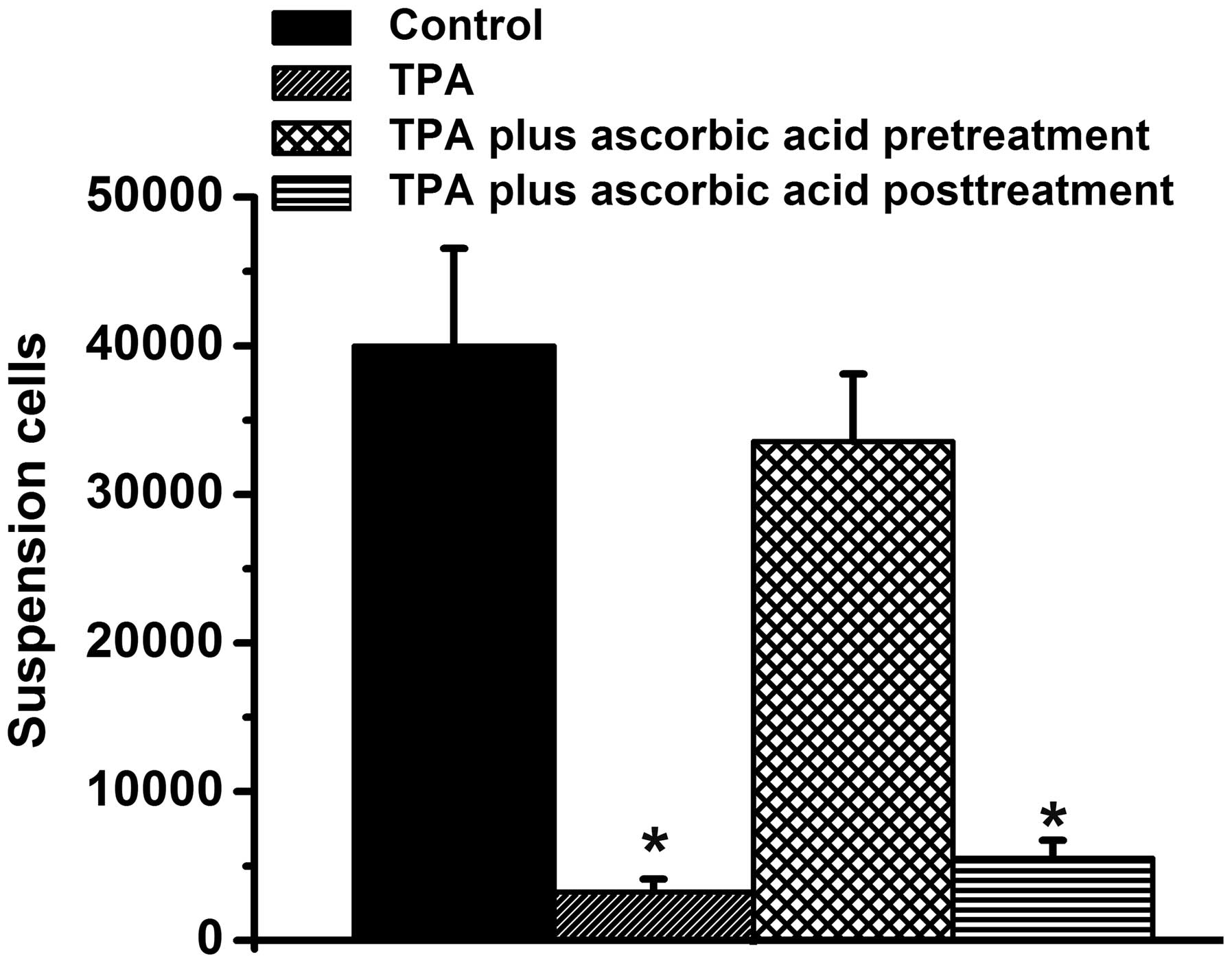
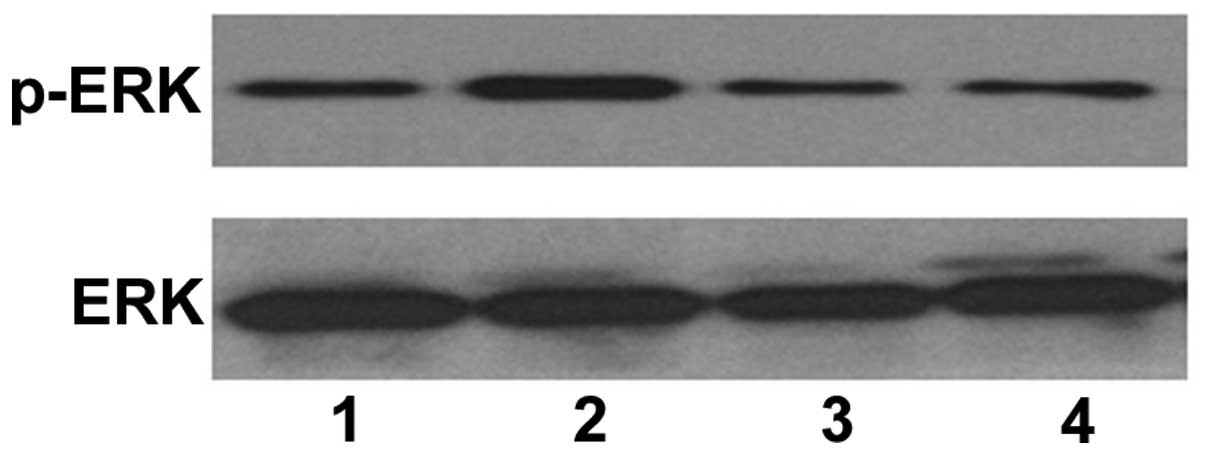
|
1
|
Trayner ID, Bustorff T, Etches AE, Mufti
GJ, Foss Y and Farzaneh F: Changes in antigen expression on
differentiating HL60 cells treated with dimethylsulphoxide,
all-trans retinoic acid, alpha1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 or
12-O-tetradecanoyl phorbol-13-acetate. Leuk Res. 22:537–547. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zylber-Katz E and Glazer RI: Phospholipid-
and Ca2+-dependent protein kinase activity and protein
phosphorylation patterns in the differentiation of human
promyelocytic leukemia cell line HL-60. Cancer Res. 45:5159–5164.
1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Congleton J, MacDonald R and Yen A: Src
inhibitors, PP2 and dasatinib, increase retinoic acid-induced
association of Lyn and c-Raf (S259) and enhance MAPK-dependent
differentiation of myeloid leukemia cells. Leukemia. 26:1180–1188.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
4
|
Ji Y, Kutner A, Verstuyf A, Verlinden L
and Studzinski GP: Derivatives of vitamins D2 and D3 activate three
MAPK pathways and upregulate pRb expression in differentiating HL60
cells. Cell Cycle. 1:410–415. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Wang N, Wang LW, Gou BD, Zhang TL and Wang
K: Realgar-induced differentiation is associated with MAPK pathways
in HL-60 cells. Cell Biol Int. 32:1497–1505. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kim SH, Yoo JC and Kim TS: Nargenicin
enhances 1,25-dihy-droxyvitamin D (3)- and all-trans retinoic
acid-induced leukemia cell differentiation via PKCbetaI/MAPK
pathways. Biochem Pharmacol. 77:1694–1701. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Stixová L, Procházková J, Soucek K,
Hofmanová J and Kozubík A: 5-Lipoxygenase inhibitors potentiate
1alpha,25-dihy-droxyvitamin D3-induced monocytic differentiation by
activating p38 MAPK pathway. Mol Cell Biochem. 330:229–238. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Battle TE, Levine RA and Yen A: Retinoic
acid-induced blr1 expression promotes ERK2 activation and cell
differentiation in HL-60 cells. Exp Cell Res. 254:287–298. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yen A, Roberson MS and Varvayanis S:
Retinoic acid selectively activates the ERK2 but not JNK/SAPK or
p38 MAP kinases when inducing myeloid differentiation. In Vitro
Cell Dev Biol Anim. 35:527–532. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yu HN, Lee YR, Noh EM, Lee KS, Song EK,
Han MK, Lee YC, Yim CY, Park J, Kim BS, et al: Tumor necrosis
factor-alpha enhances DMSO-induced differentiation of HL-60 cells
through the activation of ERK/MAPK pathway. Int J Hematol.
87:189–194. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li C, Yu Y, Wang Y, Liu L, Zhang M, Sugano
S, Wang Z and Chang Z: Both ERK and JNK are required for
enhancement of MD-2 gene expression during differentiation of HL-60
cells. Biol Cell. 100:365–375. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang J, Harrison JS and Studzinski GP:
Isoforms of p38MAPK gamma and delta contribute to differentiation
of human AML cells induced by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D (3). Exp Cell
Res. 317:117–130. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Matsumoto E, Hatanaka M, Bohgaki M and
Maeda S: PKC pathway and ERK/MAPK pathway are required for
induction of cyclin D1 and p21Waf1 during 12-o-tetradecanoylphorbol
13-acetate-induced differentiation of myeloleukemia cells. Kobe J
Med Sci. 52:181–194. 2006.
|
|
14
|
Yiang GT, Yu YL, Hu SC, Chen MH, Wang JJ
and Wei CW: PKC and MEK pathways inhibit caspase-9/-3-mediated
cytotoxicity in differentiated cells. FEBS Lett. 582:881–885. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang X, Pesakhov S, Harrison JS, Danilenko
M and Studzinski GP: ERK5 pathway regulates transcription factors
important for monocytic differentiation of human myeloid leukemia
cells. J Cell Physiol. 229:856–867. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Jamshidi F, Zhang J, Harrison JS, Wang X
and Studzinski GP: Induction of differentiation of human leukemia
cells by combinations of COX inhibitors and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin
D3 involves Raf1 but not Erk 1/2 signaling. Cell Cycle. 7:917–924.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang X, Pesakhov S, Weng A, Kafka M, Gocek
E, Nguyen M, Harrison JS, Danilenko M and Studzinski GP: ERK 5/MAPK
pathway has a major role in 1α,25-(oh) vitamin D3-induced terminal
differentiation of myeloid leukemia cells. J Steroid Biochem Mol
Biol. 144:223–227. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Uruno A, Noguchi N, Matsuda K, Nata K,
Yoshikawa T, Chikamatsu Y, Kagechika H, Harigae H, Ito S, Okamoto
H, et al: All-trans retinoic acid and a novel synthetic retinoid
tami-barotene (Am80) differentially regulate CD38 expression in
human leukemia HL-60 cells: possible involvement of protein kinase
C-delta. J Leukoc Biol. 90:235–247. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ju SM, Kang JG, Pae HO, Lee GS, Kim WS,
Lyu YS and Jeon BH: Nardostachys chinensis induces the
differentiation of human promyelocytic leukemic cells through the
activation of the protein kinase C-dependent extracellular
signal-regulated kinase signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med.
33:573–580. 2014.
|
|
20
|
Ogino T, Ozaki M and Matsukawa A:
Oxidative stress enhances granulocytic differentiation in HL 60
cells, an acute promy-elocytic leukemia cell line. Free Radic Res.
44:1328–1337. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hu XM, Yuan B, Tanaka S, Zhou Q, Onda K,
Toyoda H and Hirano T: Involvement of oxidative stress associated
with glutathione depletion and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase
activation in arsenic disulfide-induced differentiation in HL-60
cells. Leuk Lymphoma. 55:392–404. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Kambhampati S, Li Y, Verma A, Sassano A,
Majchrzak B, Deb DK, Parmar S, Giafis N, Kalvakolanu DV, Rahman A,
et al: Activation of protein kinase C delta by all-trans-retinoic
acid. J Biol Chem. 278:32544–32551. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kim SH, Kang SN, Kim HJ and Kim TS:
Potentiation of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D (3)-induced differentiation
of human promyelocytic leukemia cells into monocytes by
costunolide, a germacranolide sesquiterpene lactone. Biochem
Pharmacol. 64:1233–1242. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bondza-Kibangou P, Millot C, El Khoury V
and Millot JM: Antioxidants and doxorubicin supplementation to
modulate CD14 expression and oxidative stress induced by vitamin D3
and seocalcitol in HL60 cells. Oncol Rep. 18:1513–1519.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yamamoto T, Sakaguchi N, Hachiya M,
Nakayama F, Yamakawa M and Akashi M: Role of catalase in monocytic
differentiation of U937 cells by TPA: hydrogen peroxide as a second
messenger. Leukemia. 23:761–769. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Yan Y, Zeng W, Song S, Zhang F, He W,
Liang W and Niu Z: Vitamin C induces periodontal ligament
progenitor cell differentiation via activation of ERK pathway
mediated by PELP1. Protein Cell. 4:620–627. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mimori K, Komaki M, Iwasaki K and Ishikawa
I: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 is involved in
ascorbic acid-induced osteoblastic differentiation in periodontal
ligament cells. J Periodontol. 78:328–334. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shinozaki K, Hosokawa Y, Hazawa M,
Kashiwakura I, Okumura K, Kaku T and Nakayama E: Ascorbic acid
enhances radiation-induced apoptosis in an HL60 human leukemia cell
line. J Radiat Res. 52:229–237. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gokhalé P, Patel T, Morrison MJ and
Vissers MC: The effect of intracellular ascorbate on the
susceptibility of HL60 and Jurkat cells to chemotherapy agents.
Apoptosis. 11:1737–1746. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kang HK, Suh JH, Lee JJ, Yoon SH, Hyun JW,
Choi SW, Choi JY, Ryu KH and Chung MH: Induction of the
differentiation of HL-60 promyelocytic leukemia cells by L-ascorbic
acid. Free Radic Res. 37:773–779. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Witenberg B, Kletter Y, Kalir HH, Raviv Z,
Fenig E, Nagler A, Halperin D and Fabian I: Ascorbic acid inhibits
apoptosis induced by X irradiation in HL60 myeloid leukemia cells.
Radiat Res. 152:468–478. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Karasavvas N, Carcamo JM, Stratis G and
Golde DW: Vitamin C protects HL60 and U266 cells from arsenic
toxicity. Blood. 105:4004–4012. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cuddihy SL, Parker A, Harwood DT, Vissers
MC and Winterbourn CC: Ascorbate interacts with reduced glutathione
to scavenge phenoxyl radicals in HL60 cells. Free Radic Biol Med.
44:1637–1644. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Parker A, Cuddihy SL, Son TG, Vissers MC
and Winterbourn CC: Roles of superoxide and myeloperoxidase in
ascorbate oxidation in stimulated neutrophils and H2O2-treated HL60
cells. Free Radic Biol Med. 51:1399–1405. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Taniguchi M, A rai N, Kohno K, Ushio S and
Fukuda S: Anti-oxidative and anti-aging activities of
2-O-alpha-glucopyranosyl-L-ascorbic acid on human dermal
fibroblasts. Eur J Pharmacol. 674:126–131. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Naziroglu M, Akkus S, Soyupek F, Yalman K,
Çelik Ö, Eriş S and Uslusoy GA: Vitamins C and E treatment combined
with exercise modulates oxidative stress markers in blood of
patients with fibromyalgia: A controlled clinical pilot study.
Stress. 13:498–505. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yokoo S, Furumoto K, Hiyama E and Miwa N:
Slow-down of age-dependent telomere shortening is executed in human
skin keratinocytes by hormesis-like-effects of trace hydrogen
peroxide or by anti-oxidative effects of pro-vitamin C in common
concurrently with reduction of intracellular oxidative stress. J
Cell Biochem. 93:588–597. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kim YH, Kim CH, Cho MK, Kim KM, Lee SY,
Ahn BW, Yang SY, Kim SM and Song TB: Total peroxyl radical-trapping
ability and anti-oxidant vitamins of the umbilical venous plasma
and the placenta in pre-eclampsia. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 32:32–41.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yiang GT, Chou PL, Hung YT, Chen JN, Chang
WJ, Yu YL and Wei CW: Vitamin C enhances anticancer activity in
methotrexa-tetreated Hep3B hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncol
Rep. 32:1057–1063. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yu YL, Yiang GT, Chou PL, Tseng HH, Wu TK,
Hung YT, Lin PS, Lin SY, Liu HC, Chang WJ, et al: Dual role of
acetaminophen in promoting hepatoma cell apoptosis and kidney
fibroblast proliferation. Mol Med Rep. 9:2077–2084. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yiang GT, Chen YH, Chou PL, Chang WJ, Wei
CW and Yu YL: The NS3 protease and helicase domains of Japanese
encephalitis virus trigger cell death via caspasedependent and
independent pathways. Mol Med Rep. 7:826–830. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chen KH, Li PC, Lin WH, Chien CT and Low
BH: Depression by a green tea extract of alcohol-induced oxidative
stress and lipogenesis in rat liver. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem.
75:1668–1676. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lin BR, Yu CJ, Chen WC, Lee HS, Chang HM,
Lee YC, Chien CT and Chen CF: Green tea extract supplement reduces
D-galactosamine-induced acute liver injury by inhibition of
apoptotic and proinflammatory signaling. J Biomed Sci. 16:352009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Das D, Pintucci G and Stern A:
MAPK-dependent expression of p21 (WAF) and p27 (kip1) in
PMA-induced differentiation of HL60 cells. FEBS Lett. 472:50–52.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wei CW, Hu CC, Tang CH, Lee MC and Wang
JJ: Induction of differentiation rescues HL-60 cells from Rana
catesbeiana ribonuclease-induced cell death. FEBS Lett.
531:421–426. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Siebel A, Cubillos-Rojas M, Santos RC,
Schneider T, Bonan CD, Bartrons R, Ventura F, Rodrigues de Oliveira
J and Rosa JL: Contribution of S6K1/MAPK signaling pathways in the
response to oxidative stress: Activation of RSK and MSK by hydrogen
peroxide. PLoS One. 8:e755232013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Moslehi M, Meshkini A and Yazdanparast R:
Flavonoid baicalein modulates H2O2-induced mitogen-activated
protein kinases activation and cell death in SK-N-MC cells. Cell
Mol Neurobiol. 32:549–560. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kang KA, Lee KH, Zhang R, Piao MJ, Kang
MY, Kwak YS, Yoo BS, You HJ and Hyun JW: Protective effects of
Castanopsis cuspidate through activation of ERK and NF-kappaB on
oxidative cell death induced by hydrogen peroxide. J Toxicol
Environ Health A. 70:1319–1328. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ulrich-Merzenich G, Zeitler H, Panek D,
Bokemeyer D and Vetter H: Vitamin C promotes human endothelial cell
growth via the ERK-signaling pathway. Eur J Nutr. 46:87–94. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Park S, Park CH, Hahm ER, Kim K, Kimler
BF, Lee SJ, Park HK, Lee SH, Kim WS, Jung CW, et al: Activation of
Raf1 and the ERK pathway in response to l-ascorbic acid in acute
myeloid leukemia cells. Cell Signal. 17:111–119. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Park HJ, Ock SM, Kim HJ, Park HJ, Lee YB,
Choi JM, Cho CS, Lee JY, Cho BK and Cho DH: Vitamin C attenuates
ERK signalling to inhibit the regulation of collagen production by
LL-37 in human dermal fibroblasts. Exp Dermatol. 19:e258–e264.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Cuaranta-Monroy I, Simandi Z, Kolostyak Z,
Doan-Xuan QM, Poliska S, Horvath A, Nagy G, Bacso Z and Nagy L:
Highly efficient differentiation of embryonic stem cells into
adipocytes by ascorbic acid. Stem Cell Res. 13:88–97. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Yu J, Tu YK, Tang YB and Cheng NC:
Stemness and transdif-ferentiation of adipose-derived stem cells
using L-ascorbic acid 2-phosphate-induced cell sheet formation.
Biomaterials. 35:3516–3526. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Valenti MT, Zanatta M, Donatelli L,
Viviano G, Cavallini C, Scupoli MT and Dalle Carbonare L: Ascorbic
acid induces either differentiation or apoptosis in MG-63
osteosarcoma lineage. Anticancer Res. 34:1617–1627. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Langenbach F and Handschel J: Effects of
dexamethasone, ascorbic acid and beta-glycerophosphate on the
osteogenic differentiation of stem cells in vitro. Stem Cell Res
Ther. 4:1172013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Hadzir SN, Ibrahim SN, Abdul Wahab RM,
Zaino Abidin IZ, Senafi S, Ariffin ZZ, Abdul Razak M and Zainal
Ariffin SH: Ascorbic acid induces osteoblast differentiation of
human suspension mononuclear cells. Cytotherapy. 16:674–682. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|