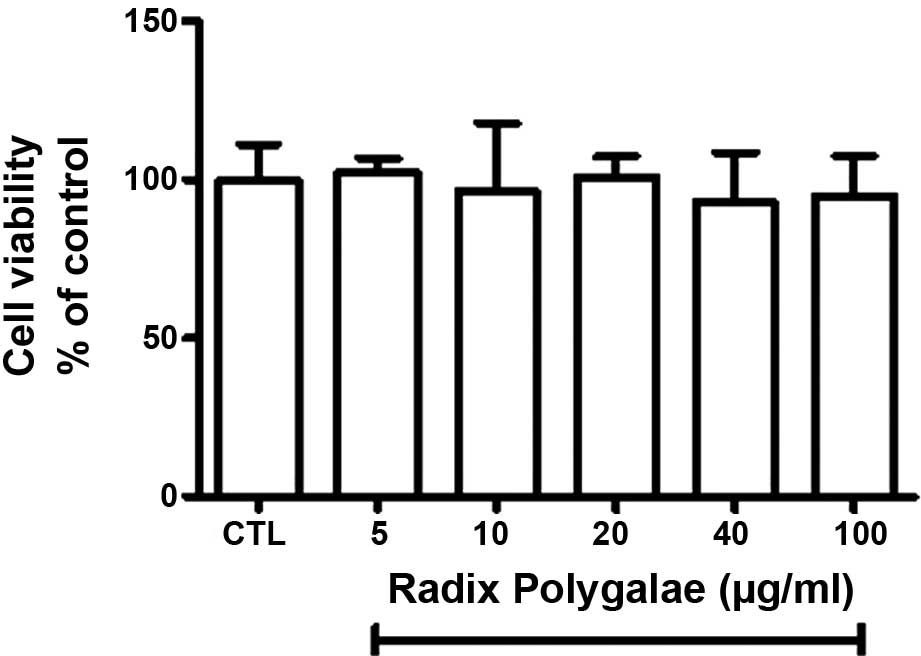
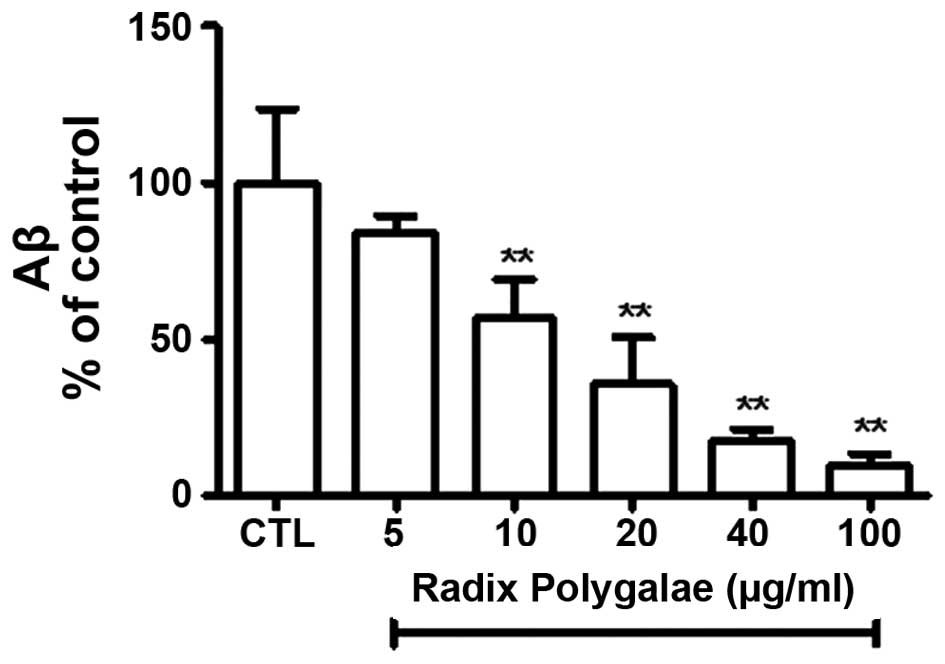
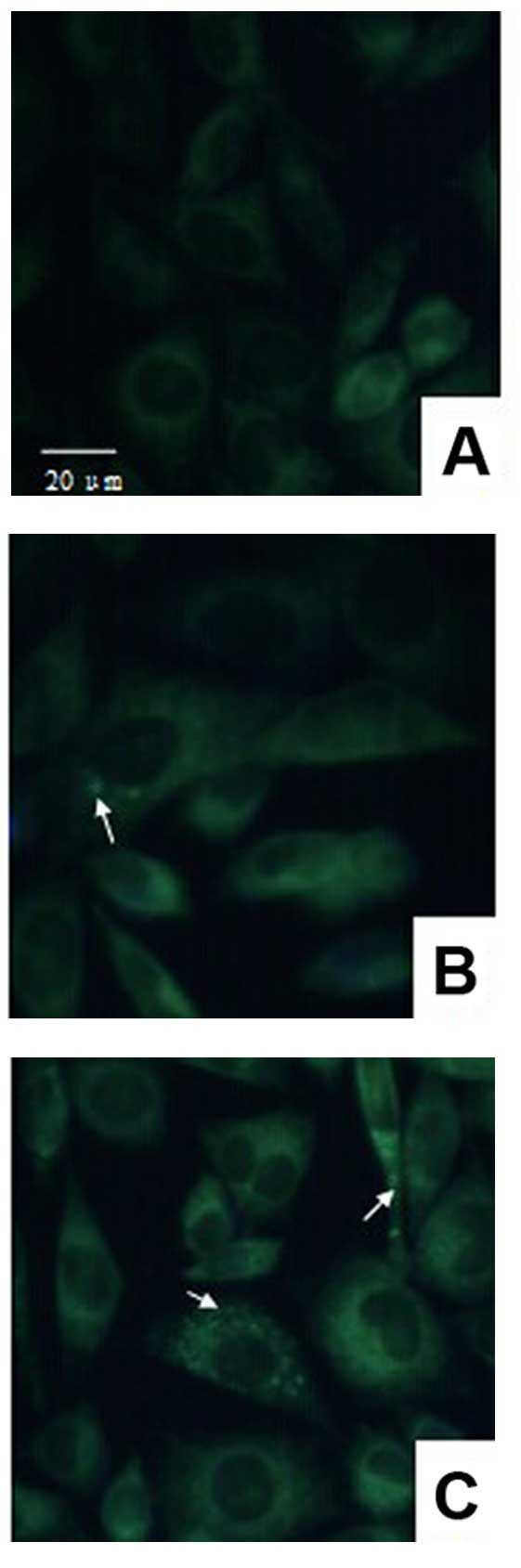
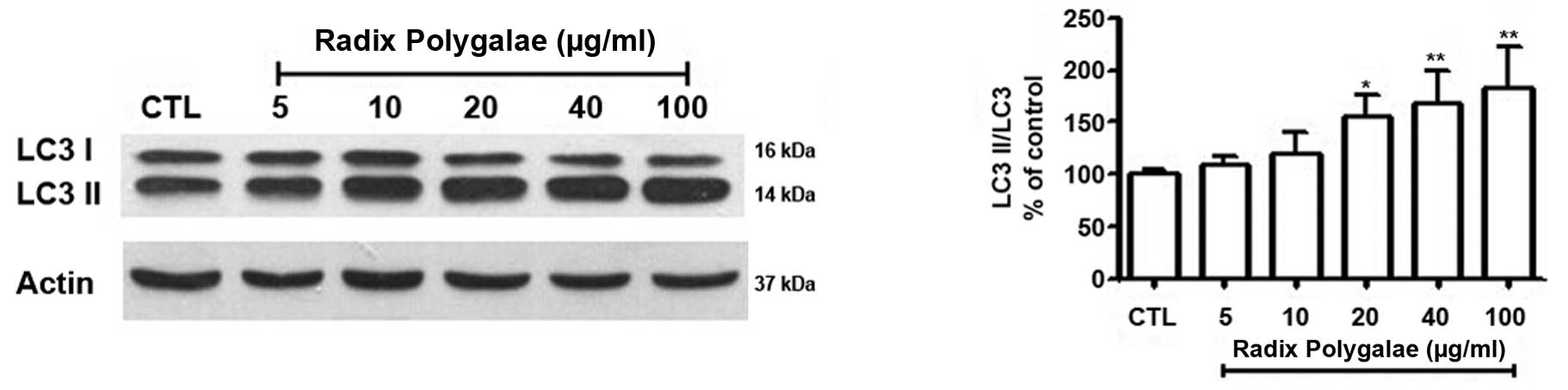
|
1
|
Feng Y and Wang X: Antioxidant therapies
for Alzheimer’s disease. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2012:4729322012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Huang Y and Mucke L: Alzheimer mechanisms
and therapeutic strategies. Cell. 148:1204–1222. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bondareff W: Age-related changes in brain
extracellular space affect processing of amyloid-β peptides in
Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 35:1–6. 2013.
|
|
4
|
Shi TY, Zhao DQ, Wang HB, et al: A new
chiral pyrrolyl α-nitronyl nitroxide radical attenuates β-amyloid
deposition and rescues memory deficits in a mouse model of
Alzheimer disease. Neurotherapeutics. 10:340–353. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
5
|
Cappai R and White AR: Amyloid β. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 31:885–889. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cavallucci V, D’Amelio M and Cecconi F: Aβ
toxicity in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurobiol. 45:366–378. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sanchez-Varo R, Trujillo-Estrada L,
Sanchez-Mejias E, et al: Abnormal accumulation of autophagic
vesicles correlates with axonal and synaptic pathology in young
Alzheimer’s mice hippocampus. Acta Neuropathol. 123:53–70. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
8
|
Zhu Z, Li C, Wang X, Yang Z, Chen J, Hu L,
Jiang H and Shen X: 2,2′,4′-trihydroxychalcone from Glycyrrhiza
glabra as a new specific BACE1 inhibitor efficiently ameliorates
memory impairment in mice. J Neurochem. 114:374–385. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Arsikin K, Kravic-Stevovic T, Jovanovic M,
Ristic B, Tovilovic G, Zogovic N, Bumbasirevic V, Trajkovic V and
Harhaji-Trajkovic L: Autophagy-dependent and -independent
involvement of AMP-activated protein kinase in 6-hydroxydopamine
toxicity to SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1822:1826–1836. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tung YT, Wang BJ, Hu MK, Hsu WM, Lee H,
Huang WP and Liao YF: Autophagy: a double-edged sword in
Alzheimer’s disease. J Biosci. 37:157–165. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Periyasamy-Thandavan S, Jiang M,
Schoenlein P and Dong Z: Autophagy: Molecular machinery, regulation
and implications for renal pathophysiology. Am J Physiol Renal
Physiol. 297:F244–F256. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cheung ZH and Ip NY: Autophagy
deregulation in neurode-generative diseases-recent advances and
future perspectives. J Neurochem. 118:317–325. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kaushik S and Cuervo AM: Autophagy as a
cell-repair mechanism: Activation of chaperone-mediated autophagy
during oxidative stress. Mol Aspects Med. 27:444–454. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Majumder S, Richardson A, Strong R and
Oddo S: Inducing autophagy by rapamycin before, but not after, the
formation of plaques and tangles ameliorates cognitive deficits.
PLoS One. 6:e254162011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chong ZZ, Shang YC, Zhang L, Wang S and
Maiese K: Mammalian target of rapamycin: Hitting the bull’s-eye for
neurological disorders. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 3:374–391. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wu X, Kihara T, Akaike A, Niidome T and
Sugimoto H: PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling regulates glutamate transporter
1 in astrocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 393:514–518. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Klionsky DJ, Meijer AJ, Codogno P, Neufeld
TP and Scott RC: Autophagy and p70S6 kinase. Autophagy. 1:59–61.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Din FV, Valanciute A, Houde VP, Zibrova D,
Green KA, Sakamoto K, Alessi DR and Dunlop MG: Aspirin inhibits
mTOR signaling, activates AMP-activated protein kinase, and induces
autophagy in colorectal cancer cells. Gastroenterology.
142:1504–15.e3. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Saiki S, Sasazawa Y, Imamichi Y, et al:
Caffeine induces apoptosis by enhancement of autophagy via
PI3K/Akt/mTOR/p70S6K inhibition. Autophagy. 7:176–187. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Lin Z, Gu J, Xiu J, Mi T, Dong J and
Tiwari JK: Traditional chinese medicine for senile dementia. Evid
Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012:6926212012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Lee HJ, Ban JY, Koh SB, Seong NS, Song KS,
Bae KW and Seong YH: Polygalae radix extract protects cultured rat
granule cells against damage induced by NMDA. Am J Chin Med.
32:599–610. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Park CH, Choi SH, Koo JW, Seo JH, Kim HS,
Jeong SJ and Suh YH: Novel cognitive improving and neuroprotective
activities of Polygala tenuifolia Willdenow extract, BT-11. J
Neurosci Res. 70:484–492. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lv J, Jia H, Jiang Y, Ruan Y, Liu Z, Yue
W, Beyreuther K, Tu P and Zhang D: Tenuifolin, an extract derived
from tenuigenin, inhibits amyloid-β secretion in vitro. Acta
Physiol (Oxf). 196:419–425. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Melo MC, Gadelha DN, Oliveira TK and
Brandt CT: Alcohol extract of Schinu sterebinthifolius raddi
(anacardiaceae) as a local antimicrobial agent in severe
autogenously fecal peritonitis in rats. Acta Cir Bras. 29(Suppl 1):
52–56. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Munafó DB and Colombo MI: A novel assay to
study autophagy: Regulation of autophagosome vacuole size by amino
acid deprivation. J Cell Sci. 114:3619–36291. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hung SY, Huang WP, Liou HC and Fu WM:
Autophagy protects neuron from Abeta-induced cytotoxicity.
Autophagy. 5:502–510. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cai Z, Yan LJ, Li K, Quazi SH and Zhao B:
Roles of AMP-activated protein kinase in Alzheimer’s disease.
Neuromolecular Med. 14:1–14. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Arbel M and Solomon B: Immunotherapy for
Alzheimer’s disease: Attacking amyloid beta from the inside. Trends
Immunol. 28:511–513. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jeon S, Bose S, Hur J, Jun K, Kim YK, Cho
KS and Koo BS: A modified formulation of Chinese traditional
medicine improves memory impairment and reduces Aβ level in the
Tg-APPswe/PS1dE9 mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J
Ethnopharmacol. 137:783–789. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lai AY and McLaurin J: Inhibition of
amyloid-beta peptide aggregation rescues the autophagic deficits in
the TgCRND8 mouse model of Alzheimer disease. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1822:1629–1637. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Eisenberg D and Jucker M: The amyloid
state of proteins in human diseases. Cell. 148:1188–1203. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gao J, Inagaki Y, Li X, Kokudo N and Tang
W: Research progress on natural products from traditional Chinese
medicine in treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Drug Discov Ther.
7:46–57. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Meraz-Ríos MA, Toral-Rios D,
Franco-Bocanegra D, Villeda-Hernández J and Campos-Peña V:
Inflammatory process in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front Integr Neurosci.
7:592013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Cuchillo-Ibáñez I, Balmaceda V,
Botella-López A, Rabano A, Avila J and Sáez-Valero J: Beta-amyloid
impairs reelin signaling. PLoS One. 8:e722972013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tokutake T, Kasuga K, Yajima R, Sekine Y,
Tezuka T, Nishizawa M and Ikeuchi T: Hyperphosphorylation of Tau
induced by naturally secreted amyloid-β at nanomolar concentrations
is modulated by insulin-dependent Akt-GSK3β signaling pathway. J
Biol Chem. 287:35222–35233. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Spilman P, Podlutskaya N, Hart MJ, Debnath
J, Gorostiza O, Bredesen D, Richardson A, Strong R and Galvan V:
Inhibition of mTOR by rapamycin abolishes cognitive deficits and
reduces amyloid-beta levels in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s
disease. PLoS One. 5:e99792010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Lafay-Chebassier C, Paccalin M, Page G,
Barc-Pain S, Perault-Pochat MC, Gil R, Pradier L and Hugon J:
mTOR/p70S6k signalling alteration by Ab exposure as well as in
APP-PS1 transgenic models and in patients with Alzheimer’s disease.
J Neurochem. 94:215–225. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lee JW, Park S, Takahashi Y and Wang HG:
The association of AMPK with ULK1 regulates autophagy. PLoS One.
5:e153942010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|