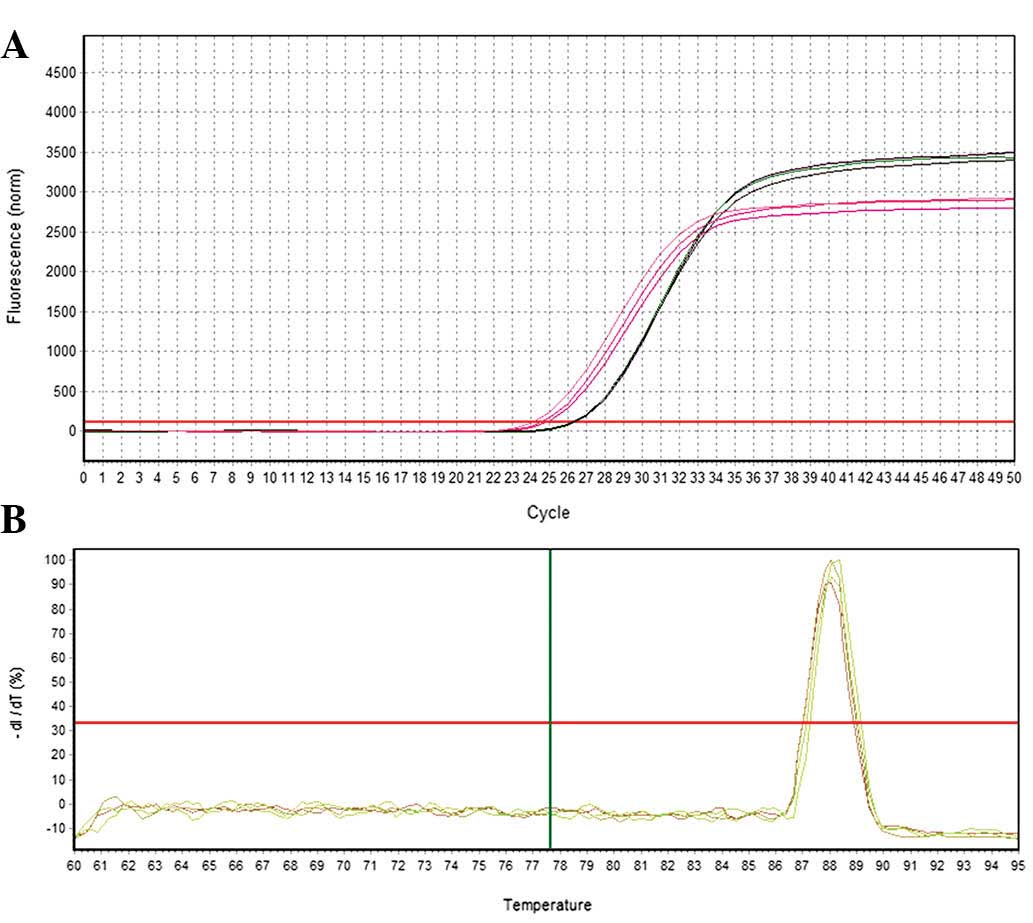
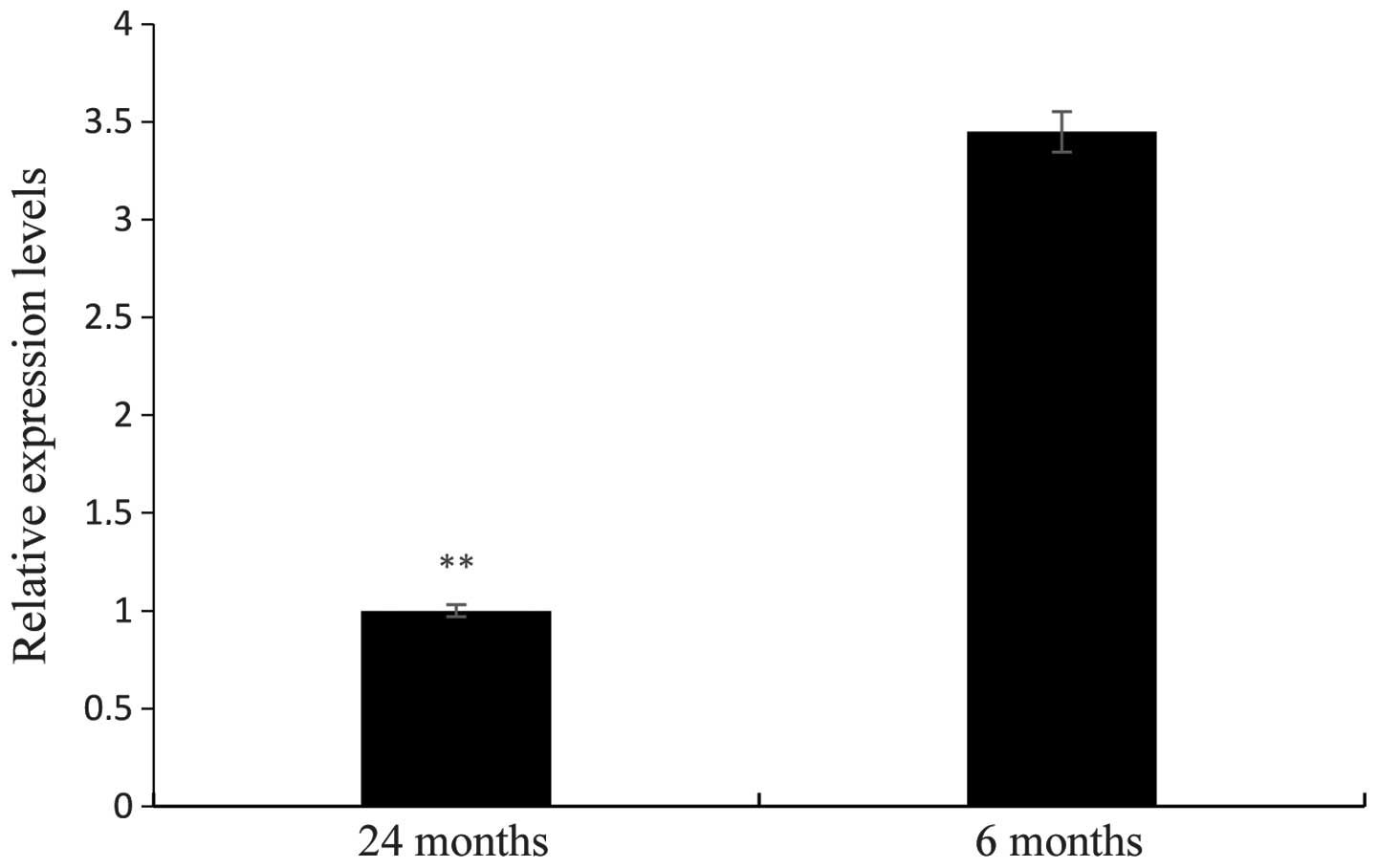
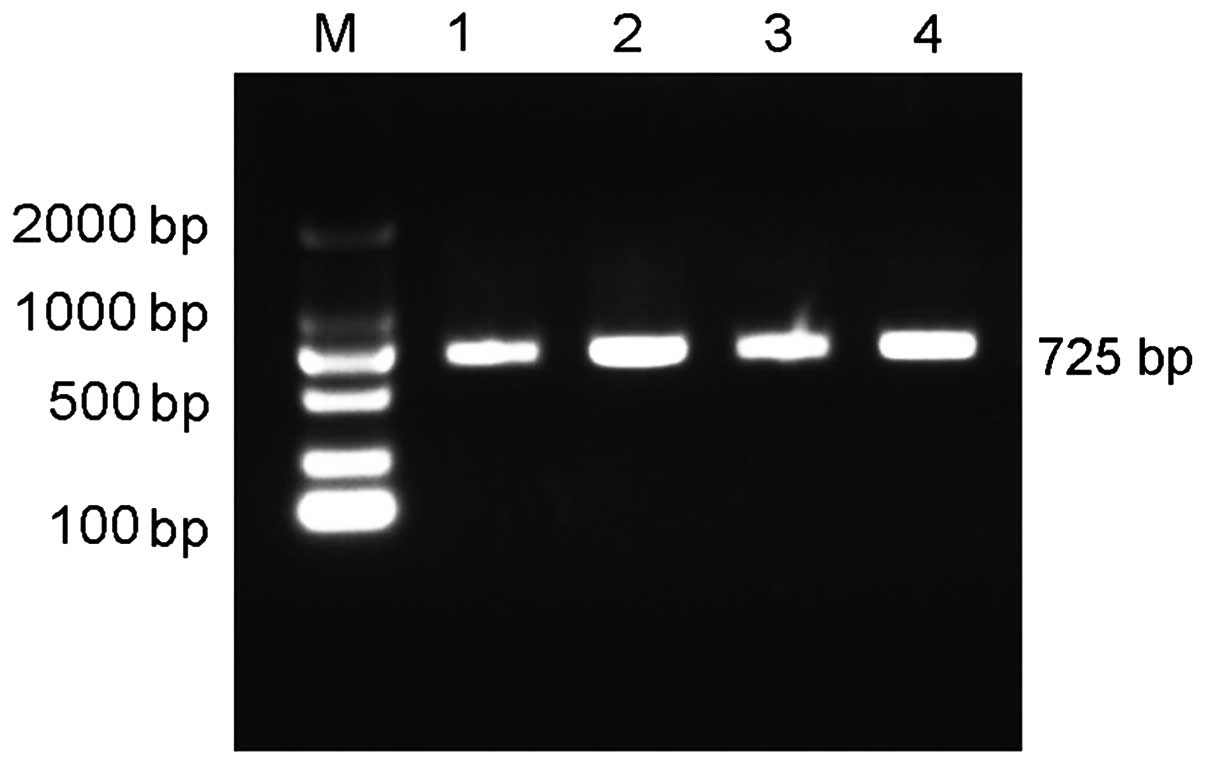
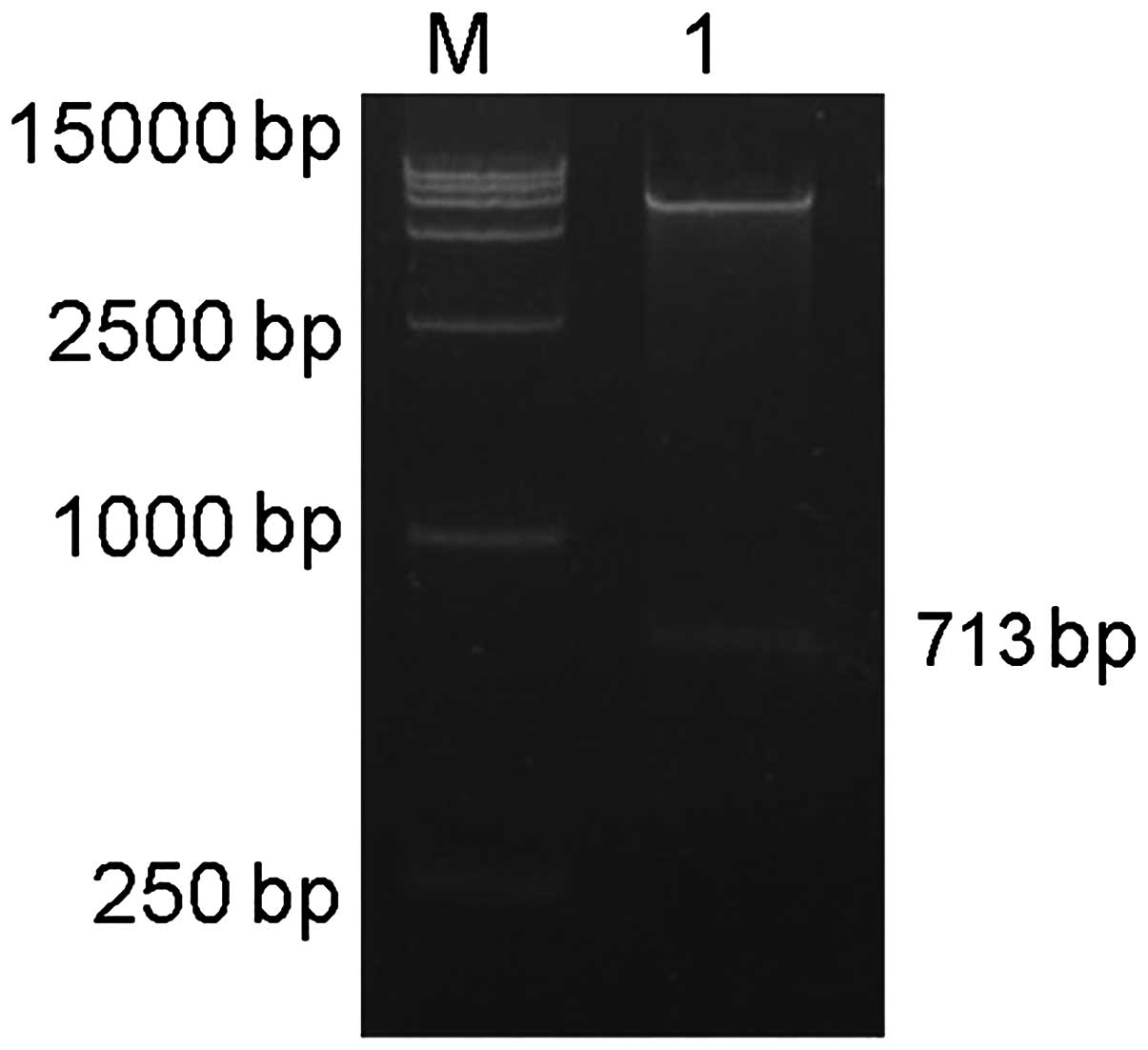
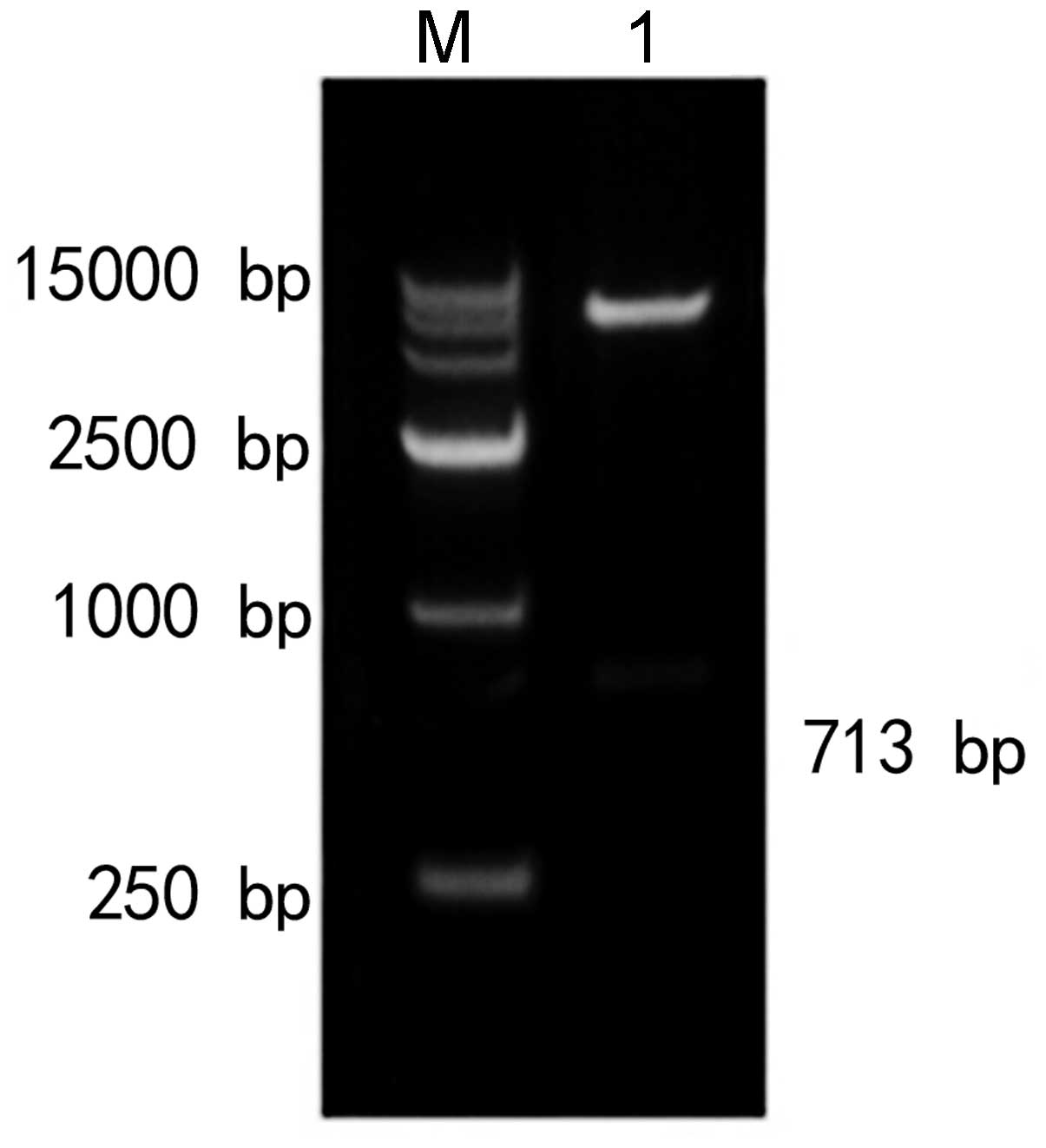
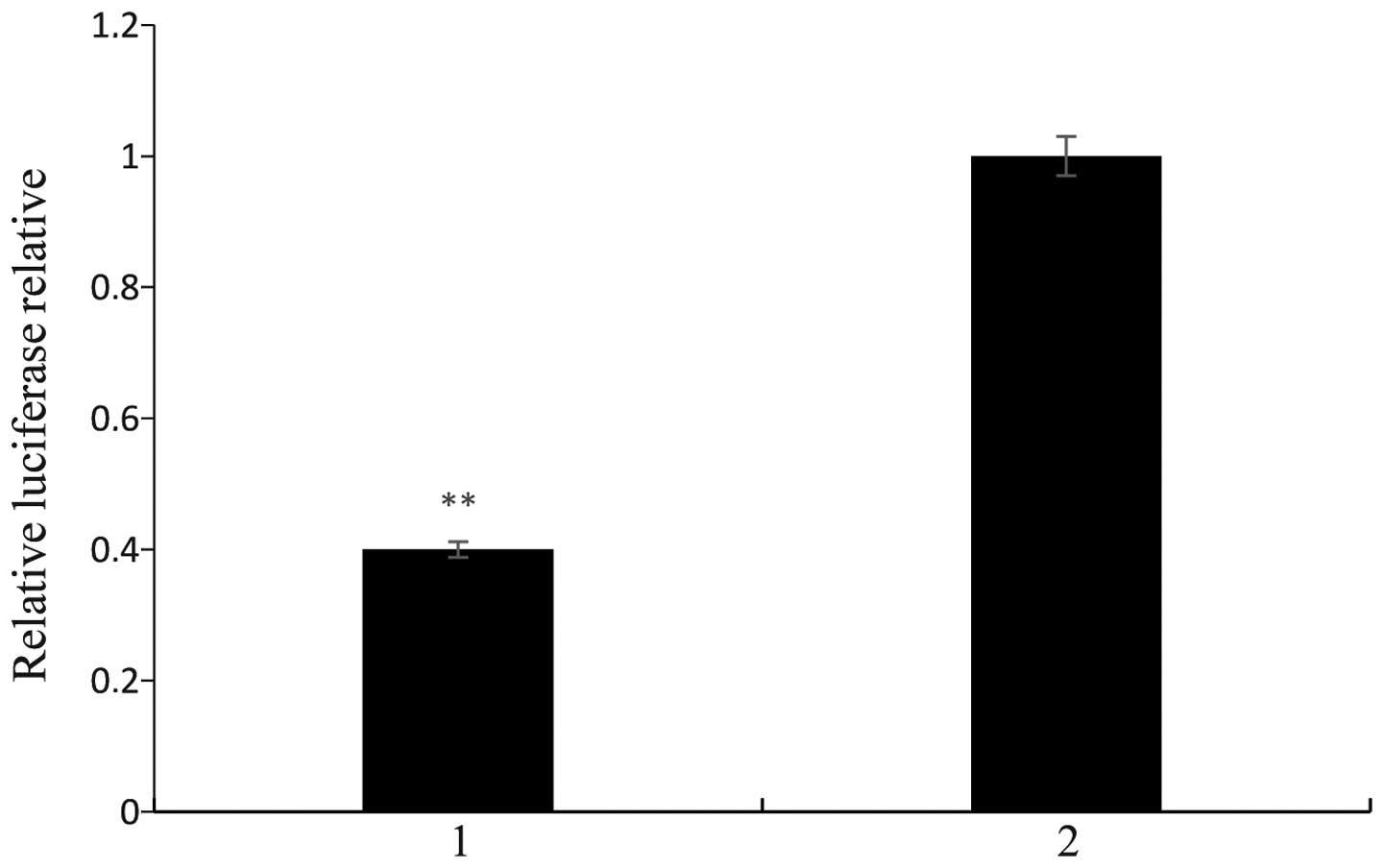
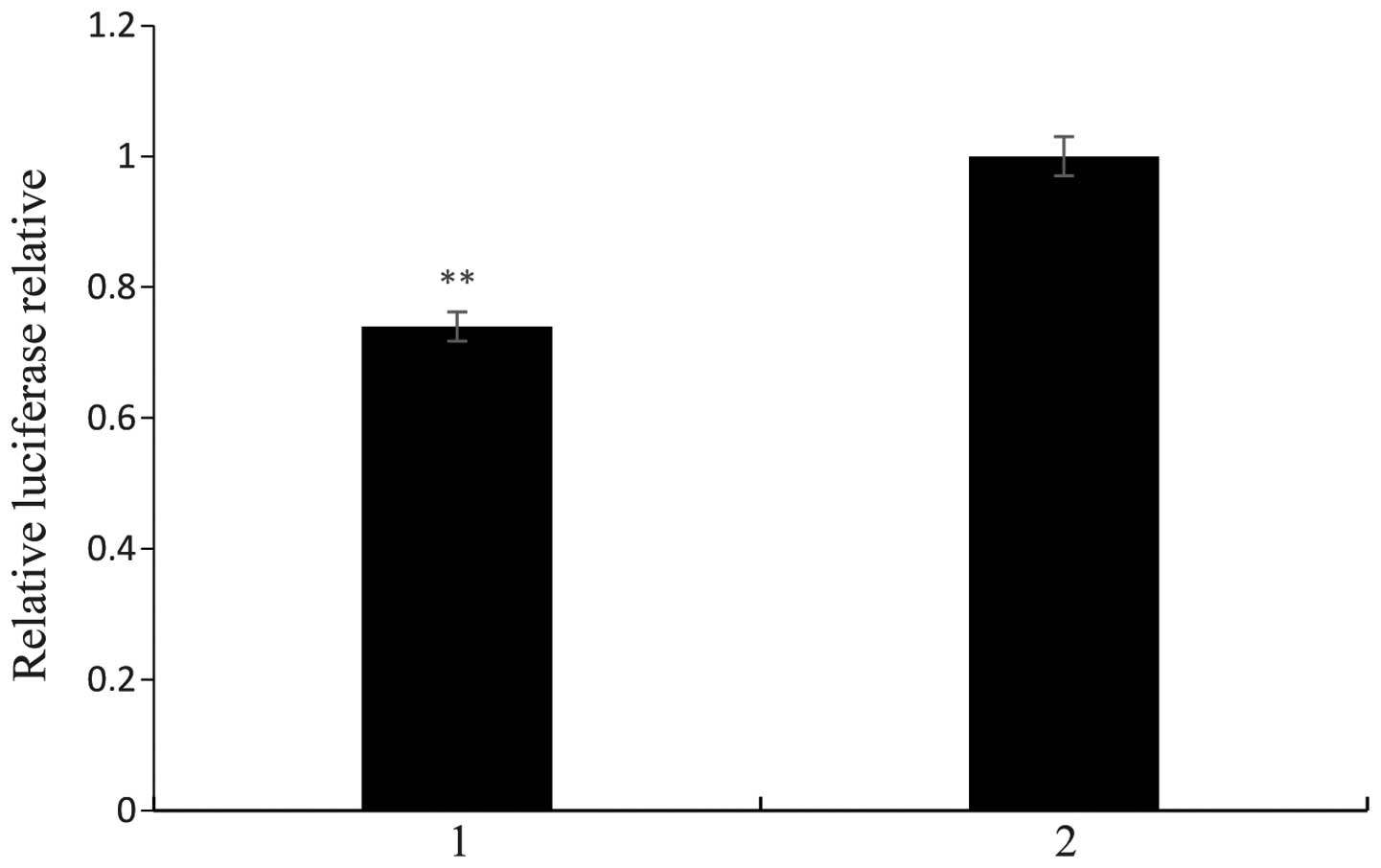
|
1
|
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL and Ambros V: The C.
elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense
complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 75:843–854. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pillai RS, Artus CG and Filipowicz W:
Tethering of human Ago proteins to mRNA mimics the miRNA-mediated
repression of protein synthesis. RNA. 10:1518–1525. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Beilharz TH, Humphreys DT and Preiss T:
miRNA Effects on mRNA closed-loop formation during translation
initiation. Prog Mol Subcell Biol. 50:99–112. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Hausser J, Landthaler M, Jaskiewicz L,
Gaidatzis D and Zavolan M: Relative contribution of sequence and
structure features to the mRNA binding of Argonaute/EIF2C-miRNA
complexes and the degradation of miRNA targets. Genome Res.
19:2009–2020. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Trakooljul N, Hicks JA and Liu HC:
Identification of target genes and pathways associated with chicken
microRNA miR-143. Anim Genet. 41:357–364. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bizuayehu TT, Fernandes JM, Johansen SD
and Babiak I: Characterization of novel precursor miRNAs using next
generation sequencing and prediction of miRNA targets in Atlantic
halibut. PLoS One. 8:e613782013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Barros-Carvalho GA, Paschoal AR,
Marcelino-Guimarães FC and Hungria M: Prediction of potential novel
microRNAs in soybean when in symbiosis. Genet Mol Res.
13:8519–8529. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Verghese ET, Drury R, Green CA, Holliday
DL, Lu X, Nash C, Speirs V, Thorne JL, Thygesen HH, Zougman A, Hull
MA, et al: MiR-26b is down-regulated in carcinoma-associated
fibroblasts from ER-positive breast cancers leading to enhanced
cell migration and invasion. J Pathol. 231:388–399. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Trompeter HI, Dreesen J, Hermann E,
Iwaniuk KM, Hafner M, Renwick N, Tuschl T and Wernet P: MicroRNAs
miR-26a, miR-26b, and miR-29b accelerate osteogenic differentiation
of unrestricted somatic stem cells from human cord blood. BMC
Genomics. 14:1112013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Alijani S, Alizadeh S, Kazemi A, Khatib
ZK, Soleimani M, Rezvani M, Minayi N, Karami F and Tayebi B:
Evaluation of the effect of miR-26b up-regulation on HbF expression
in erythroleukemic K-562 cell line. Avicenna J Med Biotechnol.
6:53–56. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lin J, Zhang L, Huang H, Huang Y, Huang L,
Wang J, Huang S, He L, Zhou Y and Jia W: MiR-26b/KPNA2 axis
inhibits epithelial ovarian carcinoma proliferation and metastasis
through downregulating OCT4. Oncotarget. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Miranda KC, Huynh T, Tay Y, Ang YS, Tam
WL, Thomson AM, Lim B and Rigoutsos I: A pattern-based method for
the identification of MicroRNA binding sites and their
corresponding heteroduplexes. Cell. 126:1203–1217. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Schmittgen TD, Zakrajsek BA, Mills AG, et
al: Quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction to
study mRNA decay: comparison of end-point and real-time methods.
Anal Biochem. 285:194–204. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hu Y, Li P, Hao S, et al: Differential
expression of microRNAs in the placentae of Chinese patients with
severe pre-eclampsia. Clin Chem Lab Med. 47:923–929. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ji Y, He Y, Liu L and Chong X: MiRNA-26b
regulates the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in
desferrioxamine-treated CNE cells. FEBS Lett. 584:961–967. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen H, Qian K, Tang ZP, et al:
Bioinformatics and microarray analysis of microRNA expression
profiles of murine embryonic stem cells, neural stem cells induced
from ESCs and isolated from E8.5 mouse neural tube. Neurol Res.
32:603–613. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Zhang Z, Florez S, Gutierrez-Hartmann A,
et al: MicroRNAs regulate pituitary development and microRNA 26b
specifically targets lymphoid enhancer factor 1 (Lef-1), which
modulates pituitary transcription factor 1 (Pit-1) expression. J
Biol Chem. 285:34718–34728. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang Z, Kim K, Li X, Moreno M, Sharp T,
Goodheart MJ, Safe S, Dupuy AJ and Amendt BA: MicroRNA-26b
represses colon cancer cell proliferation by inhibiting lymphoid
enhancer factor 1 expression. Mol Cancer Ther. 13:1942–1951. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Palagani A, Op De, Beeck K, Naulaerts S,
Diddens J, Sekhar Chirumamilla C, Van Camp G, Laukens K, Heyninck
K, Gerlo S, Mestdagh P, et al: Ectopic microRNA-150-5p
transcription sensitizes glucocorticoid therapy response in MM1S
multiple myeloma cells but fails to overcome hormone therapy
resistance in MM1R cells. PLoS One. 9:e1138422014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xu G, Shi C, Ji C, Song G, Chen L, Yang L,
Zhao Y and Guo X: Expression of microRNA-26b, an obesity-related
microRNA, is regulated by free fatty acids, glucose, dexamethasone
and growth hormone in human adipocytes. Mol Med Rep. 10:223–228.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Palumbo T, Faucz FR, Azevedo M, Xekouki P,
Iliopoulos D and Stratakis CA: Functional screen analysis reveals
miR-26b and miR-128 as central regulators of pituitary
somatomammotrophic tumor growth through activation of the PTEN-AKT
pathway. Oncogene. 32:1651–1659. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Song G, Xu G, Ji C, Shi C, Shen Y, Chen L,
Zhu L, Yang L, Zhao Y and Guo X: The role of microRNA-26b in human
adipocyte differentiation and prowliferation. Gene. 533:481–487.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Xu G, Ji C, Song G, Shi C, Shen Y, Chen L,
Yang L, Zhao Y and Guo X: Obesity associated microRNA26b regulates
the proliferation of human preadipocytes via arrest of the G1/S
transition. Mol Med Rep. 12:3648–3654. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kinch MS and Carles-Kinch K:
Overexpression and functional alterations of the EphA2 tyrosine
kinase in cancer. Clin Exp Metastasis. 20:59–68. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dodelet VC and Pasquale EB: Eph receptors
and ephrin ligands: embryogenesis to tumorigenesis. Oncogene.
19:5614–5619. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rosenbegr IM, Göke M, Kanai M, et al:
Epithelial cell kinase-B61: an autocrine loop modulating intestinal
epithelial migration and barrier function. Am J Physiol.
273:G824–G832. 1997.
|
|
27
|
Miao H, Wei BR, Peehl DM, et al:
Activation of EphA receptor tyrosine kinase inhibits the Ras/MAPK
pathway. Nat Cell Biol. 3:527–530. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fujii H, Tatsumi K, Kosaka K, et al:
EPh-ephrin A system regulates murine blastocyst attachment and
sreading. Dev Dyn. 235:3250–3258. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wu N, Zhao X, Liu M, et al: Role of
microRNA-26b in glioma development and its mediated regulation on
EphA2. PLoS One. 6:e162642011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|