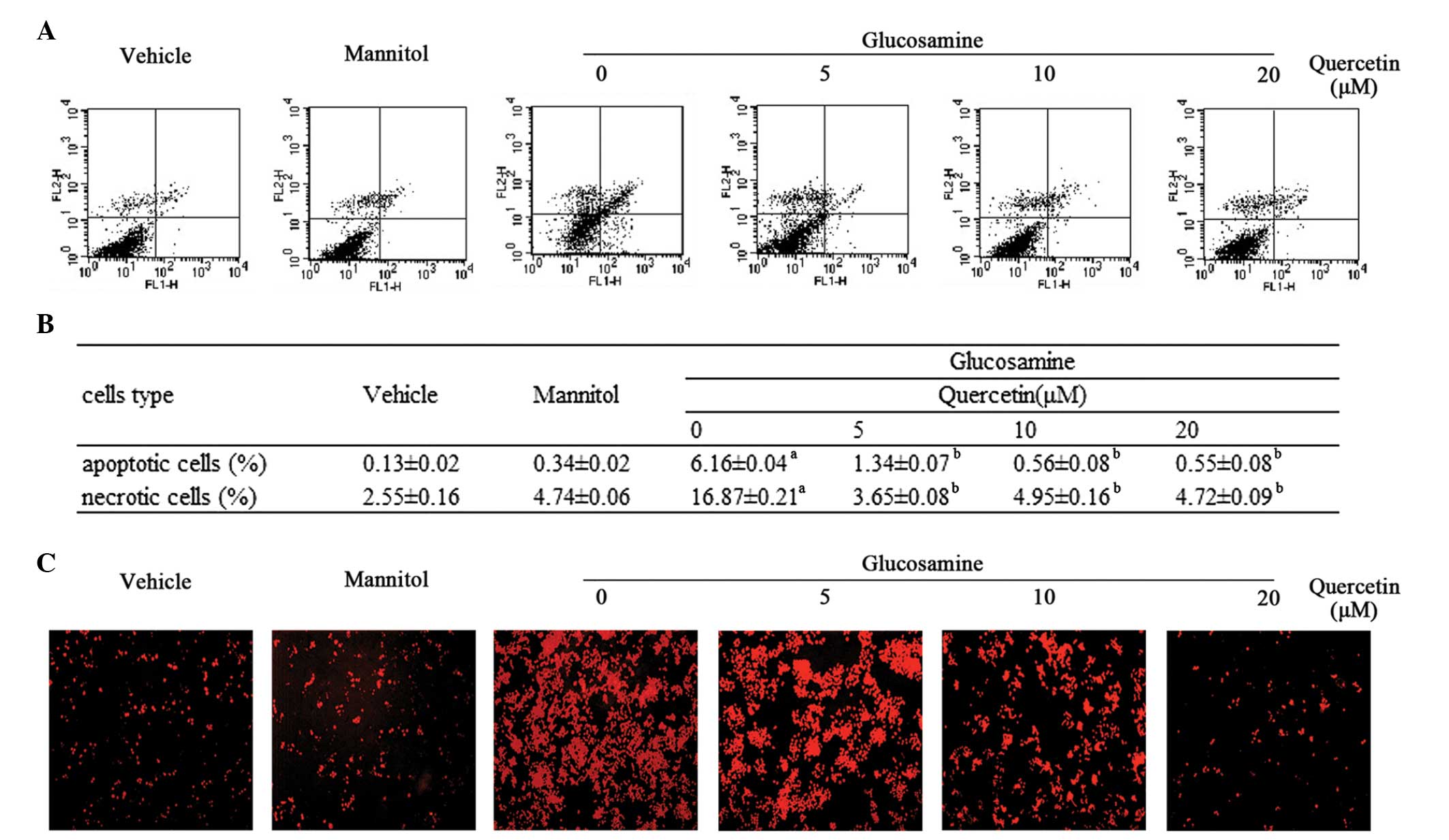
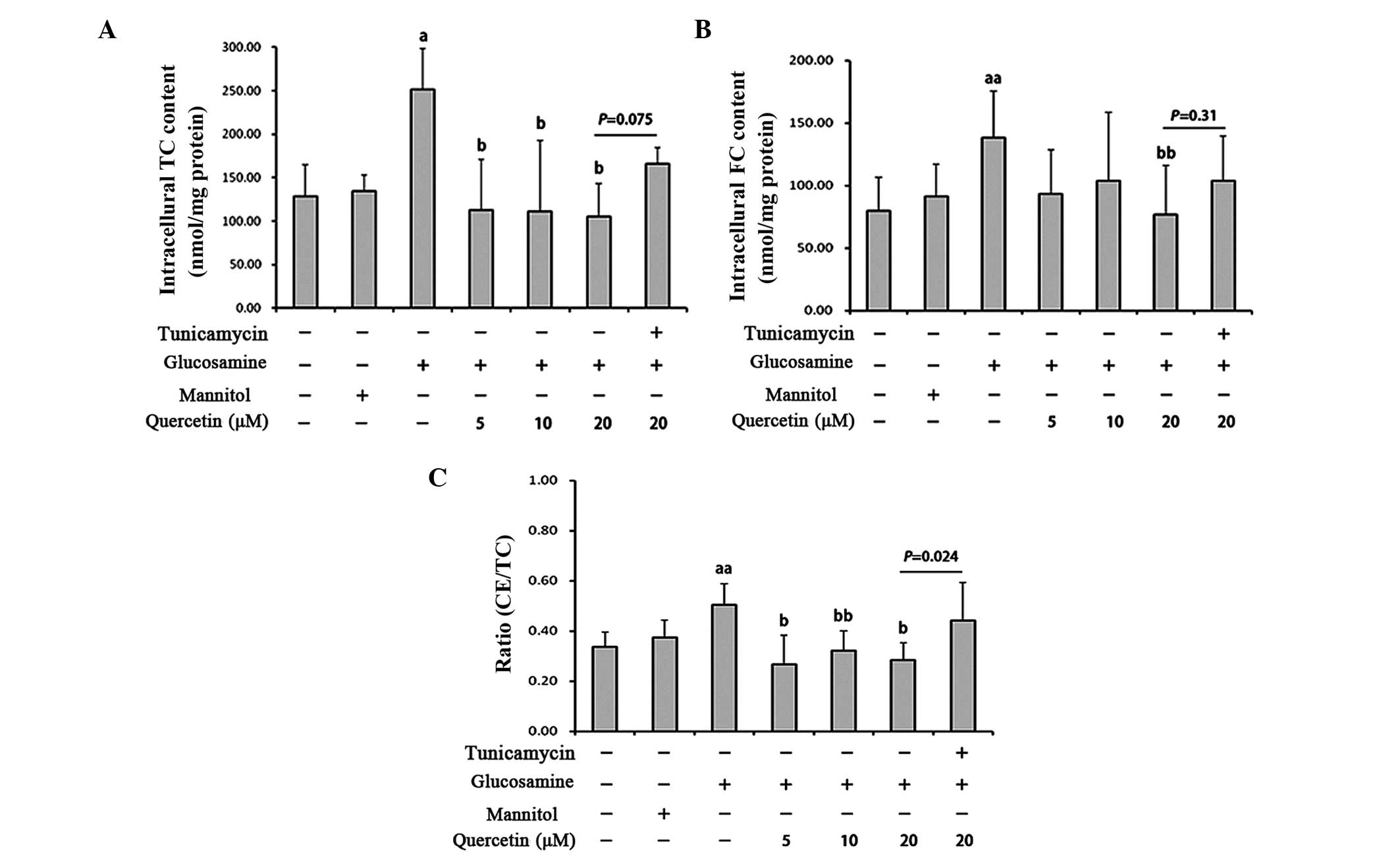
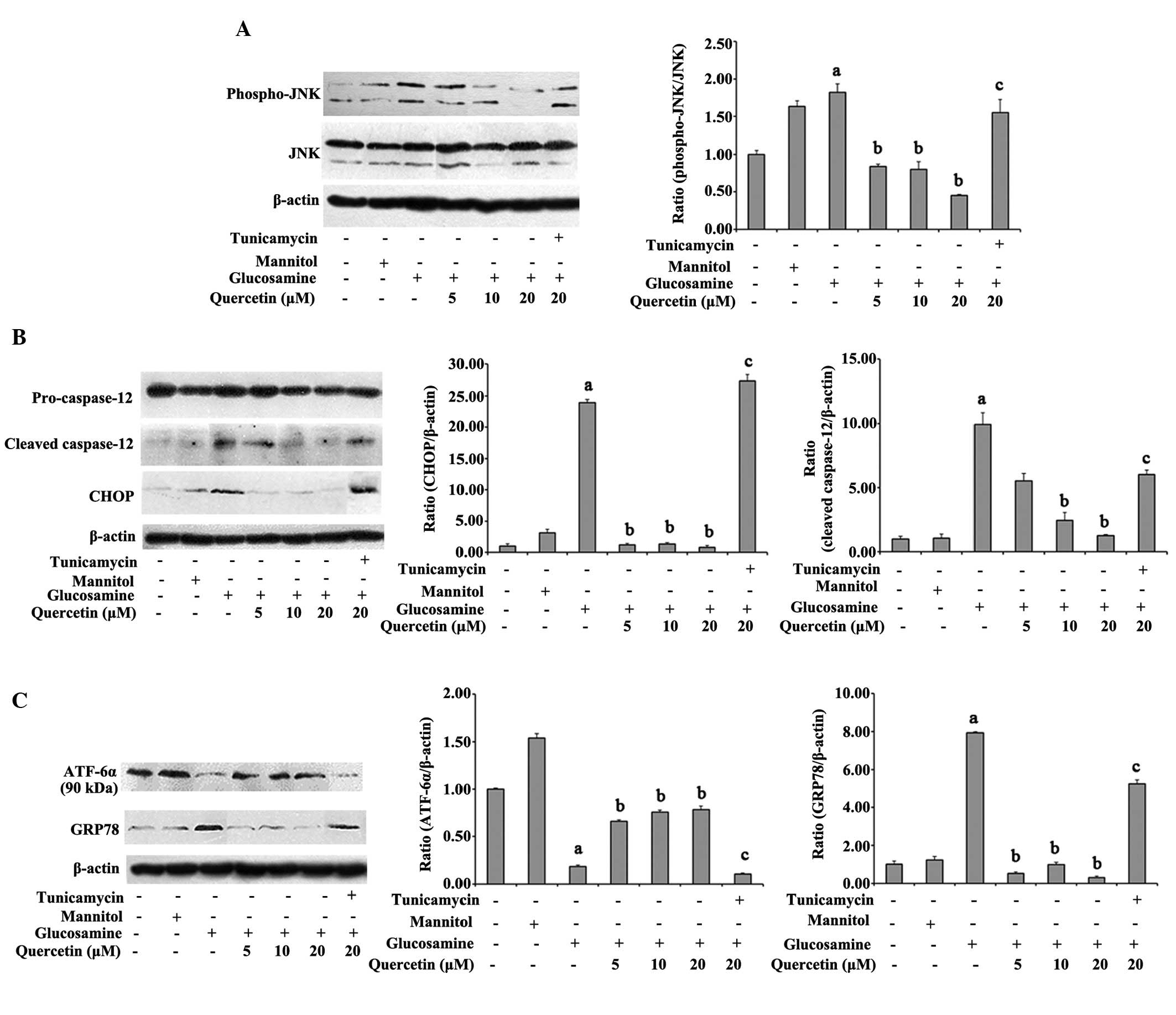
|
1
|
Stamler J, Vaccaro O, Neaton JD and
Wentworth D: Diabetes, other risk factors and 12-yr cardiovascular
mortality for men screened in the multiple risk factor intervention
trial. Diabetes Care. 16:434–444. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Whiting DR, Guariguata L, Weil C and Shaw
J: IDF diabetes atlas: Global estimates of the prevalence of
diabetes for 2011 and 2030. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 94:311–321.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Beckman JA, Creager MA and Libby P:
Diabetes and atherosclerosis: Epidemiology, pathophysiology and
management. JAMA. 287:2570–2581. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tannock LR, Kirk EA, King VL, LeBoeuf R,
Wight TN and Chait A: Glucosamine supplementation accelerates early
but not late atherosclerosis in LDL receptor-deficient mice. J
Nutr. 136:2856–2861. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Largo R, Martínez-Calatrava MJ,
Sánchez-Pernaute O, Marcos ME, Moreno-Rubio J, Aparicio C, Egido J
and Herrero-Beaumont G: Effect of a high dose of glucosamine on
systemic and tissue inflammation in an experimental model of
atherosclerosis aggravated by chronic arthritis. Am J Physiol Heart
Circ Physiol. 297:H268–H276. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nowak A, Szcześniak L, Rychlewski T,
Dylewicz P and Przywarska I: Glucosamine levels in people with
ischaemic heart disease with and without type II diabetes. Pol Arch
Med Wewn. 100:419–425. 1998.
|
|
7
|
Beriault DR, Sharma S, Shi Y, Khan MI and
Werstuck GH: Glucosamine-supplementation promotes endoplasmic
reticulum stress, hepatic steatosis and accelerated atherogenesis
in apoE−/− mice. Atherosclerosis. 219:134–140. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Werstuck GH, Khan MI, Femia G, Kim AJ,
Tedesco V, Trigatti B and Shi Y: Glucosamine-induced endoplasmic
reticulum dysfunction is associated with accelerated
atherosclerosis in a hyperglycemic mouse model. Diabetes.
55:93–101. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Qiu W, Avramoglu RK, Rutledge AC, Tsai J
and Adeli K: Mechanisms of glucosamine-induced suppression of the
hepatic assembly and secretion of apolipoprotein B-100-containing
lipo-proteins. J Lipid Res. 47:1749–1761. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Egert S, Bosy-Westphal A, Seiberl J,
Kürbitz C, Settler U, Plachta-Danielzik S, Wagner AE, Frank J,
Schrezenmeir J, Rimbach G, et al: Quercetin reduces systolic blood
pressure and plasma oxidised low-density lipoprotein concentrations
in overweight subjects with a high-cardiovascular disease risk
phenotype: A double-blinded, placebo-controlled cross-over study.
Br J Nutr. 102:1065–1074. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Larson A, Witman MA, Guo Y, Ives S,
Richardson RS, Bruno RS, Jalili T and Symons JD: Acute,
quercetin-induced reductions in blood pressure in hypertensive
individuals are not secondary to lower plasma
angiotensin-converting enzyme activity or endo-thelin-1: Nitric
oxide. Nutr Res. 32:557–564. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Edwards RL, Lyon T, Litwin SE, Rabovsky A,
Symons JD and Jalili T: Quercetin reduces blood pressure in
hypertensive subjects. J Nutr. 137:2405–2411. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pfeuffer M, Auinger A, Bley U,
Kraus-Stojanowic I, Laue C, Winkler P, Rüfer CE, Frank J,
Bösch-Saadatmandi C, Rimbach G and Schrezenmeir J: Effect of
quercetin on traits of the metabolic syndrome, endothelial function
and inflammation in men with different APOE isoforms. Nutr Metab
Cardiovasc Dis. 23:403–409. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Knab AM, Shanely RA, Henson DA, Jin F,
Heinz SA, Austin MD and Nieman DC: Influence of quercetin
supplementation on disease risk factors in community-dwelling
adults. J Am Diet Assoc. 111:542–549. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kleemann R, Verschuren L, Morrison M,
Zadelaar S, van Erk MJ, Wielinga PY and Kooistra T:
Anti-inflammatory, anti-proliferative and anti-atherosclerotic
effects of quercetin in human in vitro and in vivo models.
Atherosclerosis. 218:44–52. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Garelnabi M, Mahini H and Wilson T:
Quercetin intake with exercise modulates lipoprotein metabolism and
reduces atherosclerosis plaque formation. J Int Soc Sports Nutr.
11:222014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bhaskar S, Kumar KS, Krishnan K and Antony
H: Quercetin alleviates hypercholesterolemic diet induced
inflammation during progression and regression of atherosclerosis
in rabbits. Nutrition. 29:219–229. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Juźwiak S, Wójcicki J, Mokrzycki K,
Marchlewicz M, Białecka M, Wenda-Rózewicka L, Gawrońska-Szklarz B
and Droździk M: Effect of quercetin on experimental hyperlipidemia
and atherosclerosis in rabbits. Pharmacol Rep. 57:604–609.
2005.
|
|
19
|
Kim JH, Kang MJ, Choi HN, Jeong SM, Lee YM
and Kim JI: Quercetin attenuates fasting and postprandial
hyperglycemia in animal models of diabetes mellitus. Nutr Res
Pract. 5:107–111. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kawai Y, Nishikawa T, Shiba Y, Saito S,
Murota K, Shibata N, Kobayashi M, Kanayama M, Uchida K and Terao J:
Macrophage as a target of quercetin glucuronides in human
atherosclerotic arteries: Implication in the anti-atherosclerotic
mechanism of dietary flavonoids. J Biol Chem. 283:9424–9434. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lara-Guzman OJ, Tabares-Guevara JH,
Leon-Varela YM, Álvarez RM, Roldan M, Sierra JA, Londoño-Londoño JA
and Ramirez-Pineda JR: Proatherogenic macrophage activities are
targeted by the flavonoid quercetin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther.
343:296–306. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mao W, Fukuoka S, Iwai C, Liu J, Sharma
VK, Sheu SS, Fu M and Liang CS: Cardiomyocyte apoptosis in
autoimmune cardiomyopathy: Mediated via endoplasmic reticulum
stress and exaggerated by norepinephrine. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 293:H1636–H645. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Okada K, Minamino T, Tsukamoto Y, Liao Y,
Tsukamoto O, Takashima S, Hirata A, Fujita M, Nagamachi Y, Nakatani
T, et al: Prolonged endoplasmic reticulum stress in hypertrophic
and failing heart after aortic constriction: Possible contribution
of endoplasmic reticulum stress to cardiac myocyte apoptosis.
Circulation. 110:705–712. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yao S, Sang H, Song G, Yang N, Liu Q,
Zhang Y, Jiao P, Zong C and Qin S: Quercetin protects macrophages
from oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced apoptosis by
inhibiting the endoplasmic reticulum stress-C/EBP homologous
protein pathway. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 237:822–831. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Liu CM, Zheng GH, Ming QL, Sun JM and
Cheng C: Protective effect of quercetin on lead-induced oxidative
stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress in rat liver via the
IRE1/JNK and PI3K/Akt pathway. Free Radic Res. 47:192–201. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Chao CL, Hou YC, Chao PD, Weng CS and Ho
FM: The antioxidant effects of quercetin metabolites on the
prevention of high glucose-induced apoptosis of human umbilical
vein endothelial cells. Br J Nutr. 101:1165–1170. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Gu L, Bai W, Li S, Zhang Y, Han Y, Gu Y,
Meng G, Xie L, Wang J, Xiao Y, et al: Celastrol prevents
atherosclerosis via inhibiting LOX-1 and oxidative stress. PLoS
One. 8:e654772013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Urano F, Wang X, Bertolotti A, Zhang Y,
Chung P, Harding HP and Ron D: Coupling of stress in the ER to
activation of JNK protein kinases by transmembrane protein kinase
IRE1. Science. 287:664–666. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang K and Kaufman RJ: From
endoplasmic-reticulum stress to the inflammatory response. Nature.
454:455–462. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ozcan U, Yilmaz E, Ozcan L, Furuhashi M,
Vaillancourt E, Smith RO, Görgün CZ and Hotamisligil GS: Chemical
chaperones reduce ER stress and restore glucose homeostasis in a
mouse model of type 2 diabetes. Science. 313:1137–1140. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fribley A, Zhang K and Kaufman RJ:
Regulation of apoptosis by the unfolded protein response. Methods
Mol Biol. 559:191–204. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Khan MI, Pichna BA, Shi Y, Bowes AJ and
Werstuck GH: Evidence supporting a role for endoplasmic reticulum
stress in the development of atherosclerosis in a hyperglycaemic
mouse model. Antioxid Redox Signal. 11:2289–2298. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tabas I: Apoptosis and plaque
destabilization in atherosclerosis: The role of macrophage
apoptosis induced by cholesterol. Cell Death Differ. 11(Suppl 1):
S12–S16. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hansson GK: Inflammation, atherosclerosis
and coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med. 352:1685–1695. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Han S, Liang CP, DeVries-Seimon T,
Ranalletta M, Welch CL, Collins-Fletcher K, Accili D, Tabas I and
Tall AR: Macrophage insulin receptor deficiency increases ER
stress-induced apoptosis and necrotic core formation in advanced
atherosclerotic lesions. Cell Metab. 3:257–266. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Duan W, Paka L and Pillarisetti S:
Distinct effects of glucose and glucosamine on vascular endothelial
and smooth muscle cells: Evidence for a protective role for
glucosamine in atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 4:162005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chow JM, Shen SC, Huan SK, Lin HY and Chen
YC: Quercetin, but not rutin and quercitrin, prevention of
H2O2-induced apoptosis via anti-oxidant activity and heme oxygenase
1 gene expression in macrophages. Biochem Pharmacol. 69:1839–1851.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Garige M, Gong M, Varatharajalu R and
Lakshman MR: Quercetin up-regulates paraoxonase 1 gene expression
via sterol regulatory element binding protein 2 that translocates
from the endoplasmic reticulum to the nucleus where it specifically
interacts with sterol responsive element-like sequence in
paraoxonase 1 promoter in HuH7 liver cells. Metabolism.
59:1372–1378. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Fogelman AM, Shechter I, Seager J, Hokom
M, Child JS and Edwards PA: Malondialdehyde alteration of low
density lipoproteins leads to cholesteryl ester accumulation in
human monocyte-macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 77:2214–2218.
1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bao L, Cai X, Zhang Z and Li Y: Grape seed
procyanidin B2 ameliorates mitochondrial dysfunction and inhibits
apoptosis via the AMP-activated protein kinase-silent mating type
information regulation 2 homologue 1-PPARγ co-activator-1α axis in
rat mesangial cells under high-dose glucosamine. Br J Nutr. 1–10.
2014.Epub Ahead of Print.
|
|
41
|
Kang ES, Han D, Park J, Kwak TK, Oh MA,
Lee SA, Choi S, Park ZY, Kim Y and Lee JW: O-GlcNAc modulation at
Akt1 Ser473 correlates with apoptosis of murine pancreatic beta
cells. Exp Cell Res. 314:2238–2248. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ma J and Hart GW: Protein O-GlcNAcylation
in diabetes and diabetic complications. Expert Rev Proteomics.
10:365–380. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hawkins M, Angelov I, Liu R, Barzilai N
and Rossetti L: The tissue concentration of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine
modulates the stimulatory effect of insulin on skeletal muscle
glucose uptake. J Biol Chem. 272:4889–4895. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Marshall S, Bacote V and Traxinger RR:
Discovery of a metabolic pathway mediating glucose-induced
desensitization of the glucose transport system. Role of hexosamine
biosyn-thetic in the induction of insulin resistance. J Biol Chem.
266:4706–4712. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Burke AP, Kolodgie FD, Zieske A, Fowler
DR, Weber DK, Varghese PJ, Farb A and Virmani R: Morphologic
findings of coronary atherosclerotic plaques in diabetics: A
postmortem study. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 24:1266–1271.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Han I, Oh ES and Kudlow JE: Responsiveness
of the state of O-linked N-acetylglucosamine modification of
nuclear pore protein p62 to the extracellular glucose
concentration. Biochem J. 15:109–114. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Roshanzamir F and Yazdanparast R:
Quercetin attenuates cell apoptosis of oxidant-stressed SK-N-MC
cells while suppressing up-regulation of the defensive element,
HIF-1α. Neuroscience. 277:780–793. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Suganya N, Bhakkiyalakshmi E,
Suriyanarayanan S, Paulm urugan R and Ramkumar KM: Quercetin
ameliorates tunic-amycin-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress in
endothelial cells. Cell Prolif. 47:231–240. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Dai X, Ding Y, Zhang Z, Cai X and Li Y:
Quercetin and quercitrin protect against cytokine-induced injuries
in RINm5F β-cells via the mitochondrial pathway and NF-κB
signaling. Int J Mol Med. 31:265–271. 2013.
|
|
50
|
Xu C, Bailly-Maitre B and Reed JC:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress: Cell life and death decisions. J Clin
Invest. 115:2656–2664. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Chistiakov DA, Sobenin IA, Orekhov AN and
Bobryshev YV: Role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in
atherosclerosis and diabetic macrovascular complications. Biomed
Res Int. 6101402014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Beriault DR, Sharma S, Shi Y, Khan MI and
Werstuck GH: Glucosamine-supplementation promotes endoplasmic
reticulum stress, hepatic steatosis and accelerated atherogenesis
in apoE−/− mice. Atherosclerosis. 219:134–40. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Liu CM, Zheng GH, Ming QL, Sun JM and
Cheng C: Protective effect of quercetin on lead-induced oxidative
stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress in rat liver via the
IRE1/JNK and PI3K/Akt pathway. Free Radic Res. 47:192–201. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Xu LH, Xie H, Shi ZH, Du LD, Wing YK, Li
AM, Ke Y and Yung WH: Critical role of endoplasmic reticulum stress
in chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced deficits in synaptic
plasticity and long-term memory. Antioxid Redox Signal. May
8–2015.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
55
|
van der Kallen CJ, van Greevenbroek MM,
Stehouwer CD and Schalkwijk CG: Endoplasmic reticulum
stress-induced apoptosis in the development of diabetes: Is there a
role for adipose tissue and liver? Apoptosis. 14:1424–1434. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Minamino T and Kitakaze M: ER stress in
cardiovascular disease. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 48:1105–1110. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Zinszner H, Kuroda M, Wang X, Batchvarova
N, Lightfoot RT, Remotti H, Stevens JL and Ron D: CHOP is
implicated in programmed cell death in response to impaired
function of the endoplasmic reticulum. Genes Dev. 12:982–995. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Tsukano H, Gotoh T, Endo M, Miyata K,
Tazume H, Kadomatsu T, Yano M, Iwawaki T, Kohno K, Araki K, et al:
The endoplasmic reticulum stress-C/EBP homologous protein
pathway-mediated apoptosis in macrophages contributes to the
instability of atherosclerotic plaques. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc
Biol. 30:1925–1932. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Hu P, Han Z, Couvillon AD, Kaufman RJ and
Exton JH: Autocrine tumor necrosis factor alpha links endoplasmic
reticulum stress to the membrane death receptor pathway through
IRE1alpha-mediated NF-kappaB activation and down-regulation of
TRAF2 expression. Mol Cell Biol. 26:3071–3084. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Chen S, Zhao Y, Zhang Y and Zhang D:
Fucoidan induces cancer cell apoptosis by modulating the
endoplasmic reticulum stress cascades. PLoS One. 9:e1081572014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Nakagawa T, Zhu H, Morishima N, Li E, Xu
J, Yankner BA and Yuan J: Caspase-12 mediates
endoplasmic-reticulum-specific apoptosis and cytotoxicity by
amyloid-beta. Nature. 403:98–103. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Tabas I: The role of endoplasmic reticulum
stress in the progression of atherosclerosis. Circ Res.
107:839–850. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Yamamoto K, Sato T, Matsui T, Sato M,
Okada T, Yoshida H, Harada A and Mori K: Transcriptional induction
of mammalian ER quality control proteins is mediated by single or
combined action of ATF6alpha and XBP1. Dev Cell. 13:365–376. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Yamamoto K, Takahara K, Oyadomari S, Okada
T, Sato T, Harada A and Mori K: Induction of liver steatosis and
lipid droplet formation in ATF6alpha-knockout mice burdened with
pharmacological endoplasmic reticulum stress. Mol Biol Cell.
21:2975–2986. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Rutkowski DT, Wu J, Back SH, Callaghan MU,
Ferris SP, Iqbal J, Clark R, Miao H, Hassler JR, Fornek J, et al:
UPR pathways combine to prevent hepatic steatosis caused by ER
stress-mediated suppression of transcriptional master regulators.
Dev Cell. 15:829–840. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|