Mol Med Rep 11: [Related article:] 4047–4052, 2015; DOI:
10.3892/mmr.2015.3309
Following the publication of this article, an
interested reader drew to our attention anomalies associated with
the presentation of Figs. 1 and 4.
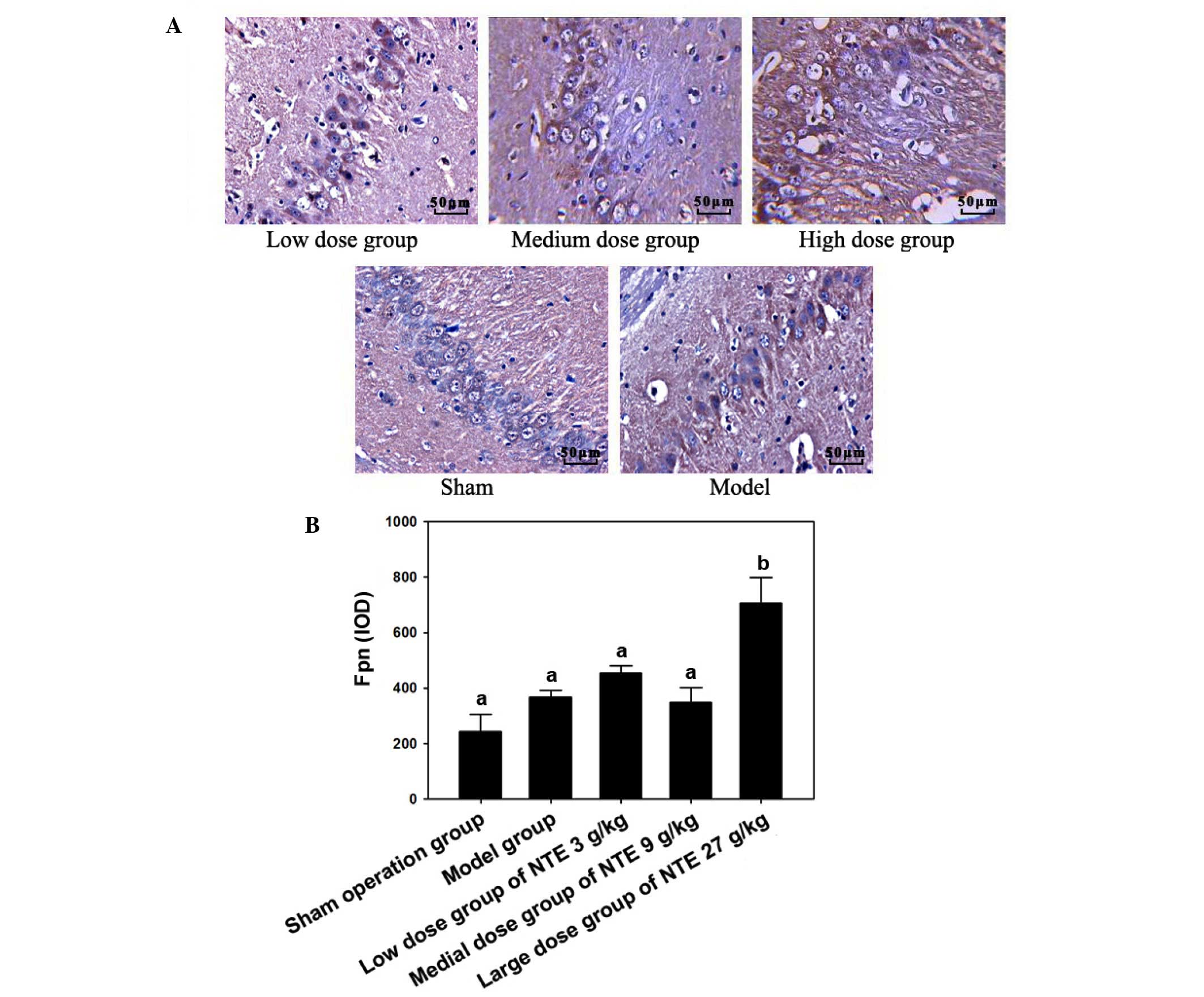
The image selected for Fig. 1A, the data pertaining to '2 h', was
inadvertently selected for Fig.
4A, the image labeled 'Sham'. Additionally, in Fig. 4, the same source image had
inadvertently been used to provide the images for the 'Low dose
group' and 'Model' panels (although the view presented differed in
these panels). On re-examining our data, we realized that these
errors had occurred during the compilation of Fig. 4, and that the images were correctly
selected for Fig. 1. An amended version of Fig. 4 is presented below, featuring
images which correctly show the data for the 'Low dose', 'Sham' and
'Model' groups. The immunohistochemical results suggested that,
following treatment with 27 g/kg naotaifang extract, the expression
of Fpn increased significantly compared with the other treatment
doses (P<0.05), whereas significant changes were not observed
among the other groups (P>0.05). The errors made in the
selection of certain images for Fig.
4A did not affect the overall conclusions reported in the
present study. We sincerely apologize for this mistake, and thank
the reader of our article who drew this matter to our attention.
Furthermore, we regret any inconvenience this mistake has
caused.