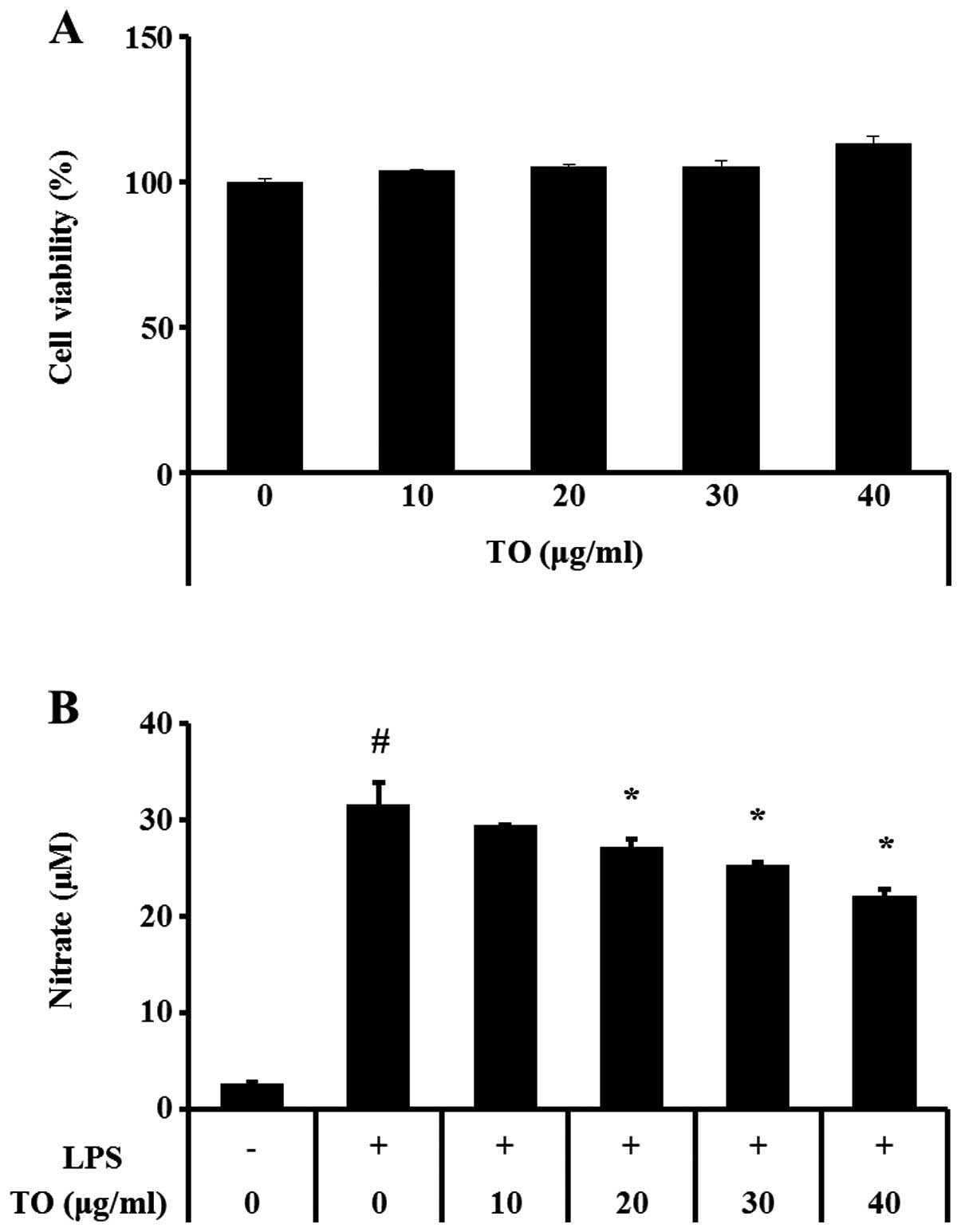
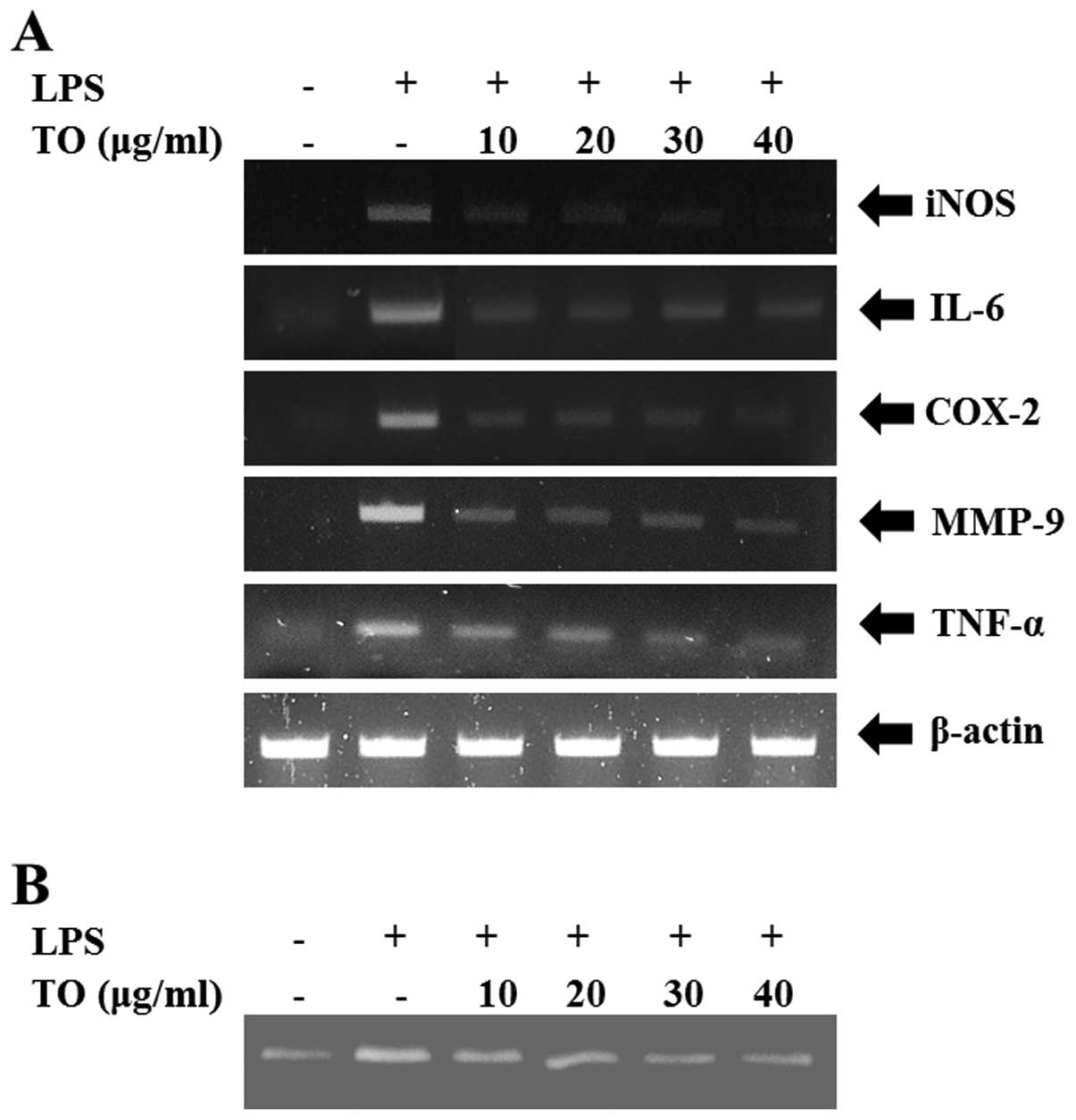
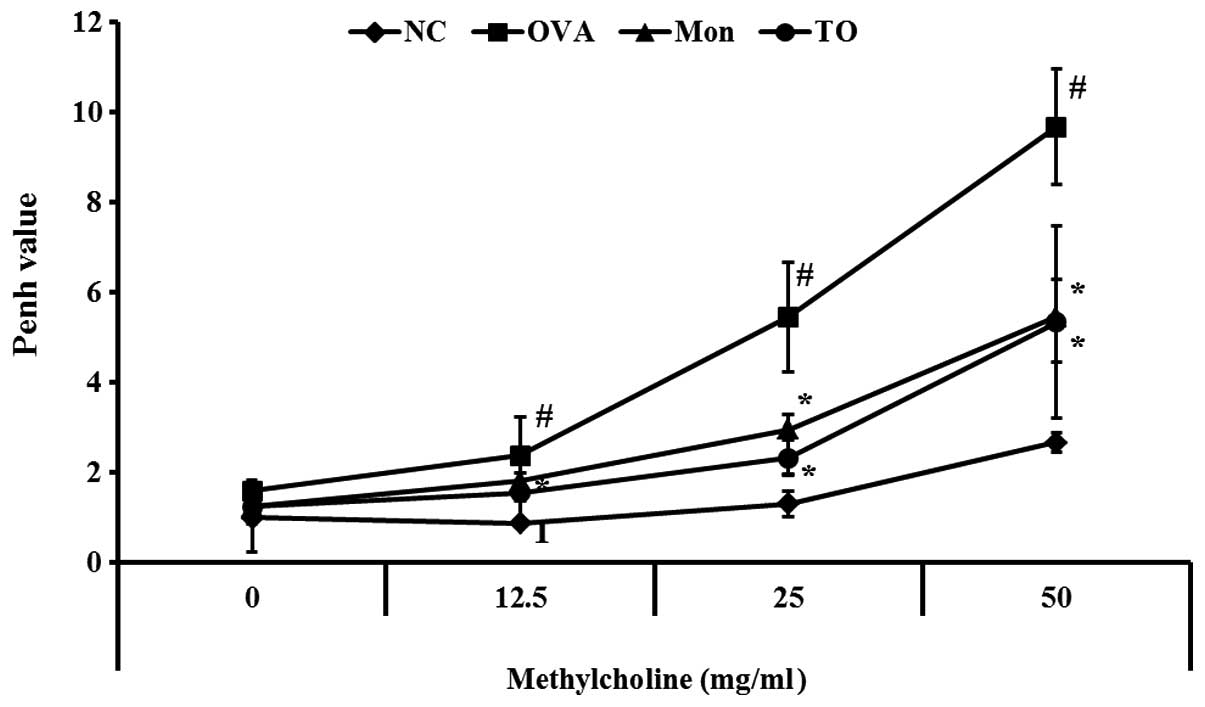
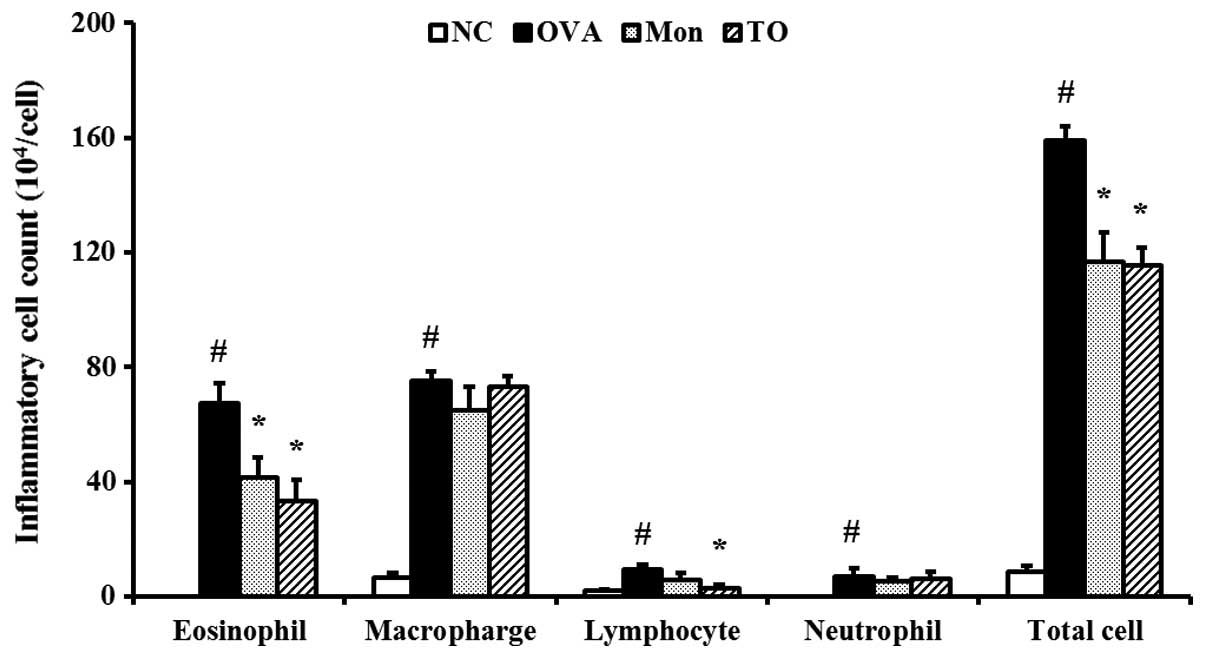
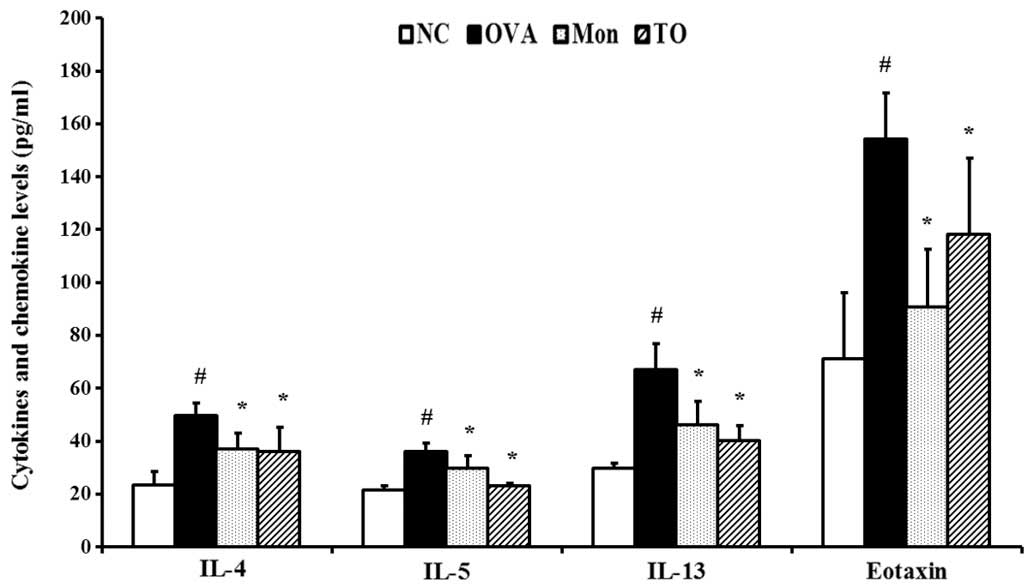
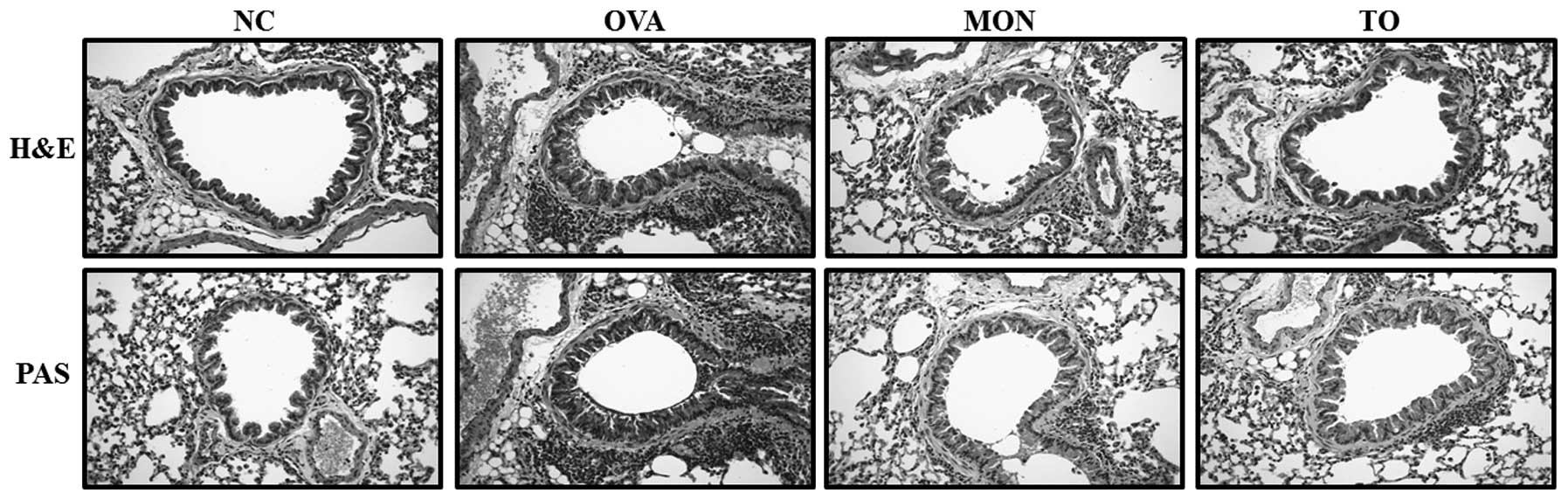
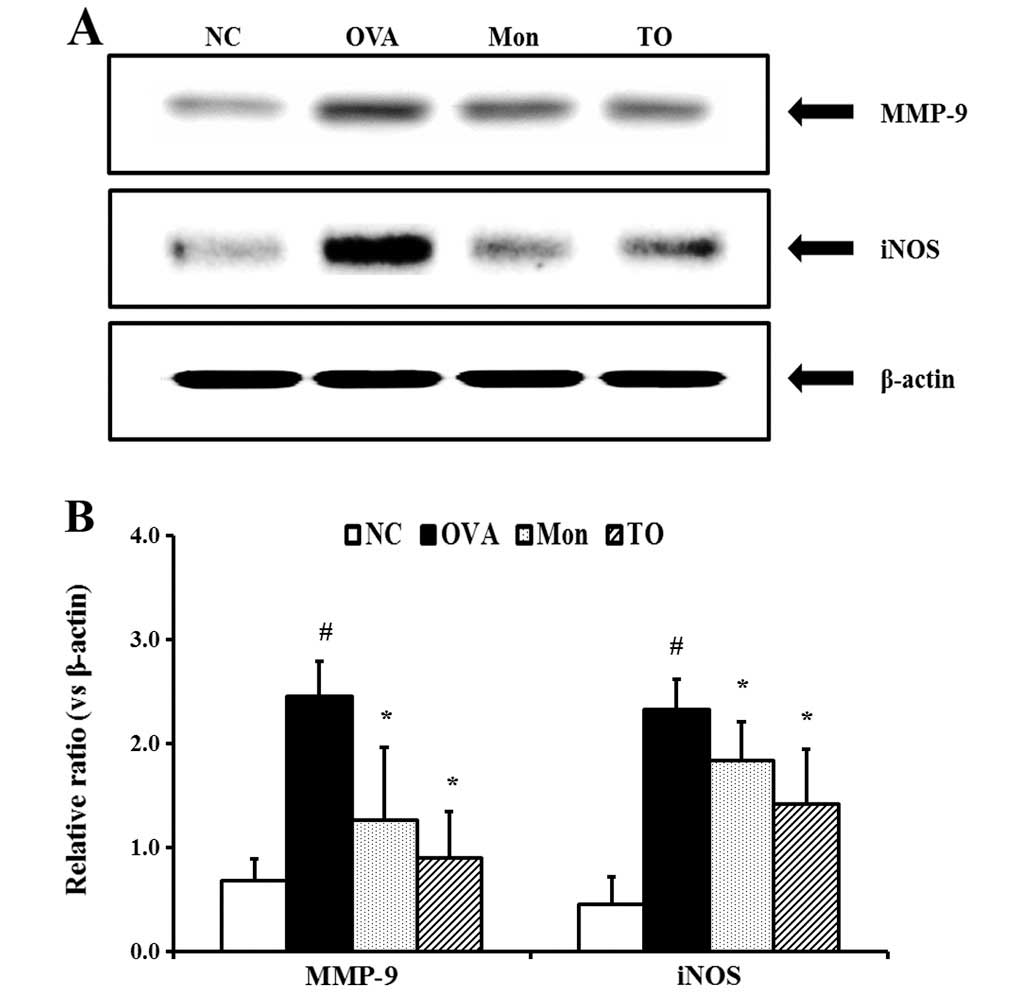
|
1
|
Lee MY, Seo CS, Lee JA, et al:
Anti-asthmatic effects of Angelica dahurica against
ovalbumin-induced airway inflammation via upregulation of heme
oxygenase-1. Food Chem Toxicol. 49:829–837. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Gueders MM, Bertholet P, Perin F, et al: A
novel formulation of inhaled doxycycline reduces allergen-induced
inflammation, hyperresponsiveness and remodeling by matrix
metalloproteinases and cytokines modulation in a mouse model of
asthma. Biochem Pharmacol. 75:514–526. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Holgate ST: The airway epithelium is
central to the pathogenesis of asthma. Allergol Int. 57:1–10. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhou DY, Du Q, Li RR, Huang M, Zhang Q and
Wei GZ: Grape seed proanthocyanidin extract attenuates airway
inflammation and hyper-responsiveness in a murine model of asthma
by downregulating inducible nitric oxide synthase. Planta Med.
77:1575–1581. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ricciardolo FL, Sterk PJ, Gaston B and
Folkerts G: Nitric oxide in health and disease of the respiratory
system. Physiol Rev. 84:731–765. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Islam T, Breton C, Salam MT, et al: Role
of inducible nitric oxide synthase in asthma risk and lung function
growth during adolescence. Thorax. 65:139–145. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Prado CM, Leick-Maldonado EA, Yano L, et
al: Effects of nitric oxide synthases in chronic allergic airway
inflammation and remodeling. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 35:457–465.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jung SH, Kim BJ, Lee EH and Osborne NN:
Isoquercitrin is the most effective antioxidant in the plant Thuja
orientalis and able to counteract oxidative-induced damage to a
transformed cell line (RGC-5 cells). Neurochem Int. 57:713–721.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lee YJ, Hwang SM, Yoon JJ, et al:
Inhibitory effect of Thuja orientalis on TNF-α-induced vascular
inflammation. Phytother Res. 24:1489–1495. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chae HS and Chin YW: Anti-allergic effects
of lambertianic acid from Thuja orientalis in mouse bone
marrow-derived mast cells. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol.
34:250–255. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Won JN, Lee SY, Song DS and Poo H:
Antiviral activity of the plant extracts from Thuja orientalis,
Aster spathulifolius, and Pinus thunbergii against influenza virus
A/PR/8/34. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 23:125–130. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xu GH, Ryoo IJ, Kim YH, Choo SJ and Yoo
ID: Free radical scavenging and antielastase activities of
flavonoids from the fruits of Thuja orientalis. Arch Pharm Res.
32:275–282. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jung HW, Kang SY, Park KH, et al: Effect
of the semen extract of Thuja orientalis on inflammatory responses
in transient focal cerebral ischemia rat model and LPS-stimulated
BV-2 microglia. Am J Chin Med. 41:99–117. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kim TH, Li H, Wu Q, Lee HJ and Ryu JH: A
new labdane diter-penoide with anti-inflammatory activity from
Thuja orientalis. J Ethnopharmacol. 146:760–767. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Heussen C and Dowdel EB: Electrophoretic
analysis of plasminogen activators in polyacrylamide gels
containing sodium dodecyl sulfate and copolymerized substrate. Anal
Biochem. 102:196–202. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Uhm TG, Kim BS and Chung IY: Eosinophil
development, regulation of eosinophil-specific genes, and role of
eosinophils in the pathogenesis of asthma. Allergy Asthma Immunol
Res. 4:68–79. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pope SM, Brandt EB, Mishra A, et al: IL-13
induces eosinophil recruitment into the lung by an IL-5- and
eotaxin-dependent mechanism. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 108:594–601.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Pope SM, Zimmermann N, Stringer KF, Karow
ML and Rothenberg ME: The eotaxin chemokines and CCR3 are
fundamental regulators of allergen-induced pulmonary eosinophilia.
J Immuno. 175:5341–5350. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Mould AW, Ramsay AJ, Matthaei KI, Young
IG, Rothernberg ME and Foster PS: The effects of IL-5 and eotaxin
expression in the lung on eosinophil trafficking and degranulation
and the induction of bronchial hyperreactivity. J Immunol.
164:2142–2150. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pease JE and Williams TJ: Chemokines and
their receptors in allergic disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
118:305–318. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hesslinger C, Strub A, Boer R, Ulrich WR,
Lehner MD and Braun C: Inhibition of inducible nitric oxide
synthase in respiratory diseases. Biochem Soc Trans. 37:886–891.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Starling CM, Prado CM, Leick-Maldonado EA,
et al: Inducible nitric oxide synthase inhibition attenuates lung
tissue responsiveness and remodeling in a model of chronic
pulmonary inflammation in guinea pigs. Respir Physiol Neurobiol.
165:185–194. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Prado CM, Yano L, Rocha G, et al: Effects
of inducible nitric oxide synthase inhibition in bronchial vascular
remodeling-induced by chronic allergic pulmonary inflammation. Exp
Lung Res. 37:259–268. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Vermaelen KY, Cataldo D, Tournoy K, et al:
Matrix metallopro-teinase-9-mediated dendritic cell recruitment
into the airways is a critical step in a mouse model of asthma. J
Immunol. 171:1016–1022. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
McMillan SJ, Kearley J, Campbell JD, et
al: Matrix metallopro-teinase-9 deficiency results in enhanced
allergen-induced airway inflammation. J Immunol. 172:2586–2594.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|