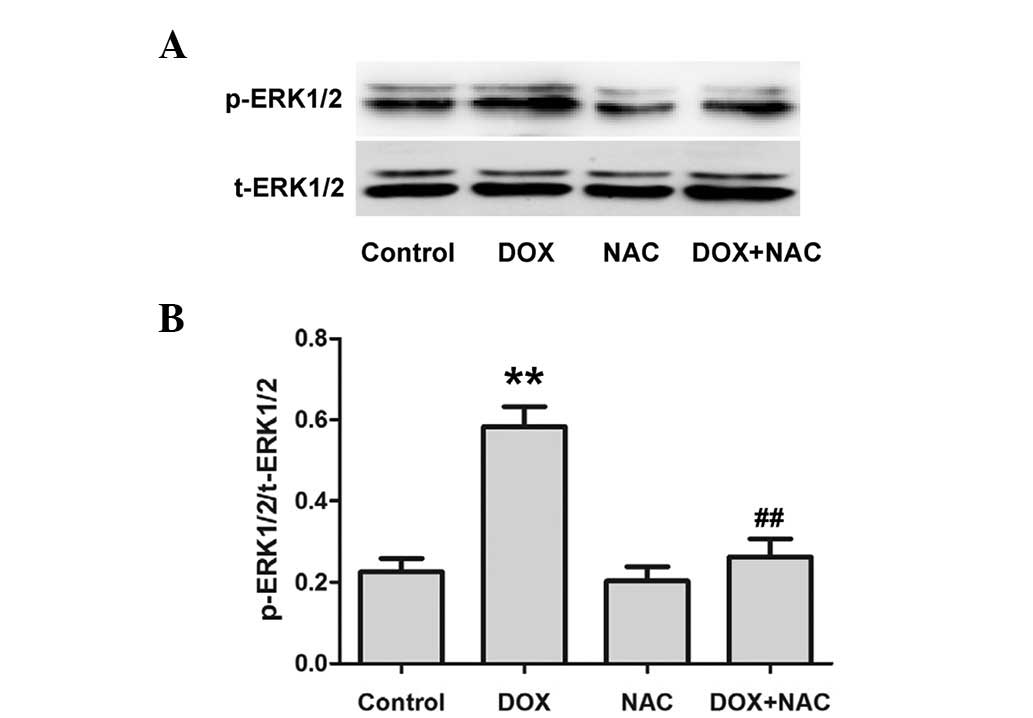
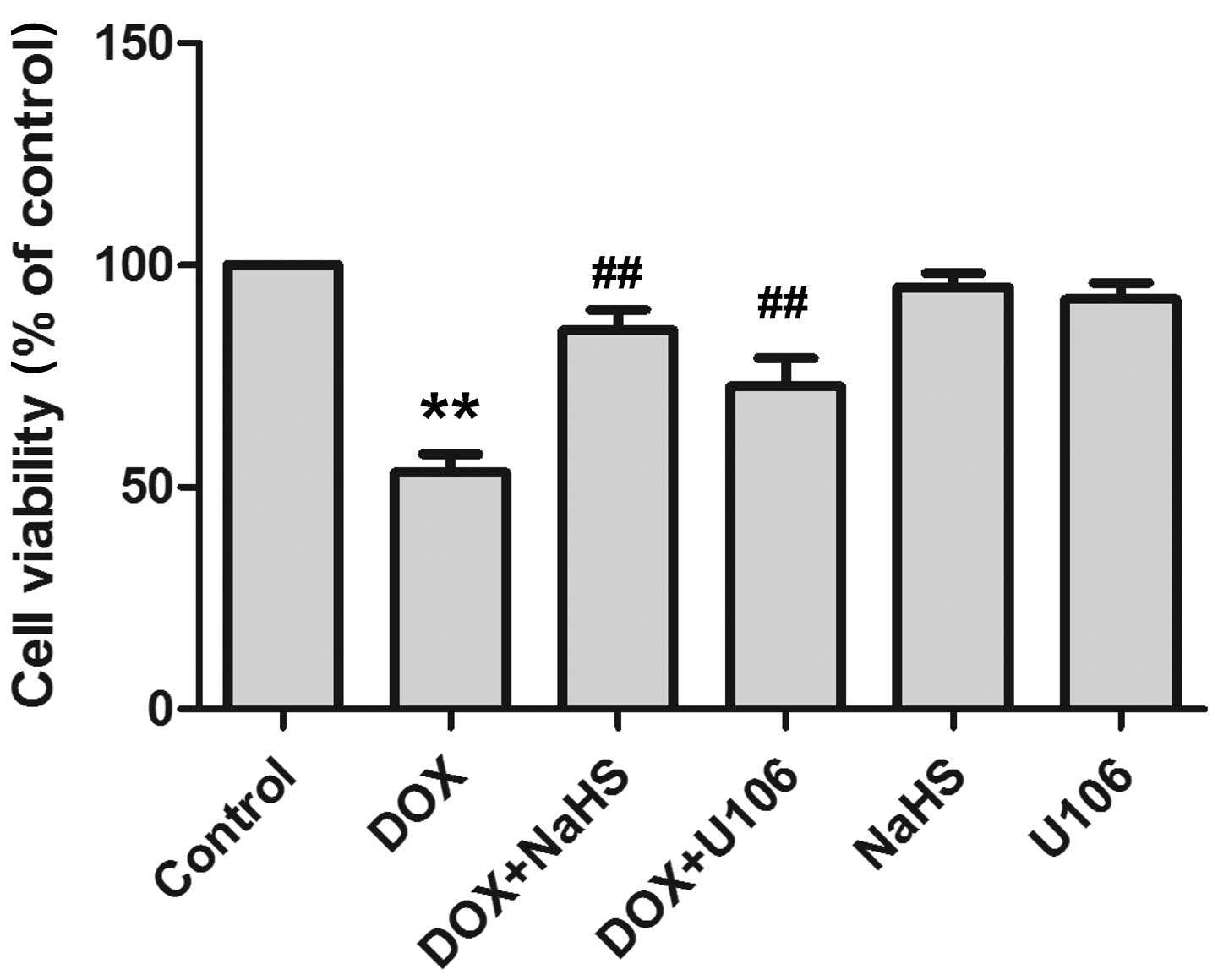
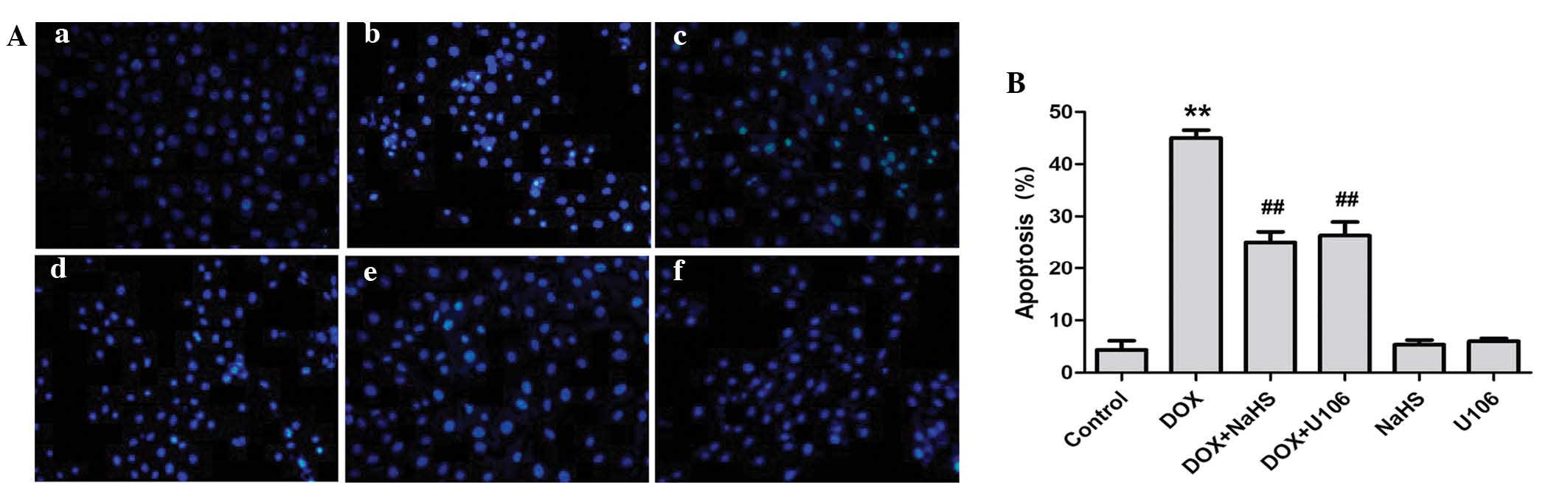
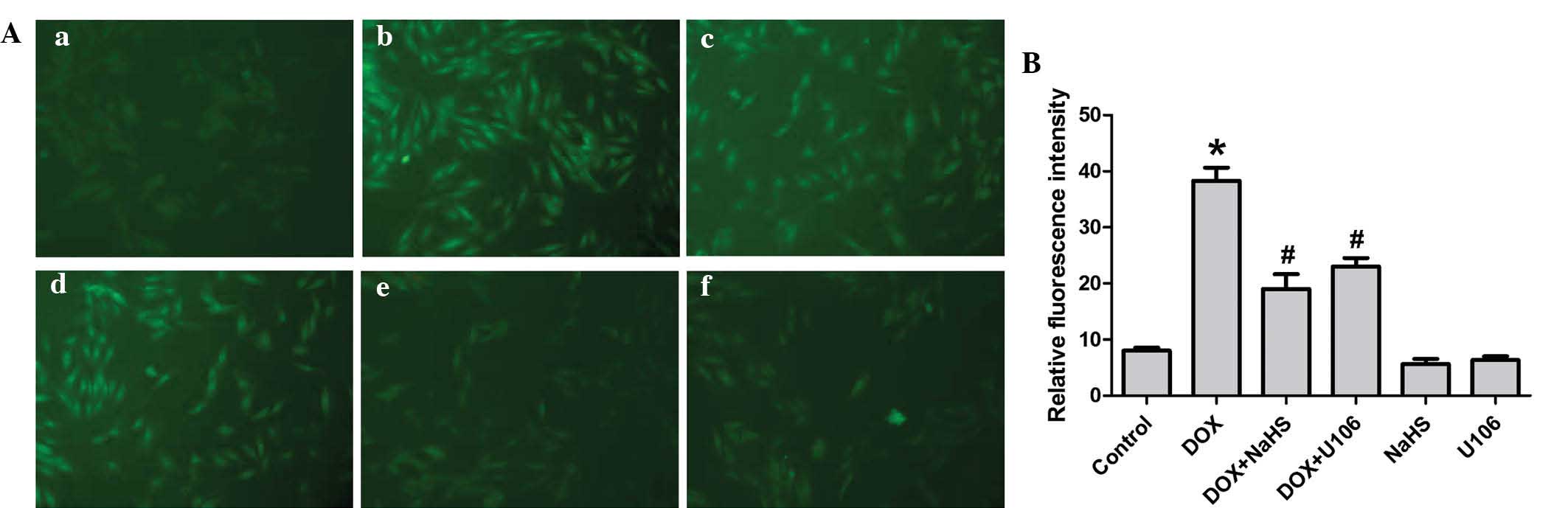
|
1
|
Menna P, Recalcati S, Cairo G and Minotti
G: An introduction to the metabolic determinants of anthracycline
cardiotoxicity. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 7:80–85. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lipshultz SE, Karnik R, Sambatakos P,
Franco VI, Ross SW and Miller TL: Anthracycline-related
cardiotoxicity in childhood cancer survivors. Curr Opin Cardiol.
29:103–112. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Spallarossa P, Garibaldi S, Altieri P,
Fabbi P, Manca V, Nasti S, Rossettin P, Ghigliotti G, Ballestrero
A, Patrone F, et al: Carvedilol prevents doxorubicin-induced free
radical release and apoptosis in cardiomyocytes in vitro. J Mol
Cell Cardiol. 37:837–846. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liu MH, Zhang Y, Lin XL, He J, Tan TP, Wu
SJ, Yu S, Chen L, Chen YD, Fu HY, et al: Hydrogen sulfide
attenuates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity through inhibiting
calreticulin expression in H9c2 cells. Mol Med Rep. Jul 2–2015.Epub
ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Zhang Y, Tang ZH, Ren Z, Qu SL, Liu MH,
Liu LS and Jiang ZS: Hydrogen sulfide, the next potent preventive
and therapeutic agent in aging and age-associated diseases. Mol
Cell Biol. 33:1104–1113. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Huang YE, Tang ZH, Xie W, Shen XT, Liu MH,
Peng XP, Zhao ZZ, Nie DB, Liu LS and Jiang ZS: Endogenous hydrogen
sulfide mediates the cardioprotection induced by ischemic
post-conditioning in the early reperfusion phase. Exp Ther Med.
4:1117–1123. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Grisanti LA, Talarico JA, Carter RL, Yu
JE, Repas AA, Radcliffe SW, Tang HA, Makarewich CA, Houser SR and
Tilley DG: β-Adrenergic receptor-mediated transactivation of
epidermal growth factor receptor decreases cardiomyocyte apoptosis
through differential subcellular activation of ERK1/2 and Akt. J
Mol Cell Cardiol. 72:39–51. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xu W, Wu W, Chen J, Guo R, Lin J, Liao X
and Feng J: Exogenous hydrogen sulfide protects H9c2 cardiac cells
against high glucose-induced injury by inhibiting the activities of
the p38 MAPK and ERK1/2 pathways. Int J Mol Med. 32:917–925.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lou H, Danelisen I and Singal PK:
Involvement of mitogen-activated protein kinases in
adriamycin-induced cardiomyopathy. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
288:H1925–H1930. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu J, Mao W, Ding B and Liang CS:
ERKs/p53 signal transduction pathway is involved in doxorubicin
induced apoptosis in H9c2 cells and cardiomyocytes. Am J Physiol
Heart Circ Physiol. 295:H1956–H1965. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Du J, Hui Y, Cheung Y, Bin G, Jiang H,
Chen X and Tang C: The possible role of hydrogen sulfide as a
smooth muscle cell proliferation inhibitor in rat cultured cells.
Heart Vessels. 19:75–80. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Oh GS, Pae HO, Lee BS, Kim BN, Kim JM, Kim
HR, Jeon SB, Jeon WK, Chae HJ and Chung HT: Hydrogen sulfide
inhibits nitric oxide production and nuclear factor-kappaB via heme
oxygenase-1 expression in RAW264.7 macrophages stimulated with
lipopolysaccharide. Free Radic Biol Med. 41:106–119. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Adhikari S and Bhatia M:
H2S-induced pancreatic acinar cell apoptosis is mediated
via JNK and p38 MAP kinase. J Cell Mol Med. 12:1374–1383. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang G, Yang W, Wu L and Wang R:
H2S, endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis of
insulin-secreting beta cells. J Biol Chem. 282:16567–16576. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Guo R, Lin J, Xu W, Shen N, Mo L, Zhang C
and Feng J: Hydrogen sulfide attenuates doxorubicin-induced
cardiotoxicity by inhibition of the p38 MAPK pathway in H9c2 cells.
Int J Mol Med. 31:644–650. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kimura H: Hydrogen sulfide: Its
production, release and functions. Amino Acids. 41:113–121. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Wang X, Wang XL, Chen HL, Wu D, Chen JX,
Wang XX, Li RL, He JH, Mo L, Cen X, et al: Ghrelin inhibits
doxorubicin cardio-toxicity by inhibiting excessive autophagy
through AMPK and p38-MAPK. Biochem Pharmacol. 88:334–350. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Guo R, Wu K, Chen J, Mo L, Hua X, Zheng D,
Chen P, Chen G, Xu W and Feng J: Exogenous hydrogen sulfide
protects against doxorubicin-induced inflammation and cytotoxicity
by inhibiting p38MAPK/NFkappaB pathway in H9c2 cardiac cells. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 32:1668–1680. 2013.
|
|
19
|
Łowicka E and Bełtowski J: Hydrogen
sulfide (H2S)-the third gas of interest for
pharmacologists. Pharmacol Rep. 59:4–24. 2007.
|
|
20
|
Ji Y, Pang QF, Xu G, Wang L, Wang JK and
Zeng YM: Exogenous hydrogen sulfide postconditioning protects
isolated rat hearts against ischemia-reperfusion injury. Eur J
Pharmacol. 587:1–7. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Osipov RM, Robich MP, Feng J, Liu Y,
Clements RT, Glazer HP, Sodha NR, Szabo C, Bianchi C and Sellke FW:
Effect of hydrogen sulfide in a porcine model of myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion: comparison of different administration
regimens and characterization of the cellular mechanisms of
protection. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 54:287–297. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sodha NR, Clements RT, Feng J, Liu Y,
Bianchi C, Horvath EM, Szabo C and Sellke FW: The effects of
therapeutic sulfide on myocardial apoptosis in response to
ischemia-reperfusion injury. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 33:906–913.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Pan TT, Feng ZN, Lee SW, Moore PK and Bian
JS: Endogenous hydrogen sulfide contributes to the cardioprotection
by metabolic inhibition preconditioning in the rat ventricular
myocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 40:119–130. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Bian JS, Yong QC, Pan TT, Feng ZN, Ali MY,
Zhou S and Moore PK: Role of hydrogen sulfide in the
cardioprotection caused by ischemic preconditioning in the rat
heart and cardiac myocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 316:670–678.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Javadov S, Jang S and Agostini B:
Crosstalk between mitogenactivated protein kinases and mitochondria
in cardiac diseases: Therapeutic perspectives. Pharmacol Ther.
144:202–225. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu J, Mao W, Ding B and Liang CS:
ERKs/p53 signal transduction pathway is involved in
doxorubicin-induced apoptosis in H9c2 cells and cardiomyocytes. Am
J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 295:H1956–H1965. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhou B, Wu LJ, Tashiro S, Onodera S,
Uchiumi F and Ikejima T: Activation of extracellular
signal-regulated kinase during silibinin-protected,
isoproterenol-induced apoptosis in rat cardiac myocytes is tyrosine
kinase pathway-mediated and protein kinase C-dependent. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 28:803–810. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jiang CM, Han LP, Li HZ, Qu YB, Zhang ZR,
Wang R, Xu CQ and Li WM: Calcium-sensing receptors induce apoptosis
in cultured neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes during
simulated ischemia/reperfusion. Cell Biol Int. 32:792–800. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gómez-Fernández JC: Functions of the
C-terminal domains of apoptosis-related proteins of the Bcl-2
family. Chem Phys Lipids. 183:77–90. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Renault TT and Manon S: Bax: Addressed to
kill. Biochimie. 93:1379–1391. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|