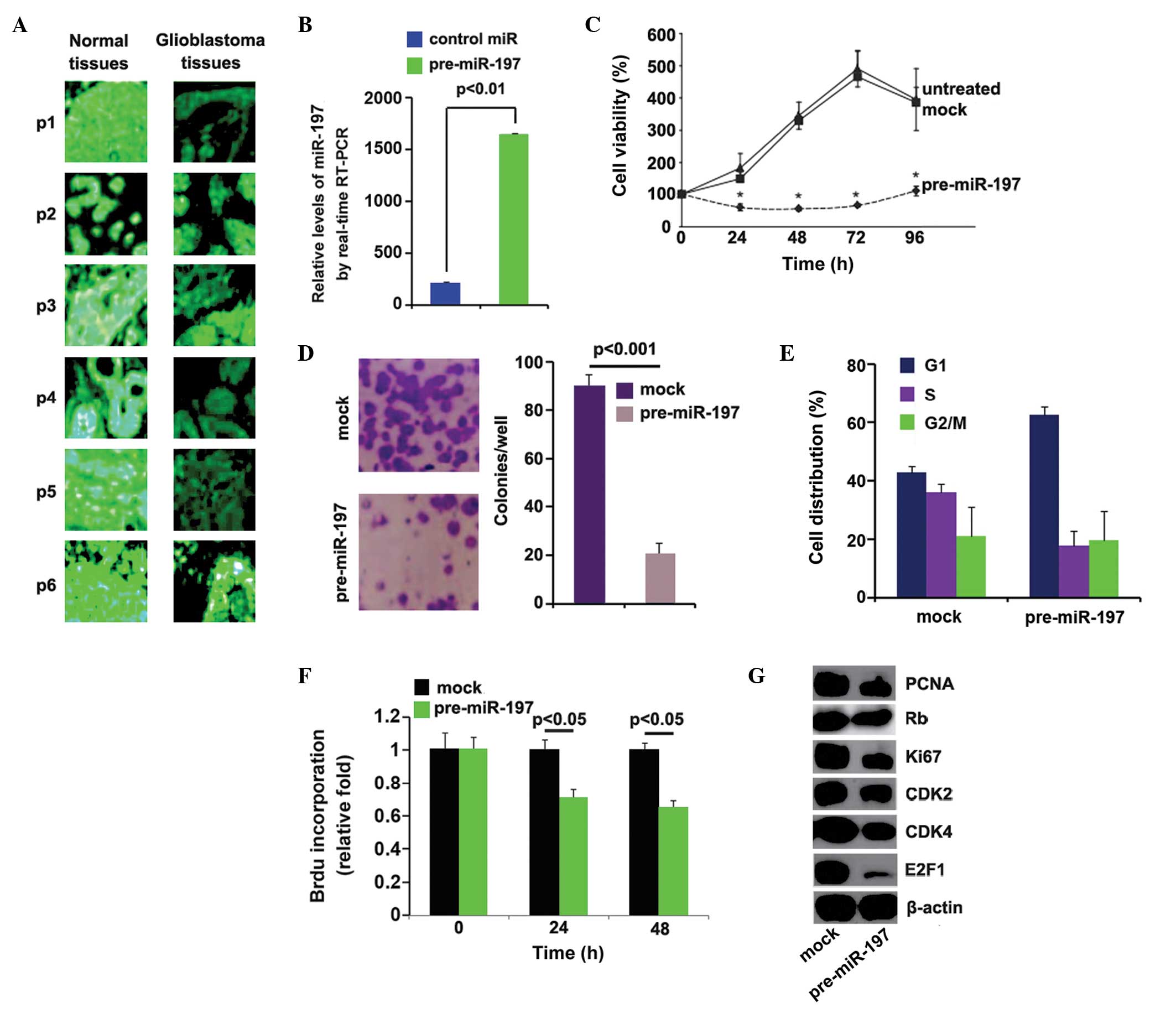
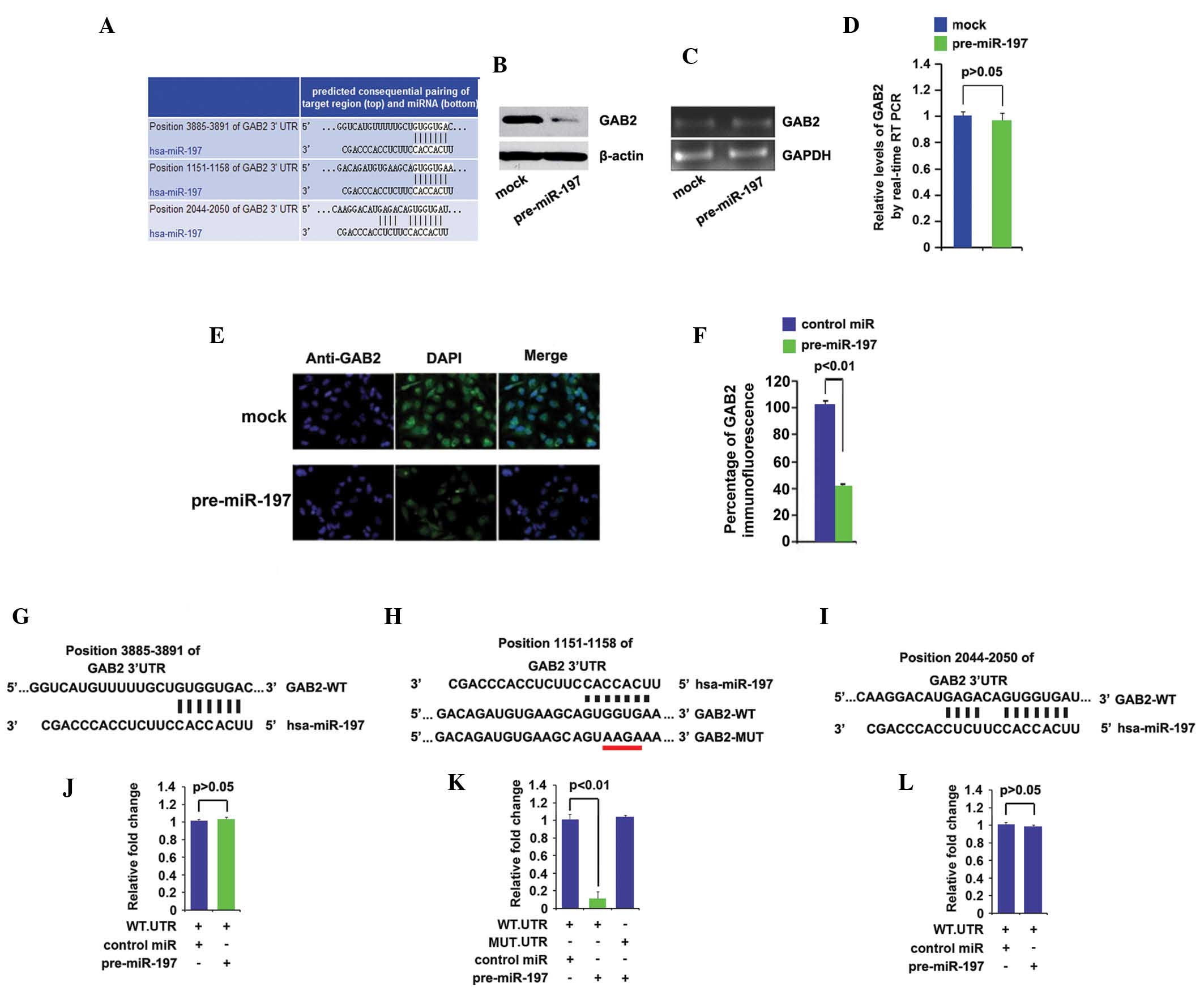
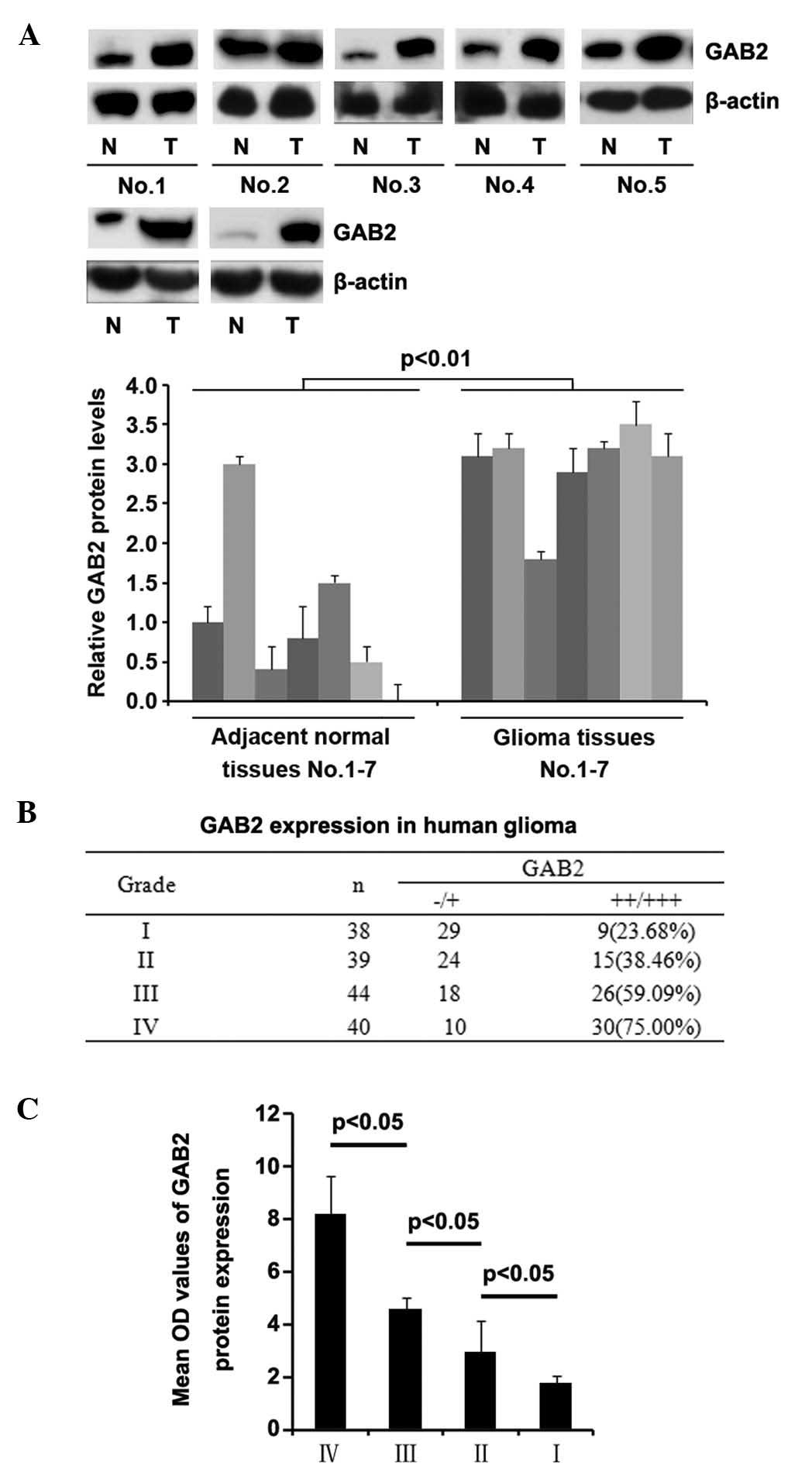
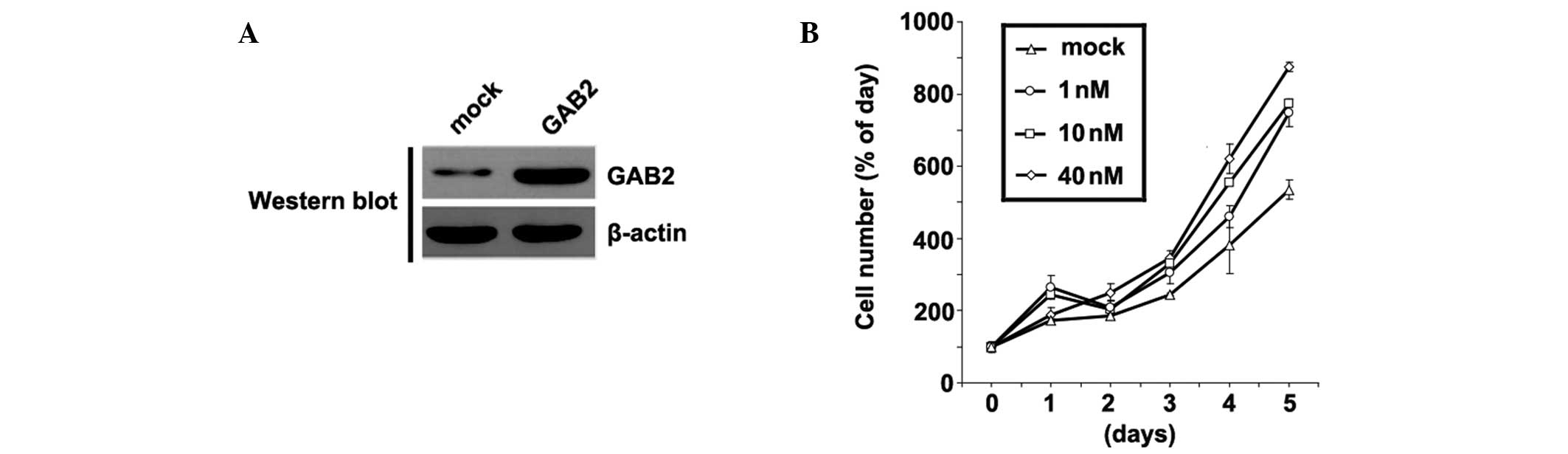
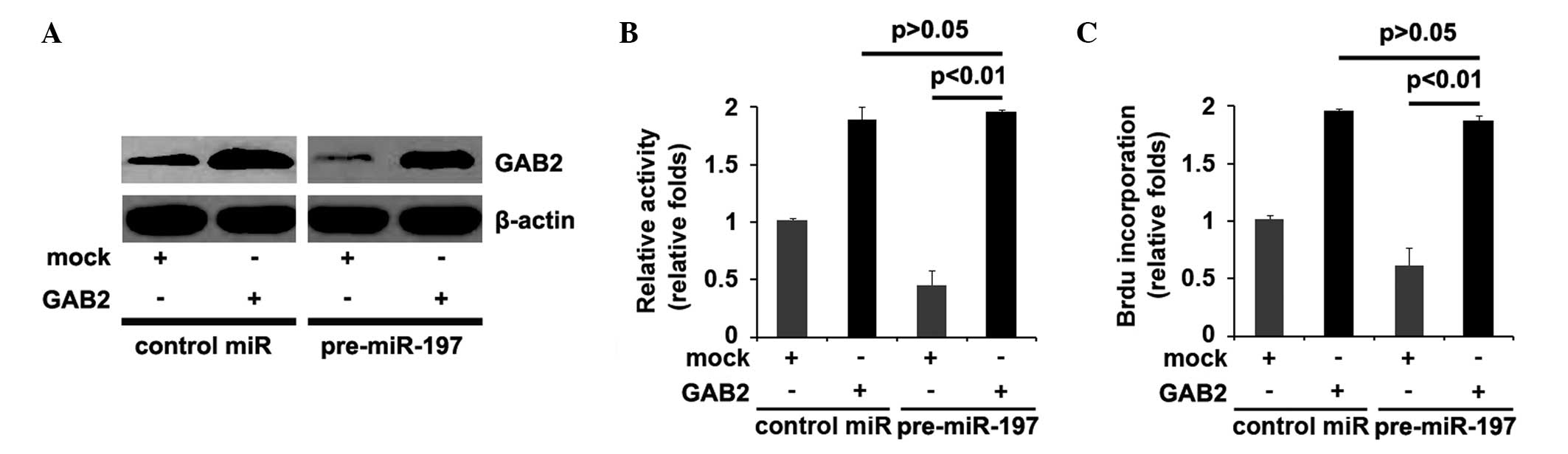
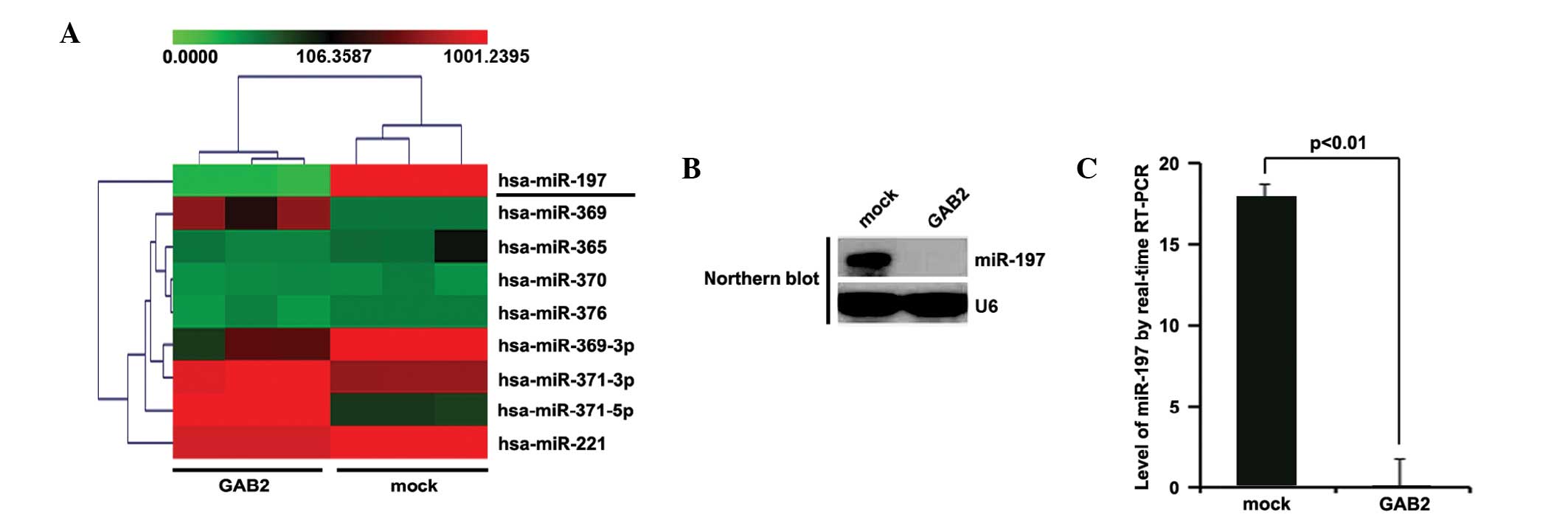
|
1
|
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL and Ambros V: The C.
elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense
complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 75:843–854. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pasquinelli AE, Reinhart BJ, Slack F,
Martindale MQ, Kuroda MI, Maller B, Hayward DC, Ball EE, Degnan B,
Müller P, et al: Conservation of the sequence and temporal
expression of let-7 heterochronic regulatory RNA. Nature.
408:86–89. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Reinhart BJ, Slack FJ, Basson M,
Pasquinelli AE, Bettinger JC, Rougvie AE, Horvitz HR and Ruvkun G:
The 21-nucleotide let-7 RNA regulates developmental timing in
Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 403:901–906. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Corsten MF, Miranda R, Kasmieh R,
Krichevsky AM, Weissleder R and Shah K: MicroRNA-21 knockdown
disrupts glioma growth in vivo and displays synergistic
cytotoxicity with neural precursor cell delivered S-TRAIL in human
gliomas. Cancer Res. 67:8994–9000. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Guessous F, Zhang Y, Kofman A, Catania A,
Li Y, Schiff D, Purow B and Abounader R: microRNA-34a is tumor
suppressive in brain tumors and glioma stem cells. Cell Cycle.
9:1031–1036. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen G, Zhu W, Shi D, Lv L, Zhang C, Liu P
and Hu W: MicroRNA-181a sensitizes human malignant glioma U87MG
cells to radiation by targeting Bcl-2. Oncol Rep. 23:997–1003.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sana J, Hajduch M, Michalek J, Vyzula R
and Slaby O: MicroRNAs and glioblastoma: Roles in core signalling
pathways and potential clinical implications. J Cell Mol Med.
15:1636–1644. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gu H and Neel BG: The 'Gab' in signal
transduction. Trends Cell Biol. 13:122–130. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nishida K and Hirano T: The role of Gab
family scaffolding adapter proteins in the signal transduction of
cytokine and growth factor receptors. Cancer Sci. 94:1029–1033.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Schwab M: Amplification of oncogenes in
human cancer cells. Bioessays. 20:473–479. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bentires-Alj M, Gil SG, Chan R, Wang ZC,
Wang Y, Imanaka N, Harris LN, Richardson A, Neel BG and Gu H: A
role for the scaffolding adapter GAB2 in breast cancer. Nat Med.
12:114–121. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Bocanegra M, Bergamaschi A, Kim YH, Miller
MA, Rajput AB, Kao J, Langerød A, Han W, Noh DY, Jeffrey SS, et al:
Focal amplification and oncogene dependency of GAB2 in breast
cancer. Oncogene. 29:774–779. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Brown LA, Kalloger SE, Miller MA, Shih
IeM, McKinney SE, Santos JL, Swenerton K, Spellman PT, Gray J,
Gilks CB and Huntsman DG: Amplification of 11q13 in ovarian
carcinoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 47:481–489. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zatkova A, Schoch C, Speleman F, Poppe B,
Mannhalter C, Fonatsch C and Wimmer K: GAB2 is a novel target of
11q amplification in AML/MDS. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 45:798–807.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Horst B, Gruvberger-Saal SK, Hopkins BD,
Bordone L, Yang Y, Chernoff KA, Uzoma I, Schwipper V, Liebau J,
Nowak NJ, et al: Gab2-mediated signaling promotes melanoma
metastasis. Am J Pathol. 174:1524–1533. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lee SH, Jeong EG, Nam SW, Lee JY, Yoo NJ
and Lee SH: Increased expression of Gab2, a scaffolding adaptor of
the tyrosine kinase signalling, in gastric carcinomas. Pathology.
39:326–329. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shi L, Sun X, Zhang J, Zhao C, Li H, Liu
Z, Fang C, Wang X, Zhao C, Zhang X, et al: Gab2 expression in
glioma and its implications for tumor invasion. Acta Oncol.
52:1739–1750. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee
WK, Burger PC, Jouvet A, Scheithauer BW and Kleihues P: The 2007
WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta
Neuropathol. 114:97–109. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Schmittgen TD, Lee EJ, Jiang J, Sarkar A,
Yang L, Elton TS and Chen C: Real-time PCR quantification of
precursor and mature microRNA. Methods. 44:31–38. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Liao XH, Lu DL, Wang N, Liu LY, Wang Y, Li
YQ, Yan TB, Sun XG, Hu P and Zhang TC: Estrogen receptor α mediates
proliferation of breast cancer MCF-7 cells via a
p21/PCNA/E2F1-dependent pathway. FEBS J. 281:927–942. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Bacus SS, Zelnick CR, Plowman G and Yarden
Y: Expression of the erbB-2 family of growth factor receptors and
their ligands in breast cancers. Implication for tumor biology and
clinical behavior. Am J Clin Pathol. 102(4 Suppl 1): S13–S24.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Eisen MB, Spellman PT, Brown PO and
Botstein D: Cluster analysis and display of genome-wide expression
patters. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 95:14863–14868. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Yu J, Ryan DG, Getsios S,
Oliveira-Fernandes M, Fatima A and Lavker RM: MicroRNA-184
antagonizes microRNA-205 to maintain SHIP2 levels in epithelia.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:19300–19305. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
He L, He X, Lim LP, de Stanchina E, Xuan
Z, Liang Y, Xue W, Zender L, Magnus J, Ridzon D, et al: A microRNA
component of the p53 tumour suppressor network. Nature.
447:1130–1134. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Novakova J, Slaby O, Vyzula R and Michalek
J: MicroRNA involvement in glioblastoma pathogenesis. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 386:1–5. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sasayama T, Nishihara M, Kondoh T, Hosoda
K and Kohmura E: MicroRNA-10b is overexpressed in malignant glioma
and associated with tumor invasive factors, uPAR and RhoC. Int J
Cancer. 125:1407–1413. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ma L, Teruya-Feldstein J and Weinberg RA:
Tumour invasion and metastasis initiated by microRNA-10b in breast
cancer. Nature. 449:682–688. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yang H, Kong W, He L, Zhao JJ, O'Donnell
JD, Wang J, Wenham RM, Coppola D, Kruk PA, Nicosia SV and Cheng JQ:
MicroRNA expression profiling in human ovarian cancer: miR-214
induces cell survival and cisplatin resistance by targeting PTEN.
Cancer Res. 68:425–433. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hayashita Y, Osada H, Tatematsu Y, Yamada
H, Yanagisawa K, Tomida S, Yatabe Y, Kawahara K, Sekido Y and
Takahashi T: A polycistronic microRNA cluster, miR-17-92, is
overexpressed in human lung cancers and enhances cell
proliferation. Cancer Res. 65:9628–9632. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang HJ, Ruan HJ, He XJ, Ma YY, Jiang XT,
Xia YJ, Ye ZY and Tao HQ: MicroRNA-101 is down-regulated in gastric
cancer and involved in cell migration and invasion. Eur J Cancer.
46:2295–2303. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Szafranska AE, Davison TS, John J, Cannon
T, Sipos B, Maghnouj A, Labourier E and Hahn SA: MicroRNA
expression alterations are linked to tumorigenesis and
non-neoplastic processes in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
Oncogene. 26:4442–4452. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yu S, Lu Z, Liu C, Meng Y, Ma Y, Zhao W,
Liu J, Yu J and Chen J: miRNA-96 suppresses KRAS and functions as a
tumor suppressor gene in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res.
70:6015–6025. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wong TS, Liu XB, Wong BY, Ng RW, Yuen AP
and Wei WI: Mature miR-184 as potential oncogenic microRNA of
squamous cell carcinoma of tongue. Clin Cancer Res. 14:2588–2592.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liang L, Wong CM, Ying Q, Fan DN, Huang S,
Ding J, Yao J, Yan M, Li J, Yao M, et al: MicroRNA-125b suppresses
human liver cancer cell proliferation and metastasis by directly
targeting oncogene LIN28B2. Hepatology. 52:1731–1740. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|