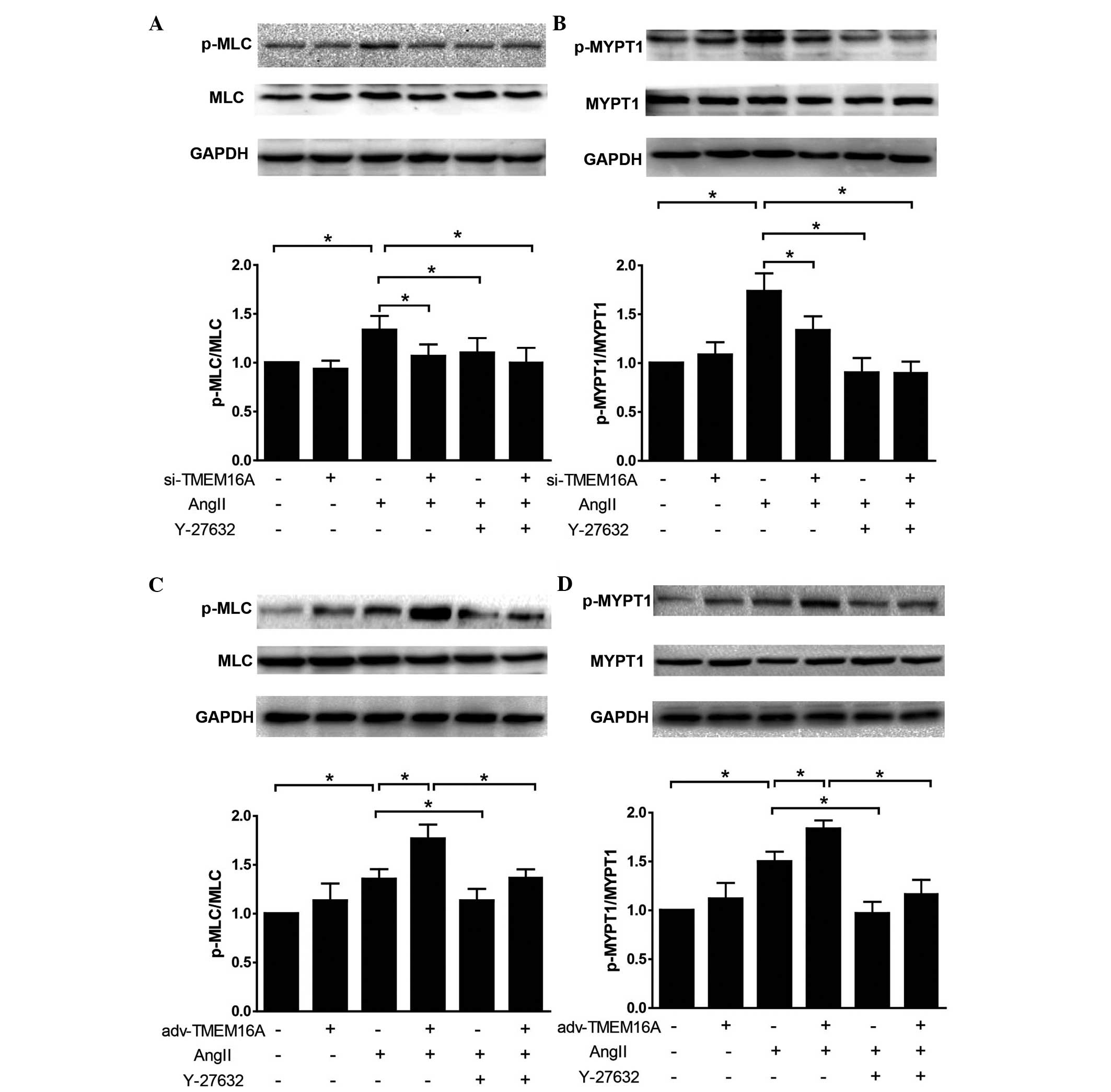
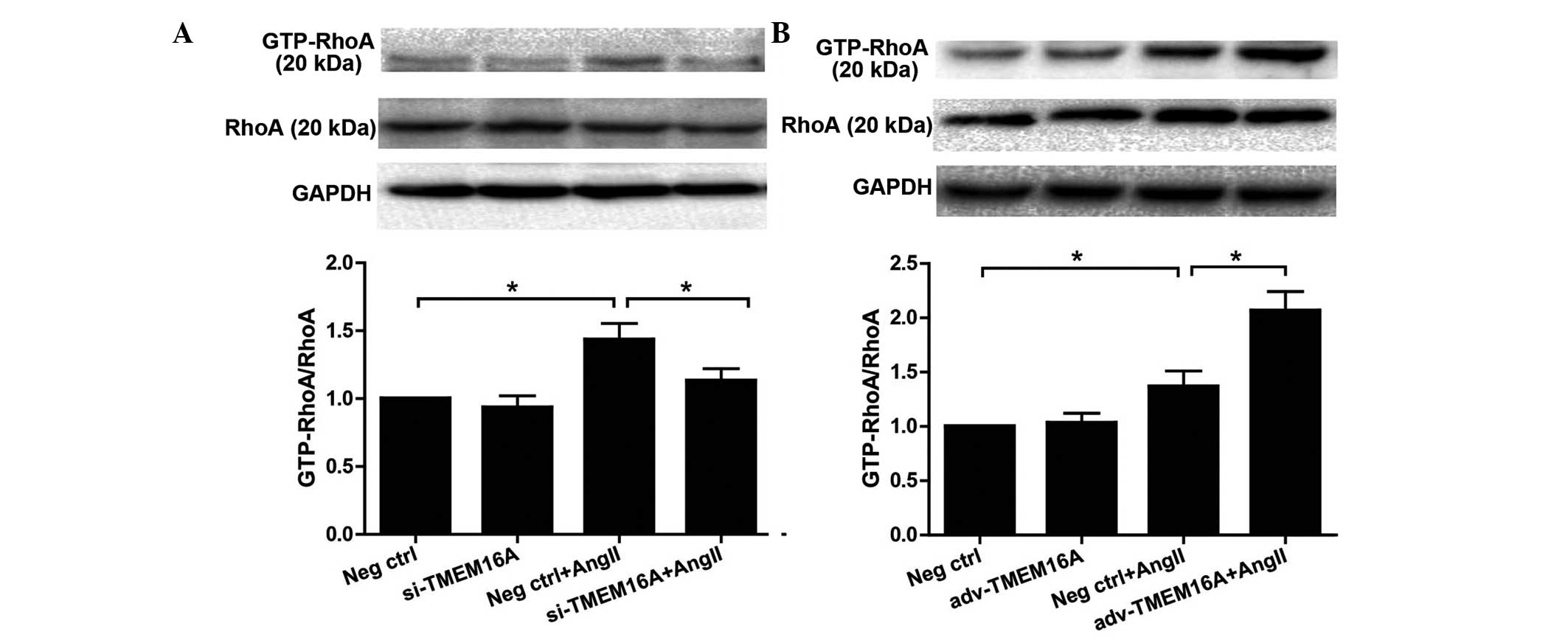
|
1
|
Heinze C, Seniuk A, Sokolov MV, Huebner
AK, Klementowicz AE, Szijártó IA, Schleifenbaum J, Vitzthum H,
Gollasch M, Ehmke H, et al: Disruption of vascular Ca2+-activated
chloride currents lowers blood pressure. J Clin Invest.
124:675–686. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jackson WF: Ion channels and vascular
tone. Hypertension. 35:173–178. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mendelsohn ME: In hypertension, the kidney
is not always the heart of the matter. J Clin Invest. 115:840–844.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yonas H, Smith HA, Durham SR, Pentheny SL
and Johnson DW: Increased stroke risk preducted by compromised
cerebral blood flow reactivity. J Neurosurg. 79:483–489. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hill MA, Zou H, Potocnik SJ, Meininger GA
and Davis MJ: Invited review: Arteriolar smooth muscle
mechanotransduction: Ca(2+) signaling pathways underlying myogenic
reactivity. J Appl Physiol (1985). 91:973–983. 2001.
|
|
6
|
Earley S and Brayden JE: Transient
receptor potential channels and vascular function. Clin Sci (Lond).
119:19–36. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Rust MB, Faulhaber J, Budack MK, Pfeffer
C, Maritzen T, Didié M, Beck FX, Boettger T, Schubert R, Ehmke H,
et al: Neurogenic mechanisms contribute to hypertension in mice
with disruption of the K-Cl cotransporter KCC3. Circ Res.
98:549–556. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Leblanc N, Ledoux J, Saleh S, Sanguinetti
A, Angermann J, O'Driscoll K, Britton F, Perrino BA and Greenwood
IA: Regulation of calcium-activated chloride channels in smooth
muscle cells: A complex picture is emerging. Can J Physiol
Pharmacol. 83:541–556. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wu MM, Lou J, Song BL, Gong YF, Li YC, Yu
CJ, Wang QS, Ma TX, Ma K, Hartzell HC, et al: Hypoxia augments the
calcium-activated chloride current carried by anoctamin-1 in
cardiac vascular endothelial cells of neonatal mice. Br J
Pharmacol. 171:3680–3692. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bulley S, Neeb ZP, Burris SK, Bannister
JP, Thomas-Gatewood CM, Jangsangthong W and Jaggar JH: TMEM16A/ANO1
channels contribute to the myogenic response in cerebral arteries.
Circ Res. 111:1027–1036. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kobori H, Nangaku M, Navar LG and
Nishiyama A: The intrarenal renin-angiotensin system: From
physiology to the pathobiology of hypertension and kidney disease.
Pharmacol Rev. 59:251–287. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang Z, Wang M, Xue SJ, Liu DH and Tang
YB: Simvastatin ameliorates angiotensin II-induced endothelial
dysfunction through restoration of Rho-BH4-eNOS-NO pathway.
Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 26:31–40. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Hilgers RH, Todd J Jr and Webb RC:
Increased PDZ-RhoGEF/RhoA/Rho kinase signaling in small mesenteric
arteries of angiotensin II-induced hypertensive rats. J Hypertens.
25:1687–1697. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Faraci FM, Lamping KG, Modrick ML, Ryan
MJ, Sigmund CD and Didion SP: Cerebral vascular effects of
angiotensin II: New insights from genetic models. J Cereb Blood
Flow Metab. 26:449–455. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Davis AJ, Shi J, Pritchard HA, Chadha PS,
Leblanc N, Vasilikostas G, Yao Z, Verkman AS, Albert AP and
Greenwood IA: Potent vasorelaxant activity of the TMEM16A inhibitor
T16A (inh)-A01. Br J Pharmacol. 168:773–784. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
16
|
Committee for the Update of the Guide for
the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals: Guide for the care and use
of laboratory animals. 8th edition. National Academies Press;
Washington, DC, USA:
|
|
17
|
Shi XL, Wang GL, Zhang Z, Liu YJ, Chen JH,
Zhou JG, Qiu QY and Guan YY: Alteration of volume-regulated
chloride movement in rat cerebrovascular smooth muscle cells during
hypertension. Hypertension. 49:1371–1377. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lamping KG, Wess J, Cui Y, Nuno DW and
Faraci FM: Muscarinic (M) receptors in coronary circulation:
Gene-targeted mice define the role of M2 and M3 receptors in
response to acetylcholine. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
24:1253–1258. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang M, Yang H, Zheng LY, Zhang Z, Tang
YB, Wang GL, Du YH, Lv XF, Liu J, Zhou JG and Guan YY:
Downregulation of TMEM16A calcium-activated chloride channel
contributes to cerebrovascular remodeling during hypertension by
promoting basilar smooth muscle cell proliferation. Circulation.
125:697–707. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yang YD, Cho H, Koo JY, Tak MH, Cho Y,
Shim WS, Park SP, Lee J, Lee B, Kim BM, et al: TMEM16A confers
receptor-activated calcium-dependent chloride conductance. Nature.
455:1210–1215. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
White CR, Elton TS, Shoemaker RL and Brock
TA: Calcium-sensitive chloride channels in vascular smooth muscle
cells. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 208:255–262. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Guibert C, Marthan R and Savineau JP:
Oscillatory Cl-current induced by angiotensin II in rat pulmonary
arterial myocytes: Ca2+ dependence and physiological implication.
Cell Calcium. 21:421–429. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bagi Z, Feher A, Cassuto J, Akula K,
Labinskyy N, Kaley G and Koller A: Increased availability of
angiotensin AT 1 receptors leads to sustained arterial constriction
to angiotensin II in diabetes-role for Rho-kinase activation. Br J
Pharmacol. 163:1059–1068. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kinlay S, Behrendt D, Wainstein M,
Beltrame J, Fang JC, Creager MA, Selwyn AP and Ganz P: Role of
endothelin-1 in the active constriction of human atherosclerotic
coronary arteries. Circulation. 104:1114–1118. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu JQ and Folz RJ: Extracellular
superoxide enhances 5-HT-induced murine pulmonary artery
vasoconstriction. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
287:L111–L118. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gao YJ and Lee RM: Hydrogen peroxide
induces a greater contraction in mesenteric arteries of
spontaneously hypertensive rats through thromboxane A(2)
production. Br J Pharmacol. 134:1639–1646. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hall JE: The kidney, hypertension, and
obesity. Hypertension. 41:625–633. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hein L: Genetic deletion and
overexpression of angiotensin II receptors. J Mol Med (Berl).
76:756–763. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Crowley SD, Tharaux PL, Audoly LP and
Coffman TM: Exploring type I angiotensin (AT1) receptor functions
through gene targeting. Acta Physiol Scand. 181:561–570. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ito K, Hirooka Y, Nakano M, Honda N,
Matsukawa R and Sunagawa K: Role of hypothalamic angiotensin type 1
receptors in pressure overload-induced mineralocorticoid receptor
activation and salt-induced sympathoexcitation. Hypertens Res.
36:513–519. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Stenman E and Edvinsson L: Cerebral
ischemia enhances vascular angiotensin AT1 receptor-mediated
contraction in rats. Stroke. 35:970–974. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Toda N, Ayaziki K and Okamura T:
Modifications by endogenous prostaglandins of angiotensin
II-induced contractions in dog and monkey cerebral and mesenteric
arteries. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 252:374–379. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Billington CK and Penn RB: Signaling and
regulation of G protein-coupled receptors in airway smooth muscle.
Respir Res. Mar 14–2003.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lu T, Zhang DM, Wang XL, He T, Wang RX,
Chai Q, Katusic ZS and Lee HC: Regulation of coronary arterial BK
channels by caveolae-mediated angiotensin II signaling in diabetes
mellitus. Circ Res. 106:1164–1173. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ilatovskaya DV, Palygin O,
Chubinskiy-Nadezhdin V, Negulyaev YA, Ma R, Birnbaumer L and
Staruschenko A: Angiotensin II has acute effects on TRPC6 channels
in podocytes of freshly isolated glomeruli. Kidney Int. 86:506–514.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Do KH, Kim MS, Kim JH, Rhim BY, Lee WS,
Kim CD and Bae SS: Angiotensin II-induced aortic ring constriction
is mediated by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/L-type calcium channel
signaling pathway. Exp Mol Med. 41:569–576. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Caputo A, Caci E, Ferrera L, Pedemonte N,
Barsanti C, Sondo E, Pfeffer U, Ravazzolo R, Zegarra-Moran O and
Galietta LJ: TMEM16A, a membrane protein associated with
calcium-dependent chloride channel activity. Science. 322:590–594.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Schroeder BC, Cheng T, Jan YN and Jan LY:
Expression cloning of TMEM16A as a calcium-activated chloride
channel subunit. Cell. 134:1019–1029. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liu B, Linley JE, Du X, Zhang X, Ooi L,
Zhang H and Gamper N: The acute nociceptive signals induced by
bradykinin in rat sensory neurons are mediated by inhibition of
M-type K+ channels and activation of Ca2+-activated Cl-channels. J
Clin Invest. 120:1240–1252. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Frings S, Reuter D and Kleene SJ: Neuronal
Ca2+-activated Cl-channels-homing in on an elusive channel species.
Prog Neurobiol. 60:247–289. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hartzell C, Putzier I and Arreola J:
Calcium-activated chloride channels. Annu Rev Physiol. 67:719–758.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Namkung W, Phuan PW and Verkman AS:
TMEM16A inhibitors reveal TMEM16A as a minor component of
calcium-activated chloride channel conductance in airway and
intestinal epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 286:2365–2374. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
43
|
Uehata M, Ishizaki T, Satoh H, Ono T,
Kawahara T, Morishita T, Tamakawa H, Yamagami K, Inui J, Maekawa M
and Narumiya S: Calcium sensitization of smooth muscle mediated by
a Rho-associated protein kinase in hypertension. Nature.
389:990–994. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Sebbagh M, Renvoizé C, Hamelin J, Riché N,
Bertoglio J and Bréard J: Caspase-3-mediated cleavage of ROCK I
induces MLC phosphorylation and apoptotic membrane blebbing. Nat
Cell Biol. 3:346–352. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Cao X, Luo T, Luo X and Tang Z:
Resveratrol prevents AngII-induced hypertension via AMPK activation
and RhoA/ROCK suppression in mice. Hypertens Res. 37:803–810. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|