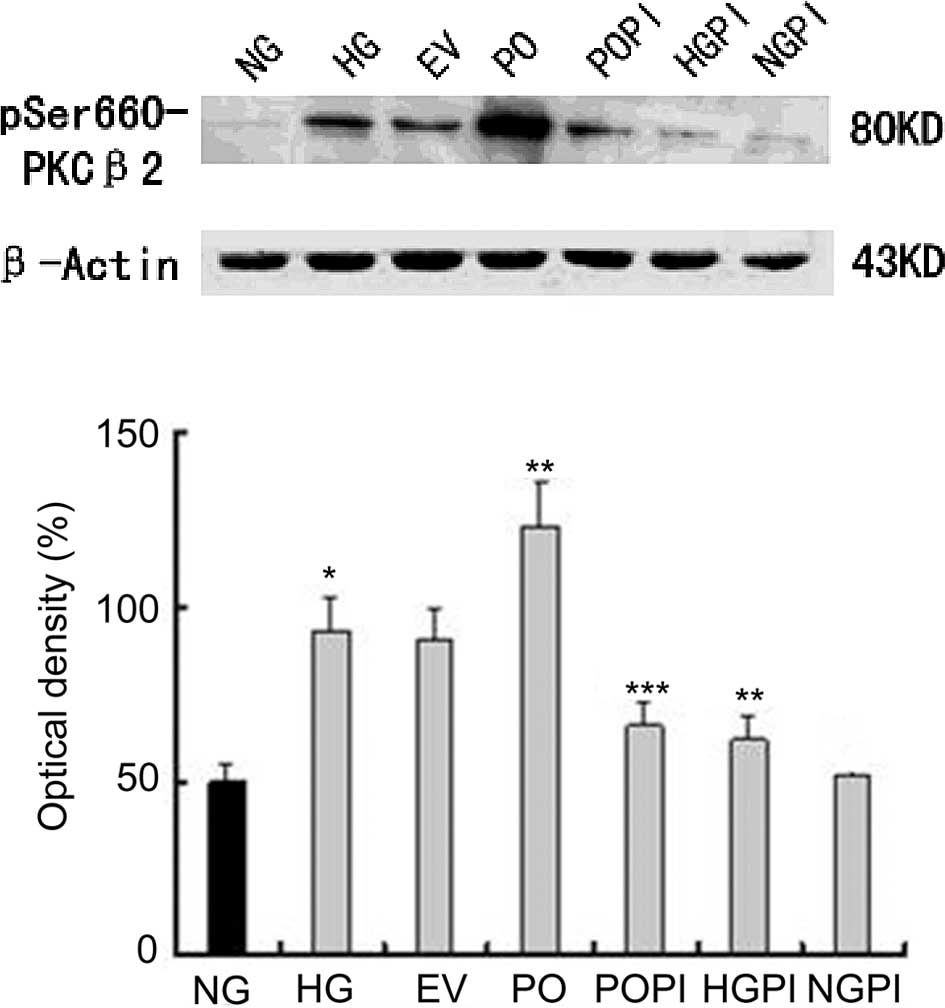
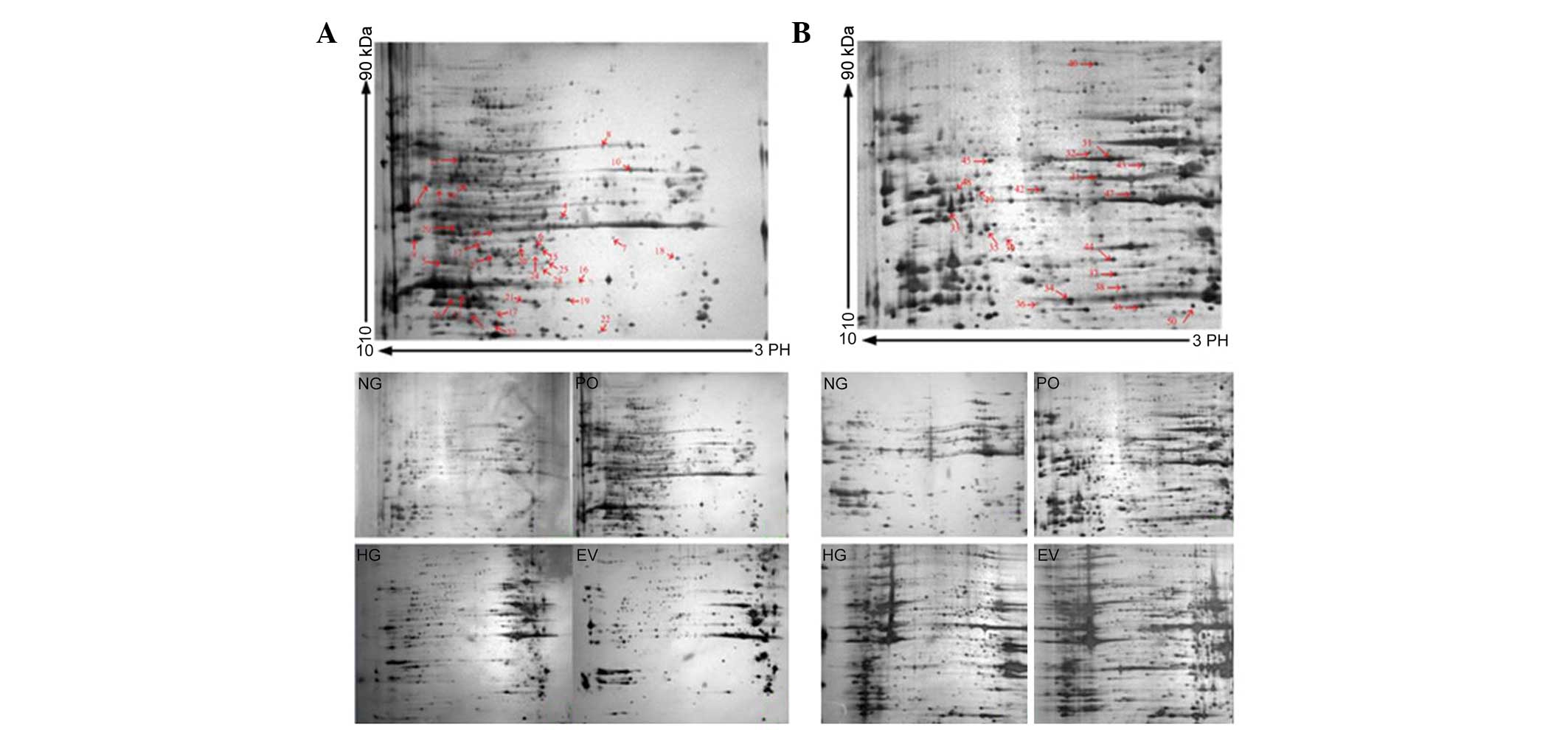
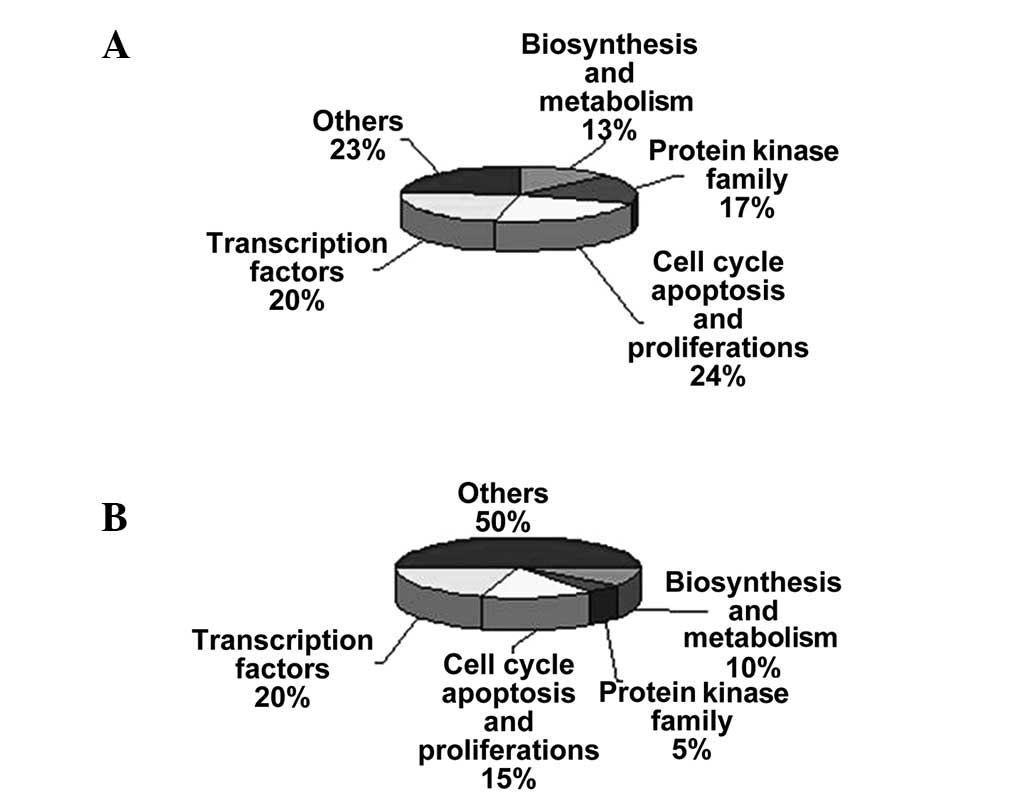
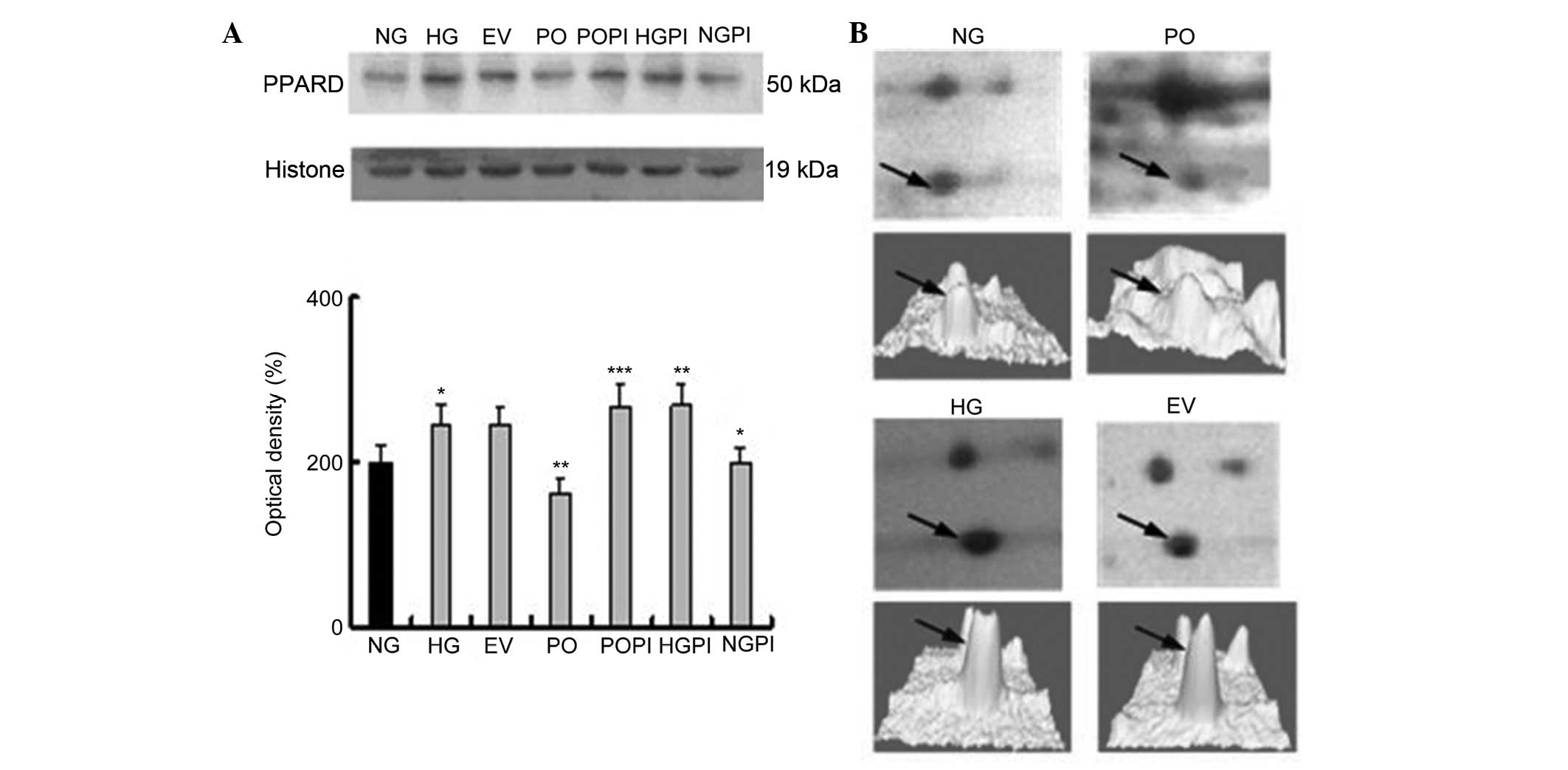
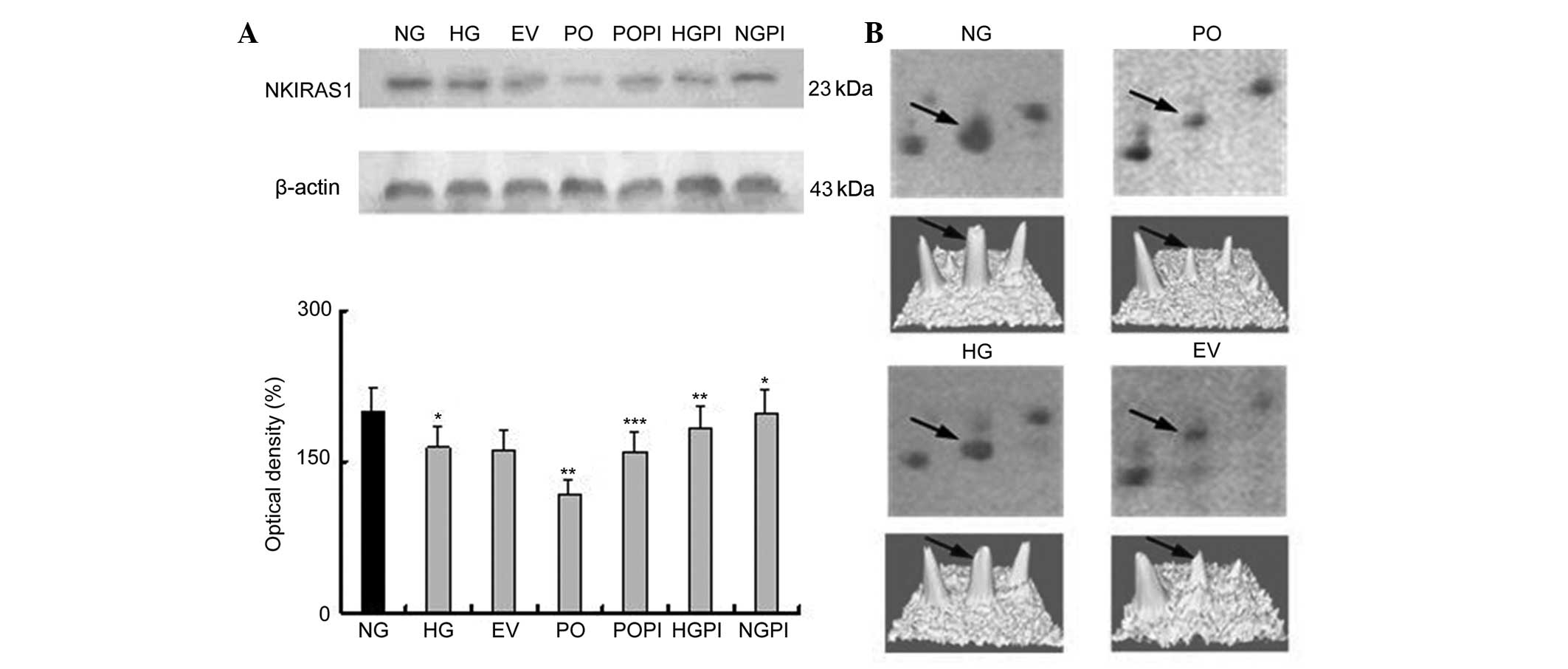
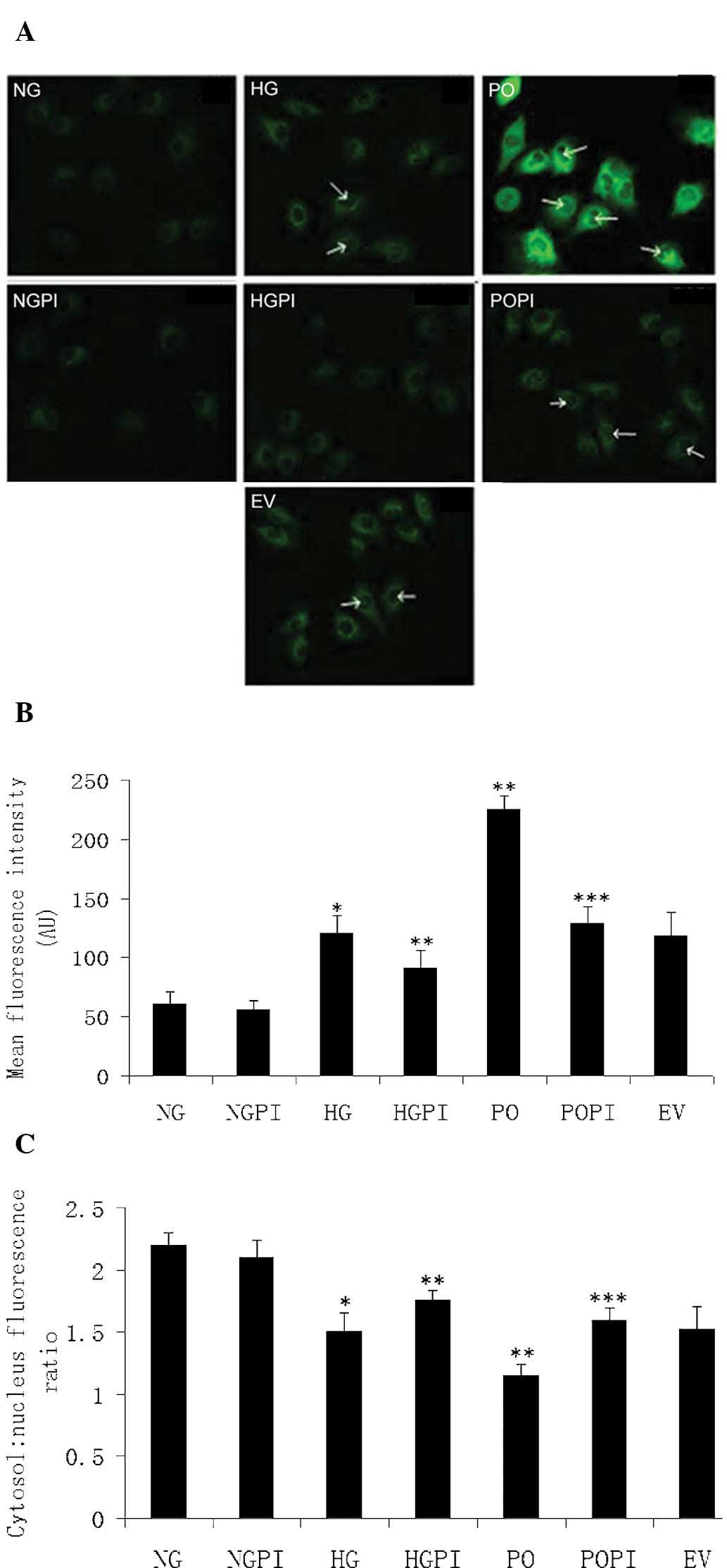
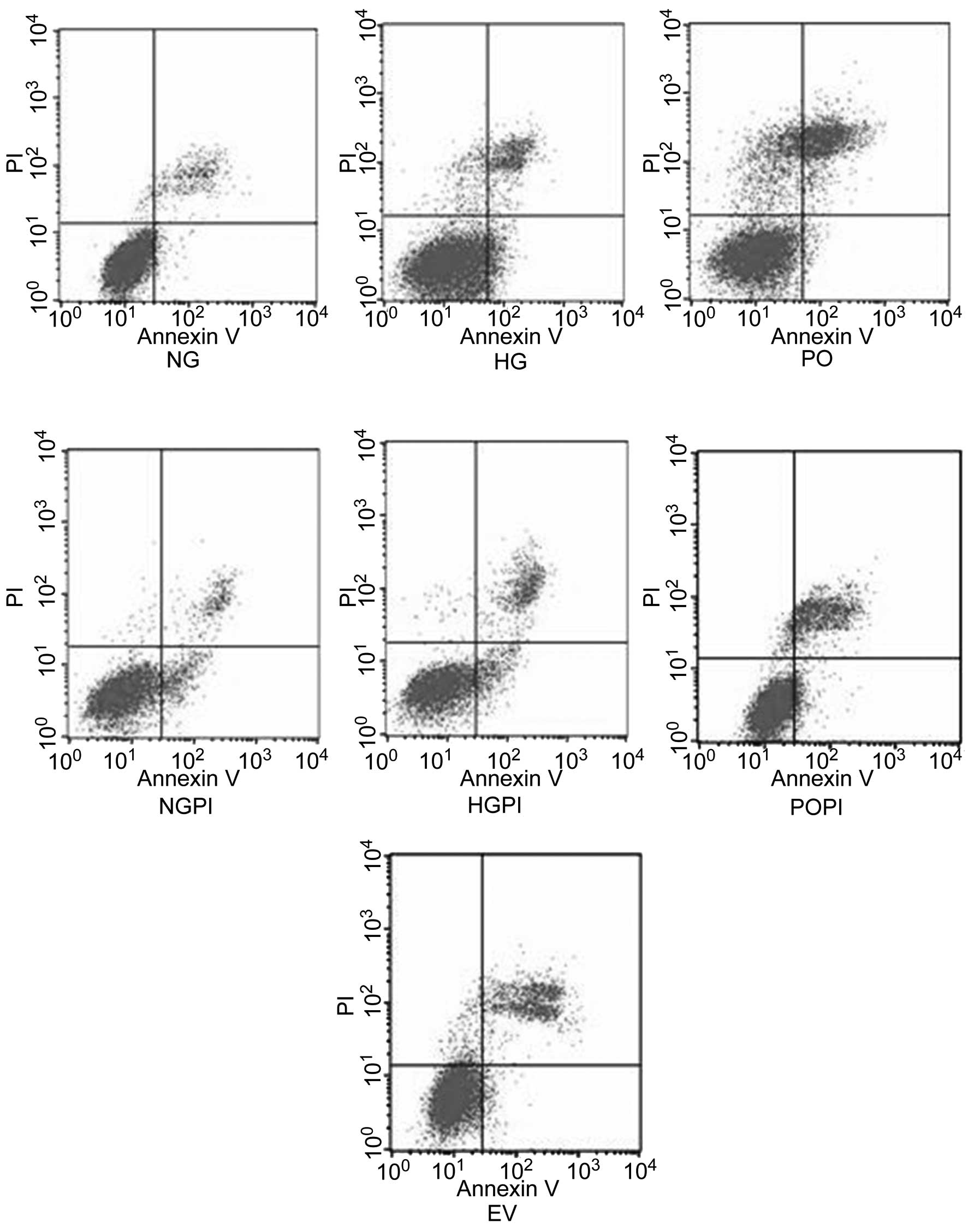
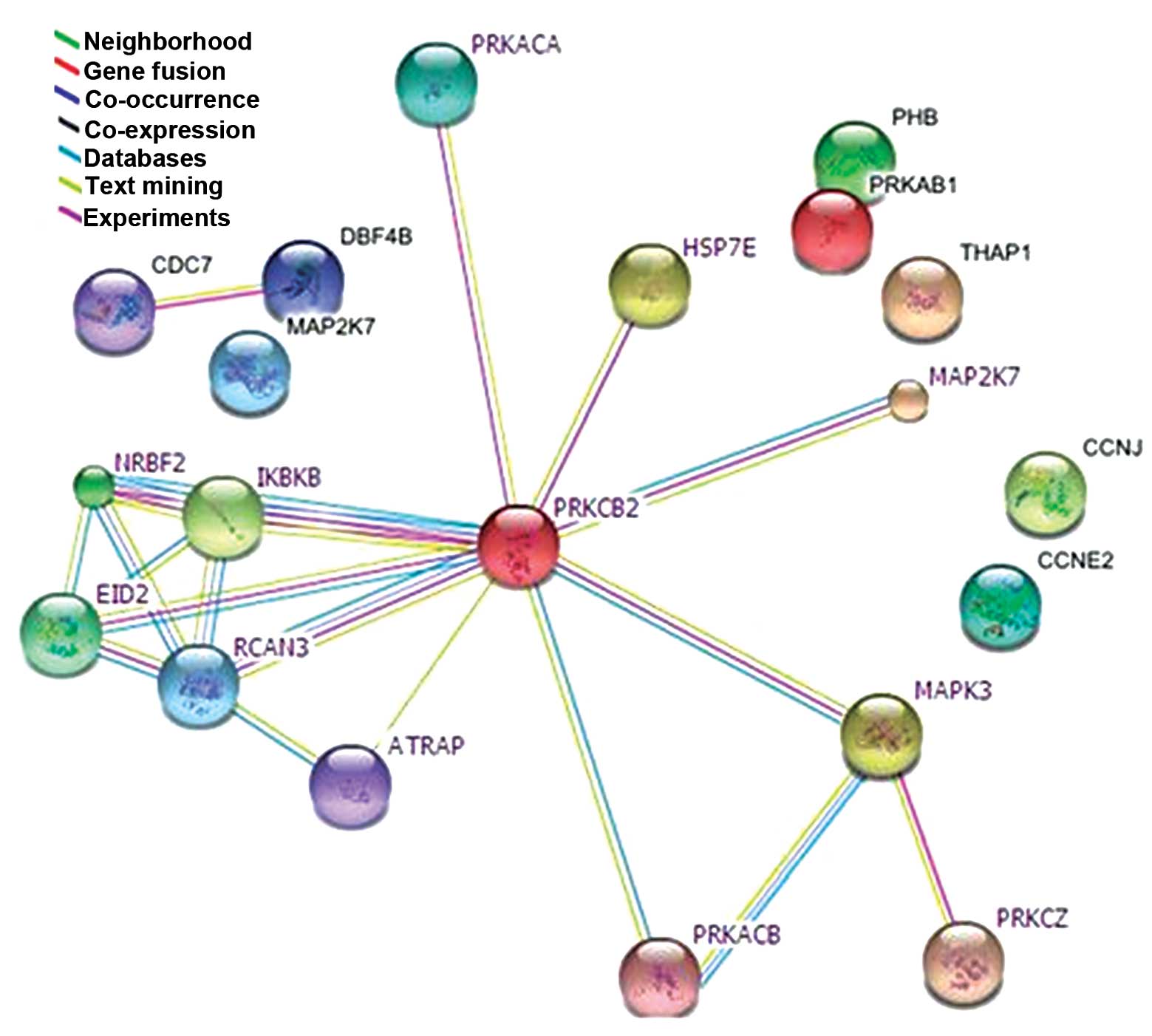
|
1
|
Yang W, Lu J, Weng J, Jia W, Ji L, Xiao J,
Shan Z, Liu J, Tian H, Ji Q, et al: Prevalence of diabetes among
men and women in China. N Engl J Med. 362:1090–1101. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bakker W, Eringa EC, Sipkema P and van
Hinsbergh VW: Endothelial dysfunction and diabetes: Roles of
hyperglycemia, impaired insulin signaling and obesity. Cell Tissue
Res. 335:165–189. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Orasanu G and Plutzky J: The pathologic
continuum of diabetic vascular disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 53(5
Suppl): S35–S42. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yuan SY, Ustinova EE, Wu MH, Tinsley JH,
Xu W, Korompai FL and Taulman AC: Protein kinase C activation
contributes to microvascular barrier dysfunction in the heart at
early stages of diabetes. Circ Res. 87:412–417. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
King GL: The role of hyperglycaemia and
hyperinsulinaemia in causing vascular dysfunction in diabetes. Ann
Med. 28:427–432. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hink U, Li H, Mollnau H, Oelze M, Matheis
E, Hartmann M, Skatchkov M, Thaiss F, Stahl RA and Warnholtz A:
Mechanisms underlying endothelial dysfunction in diabetes mellitus.
Circ Res. 88:E14–E22. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kizub IV, Klymenko KI and Soloviev AI:
Protein kinase C in enhanced vascular tone in diabetes mellitus.
Int J Cardiol. 174:230–242. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Geraldes P and King GL: Activation of
protein kinase C isoforms and its impact on diabetic complications.
Circ Res. 106:1319–1331. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Meier M, Park JK, Overheu D, Kirsch T,
Lindschau C, Gueler F, Leitges M, Menne J and Haller H: Deletion of
protein kinase C-beta isoform in vivo reduces renal hypertrophy but
not albuminuria in the streptozotocin-induced diabetic mouse model.
Diabetes. 56:346–354. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gaudreault N, Perrin RM, Guo M, Clanton
CP, Wu MH and Yuan SY: Counter regulatory effects of PKCbetaII and
PKCdelta on coronary endothelial permeability. Arterioscler Thromb
Vasc Biol. 28:1527–1533. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dangwal S, Rauch BH, Gensch T, Dai L,
Bretschneider E, Vogelaar CF, Schrör K and Rosenkranz AC: High
glucose enhances thrombin responses via protease-activated
receptor-4 in human vascular smooth muscle cells. Arterioscler
Thromb Vasc Biol. 31:624–633. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Naruse K, Rask-Madsen C, Takahara N, Ha
SW, Suzuma K, Way KJ, Jacobs JR, Clermont AC, Ueki K, Ohshiro Y, et
al: Activation of vascular protein kinase C-beta inhibits
Akt-dependent endothelial nitric oxide synthase function in
obesity-associated insulin resistance. Diabetes. 55:691–698. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lin X, Zhou B and Sun F: Protein Kinase C
β2 mediated high glucose-induced human umbilical vein endothelial
cells injury via regulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor α. China J Endocrinol Metab. 26:10–14. 2010.
|
|
14
|
Min W, Bin ZW, Quan ZB, Hui ZJ and Sheng
FG: The signal transduction pathway of PKC/NF-kappa B/c-fos may be
involved in the influence of high glucose on the cardiomyocytes of
neonatal rats. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 8:82009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Campbell M and Trimble ER: Modification of
PI3K- and MAPK-dependent chemotaxis in aortic vascular smooth
muscle cells by protein kinase CbetaII. Circ Res. 96:197–206. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Duan L, Lin XB and Zhou B: Construction
and identification of endothelial cell model with overexpressed
human protein kinase Cβ2 induced by high glucose. Acta Acad Med
Militaris Tertiae. 31:1993–1996. 2009.In Chinese.
|
|
17
|
Sun F, Zhou B, Lin X and Duan L: Proteomic
analysis identifies nuclear protein effectors in PKC-δ signaling
under high glucose-induced apoptosis in human umbilical vein
endothelial cells. Mol Med Rep. 4:865–872. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Turck N, Richert S, Gendry P, Stutzmann J,
Kedinger M, Leize E, Simon-Assmann P, Van Dorsselaer A and Launay
JF: Proteomic analysis of nuclear proteins from proliferative and
differentiated human colonic intestinal epithelial cells.
Proteomics. 4:93–105. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cargnello M and Roux PP: Activation and
function of the MAPKs and their substrates, the MAPK-activated
protein kinases. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 75:50–83. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Furukohri A, Sato N, Masai H, Arai K,
Sugino A and Waga S: Identification and characterization of a
Xenopus homolog of Dbf4, a regulatory subunit of the Cdc7 protein
kinase required for the initiation of DNA replication. J Biochem.
134:447–457. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jiang W, McDonald D, Hope TJ and Hunter T:
Mammalian Cdc7-Dbf4 protein kinase complex is essential for
initiation of DNA replication. EMBO J. 18:5703–5713. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kim JM, Sato N, Yamada M, Arai K and Masai
H: Growth regulation of the expression of mouse cDNA and gene
encoding a serine/threonine kinase related to Saccharomyces
cerevisiae CDC7 essential for G1/S transition. Structure,
chromosomal localization, and expression of mouse gene for S.
cerevisiae Cdc7-related kinase. J Biol Chem. 273:23248–23257. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jares P, Luciani MG and Blow JJ: A xenopus
Dbf4 homolog is required for Cdc7 chromatin binding and DNA
replication. BMC Mol Biol. 5:52004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Monsalve FA, Pyarasani RD, Delgado-Lopez F
and Moore-Carrasco R: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
targets for the treatment of metabolic diseases. Mediators Inflamm.
2013:5496272013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Saez ME, Grilo A, Moron FJ, Manzano L,
Martínez-Larrad MT, Gonzalez-Perez A, Ser rano-Hernando J, Ruiz A,
Ramirez-Lorca R and Serrano-Rios M: Interaction between calpain 5,
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma and peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor-delta genes: A polygenic approach
to obesity. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 7:232008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mosser DD, Caron AW, Bourget L,
Denis-Larose C and Massie B: Role of the human heat shock protein
hsp70 in protection against stress-induced apoptosis. Mol Cell
Biol. 17:5317–5327. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lin H, Wang Y, Zhang X, Liu B, Zhang W and
Cheng J: Prognostic significance of kappaB-Ras1 expression in
gliomas. Med Oncol. 29:1272–1279. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Jeong IK, Oh da H, Park SJ, Kang JH, Kim
S, Lee MS, Kim MJ, Hwang YC, Ahn KJ, Chung HY, et al: Inhibition of
NF-κB prevents high glucose-induced proliferation and plasminogen
activator inhibitor-1 expression in vascular smooth muscle cells.
Exp Mol Med. 43:684–692. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Green CJ, Pedersen M, Pedersen BK and
Scheele C: Elevated NF-κB activation is conserved in human myocytes
cultured from obese type 2 diabetic patients and attenuated by
AMP-activated protein kinase. Diabetes. 60:2810–2819. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen S, Khan ZA, Cukiernik M and
Chakrabarti S: Differential activation of NF-kappaB and AP-1 in
increased fibronectin synthesis in target organs of diabetic
complications. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 284:E1089–E1097.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Csiszar A, Wang M, Lakatta EG and Ungvari
Z: Inflammation and endothelial dysfunction during aging: Role of
NF-kappaB. J Appl Physiol (1985). 105:1333–1341. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Kouroedov A, Eto M, Joch H, Volpe M,
Lüscher TF and Cosentino F: Selective inhibition of protein kinase
Cbeta2 prevents acute effects of high glucose on vascular cell
adhesion molecule-1 expression in human endothelial cells.
Circulation. 110:91–96. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tang JR, Michaelis KA, Nozik-Grayck E,
Seedorf GJ, Hartman-Filson M, Abman SH and Wright CJ: The NF-κB
inhibitory proteins IκBα and IκBβ mediate disparate responses to
inflammation in fetal pulmonary endothelial cells. J Immunol.
190:2913–2923. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gerashchenko GV, Bogatyrova OO, Rudenko
EE, Kondratov AG, Gordiyuk VV, Zgonnyk YM, Vozianov OF, Pavlova TV,
Zabarovsky ER, Rynditch AV and Kashuba VI: Genetic and epigenetic
changes of NKIRAS1 gene in human renal cell carcinomas. Exp Oncol.
32:71–75. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Duan SZ, Usher MG and Mortensen RM: PPARs:
The vasculature, inflammation and hypertension. Curr Opin Nephrol
Hypertens. 18:128–133. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wahli W and Michalik L: PPARs at the
crossroads of lipid signaling and inflammation. Trends Endocrinol
Metab. 23:351–363. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Escher P, Braissant O, Basu-Modak S,
Michalik L, Wahli W and Desvergne B: Rat PPARs: Quantitative
analysis in adult rat tissues and regulation in fasting and
refeeding. Endocrinology. 142:4195–4202. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Reilly SM and Lee CH: PPAR delta as a
therapeutic target in metabolic disease. FEBS Lett. 582:26–31.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Wang YX, Lee CH, Tiep S, Yu RT, Ham J,
Kang H and Evans RM: Peroxisome-proliferator-activated receptor
delta activates fat metabolism to prevent obesity. Cell.
113:159–170. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lee CH, Olson P, Hevener A, Mehl I, Chong
LW, Olefsky JM, Gonzalez FJ, Ham J, Kang H, Peters JM and Evans RM:
PPARdelta regulates glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:3444–3449. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Luquet S, Lopez-Soriano J, Holst D,
Fredenrich A, Melki J, Rassoulzadegan M and Grimaldi PA: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor delta controls muscle development
and oxidative capability. FASEB J. 17:2299–2301. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wang YX, Zhang CL, Yu RT, Cho HK, Nelson
MC, Bayuga-Ocampo CR, Ham J, Kang H and Evans RM: Regulation of
muscle fiber type and running endurance by PPARdelta. PLoS Biol.
2:e2942004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Riahi Y, Sin-Malia Y, Cohen G, Alpert E,
Gruzman A, Eckel J, Staels B, Guichardant M and Sasson S: The
natural protective mechanism against hyperglycemia in vascular
endothelial cells: Roles of the lipid peroxidation product
4-hydroxydodeca-dienal and peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor delta. Diabetes. 59:808–818. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kim YH and Han HJ: High-glucose-induced
prostaglandin E (2) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
delta promote mouse embryonic stem cell proliferation. Stem Cells.
26:745–755. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Keats E and Khan ZA: Unique responses of
stem cell-derived vascular endothelial and mesenchymal cells to
high levels of glucose. PLoS One. 7:e387522012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yuan L, Hu J, Luo Y, Liu Q, Li T, Parish
CR, Freeman C, Zhu X, Ma W, Hu X, et al: Upregulation of heparanase
in high-glucose-treated endothelial cells promotes endothelial cell
migration and proliferation and correlates with Akt and
extracellular-signal-regulated kinase phosphorylation. Mol Vis.
18:1684–1695. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Su J, Zhou H, Tao Y, Guo J, Guo Z, Zhang
S, Zhang Y, Huang Y, Tang Y, Dong Q and Hu R: G-CSF protects human
brain vascular endothelial cells injury induced by high glucose,
free fatty acids and hypoxia through MAPK and Akt signaling. PLoS
One. 10:e01207072015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Neri A, Marmiroli S, Tassone P, Lombardi
L, Nobili L, Verdelli D, Civallero M, Cosenza M, Bertacchini J,
Federico M, et al: The oral protein-kinase C beta inhibitor
enzastaurin (LY317615) suppresses signalling through the AKT
pathway, inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in multiple
myeloma cell lines. Leuk Lymphoma. 49:1374–1383. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Caunt CJ and McArdle CA: ERK
phosphorylation and nuclear accumulation: Insights from single-cell
imaging. Biochem Soc Trans. 40:224–229. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Yang P and Roy SK: A novel mechanism of
FSH regulation of DNA synthesis in the granulosa cells of hamster
preantral follicles: Involvement of a protein kinase C-mediated MAP
kinase 3/1 self-activation loop. Biol Reprod. 75:149–157. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Winnicki K, Zabka A, Bernasinska J,
Matczak K and Maszewski J: Immunolocalization of dually
phosphorylated MAPKs in dividing root meristem cells of Vicia faba,
Pisum sativum, Lupinus luteus and Lycopersicon esculentum. Plant
Cell Rep. 34:905–917. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Hiraga S, Alvino GM, Chang F, Lian HY,
Sridhar A, Kubota T, Brewer BJ, Weinreich M, Raghuraman MK and
Donaldson AD: Rif1 controls DNA replication by directing protein
phosphatase 1 to reverse Cdc7-mediated phosphorylation of the MCM
complex. Genes Dev. 28:372–383. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Yamada M, Watanabe K, Mistrik M, Vesela E,
Protivankova I, Mailand N, Lee M, Masai H, Lukas J and Bartek J:
ATR-Chk1-APC/CCdh1-dependent stabilization of Cdc7-ASK (Dbf4)
kinase is required for DNA lesion bypass under replication stress.
Genes Dev. 27:2459–2472. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Zhao Y, Zhang Y, Song HB, Wu F, Wang XL,
Sun SC, Cui TX and Tang DQ: Proteomic analysis revealed the altered
kidney protein profile of a Cyld knockout mouse model. Genet Mol
Res. 14:5970–5978. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Pizzatti L, Sa LA, de Souza JM, Bisch PM
and Abdelhay E: Altered protein profile in chronic myeloid leukemia
chronic phase identified by a comparative proteomic study. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1764:929–942. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Ezkurdia I, del Pozo A, Frankish A,
Rodriguez JM, Harrow J, Ashman K, Valencia A and Tress ML:
Comparative proteomics reveals a significant bias toward
alternative protein isoforms with conserved structure and function.
Mol Biol Evol. 29:2265–2283. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|