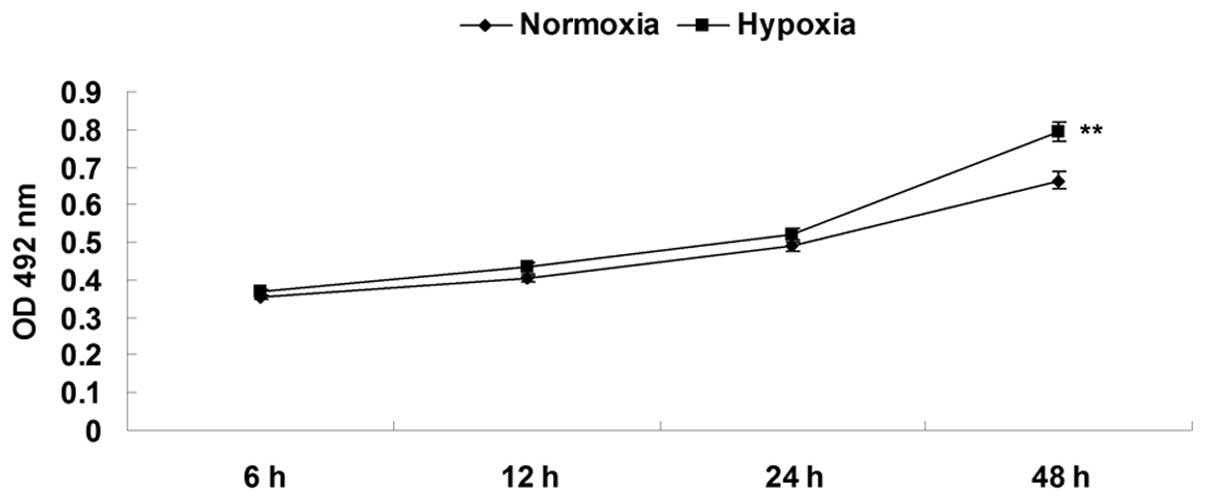
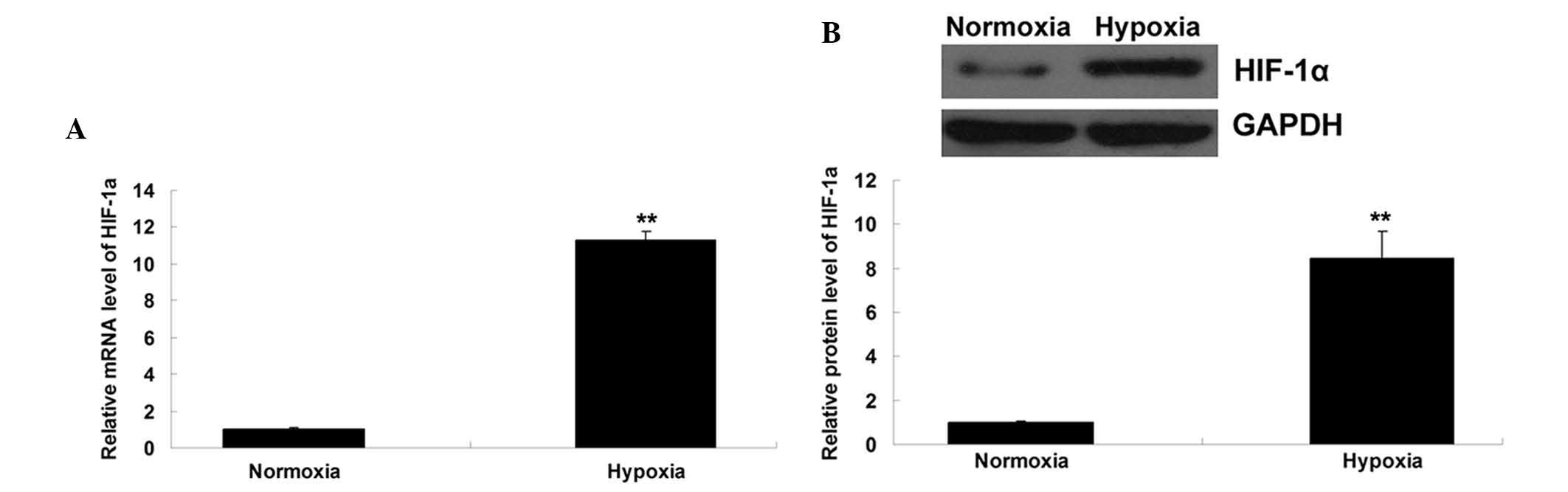
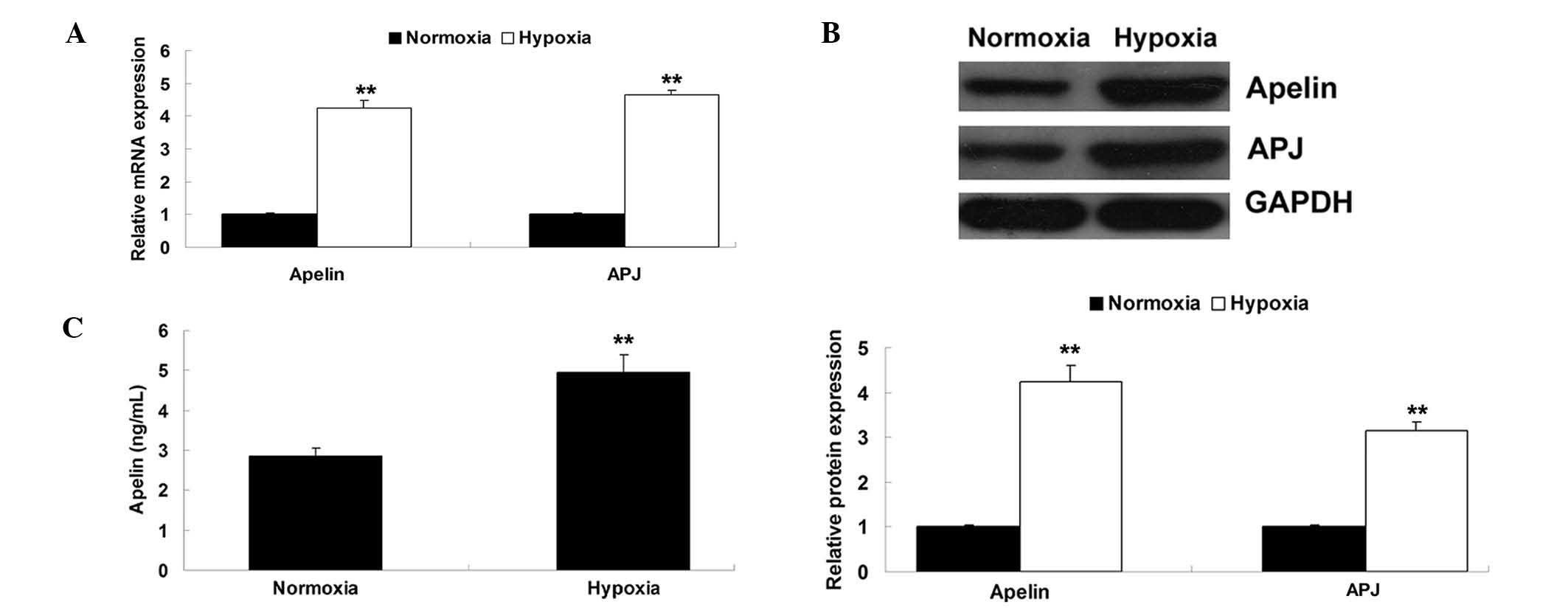
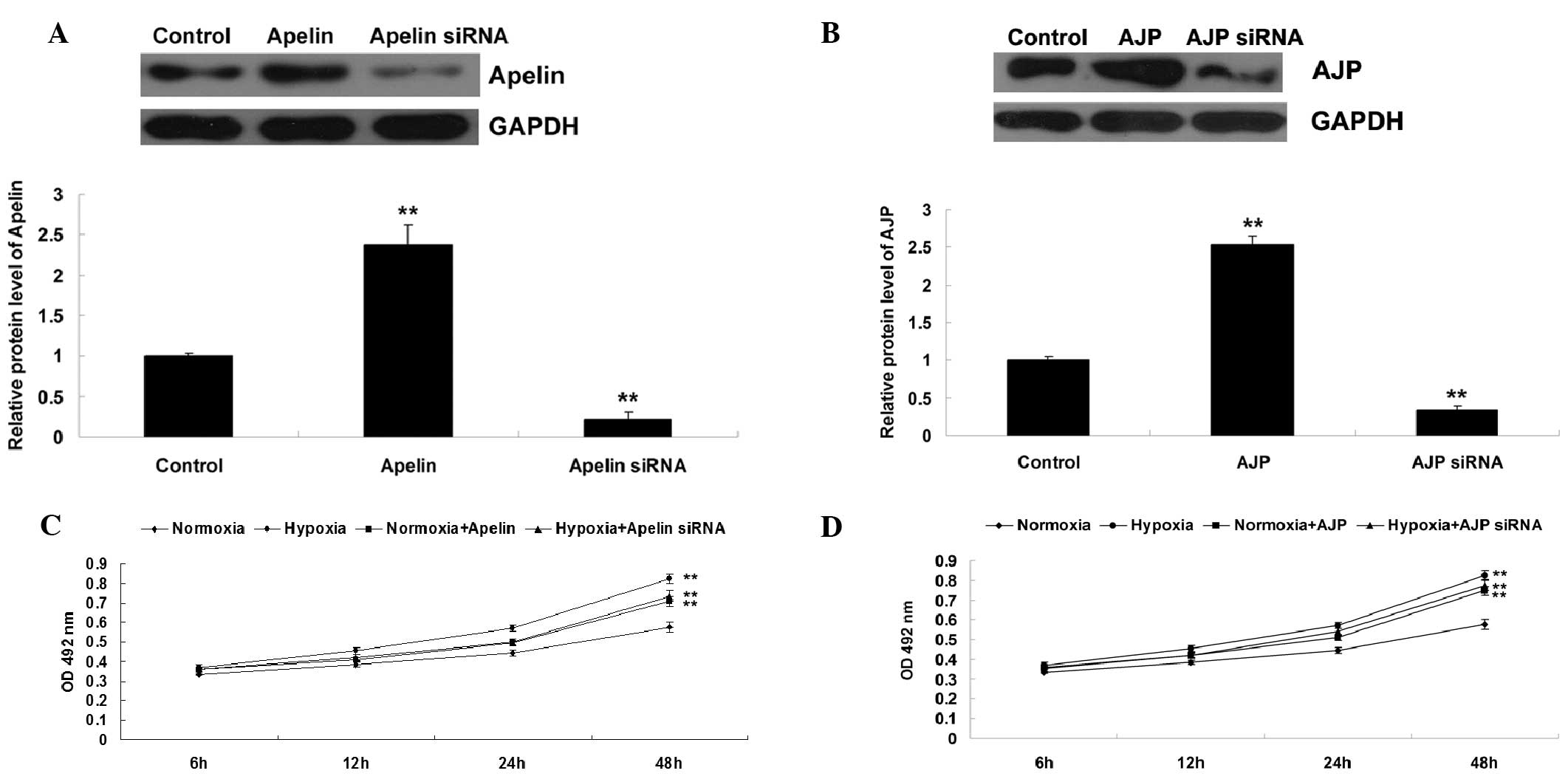
|
1
|
Ganguly R, Lytwyn MS and Pierce GN:
Differential effects of trans and polyunsaturated fatty acids on
ischemia/reperfusion injury and its associated cardiovascular
disease states. Curr Pharm Des. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Kalogeris T, Baines CP, Krenz M and
Korthuis RJ: Cell biology of ischemia/reperfusion injury. Int Rev
Cell Mol Biol. 298:229–317. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Schröder K, Kohnen A, Aicher A, et al:
NADPH oxidase Nox2 is required for hypoxia-induced mobilization of
endothelial progenitor cells. Circ Res. 105:537–544. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Simons D, Grieb G, Hristov M, et al:
Hypoxia-induced endothelial secretion of macrophage migration
inhibitory factor and role in endothelial progenitor cell
recruitment. J Cell Mol Med. 15:668–678. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Lee SH, Lee JH, Yoo SY, Hur J, Kim HS and
Kwon SM: Hypoxia inhibits cellular senescence to restore the
therapeutic potential of old human endothelial progenitor cells via
the hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha-TWIST-p21 axis. Arterioscler
Thromb Vasc Biol. 33:2407–2414. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dai T, Zheng H and Fu GS: Hypoxia confers
protection against apoptosis via the PI3K/Akt pathway in
endothelial progenitor cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 29:1425–1431.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhu G, Tang Y, Geng N, et al:
HIF-alpha/MIF and NF-kappaB/IL-6 axes contribute to the recruitment
of CD11b+Gr-1+ myeloid cells in hypoxic microenvironment of HNSCC.
Neoplasia. 16:168–179. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jiang M, Wang CQ, Wang BY and Huang DJ:
Inhibitory effect of siRNA targeting HIF-1alpha on differentiation
of peripheral blood endothelial progenitor cells. Ai Zheng.
24:1293–1300. 2005.In Chinese.
|
|
9
|
Hashimoto T, Kihara M, Imai N, et al:
Requirement of apelin-apelin receptor system for oxidative
stress-linked atherosclerosis. Am J Pathol. 171:1705–1712. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bertrand C, Pignalosa A, Wanecq E, et al:
Effects of dietary eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) supplementation in
high-fat fed mice on lipid metabolism and apelin/APJ system in
skeletal muscle. PLoS One. 8:e788742013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
O'Carroll AM, Lolait SJ, Harris LE and
Pope GR: The apelin receptor APJ: journey from an orphan to a
multifaceted regulator of homeostasis. J Endocrinol. 219:R13–R35.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ye J, Ni P, Kang L and Xu B: Apelin and
vascular endothelial growth factor are associated with mobilization
of endothelial progenitor cells after acute myocardial infarction.
J Biomed Res. 26:400–409. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Wang W, McKinnie SM, Patel VB, et al: Loss
of Apelin exacerbates myocardial infarction adverse remodeling and
ischemia-reperfusion injury: therapeutic potential of synthetic
Apelin analogues. J Am Heart Assoc. 2:e0002492013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Machalińska A: The role of circulating
endothelial progenitor cells in the development of vascular retinal
diseases. Klin Oczna. 115:158–162. 2013.In Polish.
|
|
15
|
Jiang M, Wang B, Wang C, et al: Inhibition
of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and endothelial progenitor cell
differentiation by adenoviral transfer of small interfering RNA in
vitro. J Vasc Res. 43:511–521. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Jiang M, Wang CQ, Wang BY, He B, Shao Q
and Huang DJ: Overexpression of hypoxia inducible factor-1α
(HIF-1α) promotes the differentiation of endothelial progenitor
cell ex vivo. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 14:565–570.
2006.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ronkainen VP, Ronkainen JJ, Hänninen SL,
et al: Hypoxia inducible factor regulates the cardiac expression
and secretion of apelin. FASEB J. 21:1821–1830. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Glassford AJ, Yue P, Sheikh AY, et al:
HIF-1 regulates hypoxia- and insulin-induced expression of apelin
in adipocytes. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 293:E1590–E1596.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lv D, Li H and Chen L: Apelin and APJ, a
novel critical factor and therapeutic target for atherosclerosis.
Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 45:527–533. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Kasai A, Ishimaru Y, Higashino K, et al:
Inhibition of apelin expression switches endothelial cells from
proliferative to mature state in pathological retinal angiogenesis.
Angiogenesis. 16:723–734. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li L, Zeng H and Chen JX: Apelin-13
increases myocardial progenitor cells and improves repair
postmyocardial infarction. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
303:H605–H618. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kleinz MJ and Baxter GF: Apelin reduces
myocardial reperfusion injury independently of PI3K/Akt and P70S6
kinase. Regul Pept. 146:271–277. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Tao J, Zhu W, Li Y, et al: Apelin-13
protects the heart against ischemia-reperfusion injury through
inhibition of ER-dependent apoptotic pathways in a time-dependent
fashion. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 301:H1471–H1486. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang Z, Yu B and Tao GZ: Apelin protects
against cardiomyocyte apoptosis induced by glucose deprivation.
Chin Med J (Engl). 122:2360–2365. 2009.
|
|
25
|
Liu C, Su T, Li F, et al: PI3K/Akt
signaling transduction pathway is involved in rat vascular smooth
muscle cell proliferation induced by apelin-13. Acta Biochim
Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 42:396–402. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|