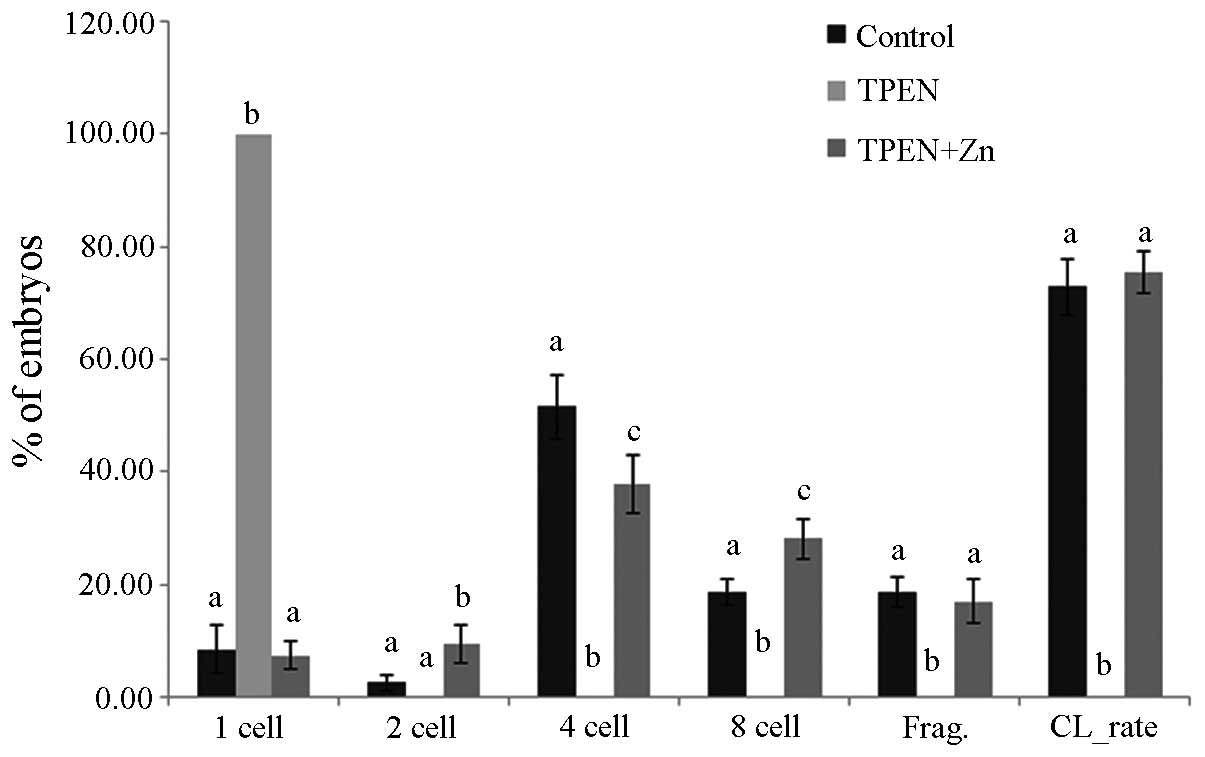
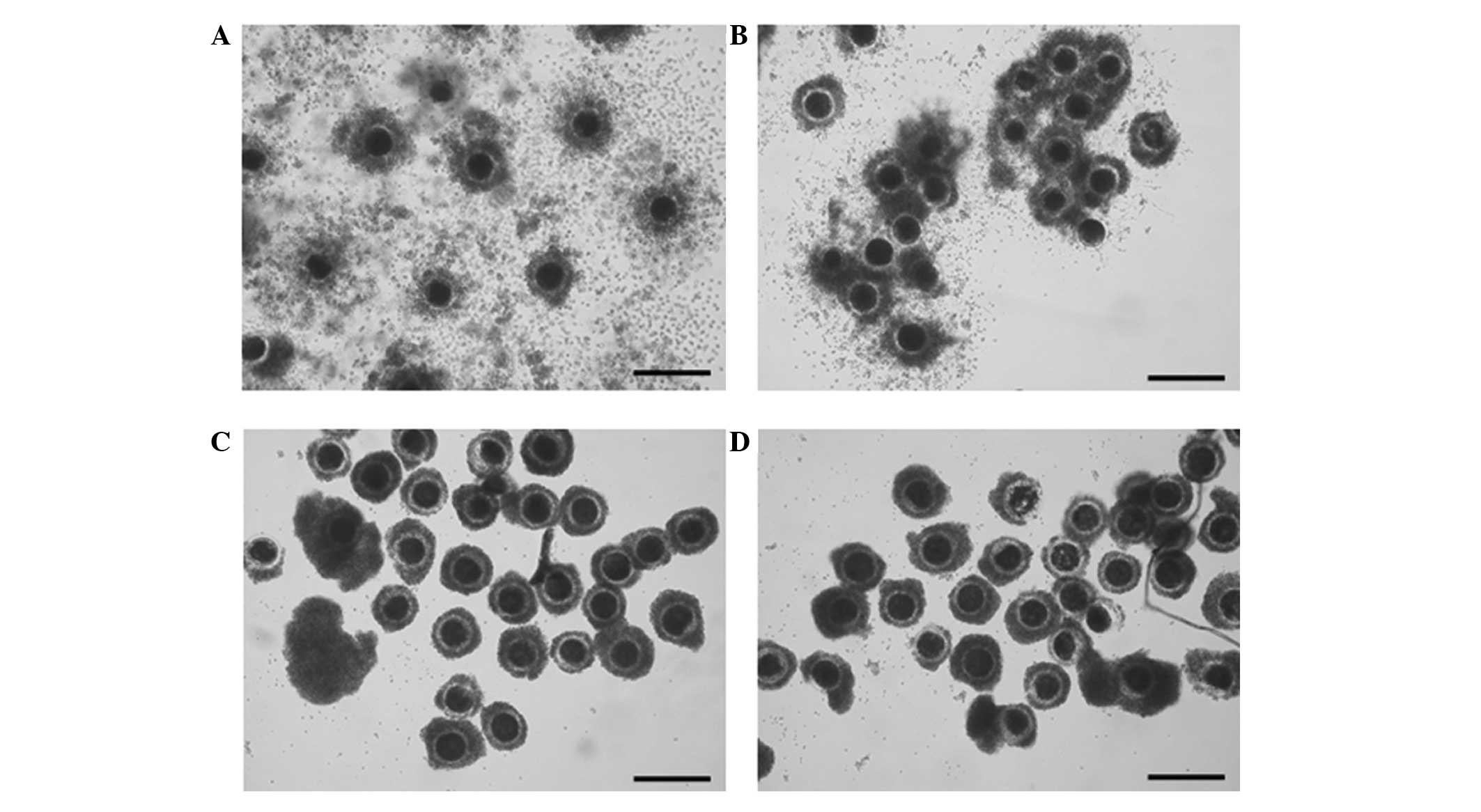
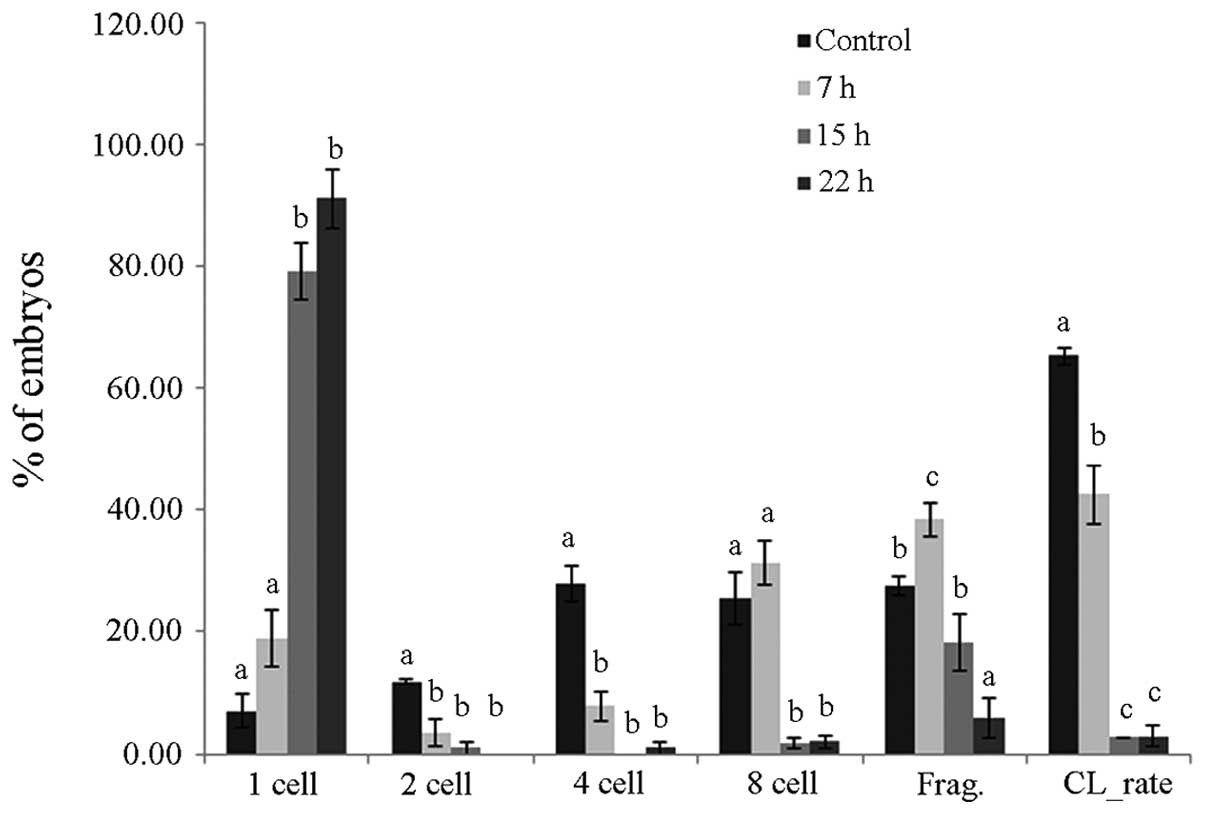
|
1
|
Sirard MA, Richard F, Blondin P and Robert
C: Contribution of the oocyte to embryo quality. Theriogenology.
65:126–136. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Mattioli M, Bacci ML, Galeati G and Seren
E: Developmental competence of pig oocytes matured and fertilized
in vitro. Theriogenology. 31:1201–1207. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Singh B, Barbe GJ and Armstrong DT:
Factors influencing resumption of meiotic maturation and cumulus
expansion of porcine oocyte-cumulus cell complexes in vitro. Mol
Reprod Dev. 36:113–119. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Funahashi H, Cantley T and Day BN:
Different hormonal requirements of pig oocyte-cumulus complexes
during maturation in vitro. J Reprod Fertil. 101:159–165. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Funahashi H and Day BN: Effects of the
duration of exposure to hormone supplements on cytoplasmic
maturation of pig oocytes in vitro. J Reprod Fertil. 98:179–185.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Illera MJ, Lorenzo PL, Illera JC and
Petters RM: Developmental competence of immature pig oocytes under
the influence of EGF, IGF-I, follicular fluid and gonadotropins
during IVM-IVF processes. Int J Dev Biol. 42:1169–1172. 1998.
|
|
7
|
Bing YZ, Naga T and Rodriguez-Martinez H:
Effects of cysteamine, fsh and estradiol-17beta on in vitro
maturation of porcine oocytes. Theriogenology. 55:867–876. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xia GL, Kikuchi K, Noguchi J and Izaike Y:
Short time priming of pig cumulus-oocyte complexes with FSH and
forskolin in the presence of hypoxanthine stimulates cumulus cells
to secrete a meiosis-activating substance. Theriogenology.
53:1807–1815. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tatemoto H, Sakurai N and Muto N:
Protection of porcine oocytes against apoptotic cell death caused
by oxidative stress during in vitro maturation: Role of cumulus
cells. Biol Reprod. 63:805–810. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cetica PD, Pintos LN, Dalvit GC and Beconi
MT: Antioxidant enzyme activity and oxidative stress in bovine
oocyte in vitro maturation. IUBMB Life. 51:57–64. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nasr-Esfahani MH, Aitken JR and Johnson
MH: Hydrogen peroxide levels in mouse oocytes and early cleavage
stage embryos developed in vitro or in vivo. Development.
109:501–507. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Luberda Z: The role of glutathione in
mammalian gametes. Reprod Biol. 5:5–17. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yoshida M, Ishigaki K, Nagai T, Chikyu M
and Pursel VG: Glutathione concentration during maturation and
after fertilization in pig oocytes: Relevance to the ability of
oocytes to form male pronucleus. Biol Reprod. 49:89–94. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jeong BS and Yang X: Cysteine, glutathione
and Percoll treatments improve porcine oocyte maturation and
fertilization in vitro. Mol Reprod Dev. 59:330–335. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Biswas D, Jeon Y, Kim GH, Jeung EB and
Hyun SH: Effect of vascular endothelia growth factor on in vitro
porcine oocyte maturation and subsequent developmental competence
after parthenogenesis. J Anim Vet Adv. 9:2924–2931. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Kwak SS, Jeung SH, Biswas D, Jeon YB and
Hyun SH: Effects of porcine granulocyte-macrophage
colony-stimulating factor on porcine in vitro-fertilized embryos.
Theriogenology. 77:1186–1197. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Walker SC, Shin T, Zaubrecher GM, Romano
JE, Johnson GA, Bazer FW and Piedrahita JA: A highly efficient
method for porcine cloning by nuclear transfer using in
vitro-matured oocytes. Cloning Stem Cells. 4:105–112. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nielsen FH: Ultratrace minerals mythical
elixirs or nutrients of concern? Bol Asoc Med P R. 83:131–133.
1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hostetler CE, Kincaid RL and Mirando MA:
The role of essential trace elements in embryonic and fetal
development in livestock. Vet J. 166:125–139. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Vallee BL and Falchuk KH: The biochemical
basis of zinc physiology. Physiol Rev. 73:79–118. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Favier AE: The role of zinc in
reproduction. Hormonal mechanisms. Biol Trace Elem Res. 32:363–382.
1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bedwal RS and Bahuguna A: Zinc, copper and
selenium in reproduction. Experientia. 50:626–640. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hostetler CE, Cronrath JD, Becker WC and
Mirando MA: Dietary supplementation of proteinated trace minerals
(OPTiMIN) in sows and replacement gilts increases mineral
concentrations in reproductive tissues. Abstracts 14th
International Congress Animal Reproduction. 1:2722000.
|
|
24
|
Wauben IP, Xing HC and Wainwright PE:
Neonatal dietary zinc deficiency in artificially reared rat pups
retards behavioral development and interacts with essential fatty
acid deficiency to alter liver and brain fatty acid composition. J
Nutr. 129:1773–1781. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sakuma S, Fujimoto Y, Miyata Y, Ohno M,
Nishida H and Fujita T: Effects of Fe (2+), Zn (2+), Cu (2+) and Se
(4+) on the synthesis and catabolism of prostaglandins in rabbit
gastric antral mucosa. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids.
54:193–197. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sakuma S, Fujimoto Y, Kitao A, Sakamoto H,
Nishida H and Fujita T: Simultaneous measurement of prostaglandin
and arachidonoyl CoA formed from arachidonic acid in rabbit kidney
medulla microsomes: The roles of Zn2+ and Cu2+ as modulators of
formation of the two products. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty
Acids. 61:105–112. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chanmugam P, Wheeler C and Hwang DH: The
effect of zinc deficiency on prostaglandin synthesis in rat testes.
J Nutr. 114:2066–2072. 1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
de Haan JB, Tymms MJ, Cristiano F and Kola
I: Expression of copper/zinc superoxide dismutase and glutathione
peroxidase in organs of developing mouse embryos, fetuses and
neonates. Pediatr Res. 35:188–196. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chesters JK: Trace element-gene
interactions with particular reference to zinc. Proc Nutr Soc.
50:123–129. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jeon Y, Yoon JD, Cai L, Hwang SU, Kim E,
Zheng Z, Lee E, Kim DY and Hyun SH: Supplementation of zinc on
oocyte in vitro maturation improves preimplatation embryonic
development in pigs. Theriogenology. 82:866–874. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jeon Y, Kwak SS, Cheong SA, Seong YH and
Hyun SH: Effect of trans-epsilon-viniferin on in vitro porcine
oocyte maturation and subsequent developmental competence in
preimplantation embryos. J Vet Med Sci. 75:1277–1286. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Treves S, Trentini PL, Ascanelli M, Bucci
G and Di Virgilio F: Apoptosis is dependent on intracellular zinc
and independent of intracellular calcium in lymphocytes. Exp Cell
Res. 211:339–343. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Smith RM and Martell AE: NIST critically
selected stability constants of metal complexes database. National
Institute of Standards and Technology; 2004, http://www.nist.gov/srd/upload/46_8.htm.
Accessed June 22nd, 2015.
|
|
34
|
Kim AM, Vogt S, O'Halloran TV and Woodruff
TK: Zinc availability regulates exit from meiosis in maturing
mammalian oocytes. Nat Chem Biol. 6:674–681. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hyun HJ, Sohn JH, Ha DW, Ahn YH, Koh JY
and Yoon YH: Depletion of intracellular zinc and copper with TPEN
results in apoptosis of cultured human retinal pigment epithelial
cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 42:460–465. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Nakatani T, Tawaramoto M, Opare Kennedy D,
Kojima A and Matsui-Yuasa I: Apoptosis induced by chelation of
intracellular zinc is associated with depletion of cellular reduced
glutathione level in rat hepatocytes. Chem Biol Interact.
125:151–163. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Pang W, Leng X, Lu H, Yang H, Song N, Tan
L, Jiang Y and Guo C: Depletion of intracellular zinc induces
apoptosis of cultured hippocampal neurons through suppression of
ERK signaling pathway and activation of caspase-3. Neurosci Lett.
552:140–145. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mendivil-Perez M, Velez-Pardo C and
Jimenez-Del-Rio M: TPEN induces apoptosis independently of zinc
chelator activity in a model of acute lymphoblastic leukemia and ex
vivo acute leukemia cells through oxidative stress and mitochondria
caspase-3- and AIF-dependent pathways. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2012:3132752012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Meerarani P, Ramadass P, Toborek M, Bauer
HC, Bauer H and Hennig B: Zinc protects against apoptosis of
endothelial cells induced by linoleic acid and tumor necrosis
factor alpha. Am J Clin Nutr. 71:81–87. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Abeydeera LR: In vitro production of
embryos in swine. Theriogenology. 57:256–273. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tanghe S, Van Soom A, Nauwynck H, Coryn M
and de Kruif A: Minireview: Functions of the cumulus oophorus
during oocyte maturation, ovulation and fertilization. Mol Reprod
Dev. 61:414–424. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Maedomari N, Kikuchi K, Ozawa M, Noguchi
J, Kaneko H, Ohnuma K, Nakai M, Shino M, Nagai T and Kashiwazaki N:
Cytoplasmic glutathione regulated by cumulus cells during porcine
oocyte maturation affects fertilization and embryonic development
in vitro. Theriogenology. 67:983–993. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kikuchi K, Somfai T, Nakai M and Nagai T:
Appearance, fate and utilization of abnormal porcine embryos
produced by in vitro maturation and fertilization. Soc Reprod
Fertil Suppl. 66:135–147. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Buendia B, Clarke PR, Félix MA, Karsenti
E, Leiss D and Verde F: Regulation of protein kinases associated
with cyclin A and cyclin B and their effect on microtubule dynamics
and nucleation in Xenopus egg extracts. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant
Biol. 56:523–532. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Albertini DF: Cytoplasmic reorganization
during the resumption of meiosis in cultured preovulatory rat
oocytes. Dev Biol. 120:121–131. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ueno S, Kurome M, Ueda H, Tomii R, Hiruma
K and Nagashima H: Effects of maturation conditions on spindle
morphology in porcine MII oocytes. J Reprod Dev. 51:405–410. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Roberts K, Raff M, Alberts B, Walter P,
Lewis J and Johnson A: Molecular Biology of the Cell. 5th edition.
Routledge; London: 2002
|
|
48
|
Kim NH, Funahashi H, Prather RS, Schatten
G and Day BN: Microtubule and microfilament dynamics in porcine
oocytes during meiotic maturation. Mol Reprod Dev. 43:248–255.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Longo FJ and Chen DY: Development of
cortical polarity in mouse eggs: involvement of the meiotic
apparatus. Dev Biol. 107:382–394. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Funahashi H, Cantley TC, Stumpf TT,
Terlouw SL and Day BN: Use of low-salt culture medium for in vitro
maturation of porcine oocytes is associated with elevated oocyte
glutathione levels and enhanced male pronuclear formation after in
vitro fertilization. Biol Reprod. 51:633–639. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zuelke KA, Jeffay SC, Zucker RM and
Perreault SD: Glutathione (GSH) concentrations vary with the cell
cycle in maturing hamster oocytes, zygotes and pre-implantation
stage embryos. Mol Reprod Dev. 64:106–112. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Brad AM, Bormann CL, Swain JE, Durkin RE,
Johnson AE, Clifford AL and Krisher RL: Glutathione and adenosine
triphosphate content of in vivo and in vitro matured porcine
oocytes. Mol Reprod Dev. 64:492–498. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Powell SR: The antioxidant properties of
zinc. J Nutr. 130(5S Suppl): 1447S–1454S. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Bray TM and Bettger WJ: The physiological
role of zinc as an antioxidant. Free Radic Biol Med. 8:281–291.
1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Sato M and Bremner I: Oxygen free radicals
and metallothionein. Free Radic Biol Med. 14:325–337. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Olin KL, Golub MS, Gershwin ME, Hendrickx
AG, Lonnerdal B and Keen CL: Extracellular superoxide dismutase
activity is affected by dietary zinc intake in nonhuman primate and
rodent models. Am J Clin Nutr. 61:1263–1267. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Ho E and Ames BN: Low intracellular zinc
induces oxidative DNA damage, disrupts p53, NFkappa B, and AP1 DNA
binding, and affects DNA repair in a rat glioma cell line. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:16770–16775. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Oteiza PI, Clegg MS, Zago MP and Keen CL:
Zinc deficiency induces oxidative stress and AP-1 activation in 3T3
cells. Free Radic Biol Med. 28:1091–1099. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Song Y, Leonard SW, Traber MG and Ho E:
Zinc deficiency affects DNA damage, oxidative stress, antioxidant
defenses, and DNA repair in rats. J Nutr. 139:1626–1631. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|