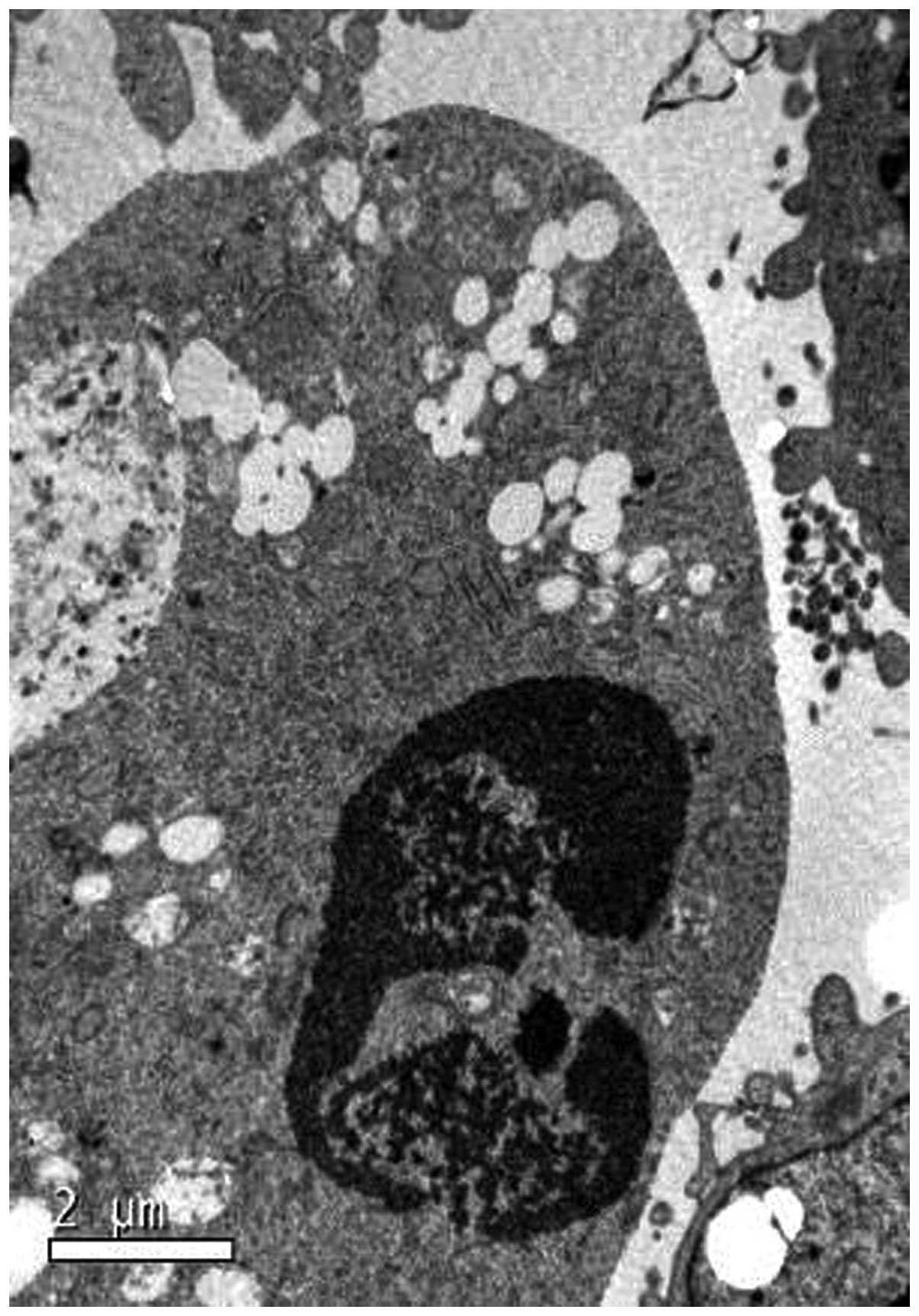
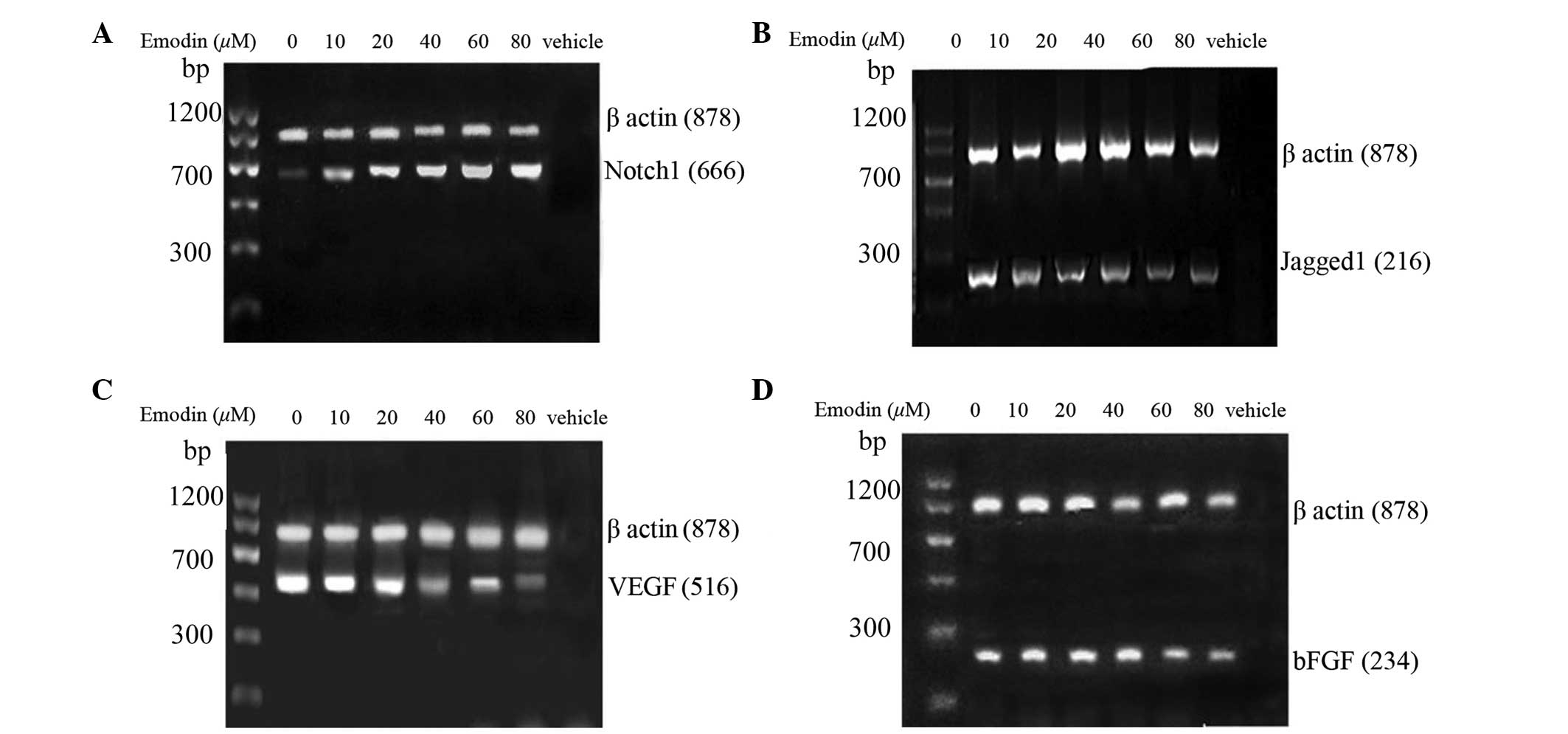
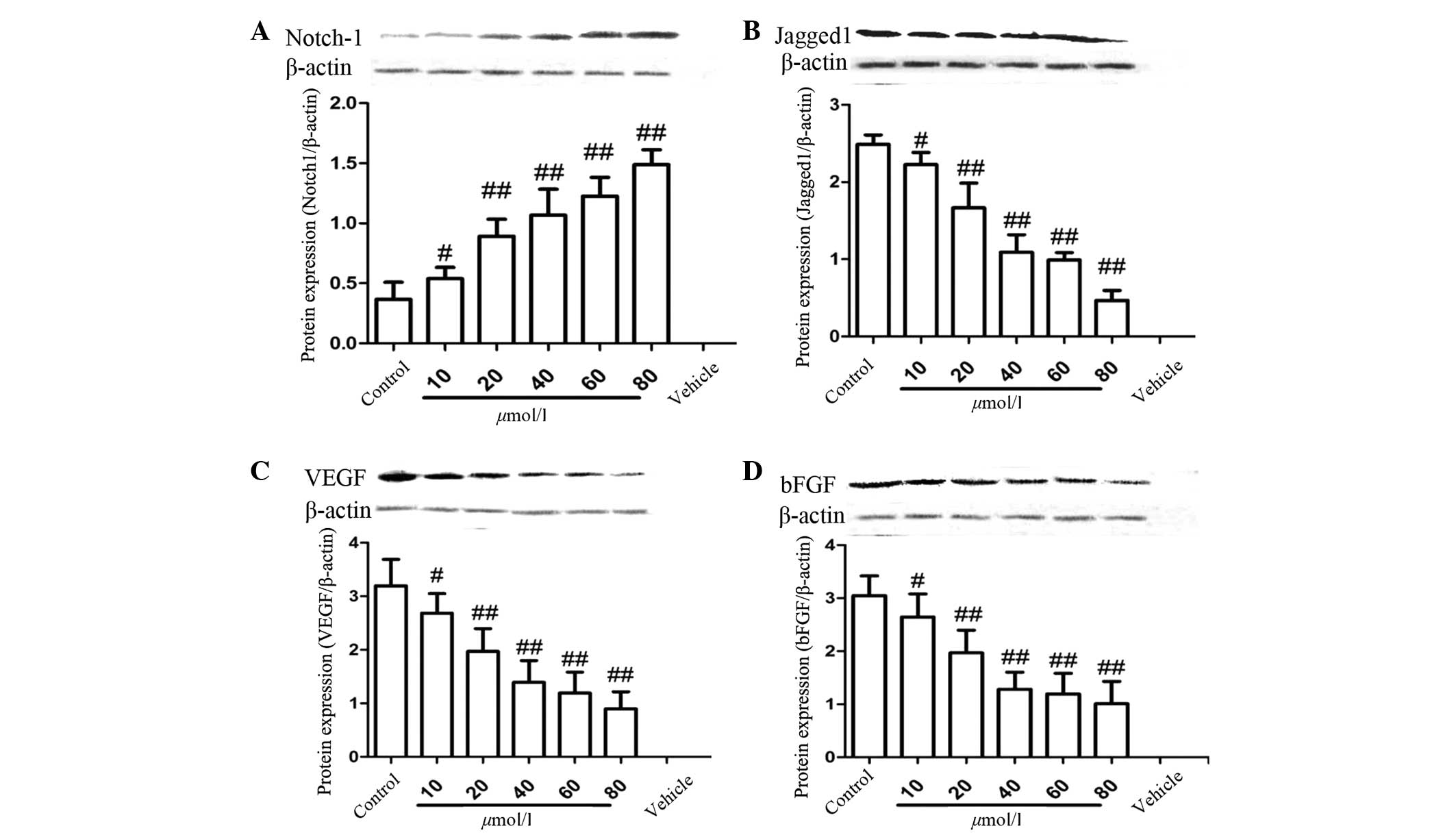
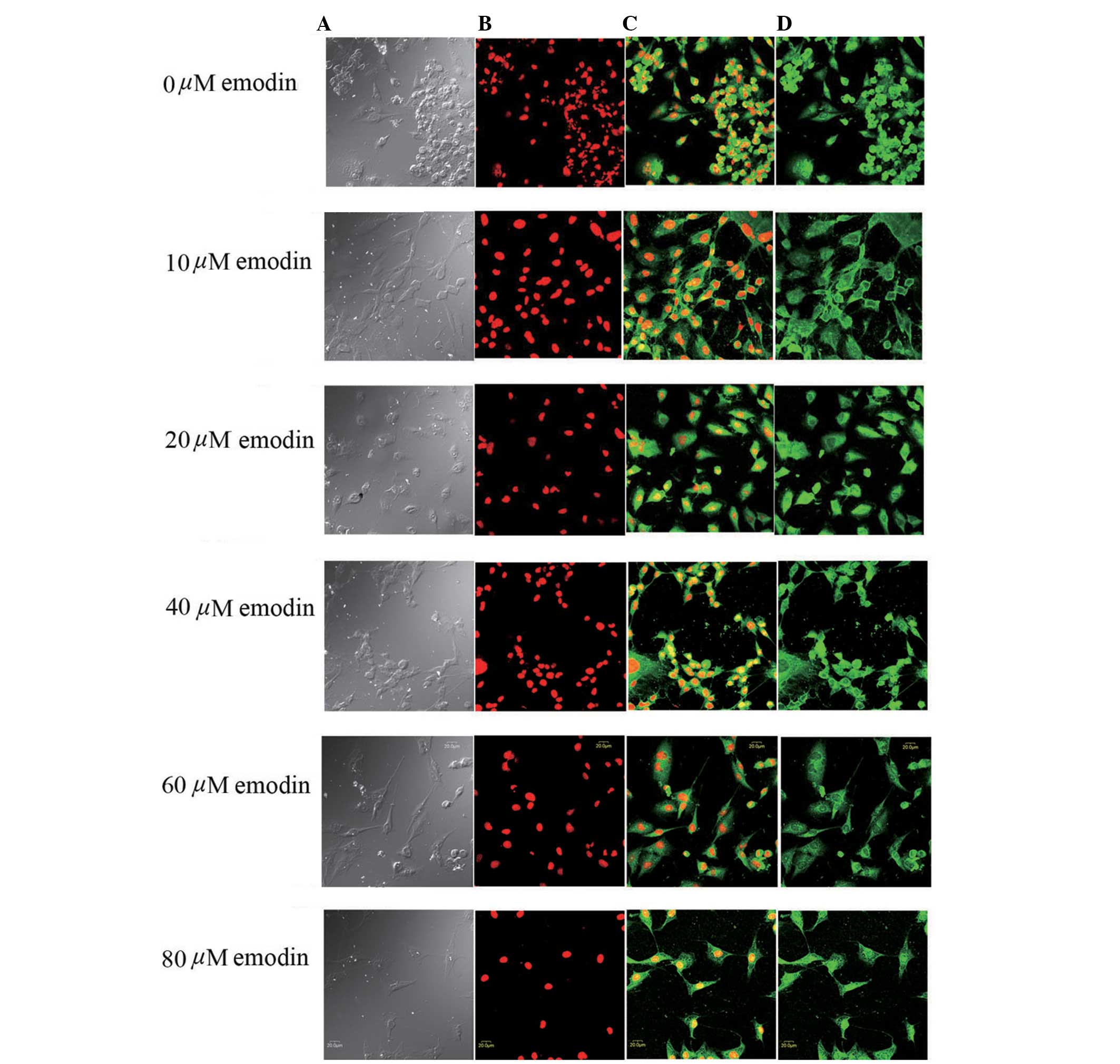
|
1
|
McDonnell TJ, Troncoso P, Brisbay SM,
Logothetis C, Chung LW, Hsieh JT, Tu SM and Campbell ML: Expression
of the protooncogene bcl-2 in the prostate and its association with
emergence of androgen-independent prostate cancer. Cancer Res.
52:6940–6944. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 63:11–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Petrylak DP: Chemotherapy for advanced
hormone refractory prostate cancer. Urology. 54(Suppl): 30–35.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pisters LL: The challenge of locally
advanced prostate cancer. Semin Oncol. 26:202–216. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Richie JP: Anti-androgens and other
hormonal therapies for prostate cancer. Urology. 54(Suppl): 15–18.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yu CX, Zhang XQ, Kang LD, Zhang PJ, Chen
WW, Liu WW, Liu QW and Zhang JY: Emodin induces apoptosis in human
prostate cancer cell LNCaP. Asian J Androl. 10:625–634. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cragg GM and Newman DJ: Plants as a source
of anti-cancer agents. J Ethnopharmacol. 100:72–79. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lin SZ, Wei WT, Chen H, Chen KJ, Tong HF,
Wang ZH, Ni ZL, Liu HB, Guo HC and Liu DL: Antitumor activity of
emodin against pancreatic cancer depends on its dual role:
Promotion of apoptosis and suppression of angiogenesis. PLoS One.
7:e421462012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Su YT, Chang HL, Shyue SK and Hsu SL:
Emodin induces apoptosis in human lung adenocarcinoma cells through
a reactive oxygen species-dependent mitochondrial signaling
pathway. Biochem Pharmacol. 70:229–241. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen YC, Shen SC, Lee WR, Hsu FL, Lin HY,
Ko CH and Tseng SW: Emodin induces apoptosis in human
promyeloleukemic HL-60 cells accompanied by activation of caspase 3
cascade but independent of reactive oxygen species production.
Biochem Pharmacol. 64:1713–1724. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Damodharan U, Ganesan R and Radhakrishnan
UC: Expression of MMP2 and MMP9 (gelatinases A and B) in human
colon cancer cells. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 165:1245–1252. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Guo HC, Bu HQ, Luo J, Wei WT, Liu DL, Chen
H, Tong HF, Wang ZH, Wu HY, Li HH, et al: Emodin potentiates the
antitumor effects of gemcitabine in PANC-1 pancreatic cancer
xenograft model in vivo via inhibition of inhibitors of apoptosis.
Int J Oncol. 40:1849–1857. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cha TL, Qiu L, Chen CT, Wen Y and Hung MC:
Emodin down-regulates androgen receptor and inhibits prostate
cancer cell growth. Cancer Res. 65:2287–2295. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shou J, Ross S, Koeppen H, de Sauvage FJ
and Gao WQ: Dynamics of notch expression during murine prostate
development and tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 61:7291–7297.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Carvalho FL, Simons BW, Eberhart CG and
Berman DM: Notch signaling in prostate cancer: A moving target.
Prostate. 74:933–945. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhao Y, Yang LF, Ye M, Gu HH and Cao Y:
Induction of apoptosis by epigallocatechin-3-gallate via
mitochondrial signal transduction pathway. Prev Med. 39:1172–1179.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Schreiber E, Harshman K, Kemler I,
Malipiero U, Schaffner W and Fontana A: Astrocytes and glioblastoma
cells express novel octamer-DNA binding proteins distinct from the
ubiquitous Oct-1 and B cell type Oct-2 proteins. Nucleic Acids Res.
18:5495–5503. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Weijzen S, Rizzo P, Braid M, Vaishnav R,
Jonkheer SM, Zlobin A, Osborne BA, Gottipati S, Aster JC, Hahn WC,
et al: Activation of Notch-1 signaling maintains the neoplastic
phenotype in human Ras-transformed cells. Nat Med. 8:979–986. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tsai T and Chen C: Ultraviolet spectrum
identification of emodin in rabbit plasma by HPLC and its
pharmacokinetics application. Asia Pac J Pharmacol. 1:53–56.
1992.
|
|
20
|
Koyama M, Kelly TR and Watanabe KA: Novel
type of potential anticancer agents derived from chrysophanol and
emodin. Some structure-activity relationship studies. J Med Chem.
31:283–284. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Huang HC, Chu SH and Chao PD:
Vasorelaxants from Chinese herbs, emodin and scoparone, possess
immunosuppressive properties. Eur J Pharmacol. 198:211–213. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhou XM and Chen QH: Biochemical study of
Chinese rhubarb. XXII. Inhibitory effect of anthraquinone
derivatives on Na+-K+-ATPase of the rabbit renal medulla and their
diuretic action. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 23:17–20. 1988.In Chinese.
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lee HZ: Effects and mechanisms of emodin
on cell death in human lung squamous cell carcinoma. Br J
Pharmacol. 134:11–20. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jing X, Ueki N, Cheng J, Imanishi H and
Hada T: Induction of apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cell
lines by emodin. Jpn J Cancer Res. 93:874–882. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Shieh DE, Chen YY, Yen MH, Chiang LC and
Lin CC: Emodin-induced apoptosis through p53-dependent pathway in
human hepatoma cells. Life Sci. 74:2279–2290. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Huang XZ, Wang J, Huang C, Chen YY, Shi
GY, Hu QS and Yi J: Emodin enhances cytotoxicity of
chemotherapeutic drugs in prostate cancer cells: The mechanisms
involve ROS-mediated suppression of multidrug resistance and
hypoxia inducible factor-1. Cancer Biol Ther. 7:468–475. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kwak HJ, Park MJ, Park CM, Moon SI, Yoo
DH, Lee HC, Lee SH, Kim MS, Lee HW, Shin WS, et al: Emodin inhibits
vascular endothelial growth factor-A-induced angiogenesis by
blocking receptor-2 (KDR/Flk-1) phosphorylation. Int J Cancer.
118:2711–2720. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhou ZD, Kumari U, Xiao ZC and Tan EK:
Notch as a molecular switch in neural stem cells. IUBMB Life.
62:618–623. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lai EC: Notch signaling: Control of cell
communication and cell fate. Development. 131:965–973. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ang HL and Tergaonkar V: Notch and
NFkappaB signaling pathways: Do they collaborate in normal
vertebrate brain development and function? BioEssays. 29:1039–1047.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chau MD, Tuft R, Fogarty K and Bao ZZ:
Notch signaling plays a key role in cardiac cell differentiation.
Mech Dev. 123:626–640. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang XD, Leow CC, Zha J, Tang Z, Modrusan
Z, Radtke F, Aguet M, de Sauvage FJ and Gao WQ: Notch signaling is
required for normal prostatic epithelial cell proliferation and
differentiation. Dev Biol. 290:66–80. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Yao J, Duan L, Fan M, Yuan J and Wu X:
Notch1 induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human cervical
cancer cells: Involvement of nuclear factor kappa B inhibition. Int
J Gynecol Cancer. 17:502–510. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Seghezzi G, Patel S, Ren CJ, Gualandris A,
Pintucci G, Robbins ES, Shapiro RL, Galloway AC, Rifkin DB and
Mignatti P: Fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF-2) induces vascular
endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression in the endothelial
cells of forming capillaries: An autocrine mechanism contributing
to angiogenesis. J Cell Biol. 141:1659–1673. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Siekmann AF, Covassin L and Lawson ND:
Modulation of VEGF signalling output by the Notch pathway.
BioEssays. 30:303–313. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|