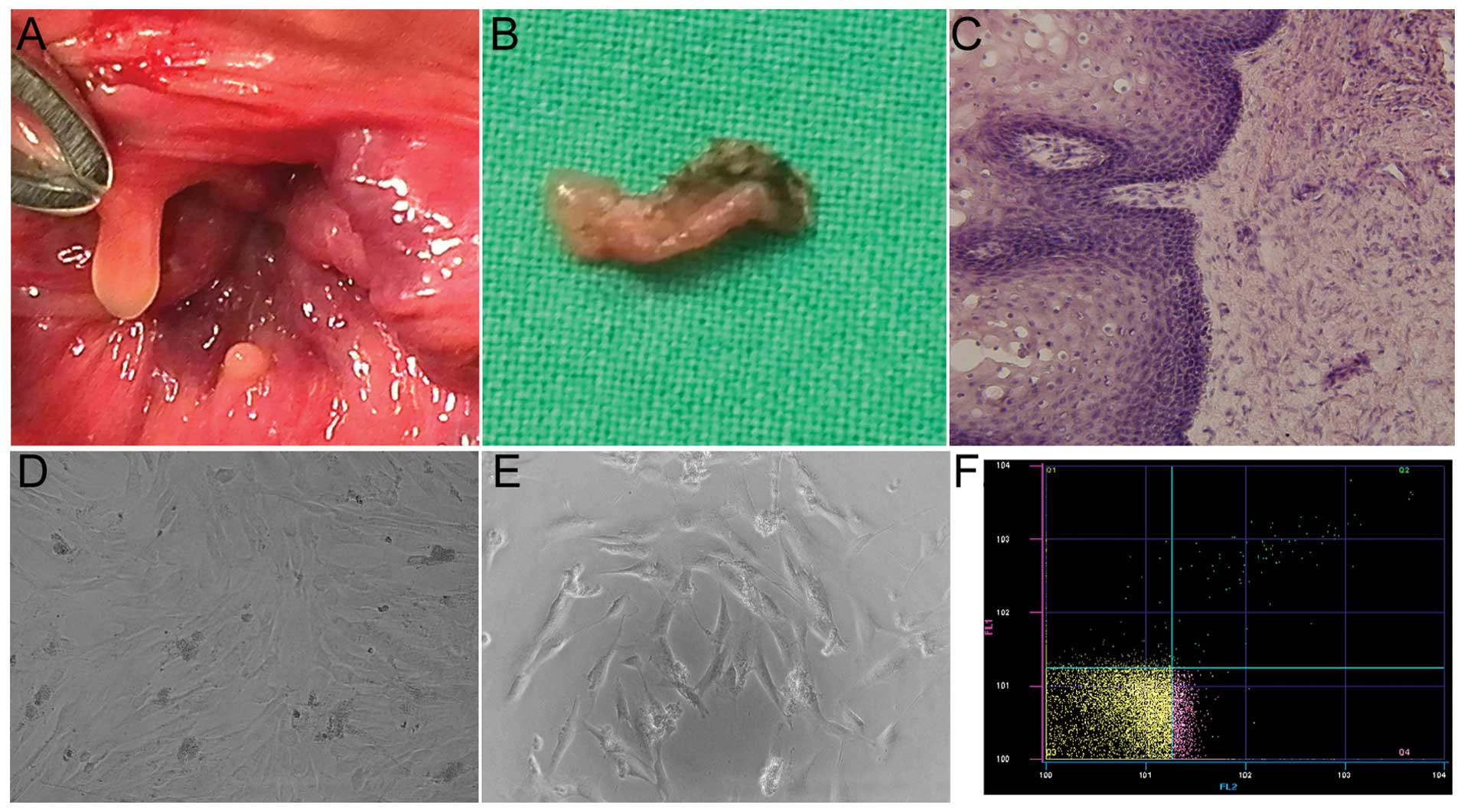
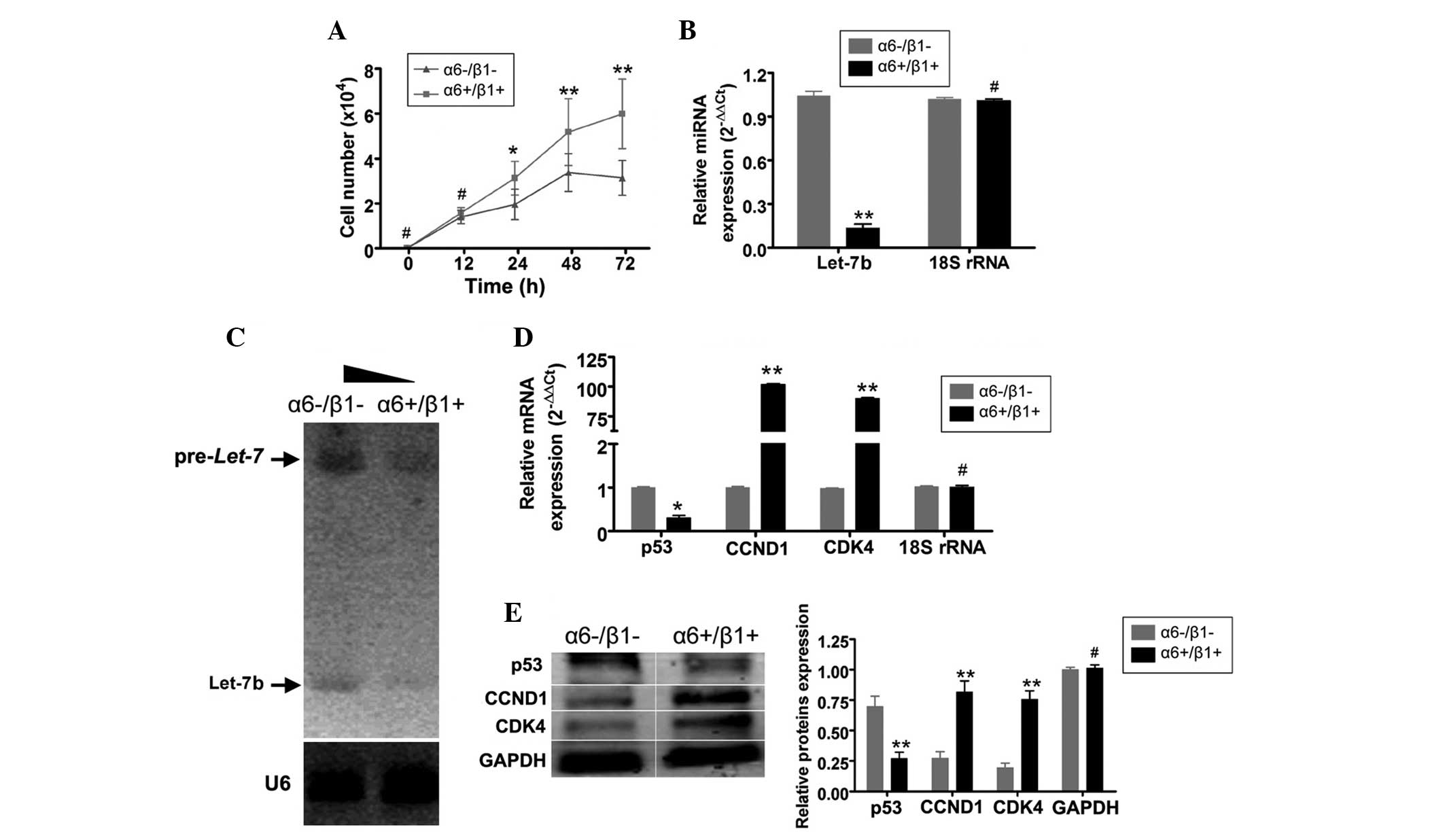
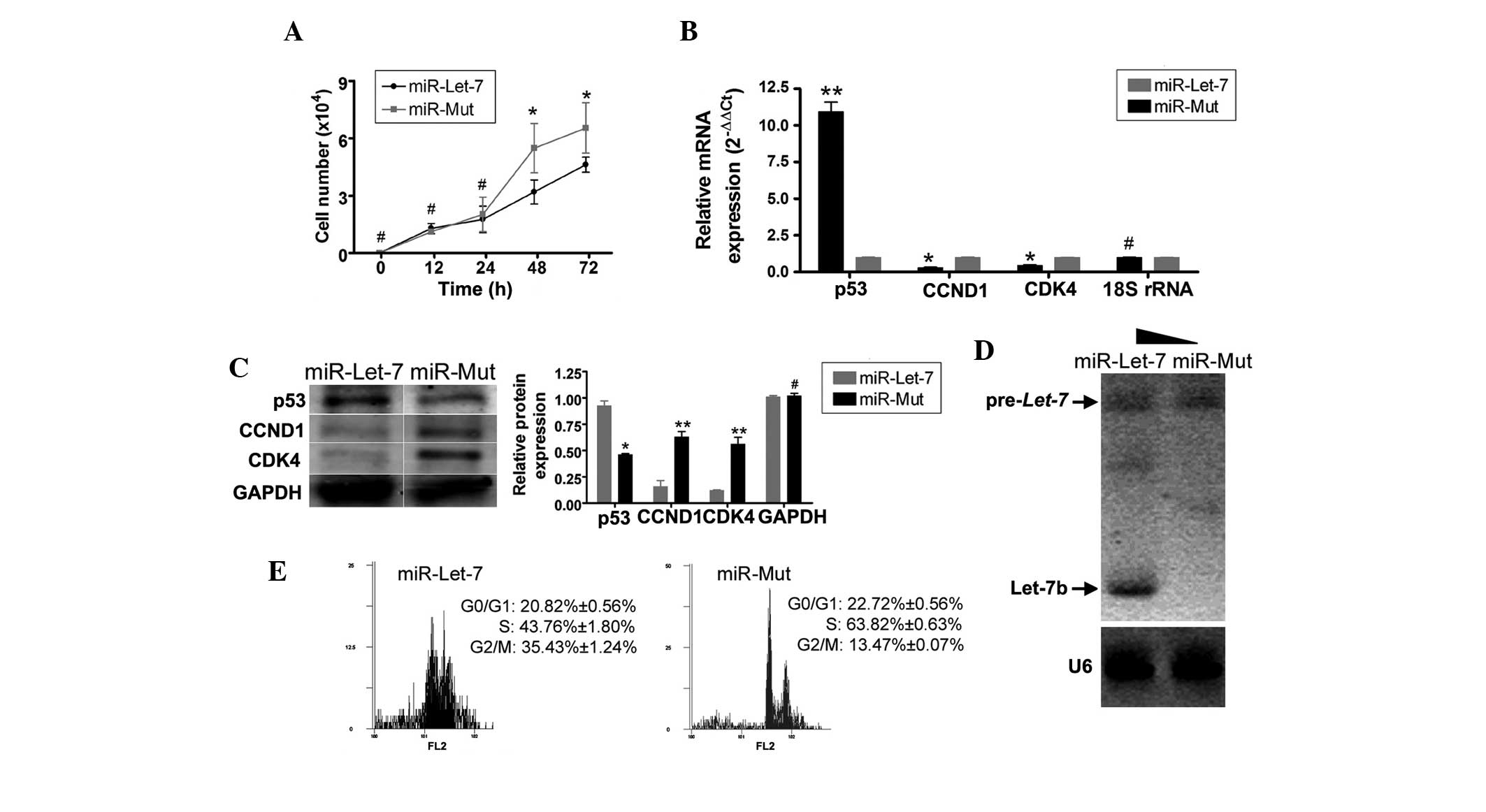
|
1
|
Gupta PJ: Hypertrophied anal papillae and
fibrous anal polyps, should they be removed during anal fissure
surgery? World J Gastroenterol. 10:2412–2414. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gupta PJ and Kalaskar S: Removal of
hypertrophied anal papillae and fibrous anal polyps increases
patient satisfaction after anal fissure surgery. Tech Coloproctol.
7:155–158. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gupta PJ: A study of the symptomatology of
hypertrophied anal papillae and fibrous anal polyps. Bratisl Lek
Listy. 106:30–33. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Reiisi S, Esmaeili F and Shirazi A:
Isolation, culture and identification of epidermal stem cells from
newborn mouse skin. In vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 46:54–59. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Janes SM, Lowell S and Hutter C: Epidermal
stem cells. J Pathol. 197:479–491. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Barthel R and Aberdam D: Epidermal stem
cells. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 19:405–413. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chen S, Takahara M, Kido M, et al:
Increased expression of an epidermal stem cell marker, cytokeratin
19, in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Dermatol.
159:952–955. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Luis NM, Morey L, Mejetta S, et al:
Regulation of human epidermal stem cell proliferation and
senescence requires polycomb-dependent and-independent functions of
Cbx4. Cell Stem Cell. 9:233–246. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Watt FM: Role of integrins in regulating
epidermal adhesion, growth and differentiation. EMBO J.
21:3919–3926. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nanba D, Toki F, Matsushita N, Matsushita
S, Higashiyama S and Barrandon Y: Actin flament dynamics impacts
keratinocyte stem cell maintenance. EMBO Mol Med. 5:640–653. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sumazin P, Yang X, Chiu HS, et al: An
extensive microRNA-mediated network of RNA-RNA interactions
regulates established oncogenic pathways in glioblastoma. Cell.
147:370–381. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Poulton JS, Huang YC, Smith L, et al: The
microRNA pathway regulates the temporal pattern of Notch signaling
in Drosophila follicle cells. Development. 138:1737–1745. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lei P, Li Y, Chen X, Yang S and Zhang J:
Microarray based analysis of microRNA expression in rat cerebral
cortex after traumatic brain injury. Brain Res. 1284:191–201. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yoo AS, Sun AX, Li L, et al:
MicroRNA-mediated conversion of human fibroblasts to neurons.
Nature. 476:228–231. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dai Y, Qiu Z, Diao Z, et al: MicroRNA-155
inhibits proliferation and migration of human extravillous
trophoblast derived HTR-8/SVneo cells via down-regulating cyclin
D1. Placenta. 33:824–829. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu T, Shen D, Xing S, et al: Attenuation
of exogenous angiotensin II stress-induced damage and apoptosis in
human vascular endothelial cells via microRNA-155 expression. Int J
Mol Med. 31:188–196. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
He L and Hannon GJ: MicroRNAs: Small RNAs
with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 5:522–531. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
El Ouaamari A, Baroukh N, Martens GA,
Lebrun P, Pipeleers D and van Obberghen E: miR-375 targets
3′-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 and regulates
glucose-induced biological responses in pancreatic beta-cells.
Diabetes. 57:2708–2717. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu T, Cheng W, Huang Y, Huang Q, Jiang L
and Guo L: Human amniotic epithelial cell feeder layers maintain
human iPS cell pluripotency via inhibited endogenous microRNA-145
and increased Sox2 expression. Exp Cell Res. 318:424–434. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Barh D, Malhotra R, Ravi B and Sindhurani
P: MicroRNA let-7: An emerging next-generation cancer therapeutic.
Curr Oncol. 17:70–80. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Schultz J, Lorenz P, Gross G, Ibrahim S
and Kunz M: MicroRNA let-7b targets important cell cycle molecules
in malignant melanoma cells and interferes with
anchorage-independent growth. Cell Res. 18:549–557. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dangi-Garimella S, Yun J, Eves EM, et al:
Raf kinase inhibitory protein suppresses a metastasis signalling
cascade involving LIN28 and let-7. EMBO J. 28:347–358. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yu F, Yao H, Zhu P, et al: Let-7 regulates
self renewal and tumorigenicity of breast cancer cells. Cell.
131:1109–1123. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu T, Huang Y, Guo L, Cheng W and Zou G:
CD44+/CD105+ human amniotic fluid mesenchymal stem cells survive
and proliferate in the ovary long-term in a mouse model of
chemotherapy-induced premature ovarian failure. Int J Med Sci.
9:592–602. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|