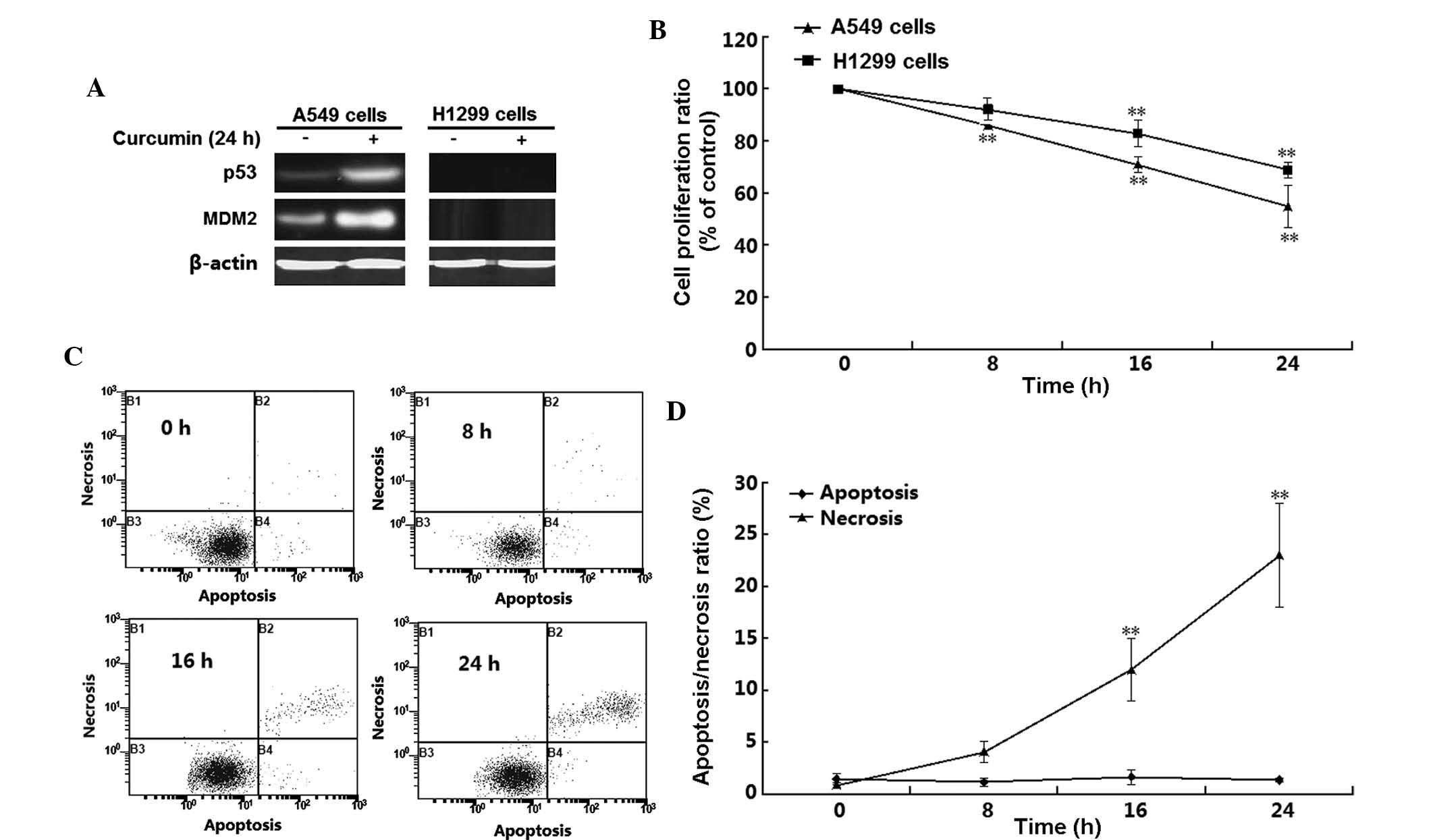
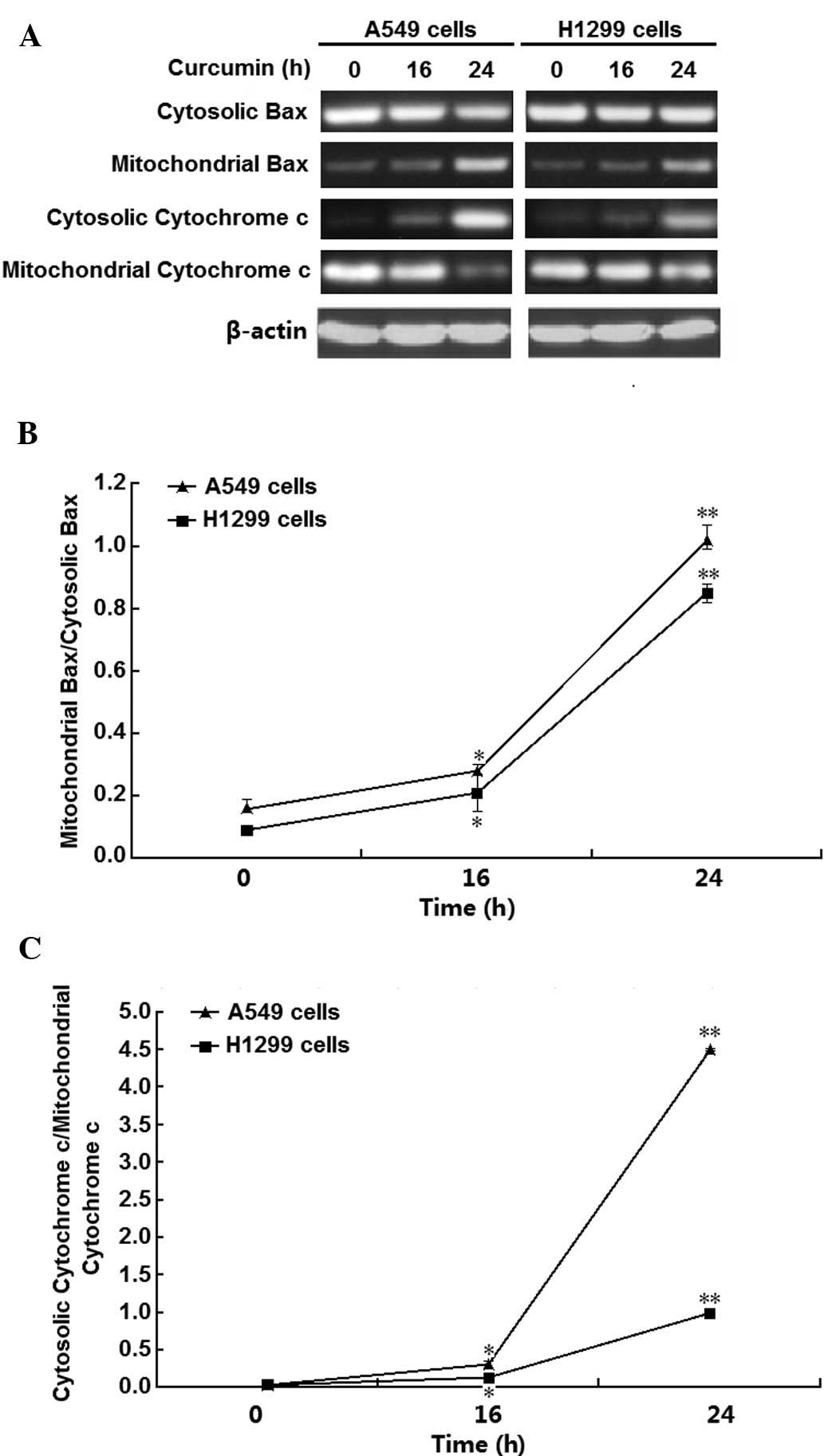
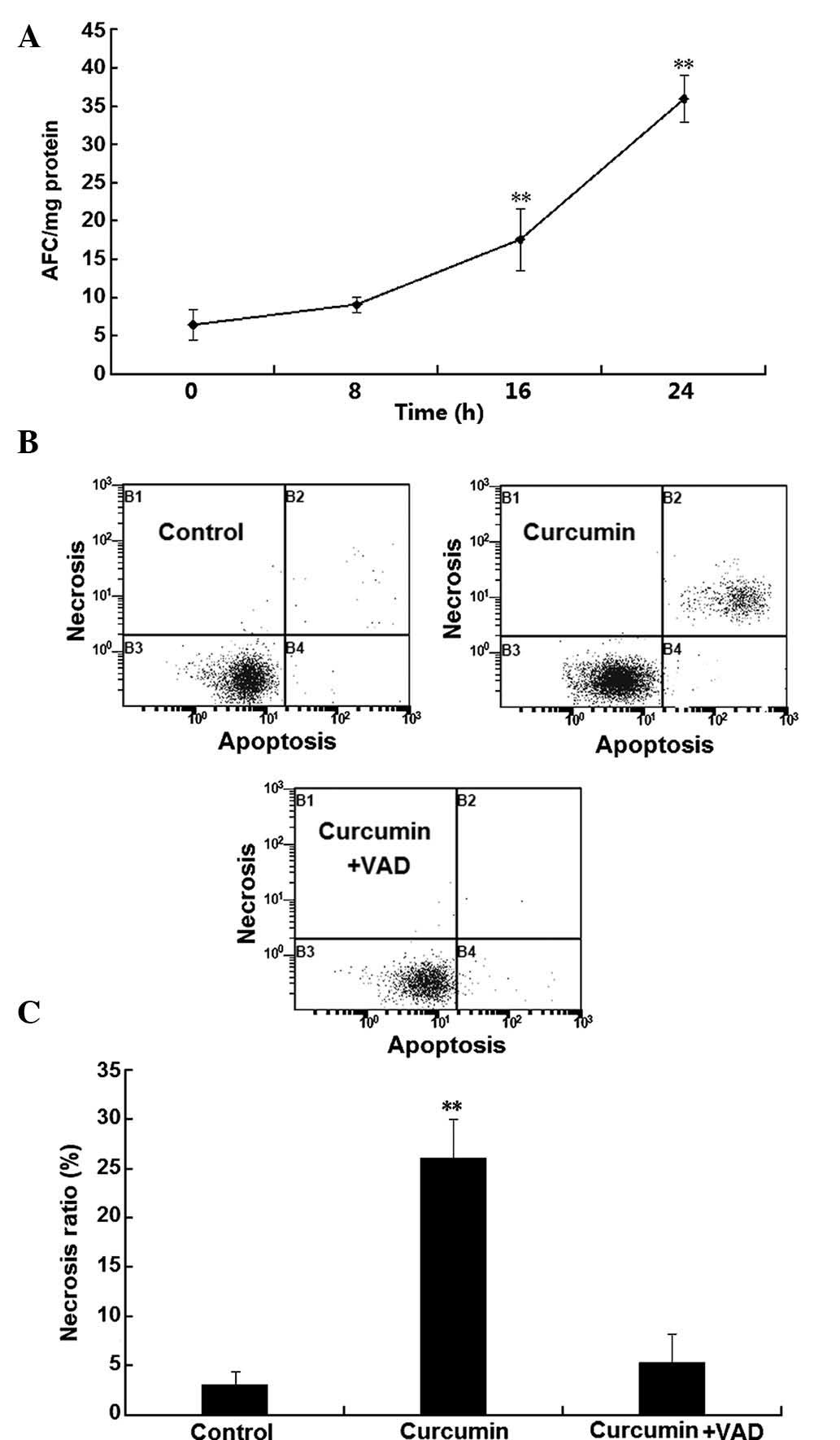
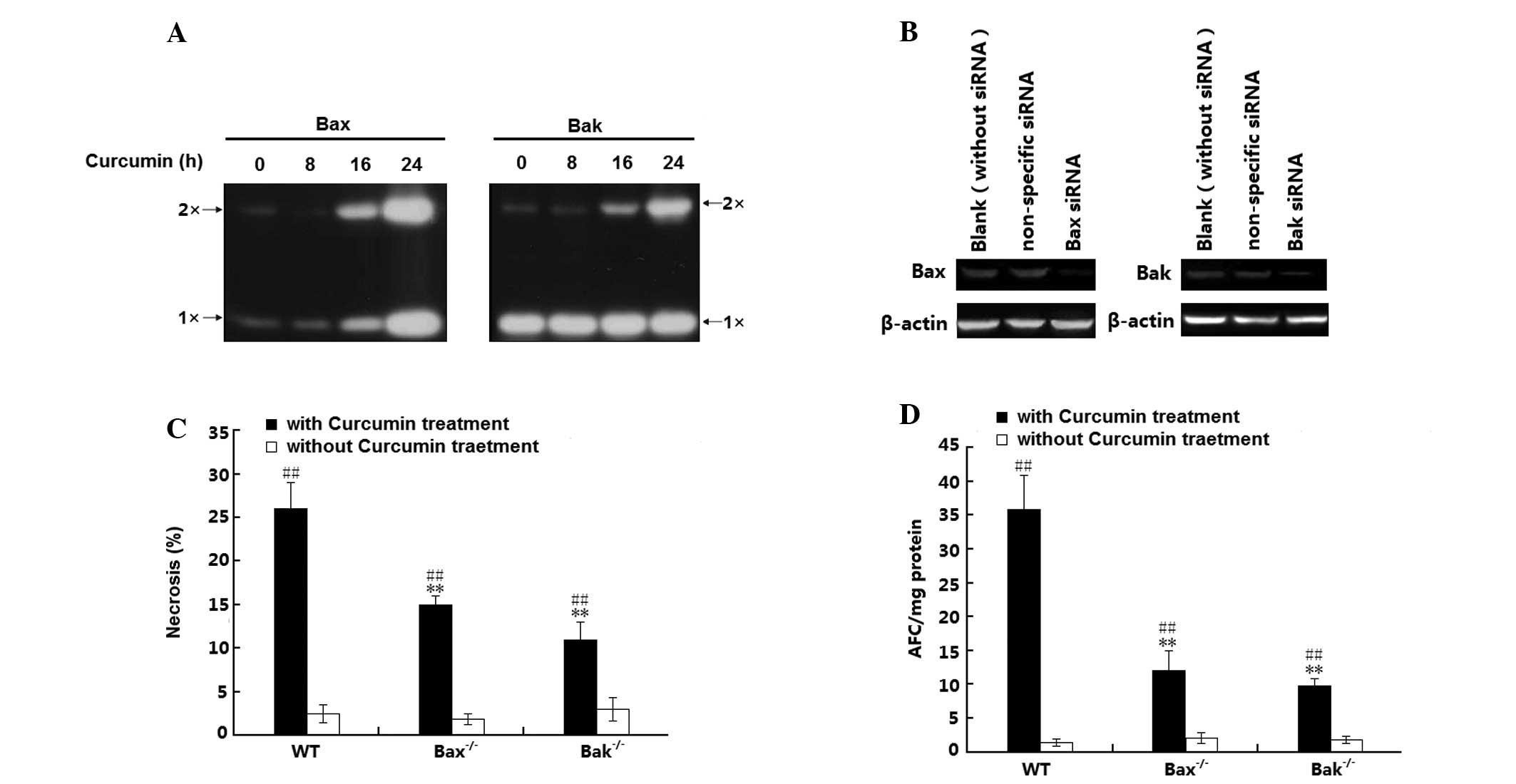
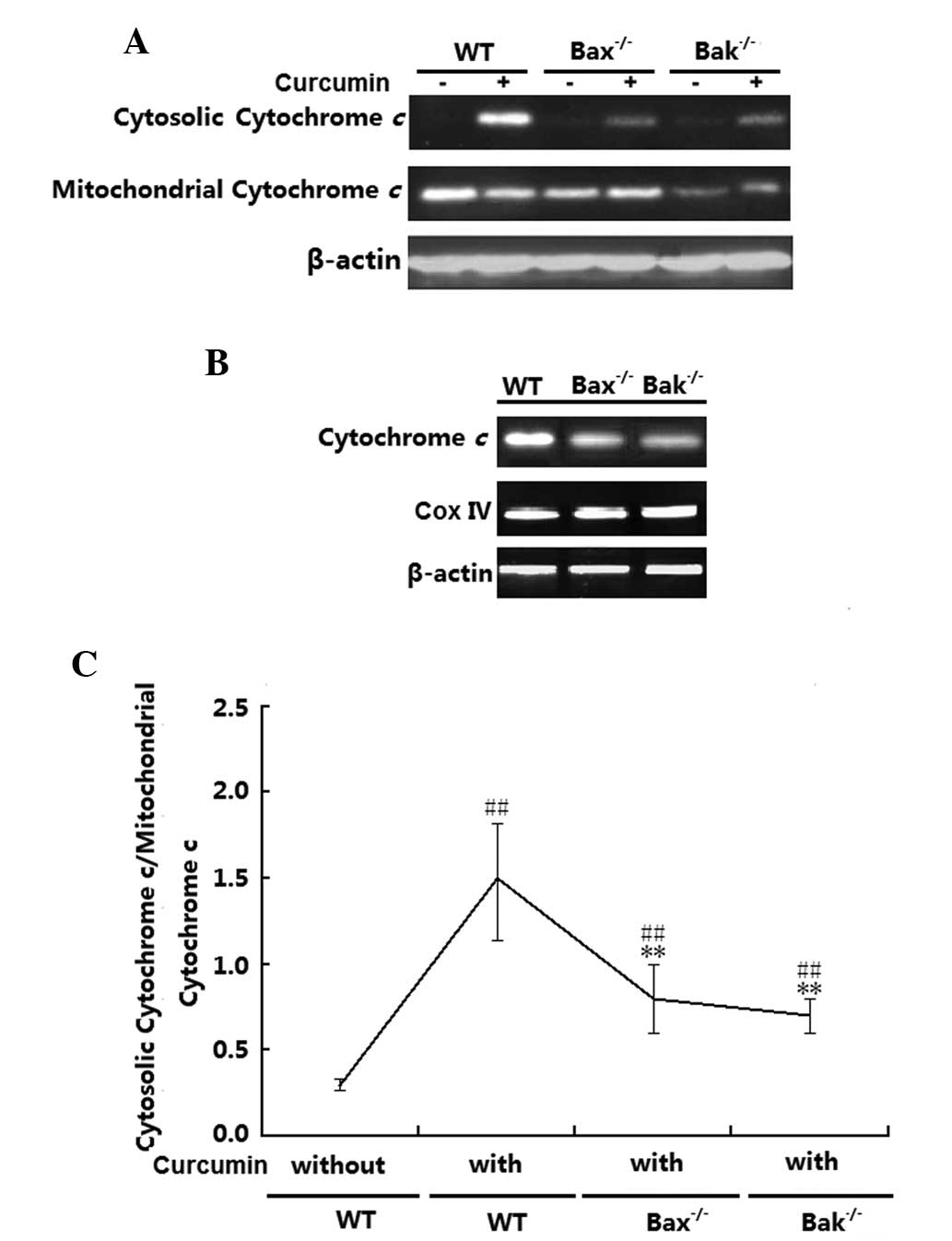
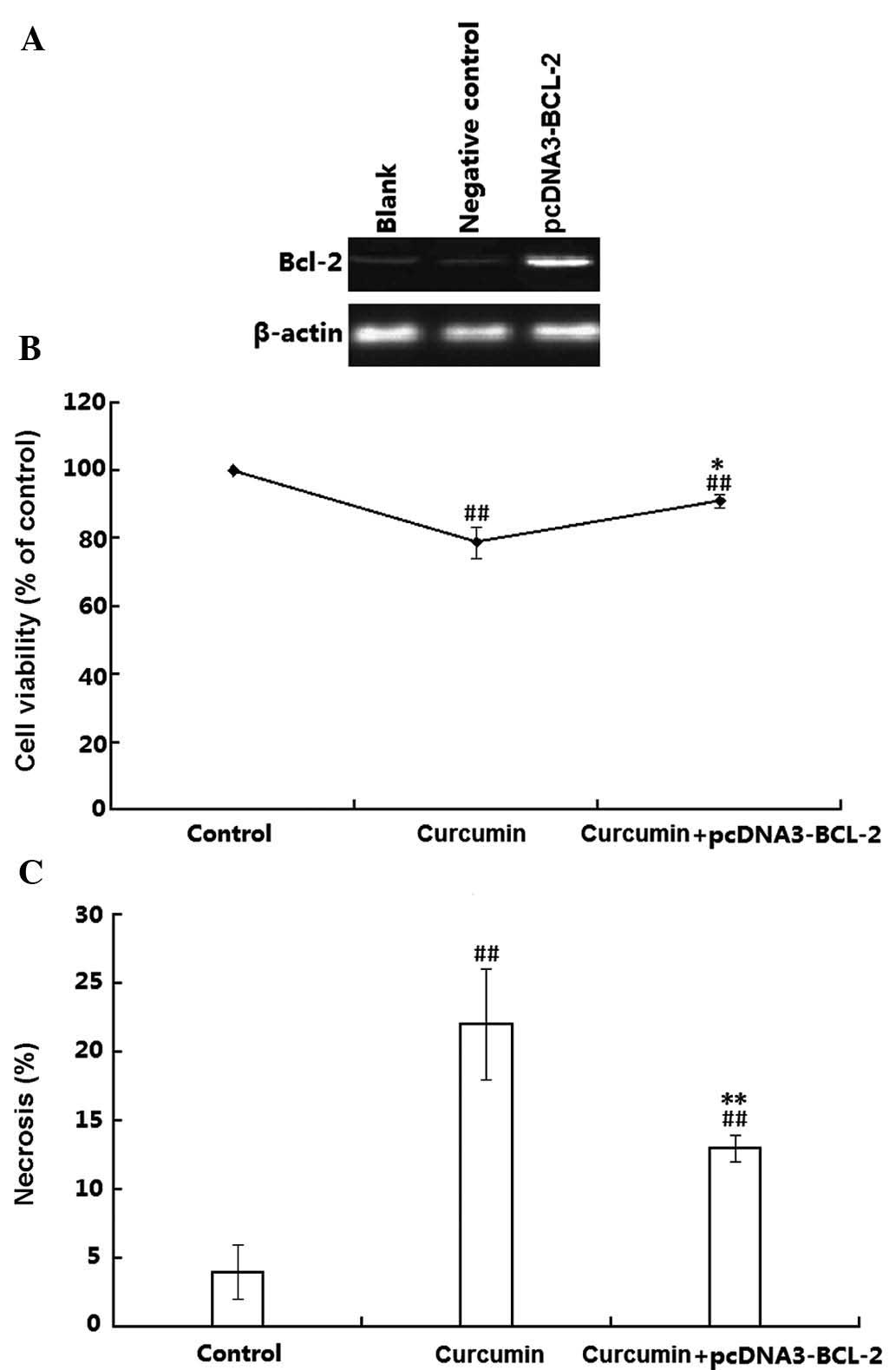
|
1
|
O'Sullivan-Coyne G, O'Sullivan GC,
O'Donovan TR, Piwocka K and McKenna SL: Curcumin induces
apoptosis-independent death in oesophageal cancer cells. Br J
Cancer. 101:1585–1595. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Friedman L, Lin L, Ball S, Bekaii-Saab T,
Fuchs J, Li PK, Li C and Lin J: Curcumin analogues exhibit enhanced
growth suppressive activity in human pancreatic cancer cells.
Anticancer Drugs. 20:444–449. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Steward WP and Gescher AJ: Curcumin in
cancer management: Recent results of analogue design and clinical
studies and desirable future research. Mol Nutr Food Res.
52:1005–1009. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shehzad A, Lee J, Huh TL and Lee YS:
Curcumin induces apoptosis in human colorectal carcinoma (HCT-15)
cells by regulating expression of Prp4 and p53. Mol Cells.
35:526–532. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Choudhuri T, Pal S, Agwarwal ML, Das T and
Sa G: Curcumin induces apoptosis in human breast cancer cells
through p53-dependent Bax induction. FEBS Lett. 512:334–340. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Alenzi FQ, Wyse RK and Altamimi WG:
Apoptosis as a tool for therapeutic agents in haematological
diseases. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 4:407–420. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Huang S, Shao K, Liu Y, Kuang Y, Li J, An
S, Guo Y, Ma H and Jiang C: Tumor-targeting and
microenvironment-responsive smart nanoparticles for combination
therapy of antiangiogenesis and apoptosis. ACS Nano. 7:2860–2871.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Griffith TS: Induction of tumor cell
apoptosis by TRAIL gene therapy. Methods Mol Biol. 542:315–334.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sosna J, Voigt S, Mathieu S, Lange A, Thon
L, Davarnia P, Herdegen T, Linkermann A, Rittger A, Chan FK, et al:
TNF-induced necroptosis and PARP-1-mediated necrosis represent
distinct routes to programmed necrotic cell death. Cell Mol Life
Sci. 71:331–348. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
10
|
Proskuryakov SY, Gabai VL and
Konoplyannikov AG: Necrosis is an active and controlled form of
programmed cell death. Biochemistry (Mosc). 67:387–408. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Vandenabeele P, W Declercq F, Van
Herreweghe, et al: The role of the kinases RIP1 and RIP3 in
TNF-induced necrosis. Sci Signal. 2010.115:re4
|
|
12
|
Baritaud M, Boujrad H, Lorenzo HK, Krantic
S and Susin SA: Histone H2AX: The missing link in AIF-mediated
caspase-independent programmed necrosis. Cell Cycle. 9:3166–3173.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Iwasaki R, Ito K, Ishida T, Hamanoue M,
Adachi S, Watanabe T and Sato Y: Catechin, green tea component,
causes caspase-independent necrosis-like cell death in chronic
myelogenous leukemia. Cancer Sci. 100:349–356. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nicotera P and Melino G: Regulation of the
apoptosis-necrosis switch. Oncogene. 23:2757–2765. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lin X, Sun T, Cai M and Shen P:
Cell-death-mode switch from necrosis to apoptosis in hydrogen
peroxide treated macrophages. Sci China Life Sci. 53:1196–1203.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bergeron L, Perez GI, Macdonald G, et al:
Defects in regulation of apoptosis in caspase-2-deficient mice.
Genes Dev. 12:1304–1314. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hosseinimehr SJ, Azadbakht M, Tanha M,
Mahmodzadeh A and Mohammadifar S: Protective effect of hawthorn
extract against genotoxicity induced by methyl methanesulfonate in
human lymphocytes. Toxicol Ind Health. 27:363–369. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kosmider B, Wojcik I, Osiecka R,
Bartkowiak J, Zyner E, Ochocki J and Liberski P: Enhanced P53 and
BAX gene expression and apoptosis in A549 cells by cis-Pt(II)
complex of 3-aminoflavone in comparison with cis-DDP. Invest New
Drugs. 23:287–297. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Song G, Mao YB, Cai QF, Yao LM, Ouyang GL
and Bao SD: Curcumin induces human HT-29 colon adenocarcinoma cell
apoptosis by activating p53 and regulating apoptosis-related
protein expression. Braz J Med Biol Res. 38:1791–1798. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yu JL, Rak JW, Coomber BL, et al: Effect
of p53 status on tumor response to antiangiogenic therapy. Science.
295:1526–1528. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tian F, Song M, Xu PR, et al: Curcumin
promotes apoptosis of esophageal squamous carcinoma cell lines
through inhibition of NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Ai Zheng.
27:566–570. 2008.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang W, Liu N, Wang X, et al:
Benzo(a)pyrene-7,8-diol-9,10-epoxide induced p53-independent
necrosis via the mitochondria-associated pathway involving Bax and
Bak activation. Hum Exp Toxicol. 34:179–190. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Guo BC and Xu YH: Bcl-2 over-expression
and activation of protein kinase C suppress the trail-induced
apoptosis in Jurkat T cells. Cell Res. 11:101–106. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bar-Sela G, Epelbaum R and Schaffer M:
Curcumin as an anti-cancer agent: Review of the gap between basic
and clinical applications. Curr Med Chem. 17:190–197. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tian C, Xing G, Xie P, et al: KRAB-type
zinc-finger protein Apak specifically regulates p53-dependent
apoptosis. Nat Cell Biol. 11:580–591. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Blankenberg FG: Apoptosis imaging:
Anti-cancer agents in medicinal chemistry. Anticancer Agents Med
Chem. 9:944–951. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Meulmeester E and Jochemsen AG: p53: A
guide to apoptosis. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 8:87–97. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xu Y: Regulation of p53 responses by
post-translational modifications. Cell Death Differ. 10:400–403.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Leibowitz BJ, Qiu W, Liu H, Cheng T, Zhang
L and Yu J: Uncoupling p53 functions in radiation-induced
intestinal damage via PUMA and p21. Mol Cancer Res. 9:616–625.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Thakur VS, Ruhul Amin AR, Paul RK, Gupta
K, Hastak K, Agarwal MK, Jackson MW, Wald DN, Mukhtar H and Agarwal
ML: p53-Dependent p21-mediated growth arrest pre-empts and protects
HCT116 cells from PUMA-mediated apoptosis induced by EGCG. Cancer
Lett. 296:225–232. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Morales-Cruz M, Figueroa CM,
Gonzalez-Robles T, et al: Activation of caspase-dependent apoptosis
by intracellular delivery of cytochrome c-based nanoparticles. J
Nanobiotechnology. 12:332014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Antignani A and Youle RJ: How do Bax and
Bak lead to permeabilization of the outer mitochondrial membrane?
Curr Opin Cell Biol. 18:685–689. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Holcakova J, Ceskova P, Hrstka R, Muller
P, Dubska L, Coates PJ, Palecek E and Vojtesek B: The cell
type-specific effect of TAp73 isoforms on the cell cycle and
apoptosis. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 13:404–420. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kim GT, Lee SH, Kim JI and Kim YM:
Quercetin regulates the sestrin 2-AMPK-p38 MAPK signaling pathway
and induces apoptosis by increasing the generation of intracellular
ROS in a p53-independent manner. Int J Mol Med. 33:863–869.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kim H, Tu HC, Ren D, et al: Stepwise
activation of BAX and BAK by tBID, BIM, and PUMA initiates
mitochondrial apoptosis. Mol Cell. 36:487–499. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Antonsson B, Montessuit S, Lauper S, et
al: Bax oligomerization is required for channel-forming activity in
liposomes and to trigger cytochrome c release from mitochondria.
Biochem J. 345(Pt 2): 271–278. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sundararajan R, Cuconati A, Nelson D and
White E: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces Bax-Bak interaction
and apoptosis, which is inhibited by adenovirus E1B 19K. J Biol
Chem. 276:45120–45127. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wachter F, Grunert M, Blaj C, Weinstock
DM, Jeremias I and Ehrhardt H: Impact of the p53 status of tumor
cells on extrinsic and intrinsic apoptosis signaling. Cell Commun
Signal. 11:272013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Mehmeti I, Gurgul-Convey E, Lenzen S and
Lortz S: Induction of the intrinsic apoptosis pathway in
insulin-secreting cells is dependent on oxidative damage of
mitochondria but independent of caspase-12 activation. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1813:1827–1835. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Buratta M, Castigli E, Sciaccaluga M,
Pellegrino RM, Spinozzi F, Roberti R and Corazzi L: Loss of
cardiolipin in palmitate-treated GL15 glioblastoma cells favors
cytochrome c release from mitochondria leading to apoptosis. J
Neurochem. 105:1019–1031. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lee HJ, Lee HJ, Lee EO, Ko SG, Bae HS, Kim
CH, Ahn KS, Lu J and Kim SH: Mitochondria-cytochrome C-caspase-9
cascade mediates isorhamnetin-induced apoptosis. Cancer Lett.
270:342–353. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Nakabayashi J and Sasaki A: A mathematical
model for apoptosome assembly: The optimal cytochrome c/Apaf-1
ratio. J Theor Biol. 242:280–287. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Adrain C and Martin SJ: The mitochondrial
apoptosome: A killer unleashed by the cytochrome seas. Trends
Biochem Sci. 26:390–397. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kihana T, Tsuda H, Teshima S, et al: High
incidence of p53 gene mutation in human ovarian cancer and its
association with nuclear accumulation of p53 protein and tumor DNA
aneuploidy. Jpn J Cancer Res. 83:978–984. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|