zhang R, Zheng J and Cao W:
Apoptosis of SAS cells induced by sonodynamic therapy using
5-aminolevulinic acid sonosensitizer. Anticancer Res. 31:39–45.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Khammanit R, Chantakru S, Kitiyanant Y and
Saikhun J: Effect of serum starvation and chemical inhibitors on
cell cycle synchronization of canine dermal fibroblasts.
Theriogenology. 70:27–34. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Banfalvi G: Overview of cell
synchronization. Methods Mol Biol. 761:1–23. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gao Z, Zheng J, Yang B, et al: Sonodynamic
therapy inhibits angiogenesis and tumor growth in a xenograft mouse
model. Cancer Lett. 335:93–99. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Vokes EE: The promise of biochemical
modulation in combined modality therapy. Semin Oncol. 21:29–33.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Humphrey RM and Dewey WC: Radiosensitivity
of normal and 5-bromodeoxyuridine treated mammalian cells during
different phases of the cell cycle. Exp Cell Res. 39:483–495. 1965.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ma LW, Moan J, Steen HB and Iani V:
Anti-tumour activity of photodynamic therapy in combination with
mitomycin C in nude mice with human colon adenocarcinoma. Br J
Cancer. 71:950–956. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shibata Y, Matsumura A, Yoshida F, et al:
Cell cycle dependency of porphyrin uptake in a glioma cell line.
Cancer Lett. 129:77–85. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Terasima T and Tolmach LJ: Variations in
several responses of HeLa cells to x-irradiation during the
division cycle. Biophys J. 3:11–33. 1963. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Meikrantz W and Schlegel R: Apoptosis and
the cell cycle. J Cell Biochem. 58:160–174. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yam CH, Fung TK and Poon RYC: Cyclin A in
cell cycle control and cancer. Cell Mol Life Sci. 59:1317–1326.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Pagano M, Pepperkok R, Verde F, Ansorge W
and Draetta G: Cyclin A is required at two points in the human cell
cycle. EMBO J. 11:961–971. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang SJ, Hasham MG, Isordia-Salas I,
Tsygankov AY, Colman RW and Guo YL: Regulation of cardiovascular
signaling by kinins and products of similar converting enzyme
systems - Upregulation of Cdc2 and cyclin A during apoptosis of
endothelial cells induced by cleaved high-molecular-weight
kininogen. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 284:H1917–H1923. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Meikrantz W and Schlegel R: Suppression of
apoptosis by dominant negative mutants of cyclin-dependent protein
kinases. J Biol Chem. 271:10205–10209. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Meikrantz W, Gisselbrecht S, Tam SW and
Schlegel R: Activation of Cyclin a-Dependent Protein-Kinases during
Apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 91:3754–3758. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Wang XH, Song YJ, Ren JS and Qu XG:
Knocking-Down Cyclin A(2) by siRNA Suppresses Apoptosis and
Switches Differentiation Pathways in K562 Cells upon Administration
with Doxorubicin. PLoS One. 4:e66652009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ekberg J and Persson J: Post-translational
modification of cyclin A1 is associated with staurosporine and TNF
alpha induced apoptosis in leukemic cells. Mol Cell Biochem.
320:115–124. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Hiromura K, Pippin JW, Blonski MJ, Roberts
JM and Shankland SJ: The subcellular localization of cyclin
dependent kinase 2 determines the fate of mesangial cells: role in
apoptosis and proliferation. Oncogene. 21:1750–1758. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|