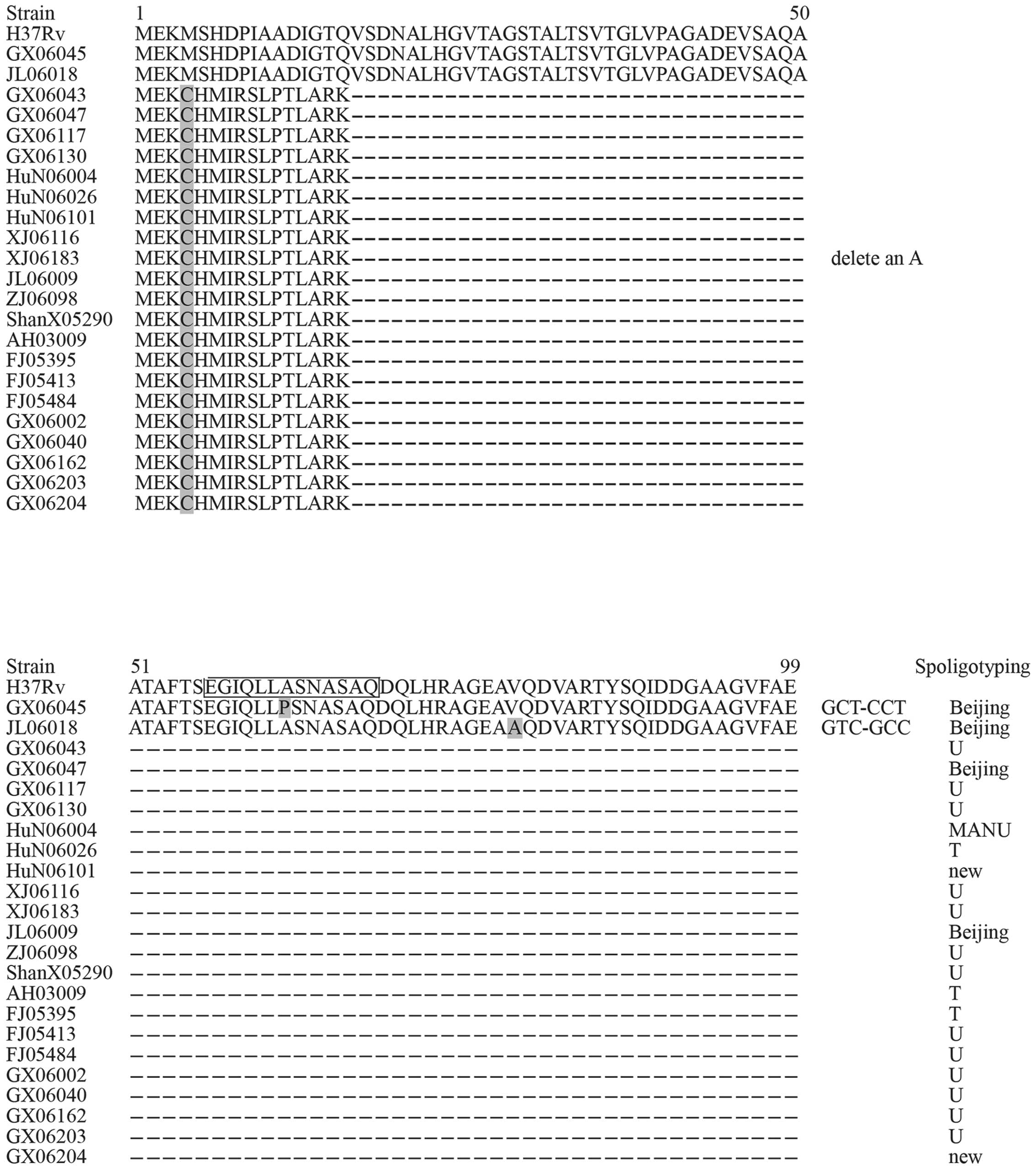
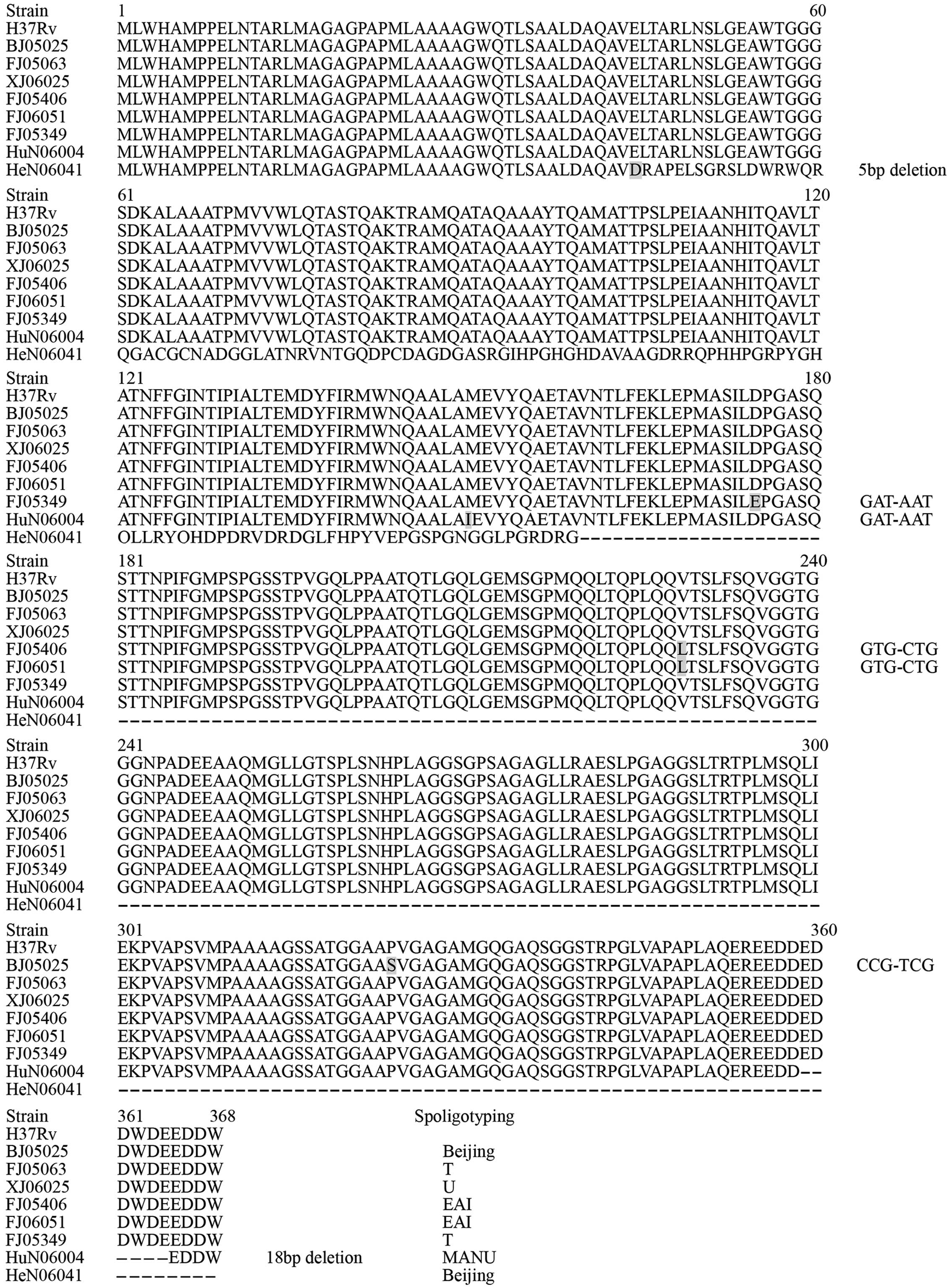
|
1
|
Liu XQ, Dosanjh D, Varia H, Ewer K, Cockle
P, Pasvol G and Lalvani A: Evaluation of T-cell responses to novel
RD1- and RD2-encoded Mycobacterium tuberculosis gene products for
specific detection of human tuberculosis infection. Infect Immun.
72:2574–2581. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mahairas GG, Sabo PJ, Hickey MJ, Singh DC
and Stover CK: Molecular analysis of genetic differences between
Mycobacterium bovis BCG and virulent M. bovis. J Bacteriol.
178:1274–1282. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hanif SN, El-Shammy AM, Al-Attiyah R and
Mustafa AS: Whole blood assays to identify Th1 cell antigens and
peptides encoded by Mycobacterium tuberculosis-specific RD1 genes.
Med Princ Pract. 17:244–249. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mustafa AS, Al-Attiyah R, Hanif SN and
Shaban FA: Efficient testing of large pools of Mycobacterium
tuberculosis RD1 peptides and identification of major antigens and
immunodominant peptides recognized by human Th1 cells. Clin Vaccine
Immunol. 15:916–924. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hanif SN, Al-Attiyah R and Mustafa AS:
Species-specific antigenic Mycobacterium tuberculosis proteins
tested by delayed-type hypersensitivity response. Int J Tuberc Lung
Dis. 14:489–494. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pym AS, Brodin P, Brosch R, Huerre M and
Cole ST: Loss of RD1 contributed to the attenuation of the live
tuberculosis vaccines Mycobacterium bovis BCG and Mycobacterium
microti. Mol Microbiol. 46:709–717. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lewis KN, Liao R, Guinn KM, Hickey MJ,
Smith S, Behr MA and Sherman DR: Deletion of RD1 from Mycobacterium
tuberculosis mimics bacille Calmette-Guérin attenuation. J Infect
Dis. 187:117–123. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Malaghini M, Thomaz-Soccol V, Probst CM,
Krieger MA, Preti H, Kritski A and Soccol CR: Recombinant antigen
production for assays of intradermoreaction for diagnosis and
surveillance of tuberculosis. J Biotechnol. 156:56–58. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tiwari B, Soory A and Raghunand TR: An
immunomodulatory role for the Mycobacterium tuberculosis region of
difference 1 locus proteins PE35 (Rv3872) and PPE68 (Rv3873). FEBS
J. 281:1556–1570. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mukhopadhyay S and Balaji KN: The PE and
PPE proteins of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Tuberculosis (Edinb).
91:441–447. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Sampson SL: Mycobacterial PE/PPE proteins
at the host-pathogen interface. Clin Dev Immunol. 2011:4972032011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Akhter Y, Ehebauer MT, Mukhopadhyay S and
Hasnain SE: The PE/PPE multigene family codes for virulence factors
and is a possible source of mycobacterial antigenic variation:
Perhaps more? Biochimie. 94:110–116. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
McEvoy CR, Cloete R, Müller B, Schürch AC,
van Helden PD, Gagneux S, Warren RM and Gey van Pittius NC:
Comparative analysis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis pe and ppe genes
reveals high sequence variation and an apparent absence of
selective constraints. PLoS One. 7:e305932012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Copin R, Coscollá M, Seiffert SN,
Bothamley G, Sutherland J, Mbayo G, Gagneux S and Ernst JD:
Sequence diversity in the pe_pgrs genes of Mycobacterium
tuberculosis is independent of human T-cell recognition. MBio.
5:e00960–e13. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Boehme CC, Nabeta P, Hillemann D, Nicol
MP, Shenai S, Krapp F, Allen J, Tahirli R, Blakemore R, Rustomjee
R, et al: Rapid molecular detection of tuberculosis and rifampin
resistance. N Engl J Med. 363:1005–1015. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dong H, Liu Z, Lv B, Zhang Y, Liu J, Zhao
X, Liu J and Wan K: Spoligotypes of Mycobacterium tuberculosis from
different provinces of China. J Clin Microbiol. 48:4102–4106. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kamerbeek J, Schouls L, Kolk A, van
Agterveld M, van Soolingen D, Kuijper S, Bunschoten A, Molhuizen H,
Shaw R, Goyal M and van Embden J: Simultaneous detection and strain
differentiation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis for diagnosis and
epidemiology. J Clin Microbiol. 35:907–914. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Brudey K, Driscoll JR, Rigouts L,
Prodinger WM, Gori A, Al-Hajoj SA, Allix C, Aristimuño L, Arora J,
Baumanis V, et al: Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex genetic
diversity: mining the fourth international spoligotyping database
(SpolDB4) for classification, population genetics and epidemiology.
BMC Microbiol. 6:232006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP,
Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm
A, Lopez R, et al: Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0.
Bioinformatics. 23:2947–2948. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hall TA: BioEdit: A user-friendly
biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for
Windows 95/98/NT. Nucl Acids Symp Ser. 41:95–98. 1999.
|
|
21
|
Ernst JD, Lewinsohn DM, Behar S, Blythe M,
Schlesinger LS, Kornfeld H and Sette A: Meeting Report: NIH
workshop on the tuberculosis immune epitope database. Tuberculosis
(Edinb). 88:366–370. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Hsu T, Hingley-Wilson SM, Chen B, Chen M,
Dai AZ, Morin PM, Marks CB, Padiyar J, Goulding C, Gingery M, et
al: The primary mechanism of attenuation of bacillus
Calmette-Guerin is a loss of secreted lytic function required for
invasion of lung interstitial tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:12420–12425. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Pym AS, Brodin P, Majlessi L, Brosch R,
Demangel C, Williams A, Griffiths KE, Marchal G, Leclerc C and Cole
ST: Recombinant BCG exporting ESAT-6 confers enhanced protection
against tuberculosis. Nat Med. 9:533–539. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Stanley SA, Raghavan S, Hwang WW and Cox
JS: Acute infection and macrophage subversion by Mycobacterium
tuberculosis require a specialized secretion system. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 100:13001–13006. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Brodin P, Rosenkrands I, Andersen P, Cole
ST and Brosch R: ESAT-6 proteins: Protective antigens and virulence
factors? Trends Microbiol. 12:500–508. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Guinn KM, Hickey MJ, Mathur SK, Zakel KL,
Grotzke JE, Lewinsohn DM, Smith S and Sherman DR: Individual
RD1-region genes are required for export of ESAT-6/CFP-10 and for
virulence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Mol Microbiol. 51:359–370.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Okkels LM, Brock I, Follmann F, Agger EM,
Arend SM, Ottenhoff TH, Oftung F, Rosenkrands I and Andersen P: PPE
protein (Rv3873) from DNA segment RD1 of Mycobacterium
tuberculosis: Strong recognition of both specific T-cell epitopes
and epitopes conserved within the PPE family. Infect Immun.
71:6116–6123. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Okkels LM and Andersen P: Protein-protein
interactions of proteins from the ESAT-6 family of. Mycobacterium
tuberculosis J Bacteriol. 186:2487–2491. 2004.
|
|
29
|
Teutschbein J, Schumann G, Möllmann U,
Grabley S, Cole ST and Munder T: A protein linkage map of the
ESAT-6 secretion system 1 (ESX-1) of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Microbiol Res. 164:253–259. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Brodin P, Majlessi L, Marsollier L, de
Jonge MI, Bottai D, Demangel C, Hinds J, Neyrolles O, Butcher PD,
Leclerc C, et al: Dissection of ESAT-6 system 1 of Mycobacterium
tuberculosis and impact on immunogenicity and virulence. Infect
Immun. 74:88–98. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
31
|
Vordermeier HM, Hewinson RG, Wilkinson RJ,
Wilkinson KA, Gideon HP, Young DB and Sampson SL: Conserved immune
recognition hierarchy of mycobacterial PE/PPE proteins during
infection in natural hosts. PLoS One. 7:e408902012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Comas I, Chakravartti J, Small PM, Galagan
J, Niemann S, Kremer K, Ernst JD and Gagneux S: Human T-cell
epitopes of Mycobacterium tuberculosis are evolutionarily
hyperconserved. Nat Genet. 42:498–503. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Parwati I, van Crevel R and van Soolingen
D: Possible underlying mechanisms for successful emergence of the
Mycobacterium tuberculosis Beijing genotype strains. Lancet Infect
Dis. 10:103–111. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kwan CK and Ernst JD: HIV and
tuberculosis: A deadly human syndemic. Clin Microbiol Rev.
24:351–376. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Mukherjee P, Dutta M, Datta P, Dasgupta A,
Pradhan R, Pradhan M, Kundu M, Basu J and Chakrabarti P: The
RD1-encoded antigen Rv3872 of Mycobacterium tuberculosis as a
potential candidate for serodiagnosis of tuberculosis. Clin
Microbiol Infect. 13:146–152. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|