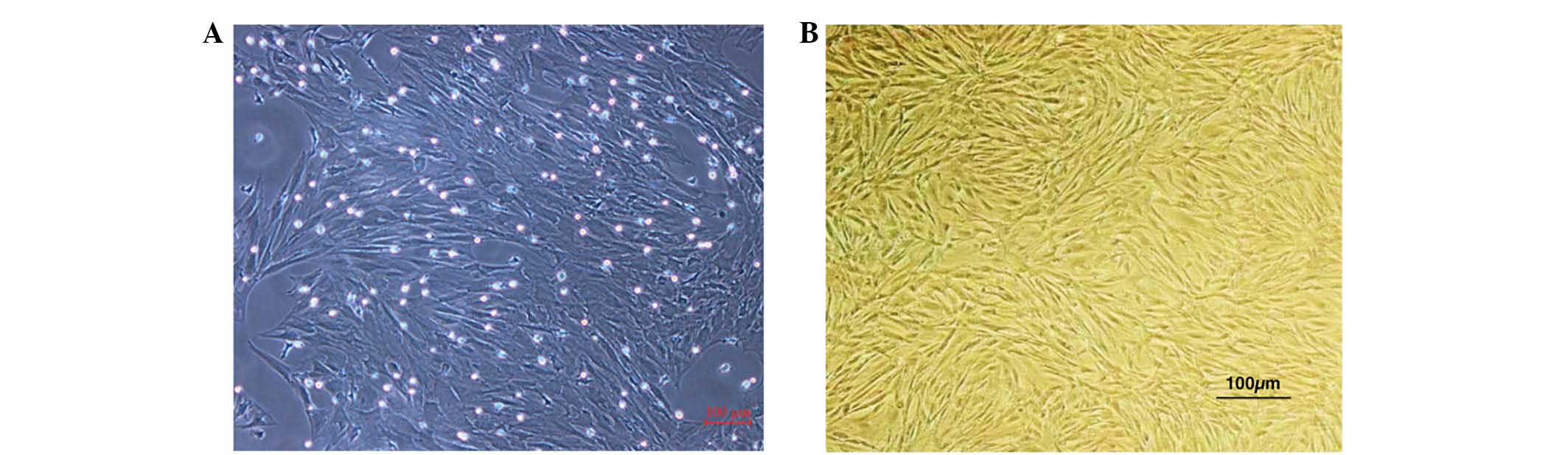
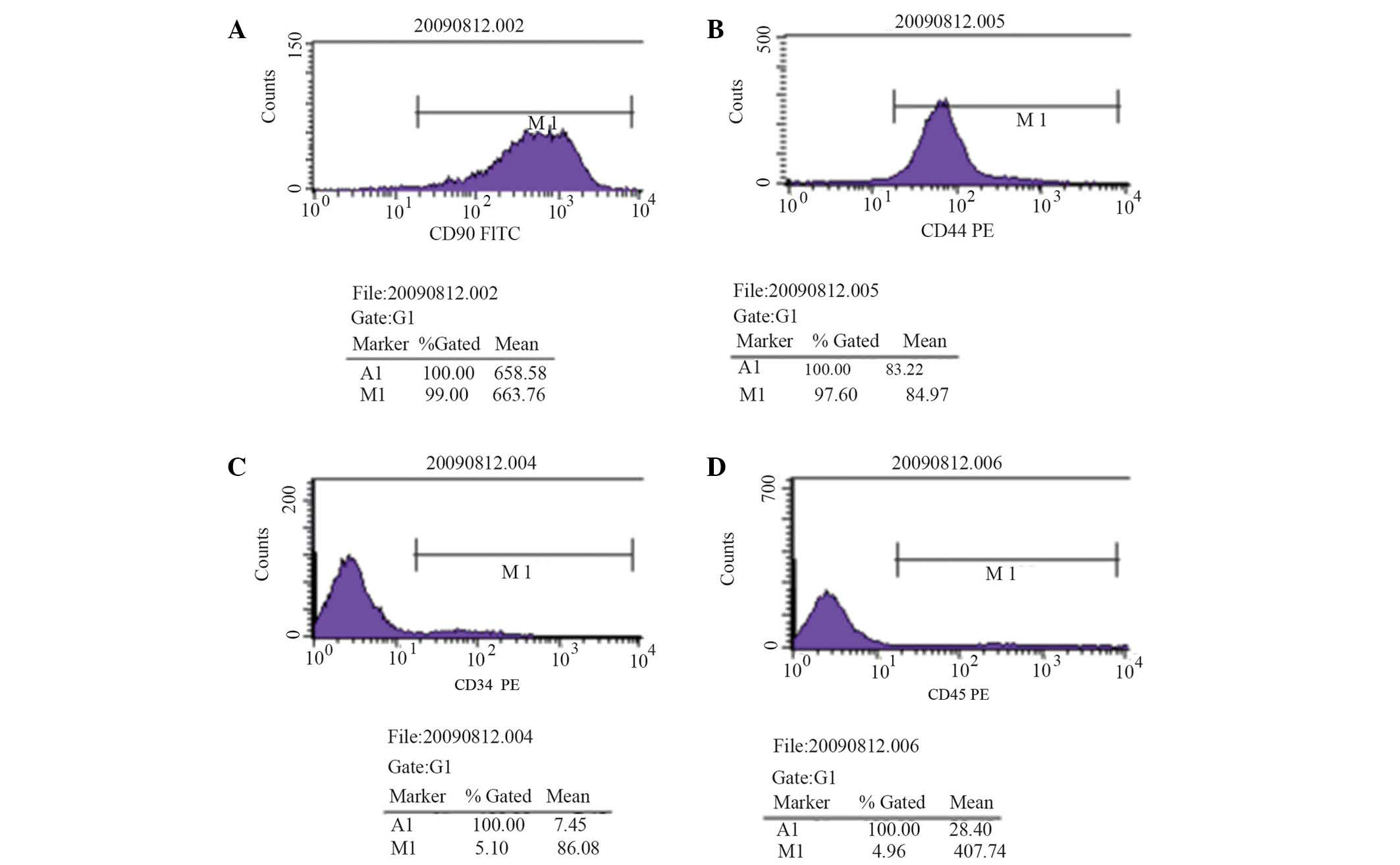
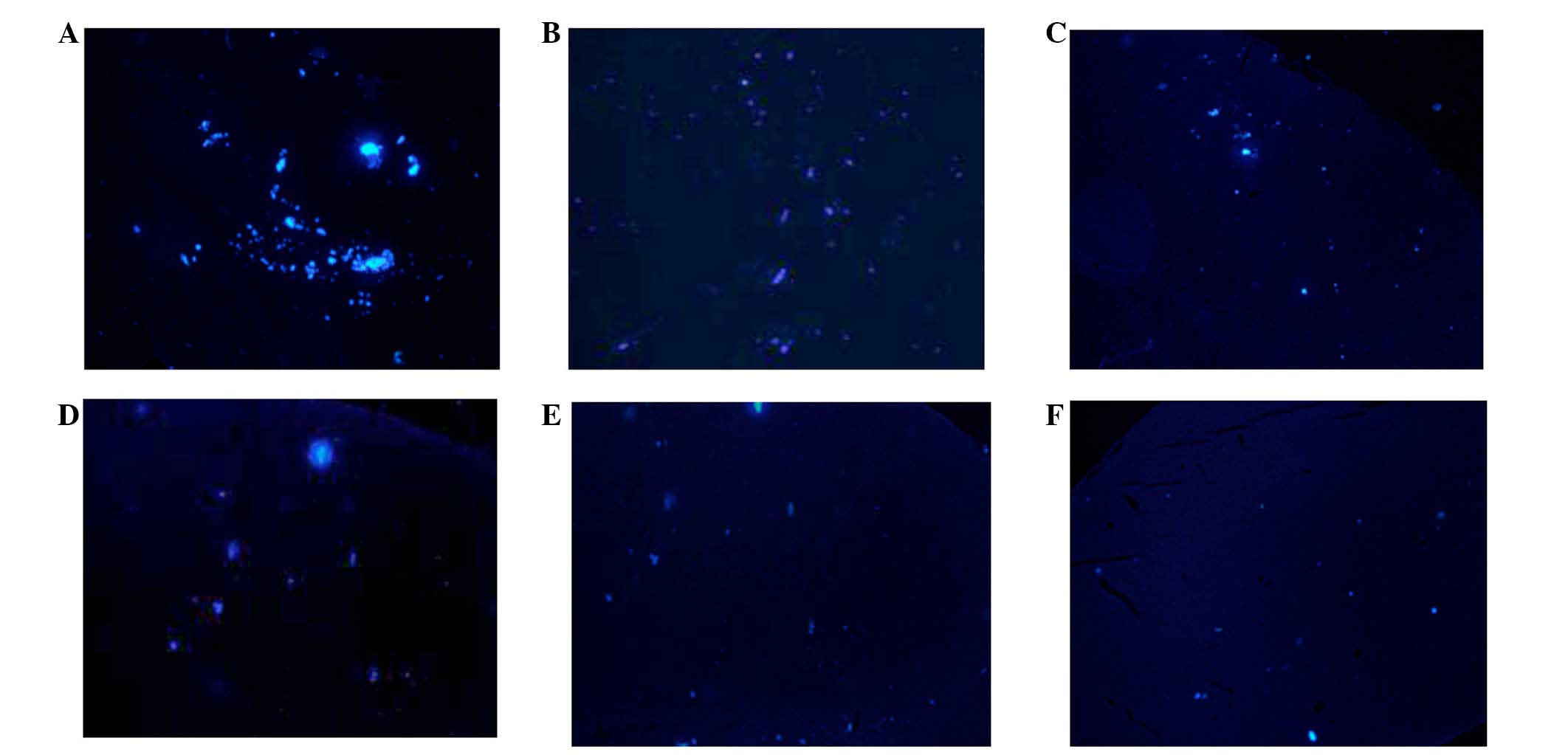
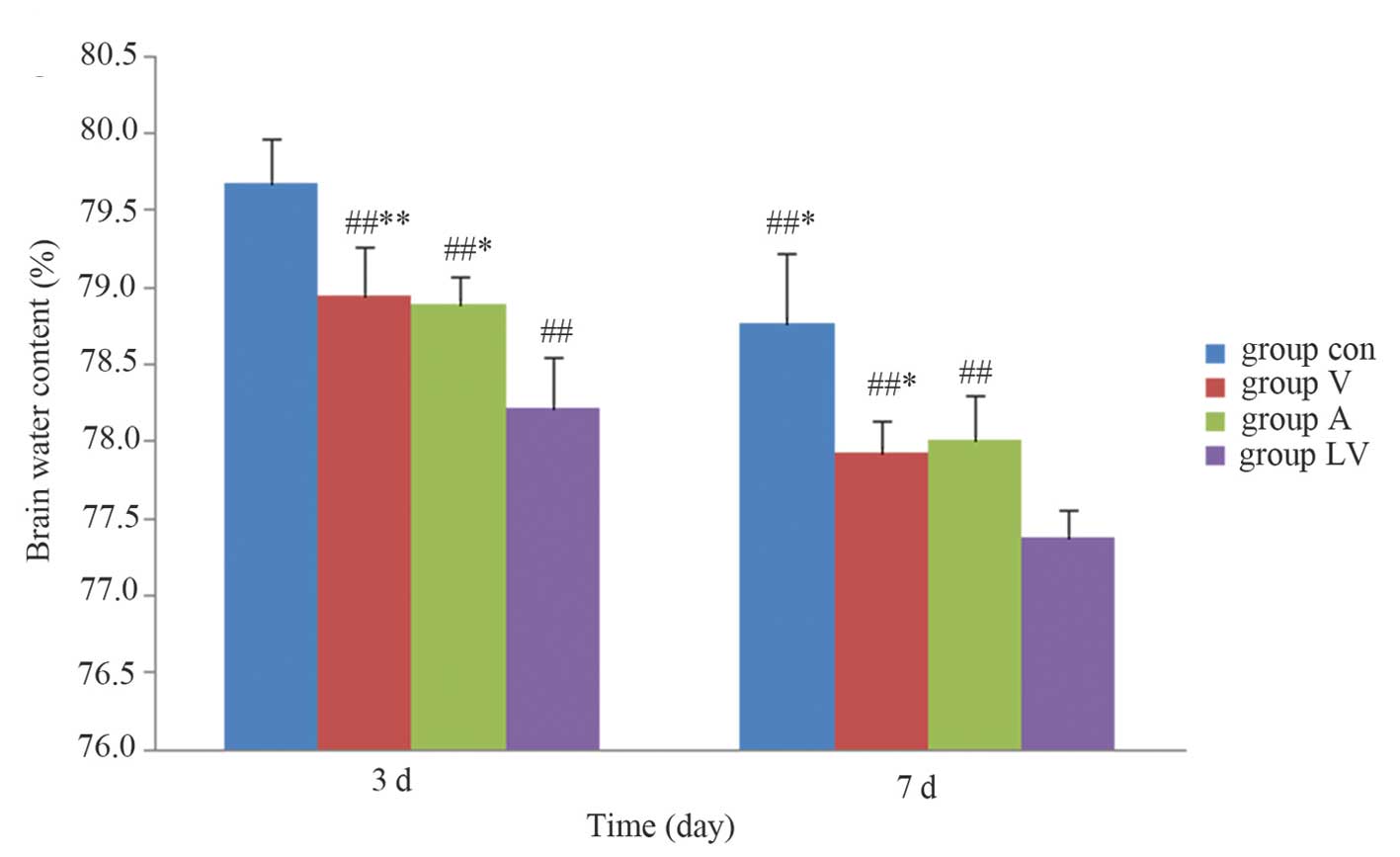
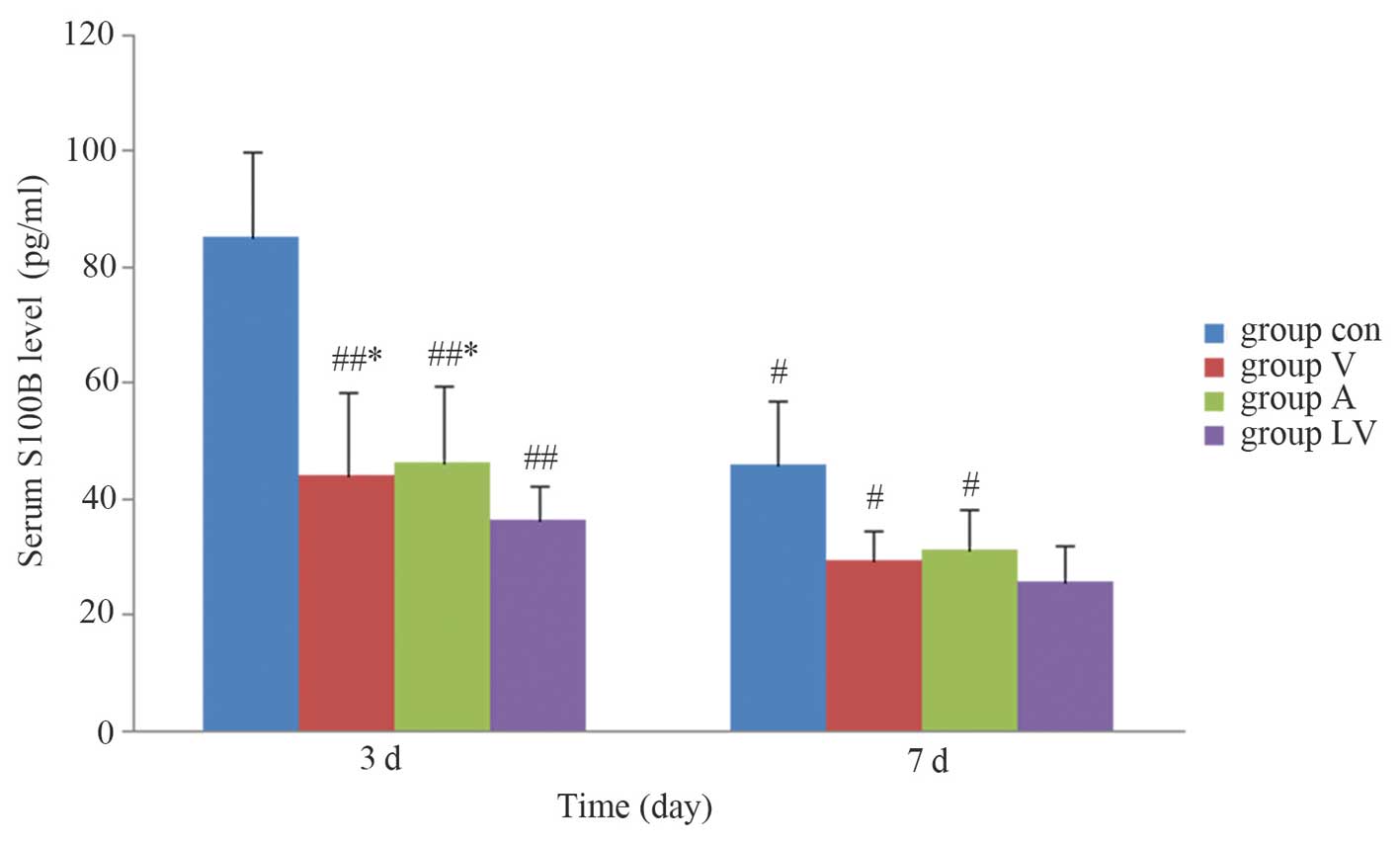
|
1
|
Thom T, Haase N, Rosamond W, Howard VJ,
Rumsfeld J, Manolio T, Zheng ZJ, Flegal K, O'Donnell C, Kittner S,
et al: Heart disease and stroke statistics - 2006 update: A report
from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke
Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation. 113:e85–e151. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Grounds MD, White JD, Rosenthal N and
Bogoyevitch MA: The role of stem cells in skeletal and cardiac
muscle repair. J Histochem Cytochem. 50:589–610. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Grove JE, Lutzko C, Priller J, Henegariu
O, Theise ND, Kohn DB and Krause DS: Marrow-derived cells as
vehicles for delivery of gene therapy to pulmonary epithelium. Am J
Respir Cell Mol Biol. 27:645–651. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Huang Zi-Tong: Improve the level of
cardiopulmonary resuscitation measures and countermeasures.
Zhonghuajizheny-ixuezazhi. 3:153–154. 2004.
|
|
5
|
Bindslev L, Haack-Sørensen M, Bisgaard K,
Kragh L, Mortensen S, Hesse B, Kjaer A and Kastrup J: Labelling of
human mesenchymal stem cells with indium-111 for SPECT imaging:
Effect on cell proliferation and differentiation. Eur J Nucl Med
Mol Imaging. 33:1171–1177. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wen M and Li SL: The studies of magnetic
resonance imaging for molecular imaging. Zhongguo Yixue Yingxiang
Jishu. 1:147–150. 2007.In Chinese.
|
|
7
|
Jing XH, Yang L, Duan XJ, Xie B, Chen W,
Li Z and Tan HB: In vivo MR imaging tracking of magnetic iron oxide
nanoparticle labeled, engineered, autologous bone marrow
mesenchymal stem cells following intra-articular injection. Joint
Bone Spine. 75:432–438. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fang X, Tang W, Sun S, Huang L, Huang Z
and Weil MH: Mechanism by which activation of delta-opioid receptor
reduces the severity of postresuscitation myocardial dysfunction.
Crit Care Med. 34:2607–2612. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hickey RW, Kochanek PM, Ferimer H,
Alexander HL, Garman RH and Graham SH: Induced hyperthermia
exacerbates neurologic neuronal histologic damage after asphyxial
cardiac arrest in rats. Crit Care Med. 31:531–535. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Friedenstein AJ, Chailakhyan RK and
Gerasimov UV: Bone marrow osteogenic stem cells: In vitro
cultivation and transplantation in diffusion chambers. Cell Tissue
Kinet. 20:263–272. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Joshi D and Behari M: Neuronal stem cells.
Neurol India. 51:323–328. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zheng W, Honmou O, Miyata K, Harada K,
Suzuki J, Liu H, Houkin K, Hamada H and Kocsis JD: Therapeutic
benefits of human mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow
after global cerebral ischemia. Brain Res. 1310:8–16. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Chen J, Li Y, Katakowski M, Chen X, Wang
L, Lu D, Lu M, Cautam SC and Chopp M: Intravenous bone marrow
stromal cell therapy reduces apoptosis and promotes endogenous cell
proliferation after stroke in female rat. J Neurosci Res.
73:778–786. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li Y, Chopp M, Chen J, Wang L, Gautam SC,
Xu YX and Zhang Z: Intrastriatal transplantation of bone marrow
nonhe-matopoietic cells improves functional recovery after stroke
in adult mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 20:1311–1319. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li N, Sarojini H, An J and Wang E:
Prosaposin in the secretome of marrow stroma-derived neural
progenitor cells protects neural cells from apoptotic death. J
Neurochem. 112:1527–1538. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li Y, Chopp M, Chen J, Wang L, Gautam SC,
Xu YX and Zhang Z: Intrastriatal transplantation of bone marrow
nonhe-matopoietic cells improves functional recovery after stroke
in adult mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 20:1311–1319. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tang WC and Sun SJ: Cardiopulmonary
resuscitation and emergency cardiovascular Beijing. Beijing Science
and Technology Press. 572–586. 2008.
|
|
18
|
Barbash IM, Chouraqui P, Baron J, Feinberg
MS, Etzion S, Tessone A, Miller L, Guetta E, Zipori D, Kedes LH, et
al: Systemic delivery of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells
to the infarcted myocardium: Feasibility, cell migration and body
distribution. Circulation. 108:863–868. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang W, Smith C, Howlett C and
Stanimirovic D: Inflammatory activation of human brain endothelial
cells by hypoxic astrocytes in vitro is mediated by IL-1beta. J
Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 20:967–978. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Schoch HJ, Fischer S and Marti HH:
Hypoxia-induced vascular endothelial growth factor expression
causes vascular leakage in the brain. Brain. 125:2549–2557. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Geocadin RG, Ghodadra R, Kimura T, Lei H,
Sherman DL, Hanley DF and Thakor NV: A novel quantitative EEG
injury measure of global cerebral isehemia. Clin Neurophysiol.
111:1779–1187. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Perasso L, Cogo CE, Giunti D, Gandolfo C,
Ruggeri P, Uccelli A and Balestrino M: Systemic administration of
mesenchymal stem cells increases neuron survival after global
cerebral ischemia in vivo (2VO). Neural Plast. 2010:5349252010.
|
|
23
|
Ohtaki H, Ylostalo JH, Foraker JE,
Robinson AP, Reger RL, Shioda S and Prockop DJ: Stem/progenitor
cells from bone marrow decrease neuronal death in global ischemia
by modulation of inflammatory/immune responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 105:14638–14643. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang L, Li Y, Chen X, Chen J, Gautam SC,
Xu Y and Chopp M: MCP-1, MIP-1, IL-8 and ischemic cerebral tissue
enhance human bone marrow stromal cell migration in interface
culture. Hematology. 7:113–117. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zimmer DB, Cornwall EH, Landar A and Song
W: The S100 protein family: History, function and expression. Brain
Res Bull. 37:417–429. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Wojtczak-Soska K and Lelonek M: S-100B
protein: An early prognostic marker after cardiac arrest. Cardiol
J. 17:532–536. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Grubb NR, Simpson C, Sherwood RA, Abraha
HD, Cobbe SM, O'Carroll RE, Deary I and Fox KA: Prediction of
cognitive dysfunction after resuscitation from out-of-hospital
cardiac arrest using serum neuron-specific enolase and protein
S-100. Heart. 93:1268–1273. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|