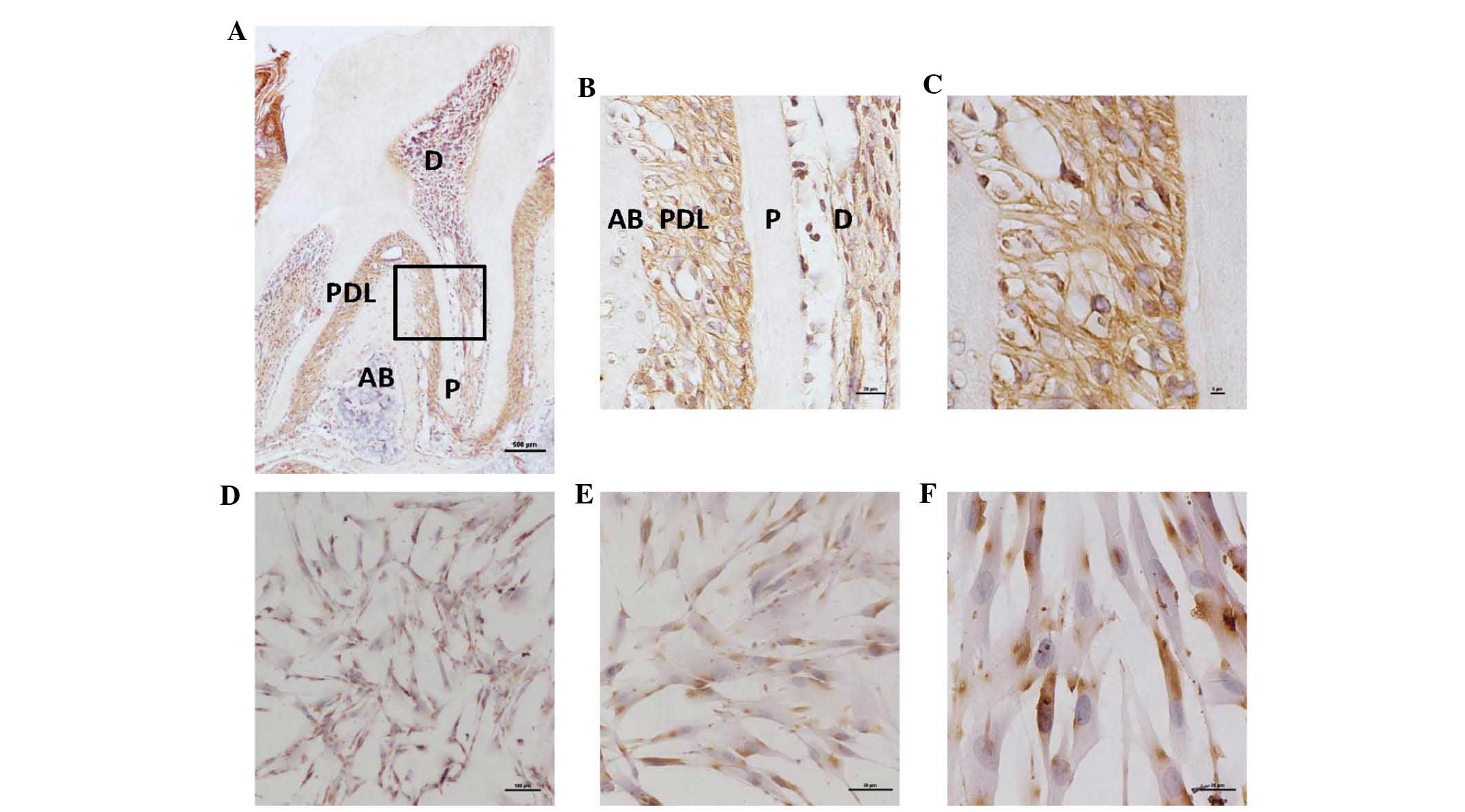
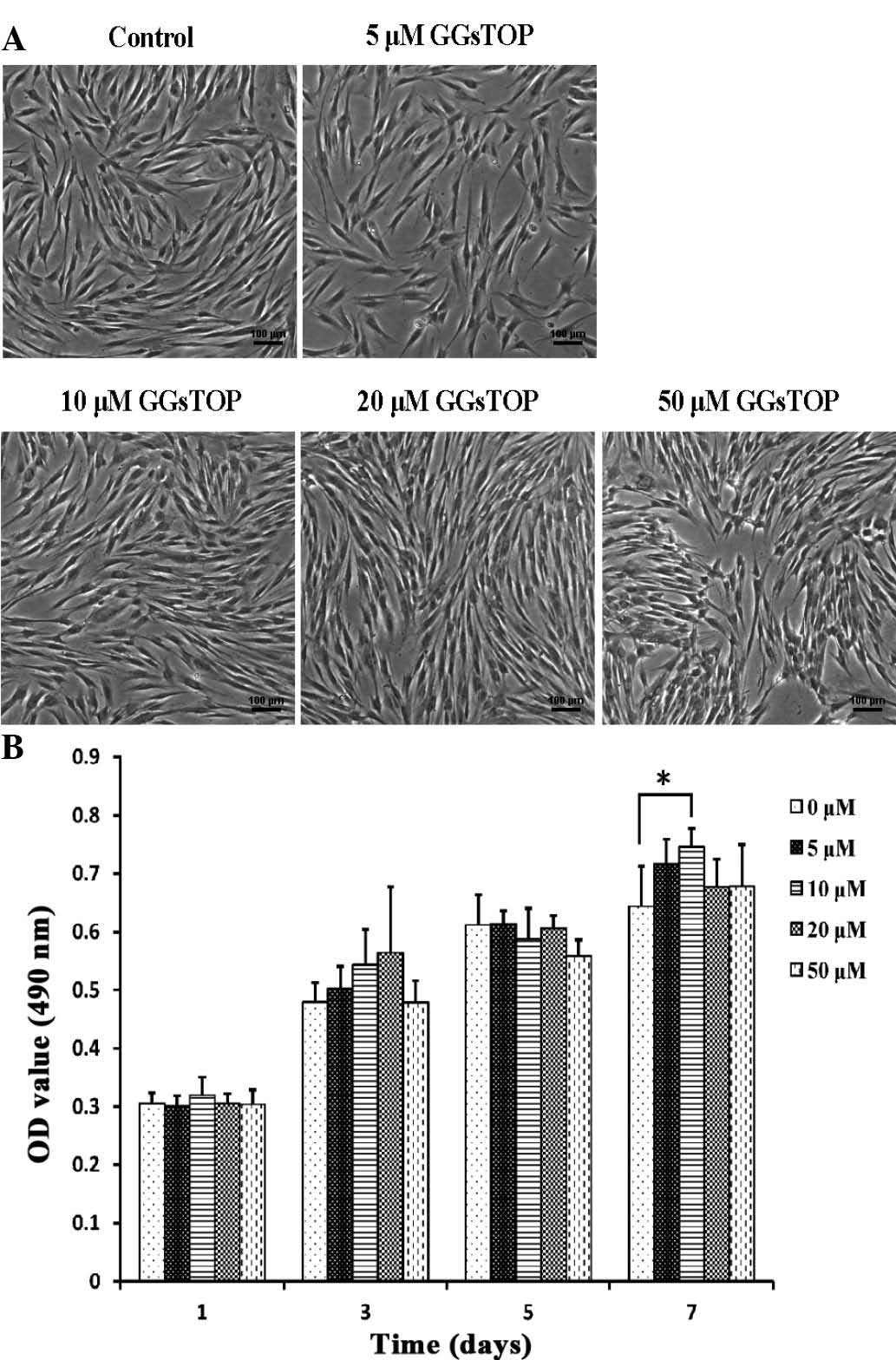
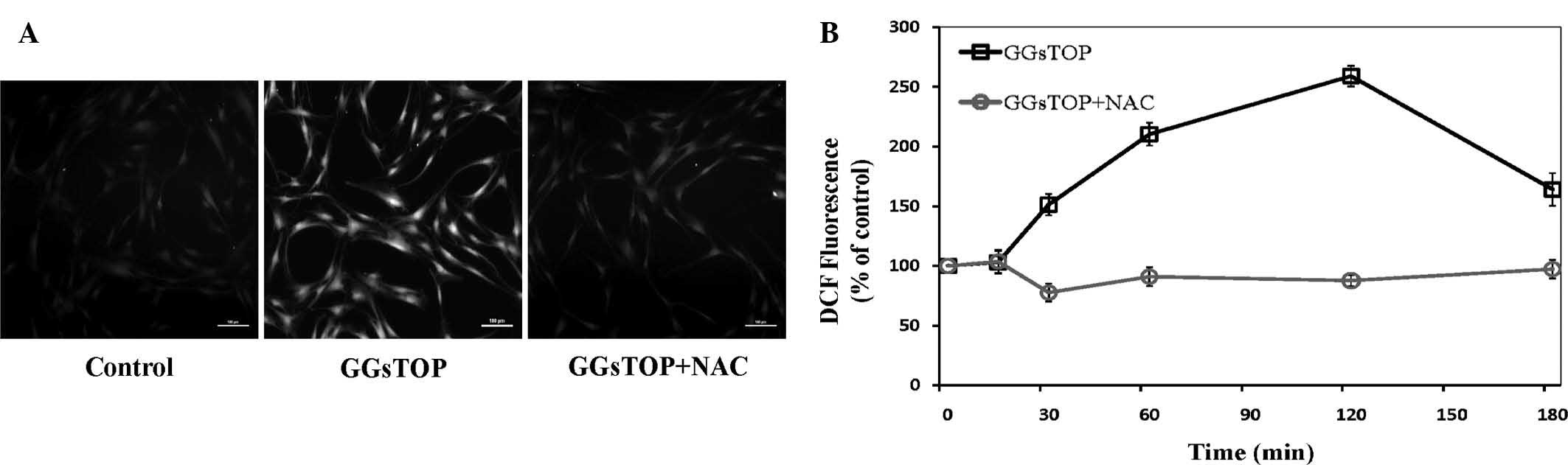
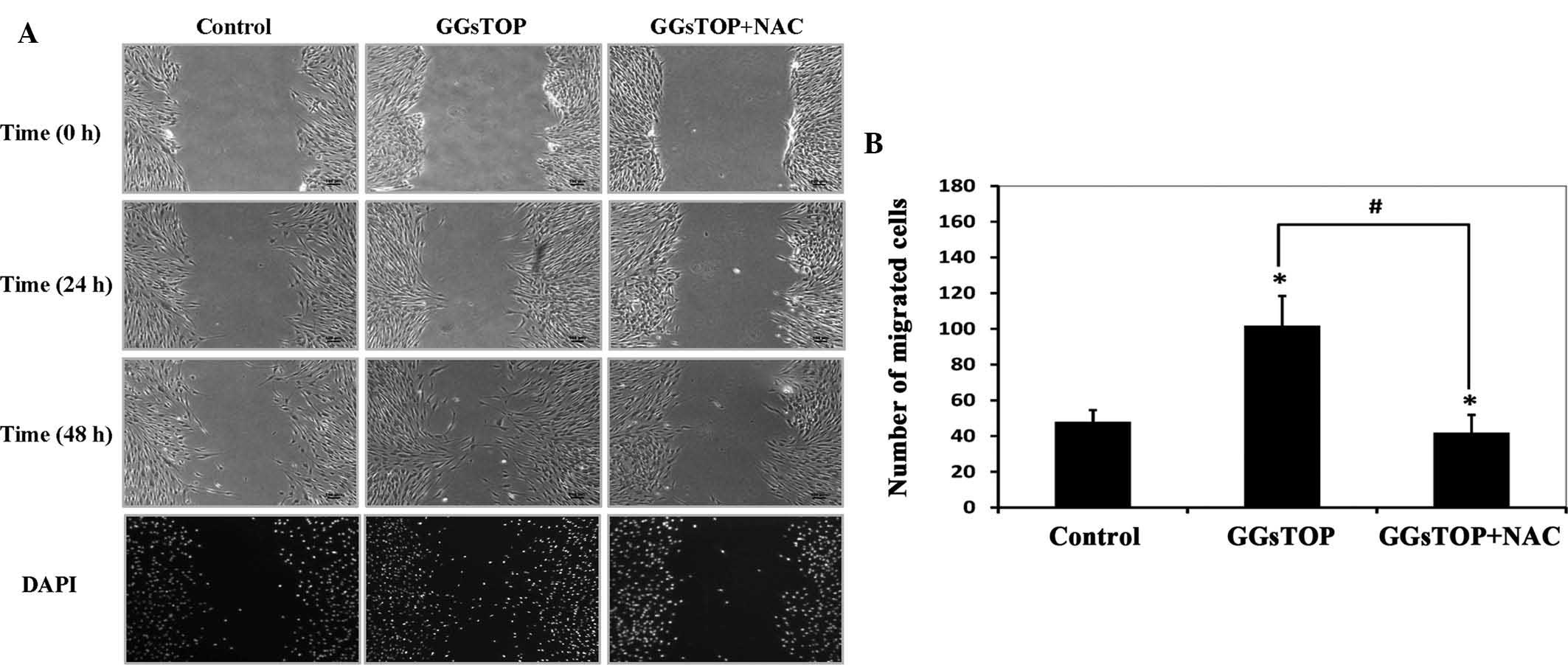
|
1
|
Nomura Y, Ishikawa M, Yashiro Y,
Sanggarnjanavanich S, Yamaguchi T, Arai C, Noda K, Takano Y,
Nakamura Y and Hanada N: Human periodontal ligament fibroblasts are
the optimal cell source for induced pluripotent stem cells.
Histochem Cell Biol. 137:719–732. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cáceres M, Martínez C, Martínez J and
Smith PC: Effects of platelet-rich and -poor plasma on the
reparative response of gingival fibroblasts. Clin Oral Implants
Res. 23:1104–1111. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Fu XJ, Peng YB, Hu YP, Shi YZ, Yao M and
Zhang X: NADPH oxidase 1 and its derived reactive oxygen species
mediated tissue injury and repair. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2014(282854)2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Chen KC, Zhou Y, Xing K, Krysan K and Lou
MF: Platelet derived growth factor (PDGF)-induced reactive oxygen
species in the lens epithelial cells: The redox signaling. Exp Eye
Res. 78:1057–1067. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lu SC: Regulation of hepatic glutathione
synthesis: Current concepts and controversies. FASEB J.
13:1169–1183. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wickham S, West MB, Cook PF and Hanigan
MH: Gamma-glutamyl compounds: Substrate specificity of
gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase enzymes. Anal Biochem. 414:208–214.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rojas E, Valverde M, Kala SV, Kala G and
Lieberman MW: Accumulation of DNA damage in the organs of mice
deficient in gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase. Mutat Res. 447:305–316.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Yamamoto S, Watanabe B, Hiratake J, Tanaka
R, Ohkita M and Matsumura Y: Preventive effect of GGs Top, a novel
and selective γ-glutamyl transpeptidase inhibitor, on
ischemia/reperfusion-induced renal injury in rats. J Pharmacol Exp
Ther. 339:945–951. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Huseby NE and Strömme JH: Practical points
regarding routine determination of gamma-glutamyl transferase
(gamma-GT) in serum with a kinetic method at 37 degrees C. Scand J
Clin Lab Invest. 34:357–363. 1974. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cannito S, Novo E, Compagnone A, Valfrè di
Bonzo L, Busletta C, Zamara E, Paternostro C, Povero D, Bandino A,
Bozzo F, et al: Redox mechanisms switch on hypoxia-dependent
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer cells. Carcinogenesis.
29:2267–2278. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gao C, Negash S, Guo HT, Ledee D, Wang HS
and Zelenka P: CDK5 regulates cell adhesion and migration in
corneal epithelial cells. Mol Cancer Res. 1:12–24. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hanigan MH and Frierson HF Jr:
Immunohistochemical detection of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase in
normal human tissue. J Histochem Cytochem. 44:1101–1108. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Eckes B, Zweers MC, Zhang ZG, et al:
Mechanical tension and integrin α2β1 regulate fibroblast functions.
J Invest Dermatol. 11:66–72. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
del Bello B, Paolicchi A, Comporti M,
Pompella A and Maellaro E: Hydrogen peroxide produced during
gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase activity is involved in prevention of
apoptosis and maintainance of proliferation in U937 cells. FASEB J.
13:69–79. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Stephan J, Franke J and Ehrenhofer-Murray
AE: Chemical genetic screen in fission yeast reveals roles for
vacuolar acidification, mitochondrial fission, and cellular GMP
levels in lifespan extension. Aging Cell. 12:574–583. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zalata A, Hafez T, Mahmoud A and Comhaire
F: Relationship between resazurin reduction test, reactive oxygen
species generation, and gamma-glutamyltransferase. Hum Reprod.
10:1136–1140. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Johnsen O, Eliasson R and Samuelson U:
Conditioning effect of seminal plasma on the lipid peroxide
potential of washed human spermatozoa. Acta Physiol Scand.
116:305–307. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu RM, Liu Y, Forman HJ, Olman M and
Tarpey MM: Glutathione regulates transforming growth
factor-beta-stimulated collagen production in fibroblasts. Am J
Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 286:L121–L128. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Tandon N, Cimetta E, Villasante A,
Kupferstein N, Southall MD, Fassih A, Xie J, Sun Y and
Vunjak-Novakovic G: Galvanic microparticles increase migration of
human dermal fibroblasts in a wound-healing model via reactive
oxygen species pathway. Exp Cell Res. 320:79–91. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Mudge BP, Harris C, Gilmont RR, Adamson BS
and Rees RS: Role of glutathione redox dysfunction in diabetic
wounds. Wound Repair Regen. 10:52–58. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Djavaheri-Mergny M, Accaoui MJ, Rouillard
D and Wietzerbin J: Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase activity mediates
NF-kappaB activation through lipid peroxidation in human leukemia
U937 cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 232:103–111. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Svegliati S, Cancello R, Sambo P, Luchetti
M, Paroncini P, Orlandini G, Discepoli G, Paterno R, Santillo M,
Cuozzo C, et al: Platelet-derived growth factor and reactive oxygen
species (ROS) regulate Ras protein levels in primary human
fibroblasts via ERK1/2. Amplification of ROS and Ras in systemic
sclerosis fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 280:36474–36482. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Choe Y, Yu JY, Son YO, Park SM, Kim JG,
Shi X and Lee JC: Continuously generated H2O2
stimulates the proliferation and osteoblastic differentiation of
human periodontal ligament fibroblasts. J Cell Biochem.
113:1426–1436. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
24
|
Bauvois B, Laouar A, Rouillard D and
Wietzerbin J: Inhibition of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase activity
at the surface of human myeloid cells is correlated with macrophage
maturation and transforming growth factor beta production. Cell
Growth Differ. 6:1163–1170. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fujita T, Shiba H, Van Dyke TE and
Kurihara H: Differential effects of growth factors and cytokines on
the synthesis of SPARC, DNA, fibronectin and alkaline phosphatase
activity in human periodontal ligament cells. Cell Biol Int.
28:281–286. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Narayanan AS and Page RC: Connective
tissues of the periodontium: A summary of current work. Coll Relat
Res. 3:33–64. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tomasek JJ, Gabbiani G, Hinz B, Chaponnier
C and Brown RA: Myofibroblasts and mechano-regulation of connective
tissue remodelling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 3:349–363. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|