|
1
|
Wang LL, Huang Y, Wang G and Chen SD: The
potential role of microRNA-146 in Alzheimer's disease: Biomarker or
therapeutic target? Med Hypotheses. 78:398–401. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Alzheimer's Association: 2013 Alzheimer's
disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 9:208–245. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Banzhaf-Strathmann J, Benito E, May S,
Arzberger T, Tahirovic S, Kretzschmar H, Fischer A and Edbauer D:
MicroRNA-125b induces tau hyperphosphorylation and cognitive
deficits in Alzheimer's disease. EMBO J. 33:1667–1680. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Giannakopoulos P, Hof PR and Bouras C:
Selective vulnerability of neocortical association areas in
Alzheimer's disease. Microsc Res Tech. 43:16–23. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Karran E, Mercken M and De Strooper B: The
amyloid cascade hypothesis for Alzheimer's disease: An appraisal
for the development of therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug Discov.
10:698–712. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lewczuk P, Kamrowski-Kruck H, Peters O,
Heuser I, Jessen F, Popp J, Bürger K, Hampel H, Frölich L, Wolf S,
et al: Soluble amyloid precursor proteins in the cerebrospinal
fluid as novel potential biomarkers of Alzheimer's disease: A
multicenter study. Mol Psychiatry. 15:138–145. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Weiner MW: Dementia in 2012: Further
insights into Alzheimer disease pathogenesis. Nat Rev Neurol.
9:65–66. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu CG, Wang JL, Li L and Wang PC:
MicroRNA-384 regulates both amyloid precursor protein and
β-secretase expression and is a potential biomarker for Alzheimer's
disease. Int J Mol Med. 34:160–166. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu CG, Song J, Zhang YQ and Wang PC:
MicroRNA-193b is a regulator of amyloid precursor protein in the
blood and cerebrospinal fluid derived exosomal microRNA-193b is a
biomarker of Alzheimer's disease. Mol Med Rep. 10:2395–2400.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chan AW and Kocerha J: The path to
microRNA therapeutics in psychiatric and neurodegenerative
disorders. Front Genet. 3:822012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Delay C, Mandemakers W and Hébert SS:
MicroRNAs in Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Dis. 46:285–290. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Delay C and Hébert SS: MicroRNAs and
Alzheimer's disease mouse models: Current insights and future
research avenues. Int J Alzheimers Dis. 2011:8949382011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL and Ambros V: The C.
elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense
complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 75:843–854. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang SE and Lin RJ: MicroRNA and
HER2-overexpressing cancer. Microrna. 2:137–147. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Alvarez-Garcia I and Miska EA: MicroRNA
functions in animal development and human disease. Development.
132:4653–4662. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Decembrini S, Bressan D, Vignali R, Pitto
L, Mariotti S, Rainaldi G, Wang X, Evangelista M, Barsacchi G and
Cremisi F: MicroRNAs couple cell fate and developmental timing in
retina. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:21179–21184. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Rosa A and Brivanlou AH: MicroRNAs in
early vertebrate development. Cell Cycle. 8:3513–3520. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lu LF and Liston A: MicroRNA in the immune
system, microRNA as an immune system. Immunology. 127:291–298.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Trang P, Weidhaas JB and Slack FJ:
MicroRNAs as potential cancer therapeutics. Oncogene. 27(Suppl 2):
S52–S57. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang WX, Huang Q, Hu Y, Stromberg AJ and
Nelson PT: Patterns of microRNA expression in normal and early
Alzheimer's disease human temporal cortex: White matter versus gray
matter. Acta Neuropathol. 121:193–205. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
22
|
Eacker SM, Dawson TM and Dawson VL:
Understanding microRNAs in neurodegeneration. Nat Rev Neurosci.
10:837–841. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
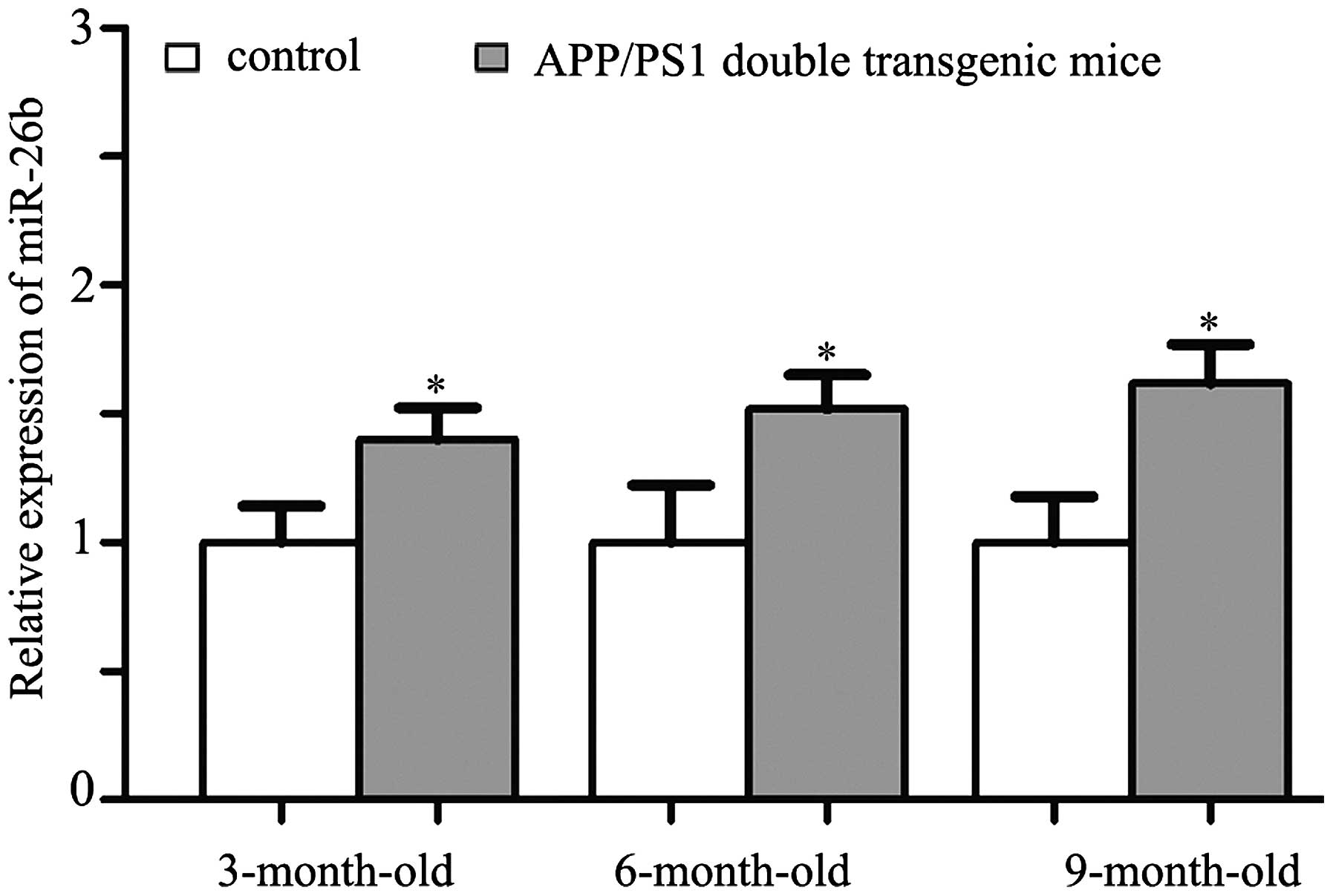
Absalon S, Kochanek DM, Raghavan V and
Krichevsky AM: MiR-26b, upregulated in Alzheimer's disease,
activates cell cycle entry, tau-phosphorylation and apoptosis in
postmitotic neurons. J Neurosci. 33:14645–14659. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2−ΔΔCt method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Zhang YC, Wang ZF, Wang Q, Wang YP and
Wang JZ: Melatonin attenuates beta-amyloid-induced inhibition of
neuro-filament expression. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 25:447–451.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li J, Kong X, Zhang J, Luo Q, Li X and
Fang L: MiRNA-26b inhibits proliferation by targeting PTGS2 in
breast cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 13:72013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ji Y, He Y, Liu L and Chong X: MiRNA-26b
regulates the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in
desferrioxamine-treated CNE cells. FEBS Lett. 584:961–967. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ji J, Shi J, Budhu A, Yu Z, Forgues M,
Roessler S, Ambs S, Chen Y, Meltzer PS, Croce CM, et al: MicroRNA
expression, survival and response to interferon in liver cancer. N
Engl J Med. 361:1437–1447. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cao J, Guo T, Dong Q, Zhang J and Li Y:
miR-26b is downregulated in human tongue squamous cell carcinoma
and regulates cell proliferation and metastasis through a
COX-2-dependent mechanism. Oncol Rep. 33:974–980. 2015.
|
|
30
|
Gao W, Shen H, Liu L, Xu J, Xu J and Shu
Y: MiR-21 over-expression in human primary squamous cell lung
carcinoma is associated with poor patient prognosis. J Cancer Res
Clin Oncol. 137:557–566. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Wu N, Zhao X, Liu M, Liu H, Yao W, Zhang
Y, Cao S and Lin X: Role of microRNA-26b in glioma development and
its mediated regulation on EphA2. PLoS One. 6:e162642011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li J, Li X, Kong X, Luo Q, Zhang J and
Fang L: MiRNA-26b inhibits cellular proliferation by targeting CDK8
in breast cancer. Int J Clin Exp Med. 7:558–565. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Dassow H and Aigner A: MicroRNAs (miRNAs)
in colorectal cancer: From aberrant expression towards therapy.
Curr Pharm Des. 19:1242–1252. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
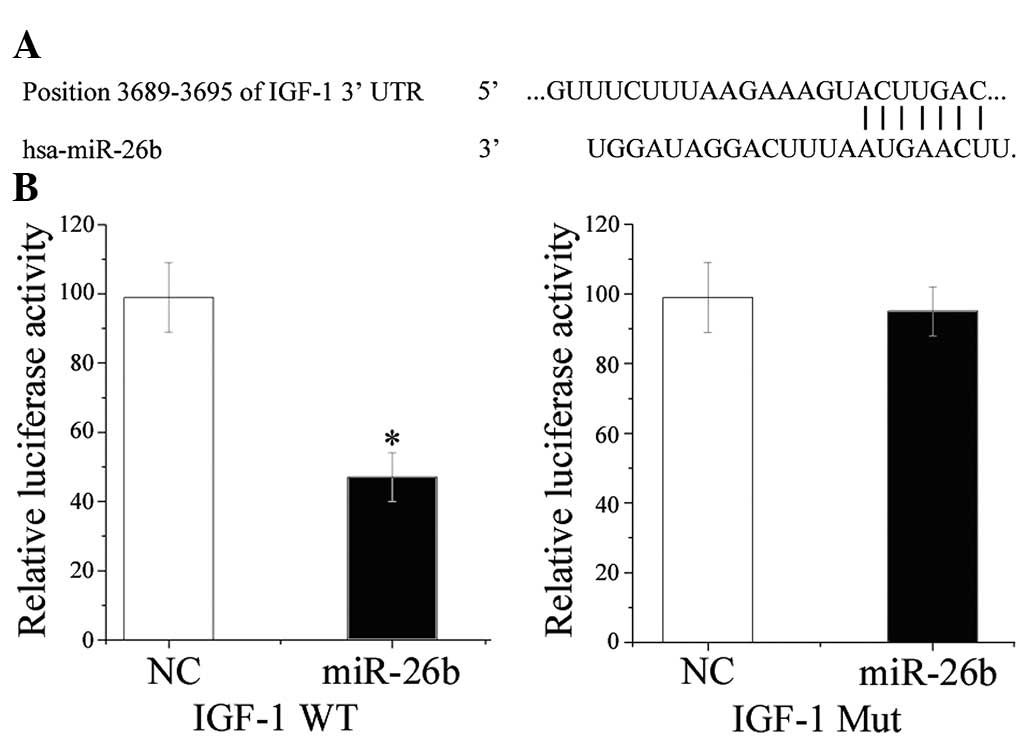
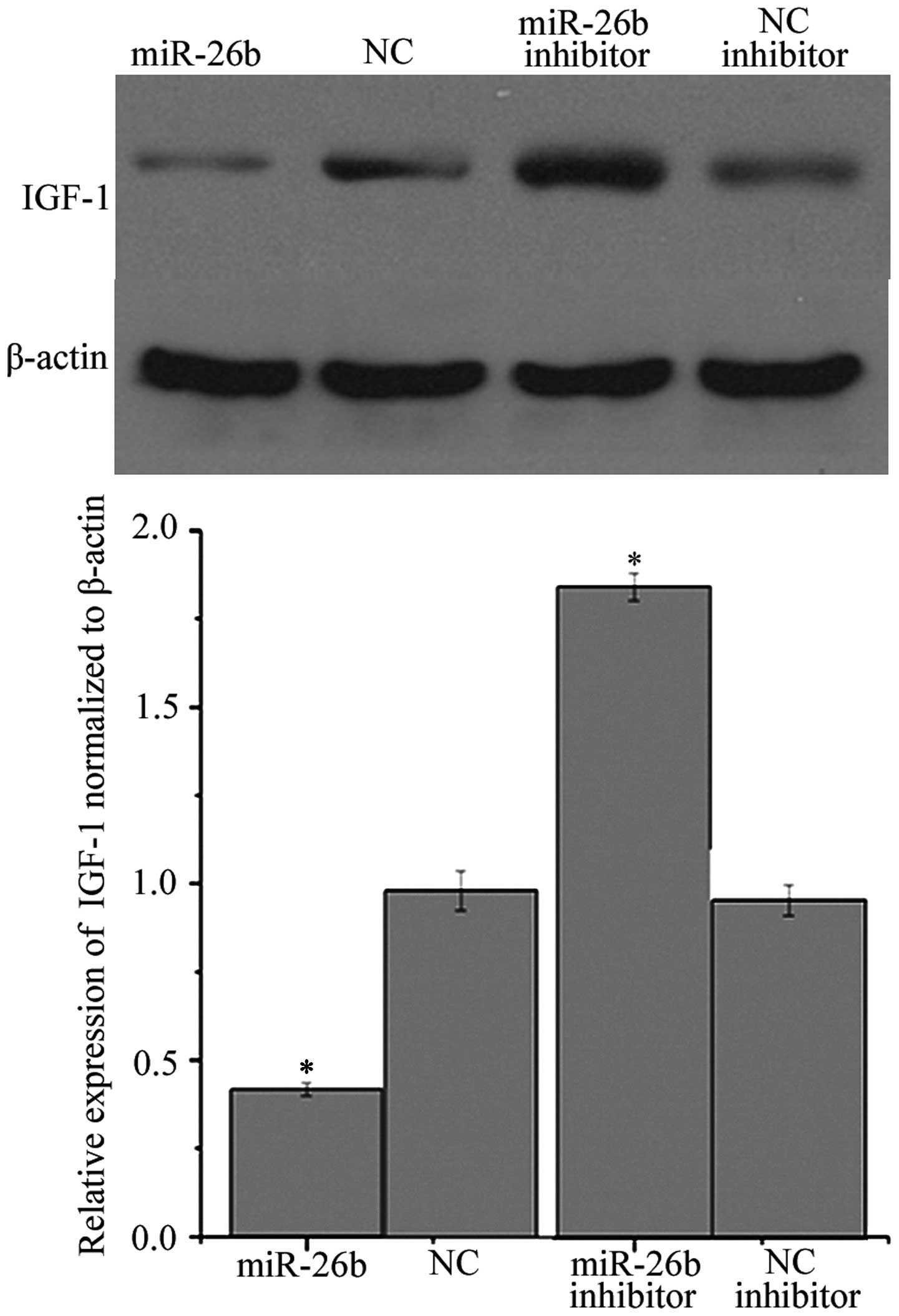
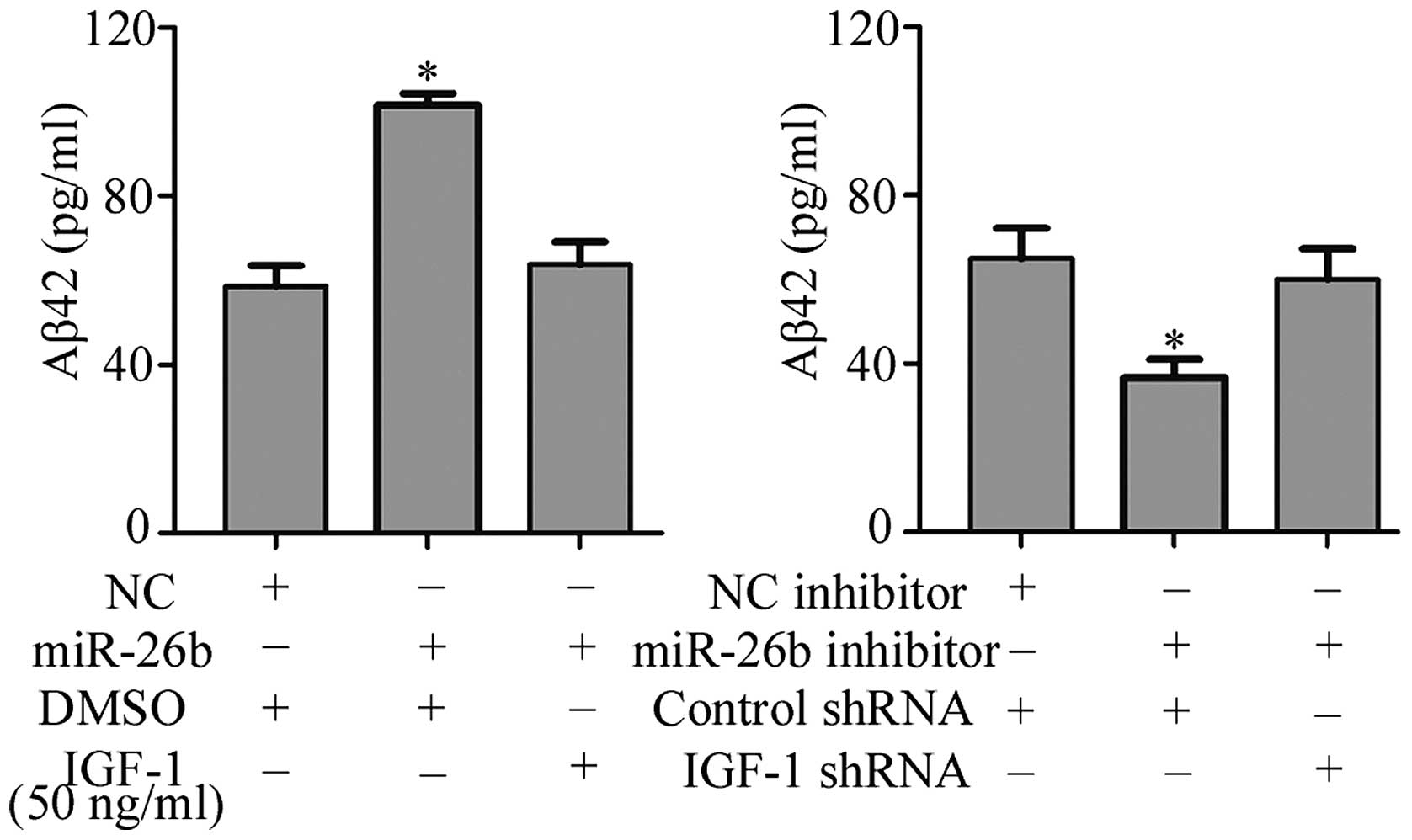
Carro E, Trejo JL, Gomez-Isla T, LeRoith D
and Torres-Aleman I: Serum insulin-like growth factor I regulates
brain amyloid-beta levels. Nat Med. 8:1390–1397. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Xiao AW, He J, Wang Q, Luo Y, Sun Y, Zhou
YP, Guan Y, Lucassen PJ and Dai JP: The origin and development of
plaques and phosphorylated tau are associated with axonopathy in
Alzheimer's disease. Neurosci Bull. 27:287–299. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jones JI and Clemmons DR: Insulin-like
growth factors and their binding proteins: Biological actions.
Endocr Rev. 16:3–34. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
van Exel E, Eikelenboom P, Comijs H, Deeg
DJ, Stek ML and Westendorp RG: Insulin-like growth factor-1 and
risk of late-onset Alzheimer's disease: Findings from a family
study. Neurobiol Aging. 35:725e7–e10. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Ye P, Xing Y, Dai Z and D'Ercole AJ: In
vivo actions of insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) on cerebellum
development in transgenic mice: Evidence that IGF-I increases
proliferation of granule cell progenitors. Brain Res Dev Brain Res.
95:44–54. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
D'Ercole AJ, Ye P and O'Kusky JR: Mutant
mouse models of insulin-like growth factor actions in the central
nervous system. Neuropeptides. 36:209–220. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Popken GJ, Hodge RD, Ye P, Zhang J, Ng W,
O'Kusky JR and D'Ercole AJ: In vivo effects of insulin-like growth
factor-I (IGF-I) on prenatal and early postnatal development of the
central nervous system. Eur J Neurosci. 19:2056–2068. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
O'Kusky JR, Ye P and D'Ercole AJ:
Insulin-like growth factor-I promotes neurogenesis and
synaptogenesis in the hippocampal dentate gyrus during postnatal
development. J Neurosci. 20:8435–8442. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wang W, Yu JT, Tan L, Liu QY, Wang HF and
Ma XY: Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1) polymorphism is
associated with Alzheimer's disease in Han Chinese. Neurosci Lett.
531:20–23. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Rollero A, Murialdo G, Fonzi S, Garrone S,
Gianelli MV, Gazzerro E, Barreca A and Polleri A: Relationship
between cognitive function, growth hormone and insulin-like growth
factor I plasma levels in aged subjects. Neuropsychobiology.
38:73–79. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Watanabe T, Miyazaki A, Katagiri T,
Yamamoto H, Idei T and Iguchi T: Relationship between serum
insulin-like growth factor-1 levels and Alzheimer's disease and
vascular dementia. J Geriatr Soc. 53:1748–1753. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Freude S, Schilbach K and Schubert M: The
role of IGF-1 receptor and insulin receptor signaling for the
pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease: From model organisms to human
disease. Curr Alzheimer Res. 6:213–223. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yankner BA, Dawes LR, Fisher S,
Villa-Komaroff L, Oster-Granite ML and Neve RL: Neurotoxicity of a
fragment of the amyloid precursor associated with Alzheimer's
disease. Science. 245:417–420. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Carro E, Trejo JL, Gerber A, Loetscher H,
Torrado J, Metzger F and Torres-Aleman I: Therapeutic actions of
insulin-like growth factor I on APP/PS2 mice with severe brain
amyloidosis. Neurobiol Aging. 27:1250–1257. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Carro E and Torres-Aleman I: Insulin-like
growth factor I and Alzheimer's disease: Therapeutic prospects?
Expert Rev Neurother. 4:79–86. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Gasparini L and Xu H: Potential roles of
insulin and IGF-1 in Alzheimer's disease. Trends Neurosci.
26:404–406. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Daválos A and Suárez Y: MiRNA-based
therapy: From bench to bedside. Pharmacol Res. 75:1–2. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|