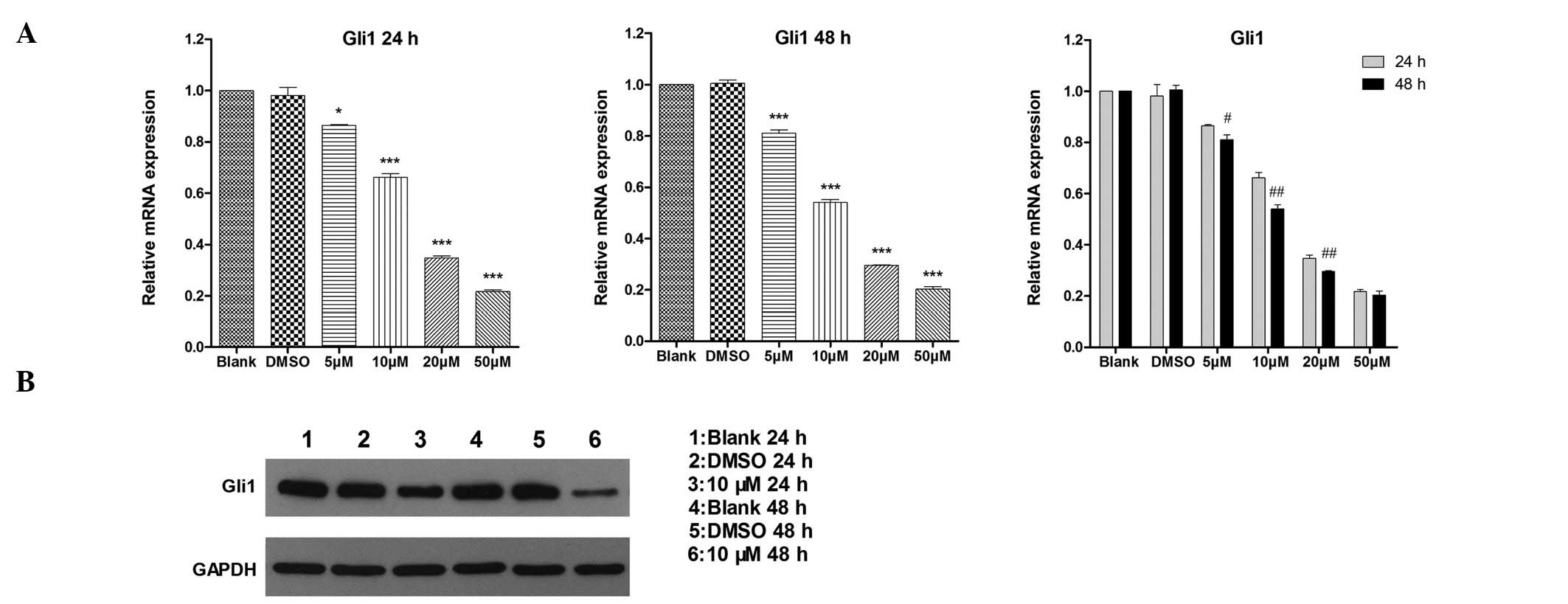
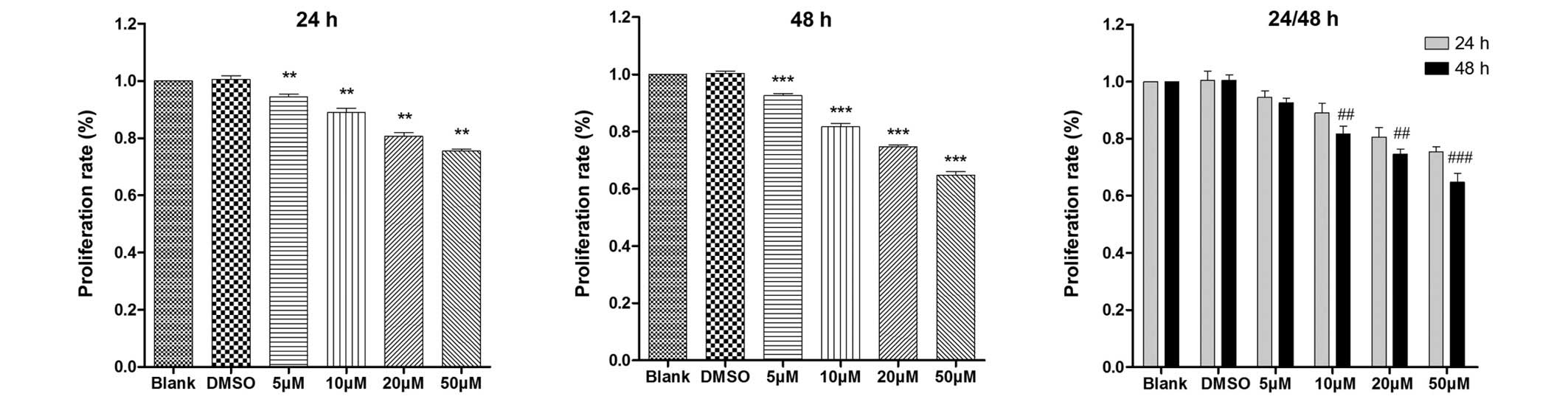
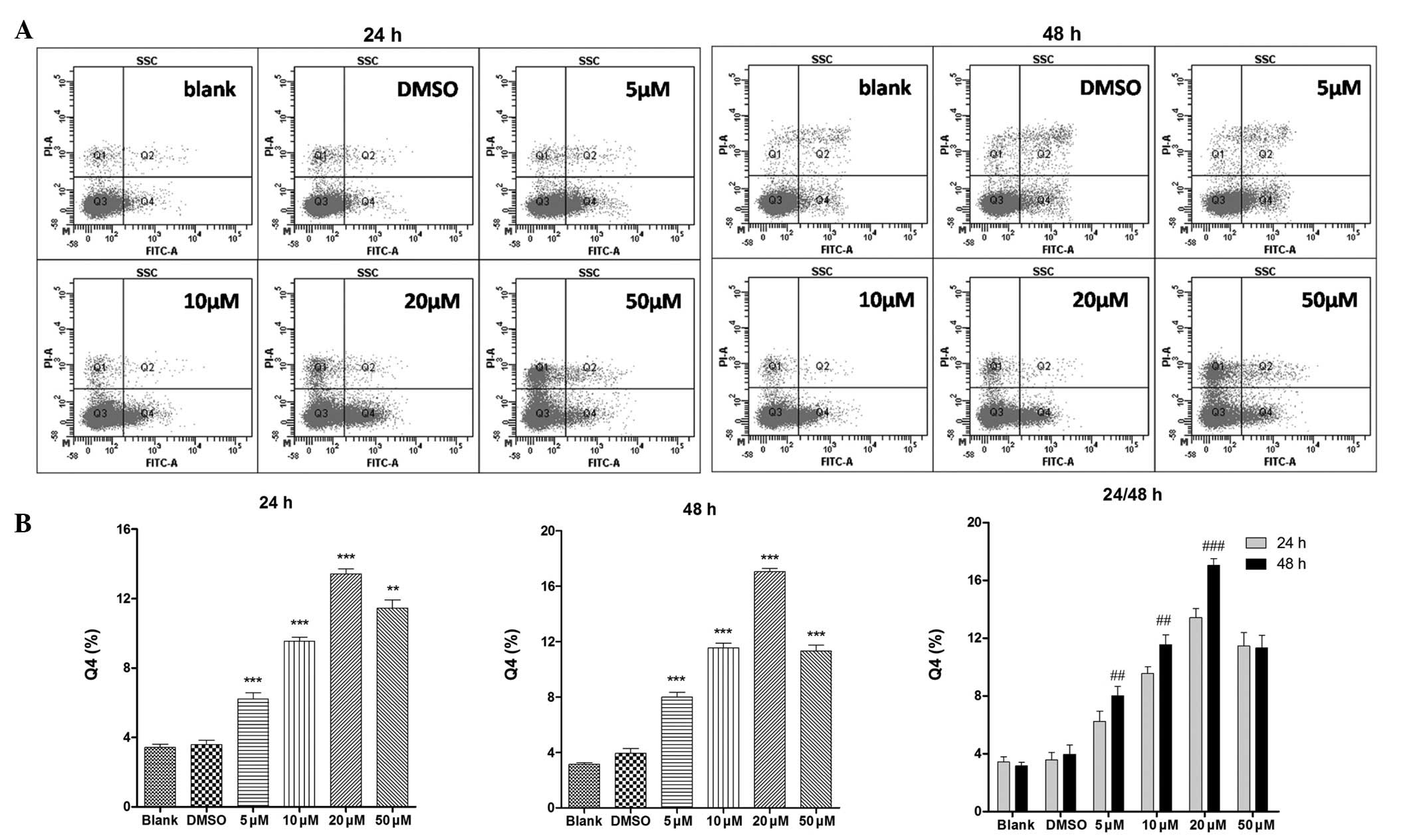
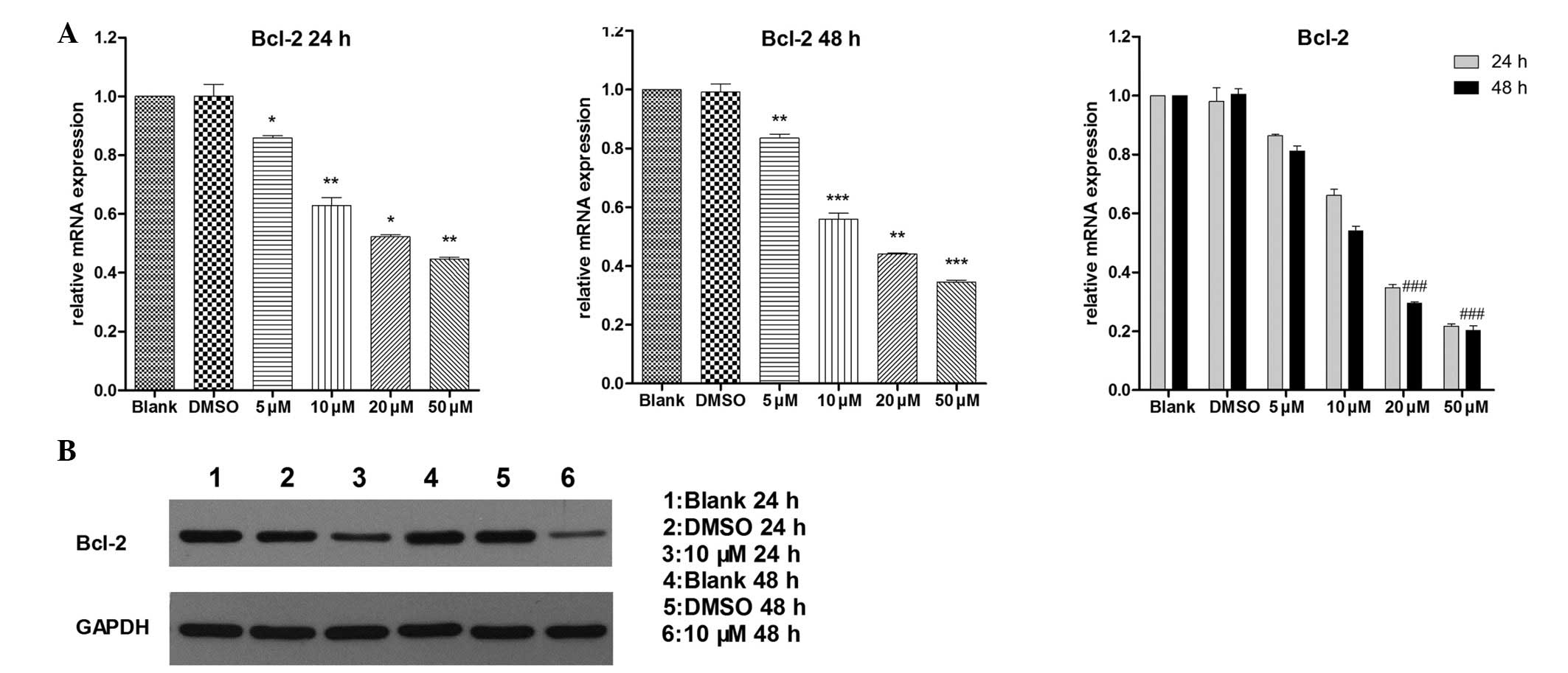
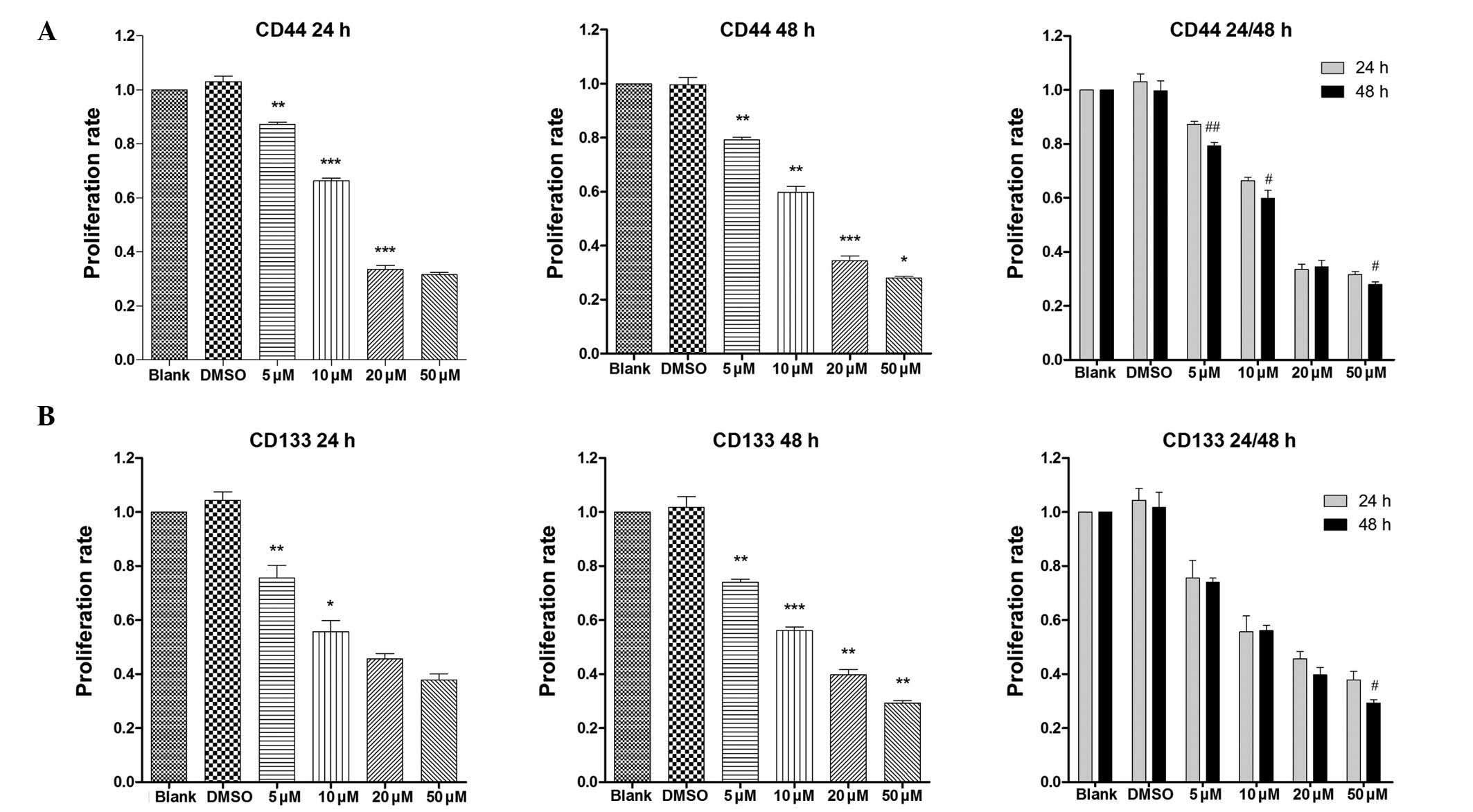
|
1
|
Anderson WF, Camargo MC, Fraumeni JF Jr,
Correa P, Rosenberg PS and Rabkin CS: Age-specific trends in
incidence of noncardia gastric cancer in US adults. JAMA.
303:1723–1728. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ferro A, Peleteiro B, Malvezzi M, Bosetti
C, Bertuccio P, Levi F, Negri E, La Vecchia C and Lunet N:
Worldwide trends in gastric cancer mortality (1980–2011), with
predictions to 2015, and incidence by subtype. Eur J Cancer.
50:1330–1344. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhang WH, Chen XZ, Liu K, Chen XL, Yang K,
Zhang B, Chen ZX, Chen JP, Zhou ZG and Hu JK: Outcomes of surgical
treatment for gastric cancer patients: 11-year experience of a
Chinese high-volume hospital. Med Oncol. 31:1502014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kwon IG, Cho I, Choi YY, Hyung WJ, Kim CB
and Noh SH: Risk factors for complications during surgical
treatment of remnant gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 18:390–396.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Vorechovský I, Benediktsson KP and
Toftgård R: The patched/hedgehog/smoothened signalling pathway in
human breast cancer: No evidence for H133Y SHH, PTCH and SMO
mutations. Eur J Cancer. 35:711–713. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Romer J and Curran T: Targeting
medulloblastoma: Small-molecule inhibitors of the Sonic Hedgehog
pathway as potential cancer therapeutics. Cancer Res. 65:4975–4978.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Athar M, Li C, Kim AL, Spiegelman VS and
Bickers DR: Sonic hedgehog signaling in Basal cell nevus syndrome.
Cancer Res. 74:4967–4975. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang Y, Wang Y, Dong J, Wei W, Song B, Min
H, Yu Y, Lei X, Zhao M, Teng W and Chen J: Developmental
hypothyroxinemia and hypothyroidism reduce proliferation of
cerebellar granule neuron precursors in rat offspring by
downregulation of the sonic hedgehog signaling pathway. Mol
Neurobiol. 49:1143–1152. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Petrova E, Rios-Esteves J, Ouerfelli O,
Glickman JF and Resh MD: Inhibitors of Hedgehog acyltransferase
block Sonic Hedgehog signaling. Nat Chem Biol. 9:247–249. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Álvarez-Buylla A and Ihrie RA: Sonic
hedgehog signaling in the postnatal brain. Semin Cell Dev Biol.
33:105–111. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen M, Qian Y, Dai J and Chu R: The sonic
hedgehog signaling pathway induces myopic development by activating
matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 in Guinea pigs. PLoS One.
9:e969522014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Schaefer GI, Perez JR, Duvall JR, Stanton
BZ, Shamji AF and Schreiber SL: Discovery of small-molecule
modulators of the Sonic Hedgehog pathway. J Am Chem Soc.
135:9675–9680. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Stanton BZ and Peng LF: Small-molecule
modulators of the Sonic Hedgehog signaling pathway. Mol Biosyst.
6:44–54. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Woodland HR: Some studies on early
embryonic development relevant to the study of cancer. J Clin
Pathol Suppl (R Coll Pathol). 7:26–30. 1974. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Martin GR: Teratocarcinomas as a model
system for the study of embryogenesis and neoplasia. Cell.
5:229–243. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Omenetti A and Diehl AM: The adventures of
sonic hedgehog in development and repair II. Sonic hedgehog and
liver development, inflammation and cancer. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 294:G595–G598. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Batsaikhan BE, Yoshikawa K, Kurita N,
Iwata T, Takasu C, Kashihara H and Shimada M: Cyclopamine decreased
the expression of sonic hedgehog and its downstream genes in colon
cancer stem cells. Anticancer Res. 34:6339–6344. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li X, Wang Z, Ma Q, Xu Q, Liu H, Duan W,
Lei J, Ma J, Wang X, Lv S, et al: Sonic hedgehog paracrine
signaling activates stromal cells to promote perineural invasion in
pancreatic cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 20:4326–4338. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen JS, Huang XH, Wang Q, Huang JQ, Zhang
LJ, Chen XL, Lei J and Cheng ZX: Sonic hedgehog signaling pathway
induces cell migration and invasion through focal adhesion
kinase/AKT signaling-mediated activation of matrix
metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and MMP-9 in liver cancer.
Carcinogenesis. 34:10–19. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Rosow DE, Liss AS, Strobel O, Fritz S,
Bausch D, Valsangkar NP, Alsina J, Kulemann B, Park JK, Yamaguchi
J, et al: Sonic Hedgehog in pancreatic cancer: From bench to
bedside, then back to the bench. Surgery. 152(3 Suppl 1): S19–S32.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rodova M, Fu J, Watkins DN, Srivastava RK
and Shankar S: Sonic hedgehog signaling inhibition provides
opportunities for targeted therapy by sulforaphane in regulating
pancreatic cancer stem cell self-renewal. PLoS One. 7:e460832012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jeng KS, Sheen IS, Jeng WJ, Yu MC, Hsiau
HI, Chang FY and Tsai HH: Activation of the sonic hedgehog
signaling pathway occurs in the CD133 positive cells of mouse liver
cancer Hepa 1–6 cells. Onco Targets Ther. 6:1047–1055. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Che L, Yuan YH, Jia J and Ren J:
Activation of sonic hedgehog signaling pathway is an independent
potential prognosis predictor in human hepatocellular carcinoma
patients. Chin J Cancer Res. 24:323–331. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Amin SH, Tibes R, Kim JE and Hybarger CP:
Hedgehog antagonist GDC-0449 is effective in the treatment of
advanced basal cell carcinoma. Laryngoscope. 120:2456–2459. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Singh BN, Fu J, Srivastava RK and Shankar
S: Hedgehog signaling antagonist GDC-0449 (Vismodegib) inhibits
pancreatic cancer stem cell characteristics: Molecular mechanisms.
PLoS One. 6:e273062011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Karlou M, Lu JF, Wu G, Maity S, Tzelepi V,
Navone NM, Hoang A, Logothetis CJ and Efstathiou E: Hedgehog
signaling inhibition by the small molecule smoothened inhibitor
GDC-0449 in the bone forming prostate cancer xenograft MDA PCa
118b. Prostate. 72:1638–1647. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li QQ, Skinner J and Bennett JE:
Evaluation of reference genes for real-time quantitative PCR
studies in Candida glabrata following azole treatment. BMC Mol
Biol. 13:222012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yang L: Incidence and mortality of gastric
cancer in China. World J Gastroenterol. 12:17–20. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Papenfuss WA, Kukar M, Oxenberg J, Attwood
K, Nurkin S, Malhotra U and Wilkinson NW: Morbidity and mortality
associated with gastrectomy for gastric cancer. Ann Surg Oncol.
21:3008–3014. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
De Luca A, Parmigiani E, Tosatto G,
Martire S, Hoshino M, Buffo A, Leto K and Rossi F: Exogenous Sonic
hedgehog modulates the pool of GABAergic interneurons during
cerebellar development. Cerebellum. 14:72–85. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Lewis S: Neural development: Double agent
sonic hedgehog. Nat Rev Neurosci. 14:666–667. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Courchet J and Polleux F: Sonic hedgehog,
BOC and synaptic development: New players for an old game. Neuron.
73:1055–1058. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Xu X, Ding H, Rao G, Arora S, Saclarides
CP, Esparaz J, Gattuso P, Solorzano CC and Prinz RA: Activation of
the Sonic Hedgehog pathway in thyroid neoplasms and its potential
role in tumor cell proliferation. Endocr Relat Cancer. 19:167–179.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Shaw A, Gipp J and Bushman W: The Sonic
Hedgehog pathway stimulates prostate tumor growth by paracrine
signaling and recapitulates embryonic gene expression in tumor
myofibroblasts. Oncogene. 28:4480–4490. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lin J, Wei L, Shen A, Cai Q, Xu W, Li H,
Zhan Y, Hong Z and Peng J: Hedyotis diffusa Willd extract
suppresses Sonic hedgehog signaling leading to the inhibition of
colorectal cancer angiogenesis. Int J Oncol. 42:651–656. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Dahmane N, Lee J, Robins P, Heller P and
Ruiz i Altaba A: Activation of the transcription factor Gli1 and
the Sonic hedgehog signalling pathway in skin tumours. Nature.
389:876–881. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Fan H, Oro AE, Scott MP and Khavari PA:
Induction of basal cell carcinoma features in transgenic human skin
expressing Sonic Hedgehog. Nat Med. 3:788–792. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Dreno B, Basset-Seguin N, Caro I, Yue H
and Schadendorf D: Clinical benefit assessment of vismodegib
therapy in patients with advanced basal cell carcinoma. Oncologist.
19:790–796. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yin VT, Sniegowski M and Esmaeli B:
Indications and limitations of vismodegib for basal cell carcinoma.
JAMA Ophthalmol. 132:905–906. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kim EJ, Sahai V, Abel EV, Griffith KA,
Greenson JK, Takebe N, Khan GN, Blau JL, Craig R, Balis UG, et al:
Pilot clinical trial of hedgehog pathway inhibitor GDC-0449
(Vismodegib) in combination with gemcitabine in patients with
metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res.
20:5937–5945. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lorusso PM, Jimeno A, Dy G, Adjei A,
Berlin J, Leichman L, Low JA, Colburn D, Chang I, Cheeti S, et al:
Pharmacokinetic dose-scheduling study of hedgehog pathway inhibitor
vismodegib (GDC-0449) in patients with locally advanced or
metastatic solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 17:5774–5782. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Tang SN, Fu J, Nall D, Rodova M, Shankar S
and Srivastava RK: Inhibition of sonic hedgehog pathway and
pluripotency maintaining factors regulate human pancreatic cancer
stem cell characteristics. Int J Cancer. 131:30–40. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
43
|
Heiden KB, Williamson AJ, Doscas ME, Ye J,
Wang Y, Liu D, Xing M, Prinz RA and Xu X: The sonic hedgehog
signaling pathway maintains the cancer stem cell self-renewal of
anaplastic thyroid cancer by inducing snail expression. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 99:E2178–E2187. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|