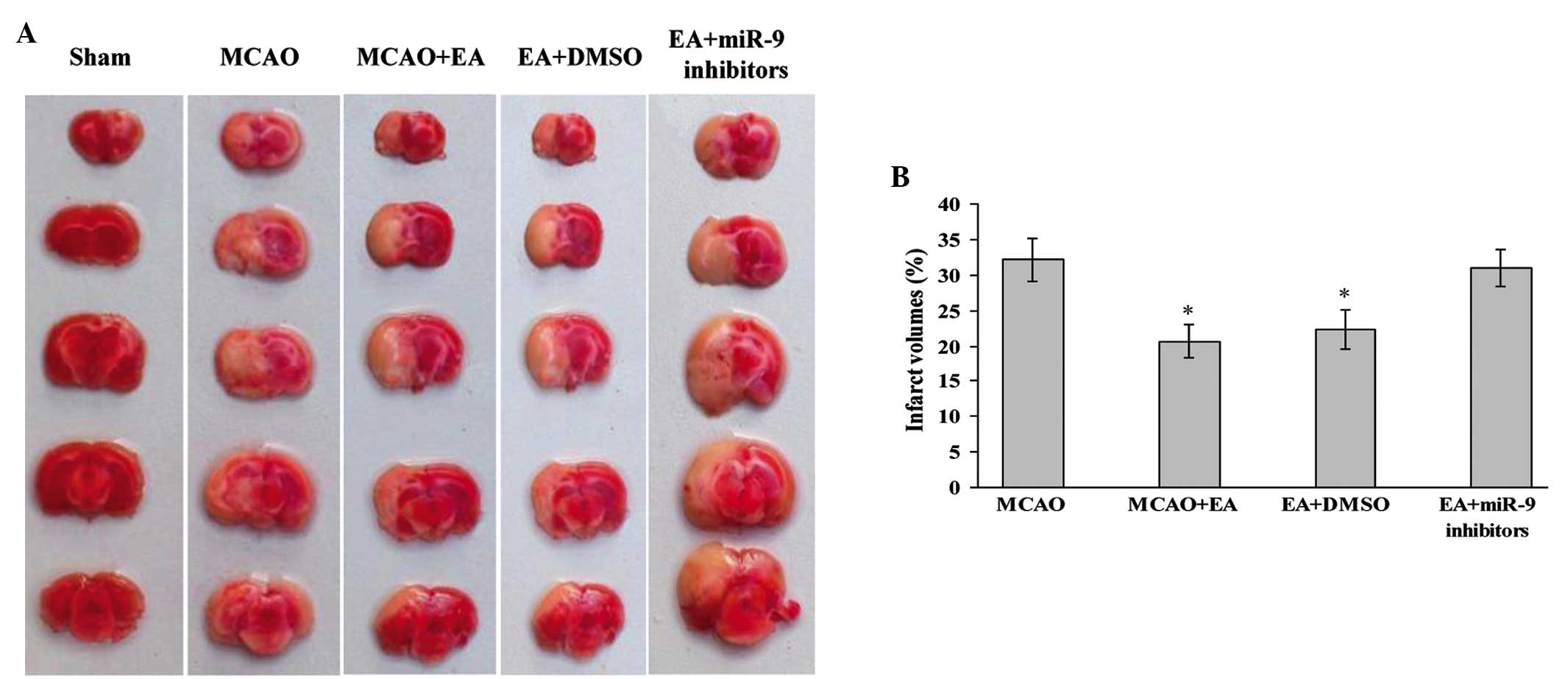
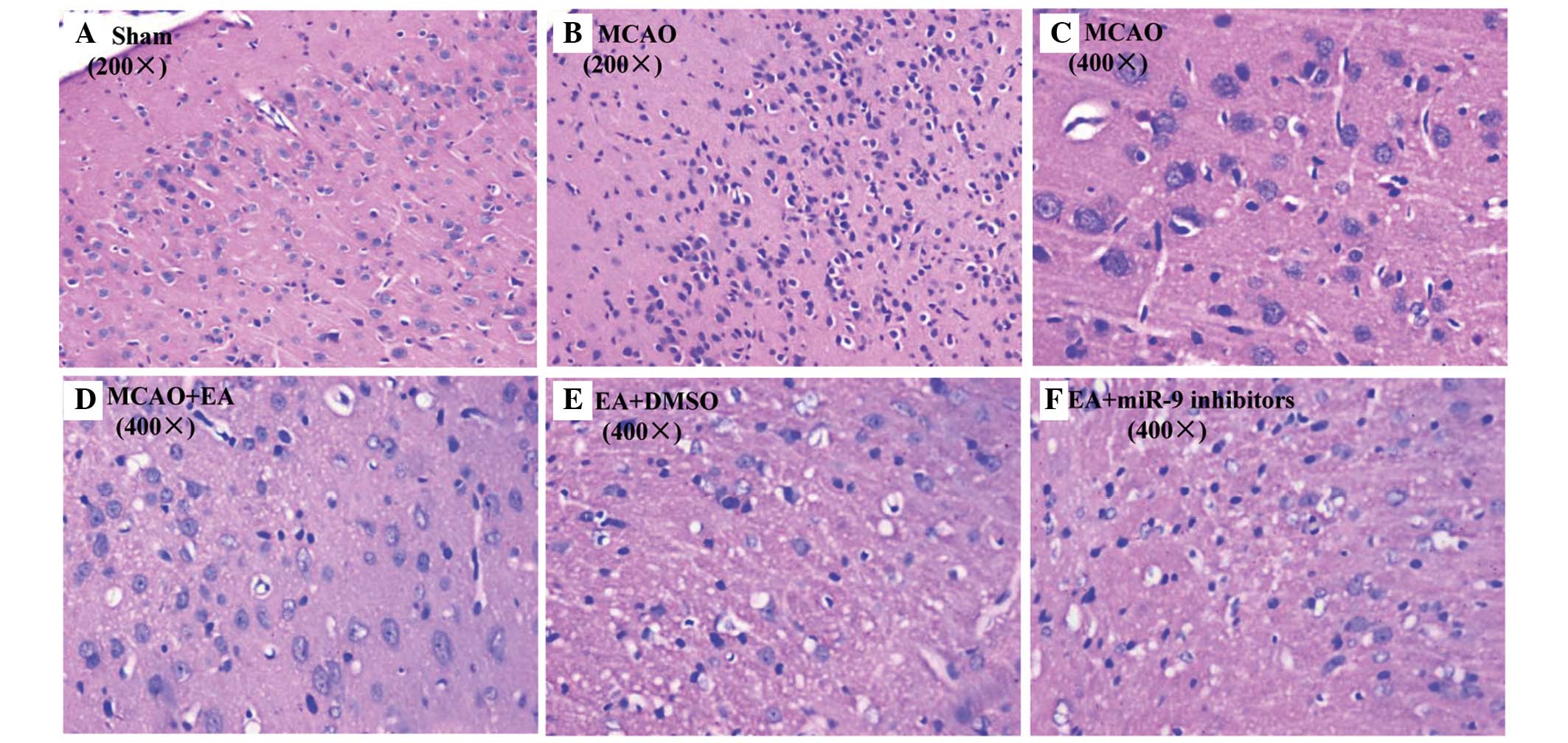
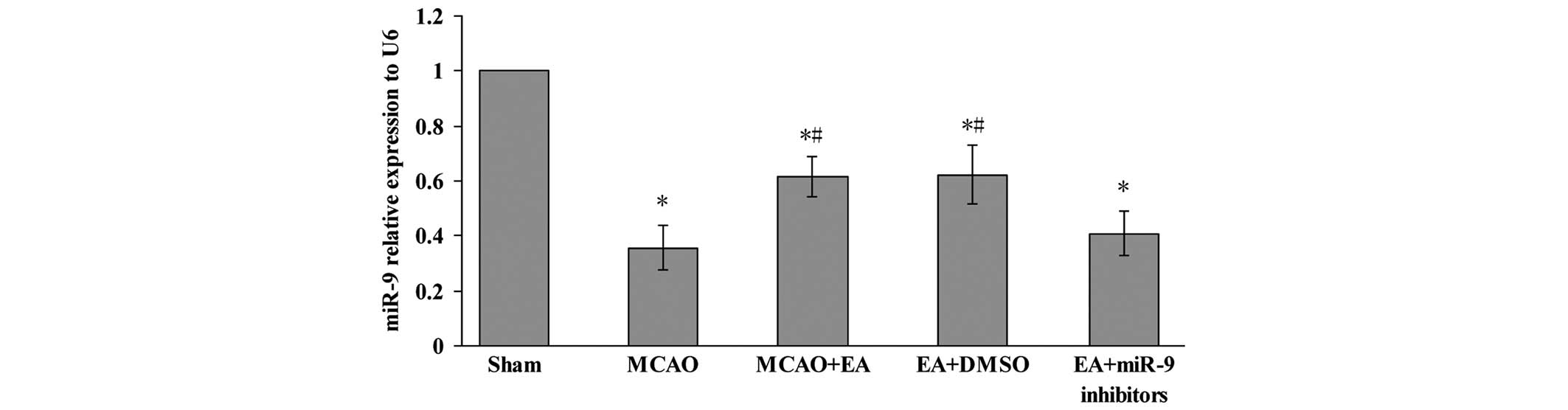
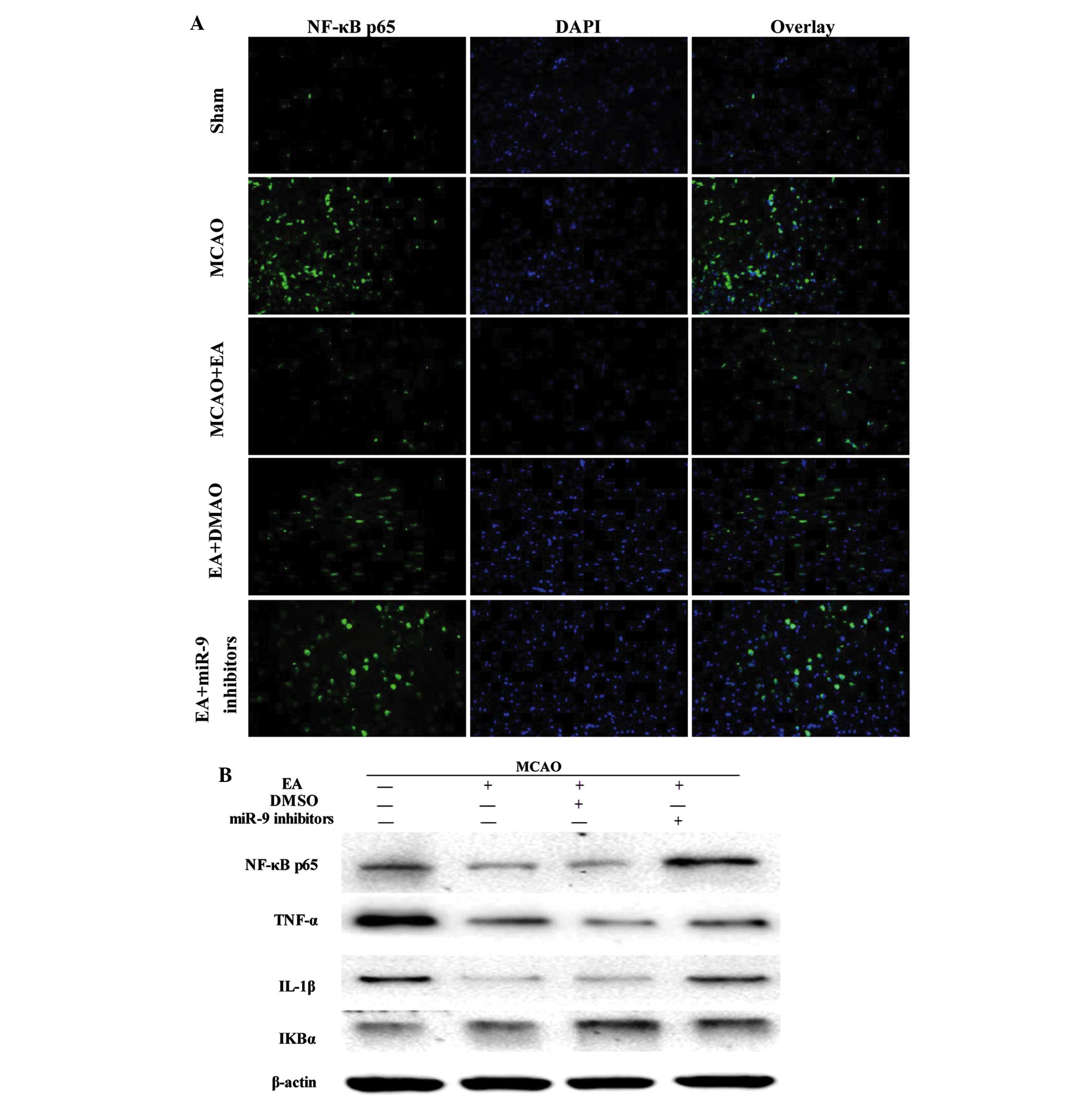
|
1
|
Cullen BR: Transcription and processing of
human microRNA precursors. Mol Cell. 16:861–865. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Doench JG and Sharp PA: Specificity of
microRNA target selection in translational repression. Genes Dev.
18:504–511. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
O'Connell RM, Rao DS and Baltimore D:
MicroRNA regulation of inflammatory responses. Annu Rev Immunol.
30:295–312. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Akerblom M, Sachdeva R, Quintino L,
Wettergren EE, Chapman KZ, Manfre G, Lindvall O, Lundberg C and
Jakobsson J: Visualization and genetic modification of resident
brain microglia using lentiviral vectors regulated by microRNA-9.
Nat Commun. 4:17702013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yao H, Ma R, Yang L, Hu G, Chen X, Duan M,
Kook Y, Niu F, Liao K, Fu M, et al: MiR-9 promotes microglial
activation by targeting MCPIP1. Nat Commun. 5:43862014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Guo LM, Pu Y, Han Z, Liu T, Li YX, Liu M,
Li X and Tang H: MicroRNA-9 inhibits ovarian cancer cell growth
through regulation of NF-kappaB1. FEBS J. 276:5537–5546. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang J, Gu Z, Ni P, Qiao Y, Chen C, Liu X,
Lin J, Chen N and Fan Q: NF-kappaB P50/P65 hetero-dimer mediates
differential regulation of CD166/ALCAM expression via interaction
with micoRNA-9 after serum deprivation, providing evidence for a
novel negative auto-regulatory loop. Nucleic Acids Res.
39:6440–6455. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lukiw WJ: NF-κB-regulated micro RNAs
(miRNAs) in primary human brain cells. Exp Neurol. 235:484–490.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
9
|
Liu XS, Chopp M, Zhang RL, Tao T, Wang XL,
Kassis H, Hozeska-Solgot A, Zhang L, Chen C and Zhang ZG: MicroRNA
profiling in subventricular zone after stroke: MiR-124a regulates
proliferation of neural progenitor cells through Notch signaling
pathway. PLoS One. 6:e234612011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu Y, Zhang J, Han R, Liu H, Sun D and
Liu X: Downregulation of serum brain specific microRNA is
associated with inflammation and infarct volume in acute ischemic
stroke. J Clin Neurosci. 22:291–295. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Chen W, Gu HW, Ma WP, Li QS, Yu Q, Liu XQ,
Liu SH, Li WH, Liu HL and Dai MT: Multicentral randomized
controlled study on effects of acupuncture at Zusanli (ST 36) and
Xuanzhong (GB 39) on cerebrovascular function in the patient of
ischemic stroke. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 26:851–853. 2006.In
Chinese.
|
|
12
|
Lan L, Tao J, Chen A, Xie G, Huang J, Lin
J, Peng J and Chen L: Electroacupuncture exerts anti-inflammatory
effects in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injured rats via
suppression of the TLR4/NF-κB pathway. Int J Mol Med. 31:75–80.
2013.
|
|
13
|
Jin Z, Liang J, Wang J and Kolattukudy PE:
Delayed brain ischemia tolerance induced by electroacupuncture
pretreatment is mediated via MCP-induced protein 1. J
Neuroinflammation. 10:632013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xue X, You Y, Tao J, Ye X, Huang J, Yang
S, Lin Z, Hong Z, Peng J and Chen L: Electro-acupuncture at points
of Zusanli and Quchi exerts anti-apoptotic effect through the
modulation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Neurosci Lett. 558:14–19.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Lu T, Song QH, Xu RM, Guo YH, Wang F, Hu
JP, Wang Y and Zhang LY: Dance combined with magnetic pulse
stimulates the ability of walk and balance in elder people. Int J
Clin Exp Med. 8:4381–4386. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhao H, Wang J, Gao L, Wang R, Liu X, Gao
Z, Tao Z, Xu C, Song J, Ji X and Luo Y: MiRNA-424 protects against
permanent focal cerebral ischemia injury in mice involving
suppressing microglia activation. Stroke. 44:1706–1713. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S and
Cummins R: Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without
craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 20:84–91. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhuang L, He J, Zhuang X and Lu L: Quality
of reporting on randomized controlled trials of acupuncture for
stroke rehabilitation. BMC Complement Altern Med. 14:1512014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chang L, He PL, Zhou ZZ and Li YH:
Efficacy observation of dysphagia after acute stroke treated with
acupuncture and functional electric stimulation. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu.
34:737–740. 2014.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sze FK, Wong E, Or KK, Lau J and Woo J:
Does acupuncture improve motor recovery after stroke? A
meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Stroke.
33:2604–2619. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shen PF, Kong L, Ni LW, Guo HL, Yang S,
Zhang LL, Zhang ZL, Guo JK, Xiong J, Zhen Z, et al: Acupuncture
intervention in ischemic stroke: A randomized controlled
prospective study. Am J Chin Med. 40:685–693. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang H, Xie Y, Zhang Q, Xu N, Zhong H,
Dong H, Liu L, Jiang T, Wang Q and Xiong L: Transcutaneous electric
acupoint stimulation reduces intra-operative remifentanil
consumption and alleviates postoperative side-effects in patients
undergoing sinusotomy: A prospective, randomized,
placebo-controlled trial. Br J Anaesth. 112:1075–1082. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Harari OA and Liao JK: NF-κB and innate
immunity in ischemic stroke. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1207:32–40. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Feng X, Yang S, Liu J, Huang J, Peng J,
Lin J, Tao J and Chen L: Electroacupuncture ameliorates cognitive
impairment through inhibition of NF-κB-mediated neuronal cell
apoptosis in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injured rats. Mol Med
Rep. 7:1516–1522. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang ZK, Ni GX, Liu K, Xiao ZX, Yang BW,
Wang J and Wang S: Research on the changes of IL-1 receptor and
TNF-alpha receptor in rats with cerebral ischemia reperfusion and
the chronergy of acupuncture intervention. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu.
32:1012–1018. 2012.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Alvarez-Garcia I and Miska EA: MicroRNA
functions in animal development and human disease. Development.
132:4653–4662. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ambros V: MicroRNA pathways in flies and
worms: Growth, death, fat, stress and timing. Cell. 113:673–676.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Quinn SR and O'Neill LA: A trio of
microRNAs that control Toll-like receptor signalling. Int Immunol.
23:421–425. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sheedy FJ, Palsson-McDermott E, Hennessy
EJ, Martin C, O'Leary JJ, Ruan Q, Johnson DS, Chen Y and O'Neill
LA: Negative regulation of TLR4 via targeting of the
proinflammatory tumor suppressor PDCD4 by the microRNA miR-21. Nat
Immunol. 11:141–147. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
El Gazzar M and McCall CE: MicroRNAs
distinguish translational from transcriptional silencing during
endotoxin tolerance. J Biol Chem. 285:20940–20951. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tili E, Michaille JJ, Cimino A, Costinean
S, Dumitru CD, Adair B, Fabbri M, Alder H, Liu CG, Calin GA and
Croce CM: Modulation of miR-155 and miR-125b levels following
lipopolysaccharide/TNF-alpha stimulation and their possible roles
in regulating the response to endotoxin shock. J Immunol.
179:5082–5089. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu DZ, Tian Y, Ander BP, Xu H, Stamova
BS, Zhan X, Turner RJ, Jickling G and Sharp FR: Brain and blood
microRNA expression profiling of ischemic stroke, intracerebral
hemorrhage and kainate seizures. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.
30:92–101. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Thulin P, Wei T, Werngren O, Cheung L,
Fisher RM, Grandér D, Corcoran M and Ehrenborg E: MicroRNA-9
regulates the expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor δ in human monocytes during the inflammatory response. Int
J Mol Med. 31:1003–1010. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Bazzoni F, Rossato M, Fabbri M, Gaudiosi
D, Mirolo M, Mori L, Tamassia N, Mantovani A, Cassatella MA and
Locati M: Induction and regulatory function of miR-9 in human
monocytes and neutrophils exposed to proinflammatory signals. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:5282–5287. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Delaloy C and Gao FB: MicroRNA-9
multitasking near organizing centers. Nat Neurosci. 11:625–626.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Coolen M and Bally-Cuif L: MicroRNAs in
brain development and physiology. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 19:461–470.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wan HY, Guo LM, Liu T, Liu M, Li X and
Tang H: Regulation of the transcription factor NF-kappaB1 by
microRNA-9 in human gastric adenocarcinoma. Mol Cancer. 9:162010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|