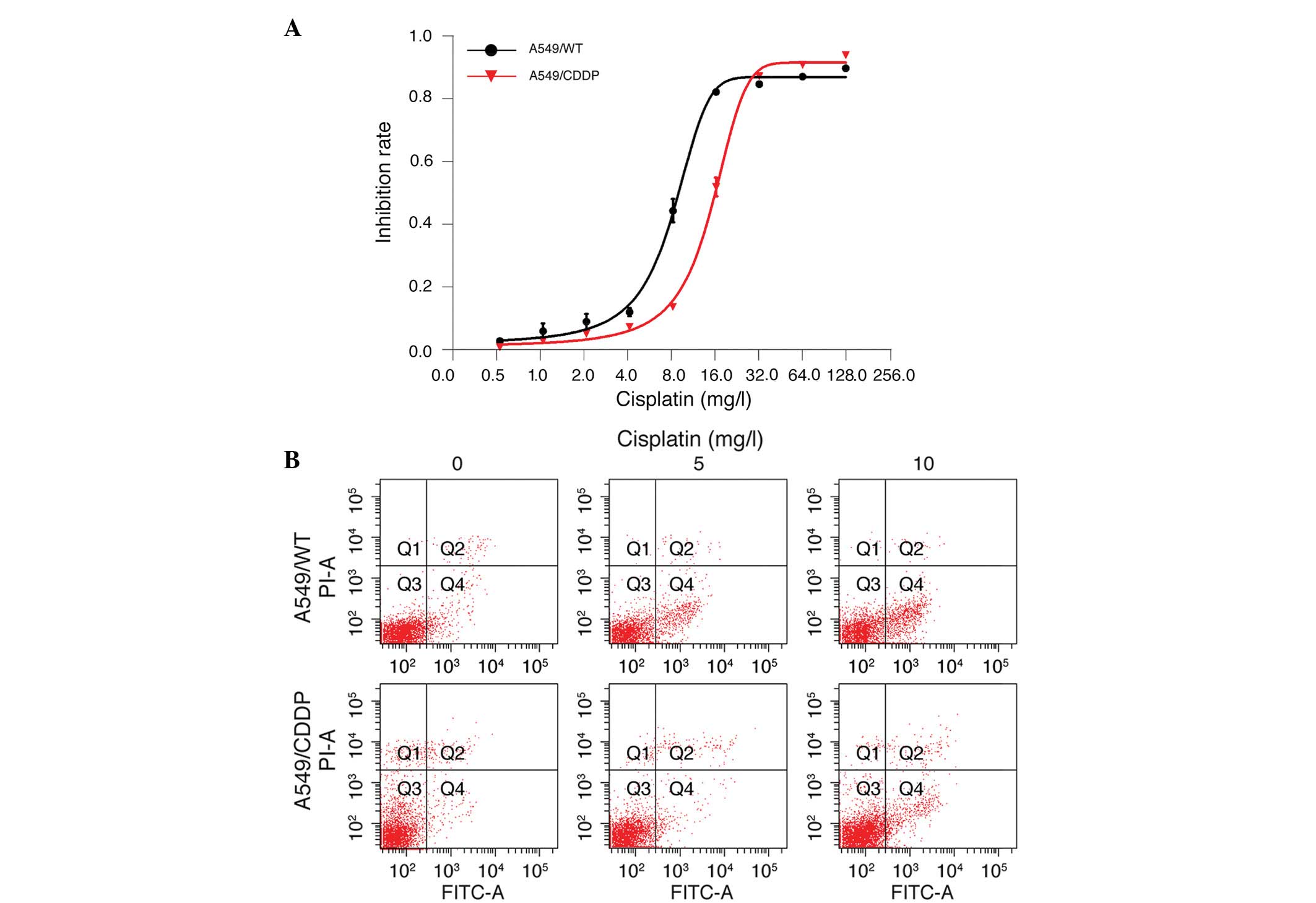
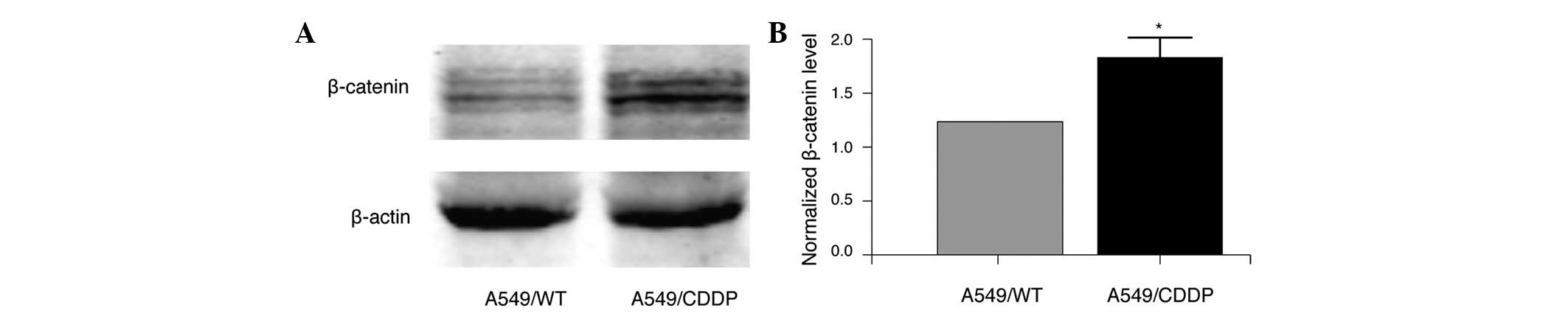
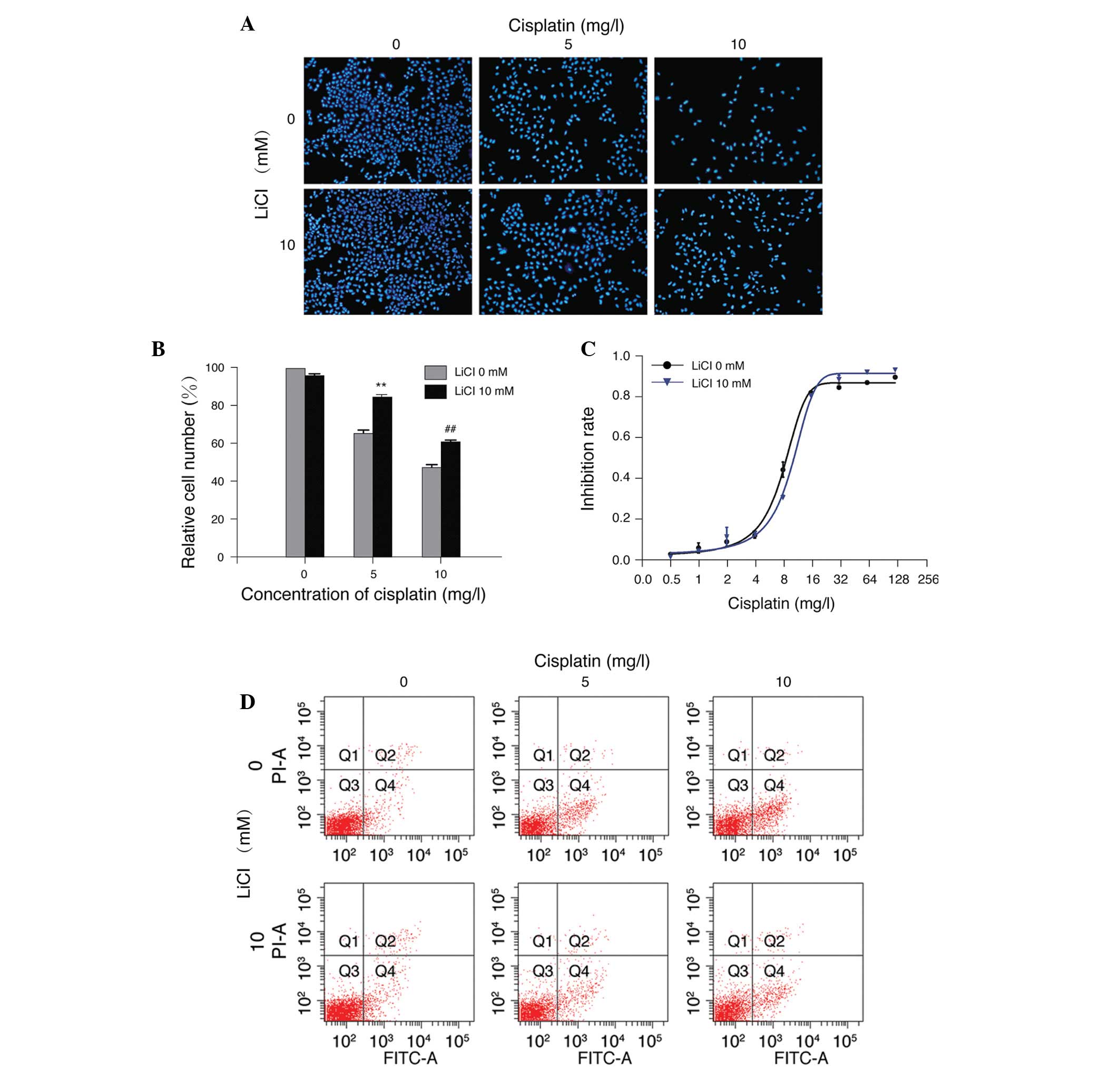
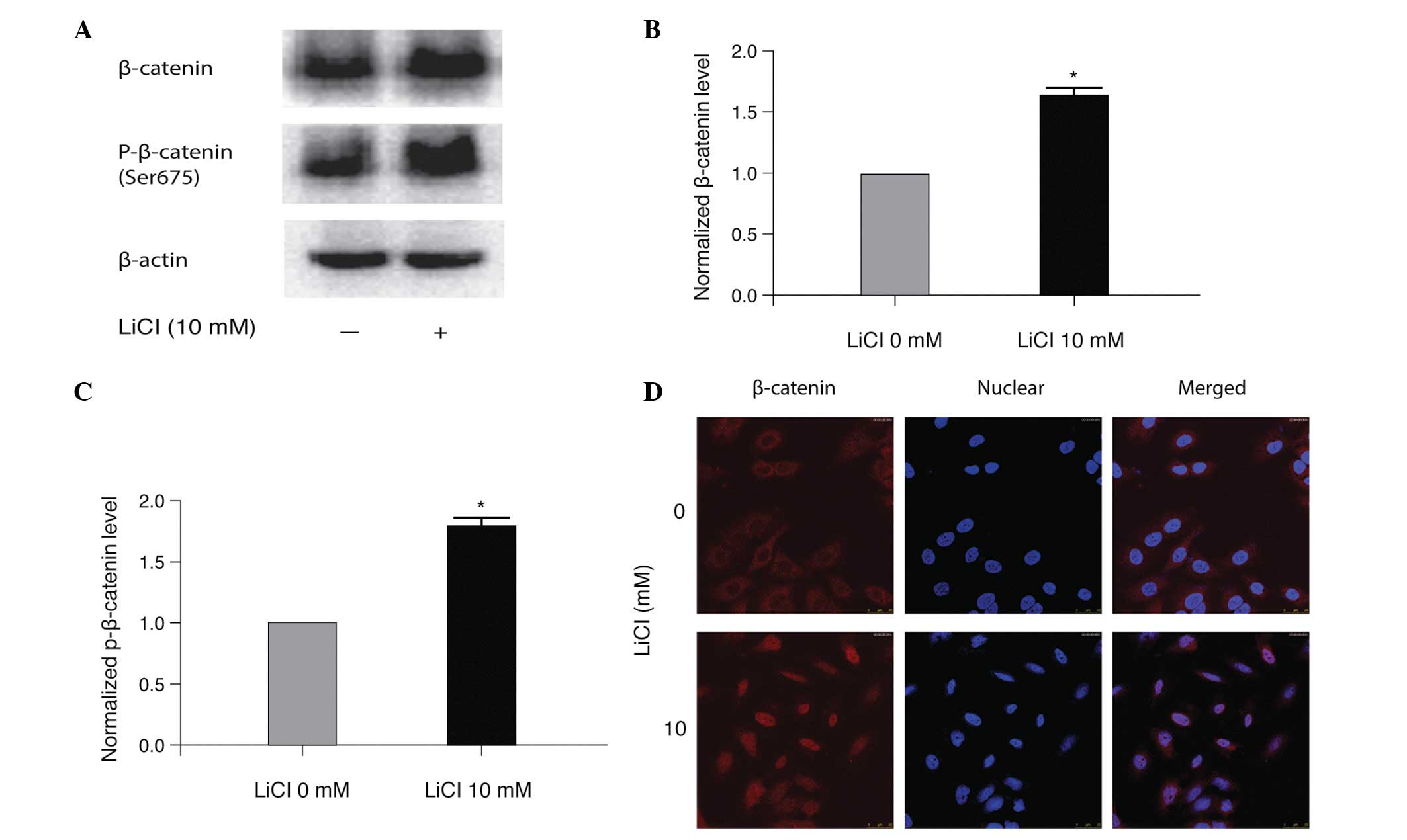
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Prokop M: Lung cancer screening: The
radiologist's perspective. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 35:91–98.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
MacDonagh L, Gray SG, Finn SP, Cuffe S,
O'Byrne KJ and Barr MP: The emerging role of microRNAs in
resistance to lung cancer treatments. Cancer Treat Rev. 41:160–169.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dasari S and Tchounwou PB: Cisplatin in
cancer therapy: Molecular mechanisms of action. Eur J Pharmacol.
740:364–378. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang G, Reed E and Li QQ: Molecular basis
of cellular response to cisplatin chemotherapy in non-small cell
lung cancer (Review). Oncol Rep. 12:955–965. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Stewart DJ: Wnt signaling pathway in
non-small cell lung cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 106:djt3562014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Xia Y, He Z, Liu B, Wang P and Chen Y:
Downregulation of Meg3 enhances cisplatin resistance of lung cancer
cells through activation of the WNT/β-catenin signaling pathway.
Mol Med Rep. 12:4530–4537. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Teng Y, Wang X, Wang Y and Ma D:
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling regulates cancer stem cells in lung
cancer A549 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 392:373–379. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xie C, Pan Y, Hao F, Gao Y, Liu Z, Zhang
X, Xie L, Jiang G, Li Q and Wang E: C-Myc participates in
β-catenin-mediated drug resistance in A549/DDP lung adenocarcinoma
cells. APMIS. 122:1251–1258. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gao Y, Liu Z, Zhang X, He J, Pan Y, Hao F,
Xie L, Li Q, Qiu X and Wang E: Inhibition of cytoplasmic GSK-3β
increases cisplatin resistance through activation of Wnt/β-catenin
signaling in A549/DDP cells. Cancer Lett. 336:231–239. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ding Y, Shen S, Lino AC, Curotto de
Lafaille MA and Lafaille JJ: Beta-catenin stabilization extends
regulatory T cell survival and induces anergy in nonregulatory T
cells. Nat Med. 14:162–169. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Beurel E, Kornprobst M, Blivet-Van
Eggelpoel MJ, Ruiz-Ruiz C, Cadoret A, Capeau J and Desbois-Mouthon
C: GSK-3beta inhibition by lithium confers resistance to
chemotherapy-induced apoptosis through the repression of CD95
(Fas/APO-1) expression. Exp Cell Res. 300:354–364. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cai G, Wang J, Xin X, Ke Z and Luo J:
Phosphorylation of glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta at serine 9
confers cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer cells. Int J Oncol.
31:657–662. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Volkmann N, Marassi FM, Newmeyer DD and
Hanein D: The rheostat in the membrane: BCL-2 family proteins and
apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 21:206–215. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
16
|
Xiong S, Mu T, Wang G and Jiang X:
Mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in mammals. Protein Cell.
5:737–749. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xie H, Huang Z, Sadim MS and Sun Z:
Stabilized beta-catenin extends thymocyte survival by up-regulating
Bcl-xL. J Immunol. 175:7981–7988. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kang MH and Reynolds CP: Bcl-2 inhibitors:
Targeting mitochondrial apoptotic pathways in cancer therapy. Clin
Cancer Res. 15:1126–1132. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Arend RC, Londono-Joshi AI, Straughn JM Jr
and Buchsbaum DJ: The Wnt/β-catenin pathway in ovarian cancer: A
review. Gynecol Oncol. 131:772–779. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Holland JD, Klaus A, Garratt AN and
Birchmeier W: Wnt signaling in stem and cancer stem cells. Curr
Opin Cell Biol. 25:254–264. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhao H, Wei W, Sun Y, Gao J, Wang Q and
Zheng J: Interference with the expression of β-catenin reverses
cisplatin resistance in A2780/DDP cells and inhibits the
progression of ovarian cancer in mouse model. DNA Cell Biol.
34:55–62. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Dahmani R, Just PA and Perret C: The
Wnt/β-catenin pathway as a therapeutic target in human
hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol.
35:709–713. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yeh CT, Rao YK, Ye M, Wu WS, Chang TC,
Wang LS, Wu CH, Wu AT and Tzeng YM: Preclinical evaluation of
destruxin B as a novel Wnt signaling target suppressing
proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer using
non-invasive bioluminescence imaging. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
261:31–41. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kamal A, Faazil S and Malik MS:
Apoptosis-inducing agents: A patent review 2010–2013. Expert Opin
Ther Pat. 24:339–354. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Choi PS, Li Y and Felsher DW: Addiction to
multiple oncogenes can be exploited to prevent the emergence of
therapeutic resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 111:E3316–3324.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li W, Tong H, Huang X, Wang W, Wu H and
Lin S: High levels of β-catenin promote IFNγ-induced apoptosis in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncol Lett. 4:1092–1096.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|