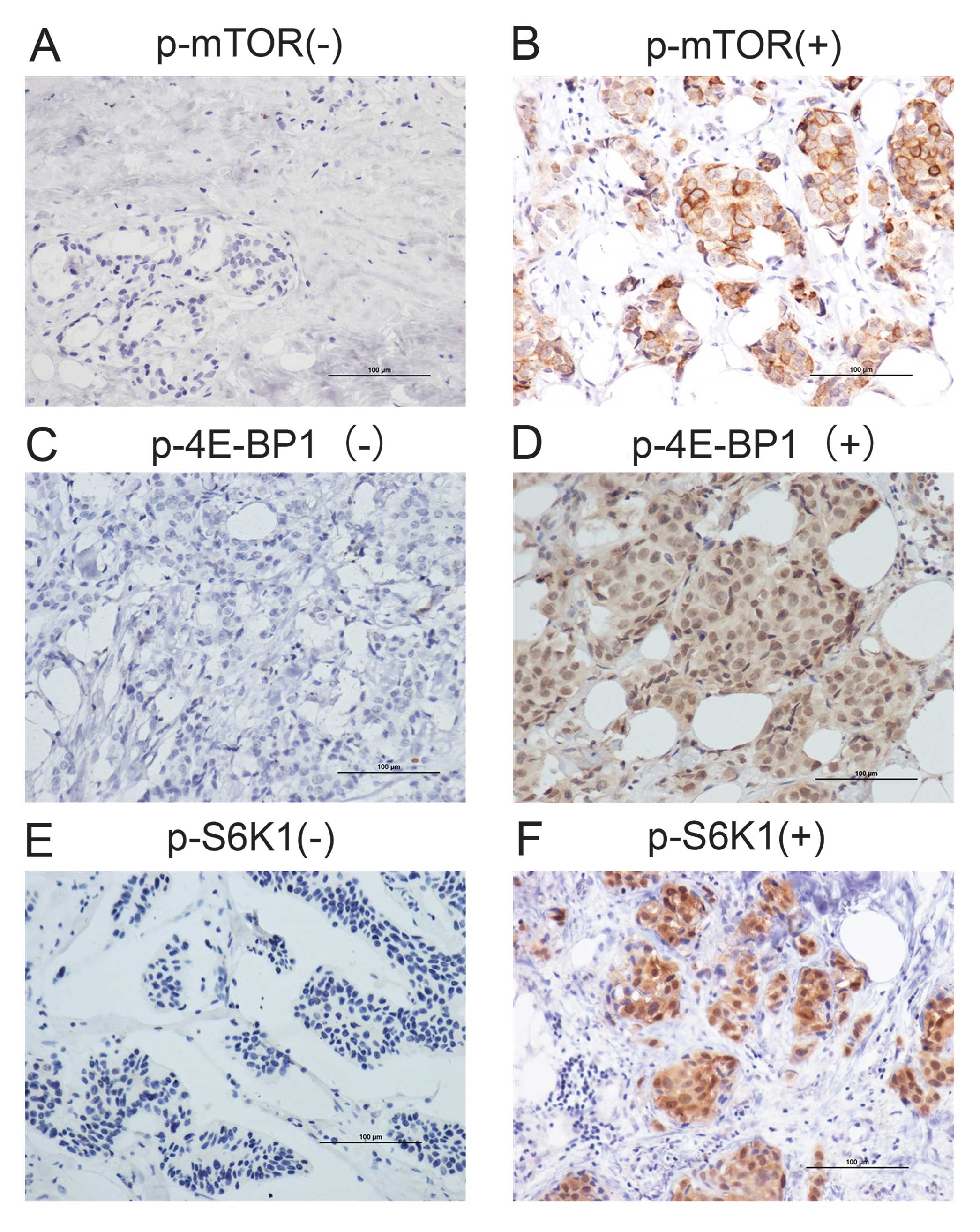
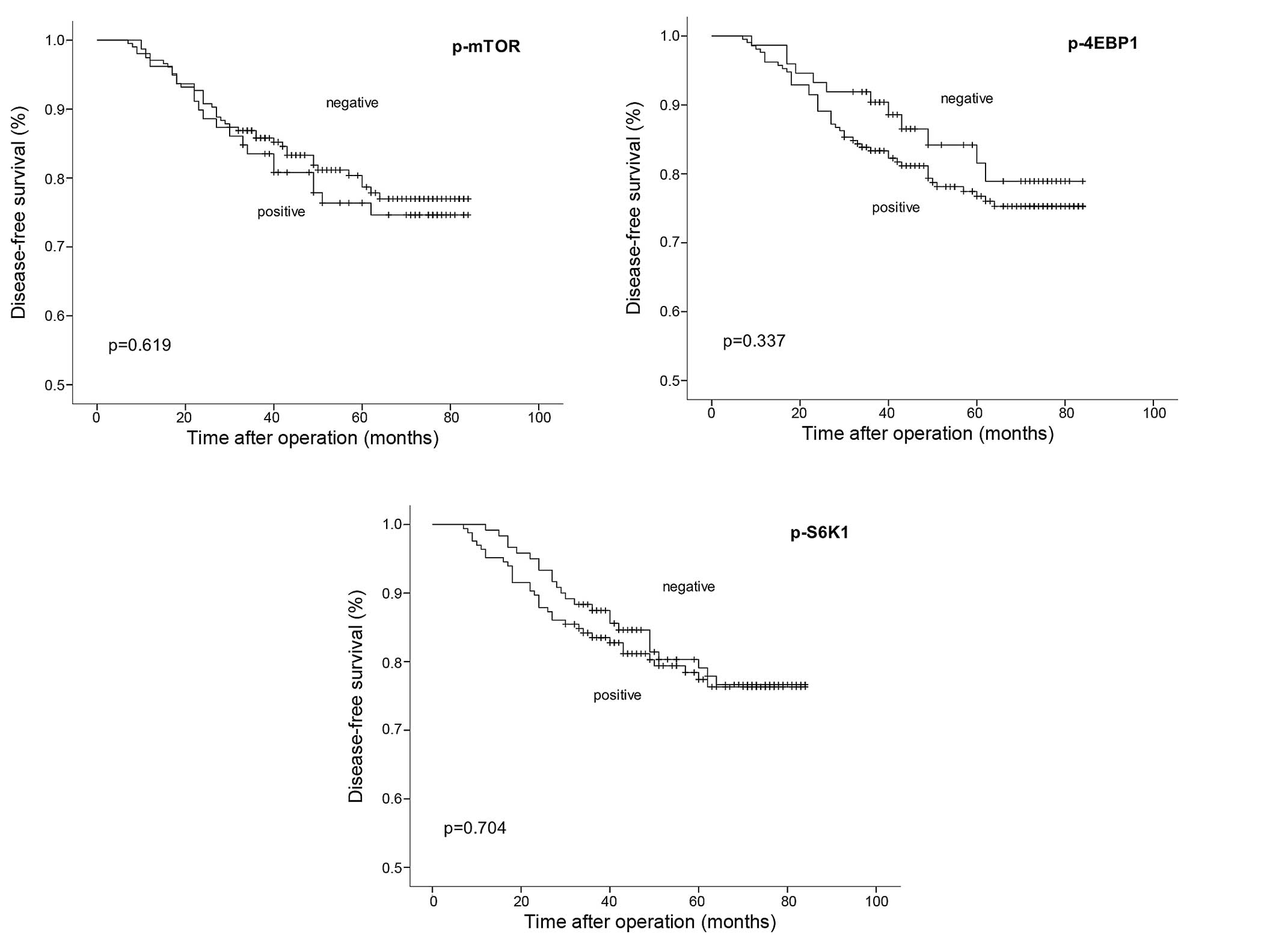
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Héry C, Ferlay J, Boniol M and Autier P:
Changes in breast cancer incidence and mortality in middle-aged and
elderly women in 28 countries with Caucasian majority populations.
Ann Oncol. 19:1009–1018. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J and Pisani P:
Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 55:74–108. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
den Hollander P, Savage MI and Brown PH:
Targeted therapy for breast cancer prevention. Front Oncol.
3:2502013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Levi F, Bosetti C, Lucchini F, Negri E and
La Vecchia C: Monitoring the decrease in breast cancer mortality in
Europe. Eur J Cancer Prev. 14:497–502. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Guertin DA and Sabatini DM: Defining the
role of mTOR in cancer. Cancer Cell. 12:9–22. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dai DL, Martinka M and Li G: Prognostic
significance of activated Akt expression in melanoma: A
clinicopathologic study of 292 cases. J Clin Oncol. 23:1473–1482.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kreisberg JI, Malik SN, Prihoda TJ, et al:
Phosphorylation of Akt (Ser473) is an excellent predictor of poor
clinical outcome in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 64:5232–5236.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nakanishi K, Sakamoto M, Yamasaki S, Todo
S and Hirohashi S: Akt phosphorylation is a risk factor for early
disease recurrence and poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Cancer. 103:307–312. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Cutler NS, Heitman J and Cardenas ME: TOR
kinase homologs function in a signal transduction pathway that is
conserved from yeast to mammals. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 155:135–142.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shaw RJ and Cantley LC: Ras, PI(3)K and
mTOR signalling controls tumour cell growth. Nature. 441:424–430.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Copp J, Manning G and Hunter T:
TORC-specific phosphorylation of mammalian target of rapamycin
(mTOR): Phospho-Ser2481 is a marker for intact mTOR signaling
complex 2. Cancer Res. 69:1821–1827. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ma XM and Blenis J: Molecular mechanisms
of mTOR-mediated translational control. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
10:307–318. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Proud CG: Role of mTOR signalling in the
control of translation initiation and elongation by nutrients. Curr
Top Microbiol Immunol. 279:215–244. 2004.
|
|
15
|
Gera JF, Mellinghoff IK, Shi Y, et al: AKT
activity determines sensitivity to mammalian target of rapamycin
(mTOR) inhibitors by regulating cyclin D1 and c-myc expression. J
Biol Chem. 279:2737–2746. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Seeliger H, Guba M, Kleespies A, Jauch KW
and Bruns CJ: Role of mTOR in solid tumor systems: A therapeutical
target against primary tumor growth, metastases, and angiogenesis.
Cancer Metastasis Rev. 26:611–621. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yu G, Wang J, Chen Y, et al:
Overexpression of phosphorylated mammalian target of rapamycin
predicts lymph node metastasis and prognosis of chinese patients
with gastric cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 15:1821–1829. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Samuels Y, Wang Z, Bardelli A, et al: High
frequency of mutations of the PIK3CA gene in human cancers.
Science. 304:5542004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pérez-Tenorio G, Alkhori L, Olsson B, et
al: PIK3CA mutations and PTEN loss correlate with similar
prognostic factors and are not mutually exclusive in breast cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 13:3577–3584. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Noh WC, Mondesire WH, Peng J, et al:
Determinants of rapamycin sensitivity in breast cancer cells. Clin
Cancer Res. 10:1013–1023. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
No JH, Jeon YT, Park IA, et al: Expression
of mTOR protein and its clinical significance in endometrial
cancer. Med Sci Monit. 15:BR301–BR305. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Meric-Bernstam F and Gonzalez-Angulo AM:
Targeting the mTOR signaling network for cancer therapy. J Clin
Oncol. 27:2278–2287. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lane HA, Wood JM, McSheehy PM, et al: mTOR
inhibitor RAD001 (everolimus) has antiangiogenic/vascular
properties distinct from a VEGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Clin
Cancer Res. 15:1612–1622. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yu K, Toral-Barza L, Discafani C, et al:
mTOR, a novel target in breast cancer: The effect of CCI-779, an
mTOR inhibitor, in preclinical models of breast cancer. Endocr
Relat Cancer. 8:249–258. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chan S: Targeting the mammalian target of
rapamycin (mTOR): A new approach to treating cancer. Br J Cancer.
91:1420–1424. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Georgakis GV and Younes A: From Rapa Nui
to rapamycin: Targeting PI3K/Akt/mTOR for cancer therapy. Expert
Rev Anticancer Ther. 6:131–140. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
O'Reilly KE, Rojo F, She QB, et al: mTOR
inhibition induces upstream receptor tyrosine kinase signaling and
activates Akt. Cancer Res. 66:1500–1508. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Heinonen H, Nieminen A, Saarela M, et al:
Deciphering downstream gene targets of PI3K/mTOR/p70S6K pathway in
breast cancer. BMC Genomics. 9:3482008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Dillon RL, White DE and Muller WJ: The
phosphatidyl inositol 3-kinase signaling network: Implications for
human breast cancer. Oncogene. 26:1338–1345. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bose S, Chandran S, Mirocha JM and Bose N:
The Akt pathway in human breast cancer: A tissue-array-based
analysis. Mod Pathol. 19:238–245. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Bakarakos P, Theohari I, Nomikos A, et al:
Immunohistochemical study of PTEN and phosphorylated mTOR proteins
in familial and sporadic invasive breast carcinomas.
Histopathology. 56(8): 76–88. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Mondesire WH, Jian W, Zhang H, et al:
Targeting mammalian target of rapamycin synergistically enhances
chemotherapy-induced cytotoxicity in breast cancer cells. Clin
Cancer Res. 10:7031–7042. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zeng Q, Yang Z, Gao YJ, et al: Treating
triple-negative breast cancer by a combination of rapamycin and
cyclophosphamide: An in vivo bioluminescence imaging study. Eur J
Cancer. 46:1132–1143. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Volinsky N, McCarthy CJ, von Kriegsheim A,
et al: Signalling mechanisms regulating phenotypic changes in
breast cancer cells. Biosci Rep. 35:e001782015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li G, Shan C, Liu L, et al: Tanshinone IIA
inhibits HIF-1α and VEGF expression in breast cancer cells via
mTOR/p70S6K/RPS6/4E-BP1 signaling pathway. PLoS One.
10:e01174402015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Wang L, Wu J, Lu J, Ma R, Sun D and Tang
J: Regulation of the cell cycle and PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway
by tanshinone I in human breast cancer cell lines. Mol Med Rep.
11:931–939. 2015.
|
|
37
|
Remmele W and Stegner HE: Recommendation
for uniform defnition of an immunoreactive score (IRS) for
immunohistochemical estrogen receptor detection (ER-ICA) in breast
cancer tissue. Pathologe. 8:138–140. 1987.In German. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ueng SH, Chen SC, Chang YS, et al:
Phosphorylated mTOR expression correlates with poor outcome in
early-stage triple negative breast carcinomas. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 5:806–813. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Rojo F, Najera L, Lirola J, et al:
4E-binding protein 1, a cell signaling hallmark in breast cancer
that correlates with pathologic grade and prognosis. Clin Cancer
Res. 13:81–89. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Jacinto E and Hall MN: Tor signalling in
bugs, brain and brawn. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 4:117–126. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Bachmann RA, Kim JH, Wu AL, Park IH and
Chen J: A nuclear transport signal in mammalian target of rapamycin
is critical for its cytoplasmic signaling to S6 kinase 1. J Biol
Chem. 281:7357–7363. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Korkolopoulou P, Levidou G, El-Habr EA, et
al: Phosphorylated 4E-binding protein 1 (p-4E-BP1): A novel
prognostic marker in human astrocytomas. Histopathology.
61:293–305. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhang X, Shu L, Hosoi H, Murti KG and
Houghton PJ: Predominant nuclear localization of mammalian target
of rapamycin in normal and malignant cells in culture. J Biol Chem.
277:28127–28134. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Rong L, Livingstone M, Sukarieh R, et al:
Control of eIF4E cellular localization by eIF4E-binding proteins,
4E-BPs. RNA. 14:1318–1327. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Vega F, Medeiros LJ, Leventaki V, et al:
Activation of mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway
contributes to tumor cell survival in anaplastic lymphoma
kinase-positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Cancer Res.
66:6589–6597. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Li XY, Zhang LQ, Zhang XG, et al:
Association between AKT/mTOR signalling pathway and malignancy
grade of human gliomas. J Neurooncol. 103:453–458. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Xiao L, Wang YC, Li WS and Du Y: The role
of mTOR and phospho-p70S6K in pathogenesis and progression of
gastric carcinomas: An immunohistochemical study on tissue
microarray. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 28:1522009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Hara K, Yonezawa K, Weng QP, Kozlowski MT,
Belham C and Avruch J: Amino acid sufficiency and mTOR regulate p70
S6 kinase and eIF-4E BP1 through a common effector mechanism. J
Biol Chem. 273:14484–14494. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Weng QP, Kozlowski M, Belham C, Zhang A,
Comb MJ and Avruch J: Regulation of the p70 S6 kinase by
phosphorylation in vivo. Analysis using site-specific
anti-phosphopeptide antibodies. J Biol Chem. 273:16621–16629. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Sarbassov DD, Guertin DA, Ali SM and
Sabatini DM: Phosphorylation and regulation of Akt/PKB by the
rictor-mTOR complex. Science. 307:1098–1101. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Chaux A, Albadine R, Schultz L, et al:
Dysregulation of the mammalian target of rapamycin pathway in
chromophobe renal cell carcinomas. Hum Pathol. 44:2323–2330. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Darb-Esfahani S, Faggad A, Noske A, et al:
Phospho-mTOR and phospho-4EBP1 in endometrial adenocarcinoma:
Association with stage and grade in vivo and link with response to
rapamycin treatment in vitro. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 135:933–941.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Annovazzi L, Mellai M, Caldera V, Valente
G, Tessitore L and Schiffer D: mTOR, S6 and AKT expression in
relation to proliferation and apoptosis/autophagy in glioma.
Anticancer Res. 29:3087–3094. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
van der Hage JA, van den Broek LJ, Legrand
C, et al: Overexpression of P70 S6 kinase protein is associated
with increased risk of locoregional recurrence in node-negative
premenopausal early breast cancer patients. Br J Cancer.
90:1543–1550. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Zhou L, Huang Y, Li J and Wang Z: The mTOR
pathway is associated with the poor prognosis of human
hepatocellular carcinoma. Med Oncol. 27:255–261. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Zhou X, Tan M, Stone Hawthorne V, et al:
Activation of the Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin/4E-BP1 pathway
by ErbB2 overexpression predicts tumor progression in breast
cancers. Clin Cancer Res. 10:6779–6788. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Pelloski CE, Lin E, Zhang L, et al:
Prognostic associations of activated mitogen-activated protein
kinase and Akt pathways in glioblastoma. Clin Cancer Res.
12:3935–3941. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Chakravarti A, Zhai G, Suzuki Y, et al:
The prognostic significance of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
pathway activation in human gliomas. J Clin Oncol. 22:1926–1933.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Ermoian RP, Kaprealian T, Lamborn KR, et
al: Signal transduction molecules in gliomas of all grades. J
Neurooncol. 91:19–26. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|