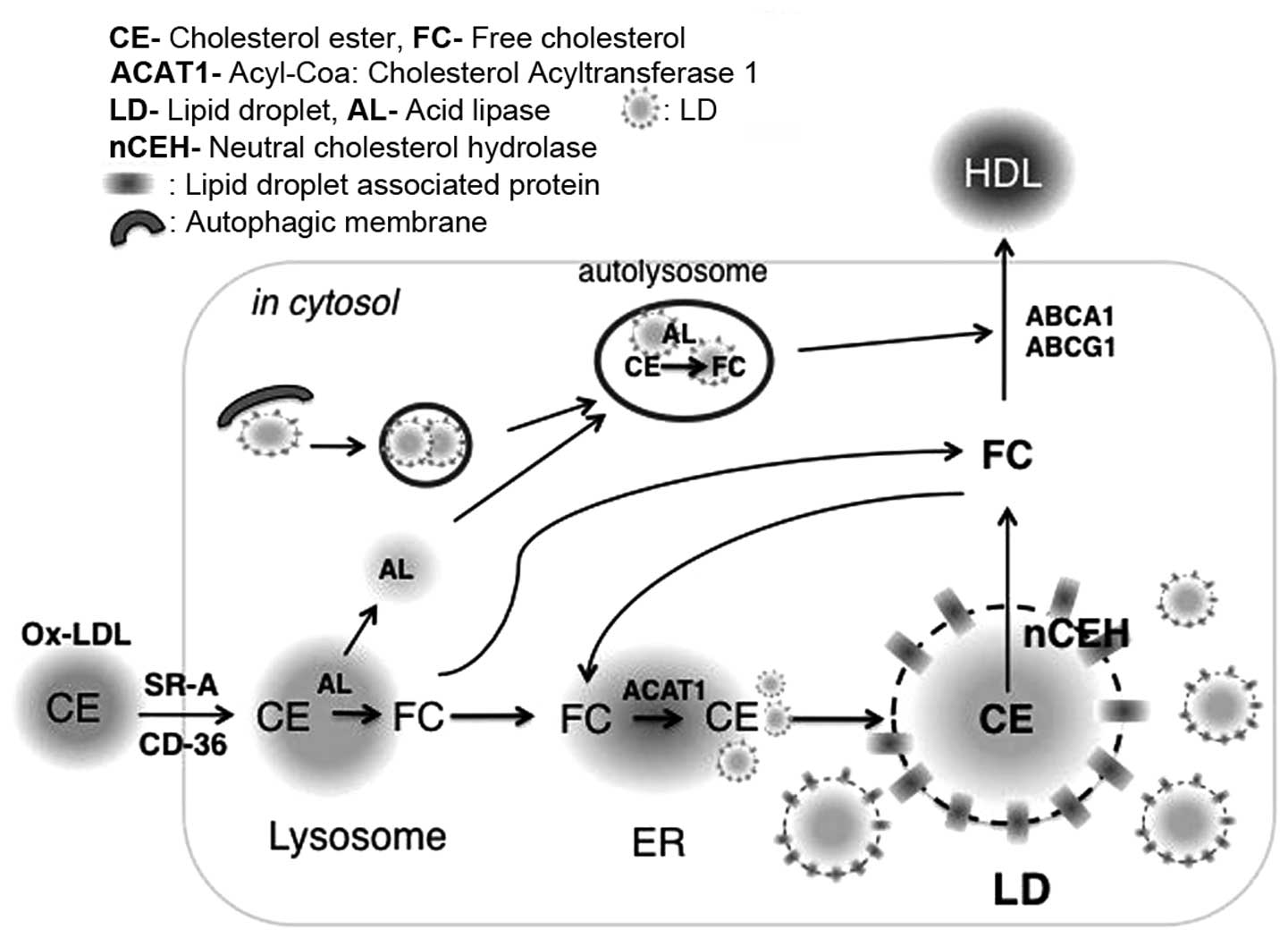
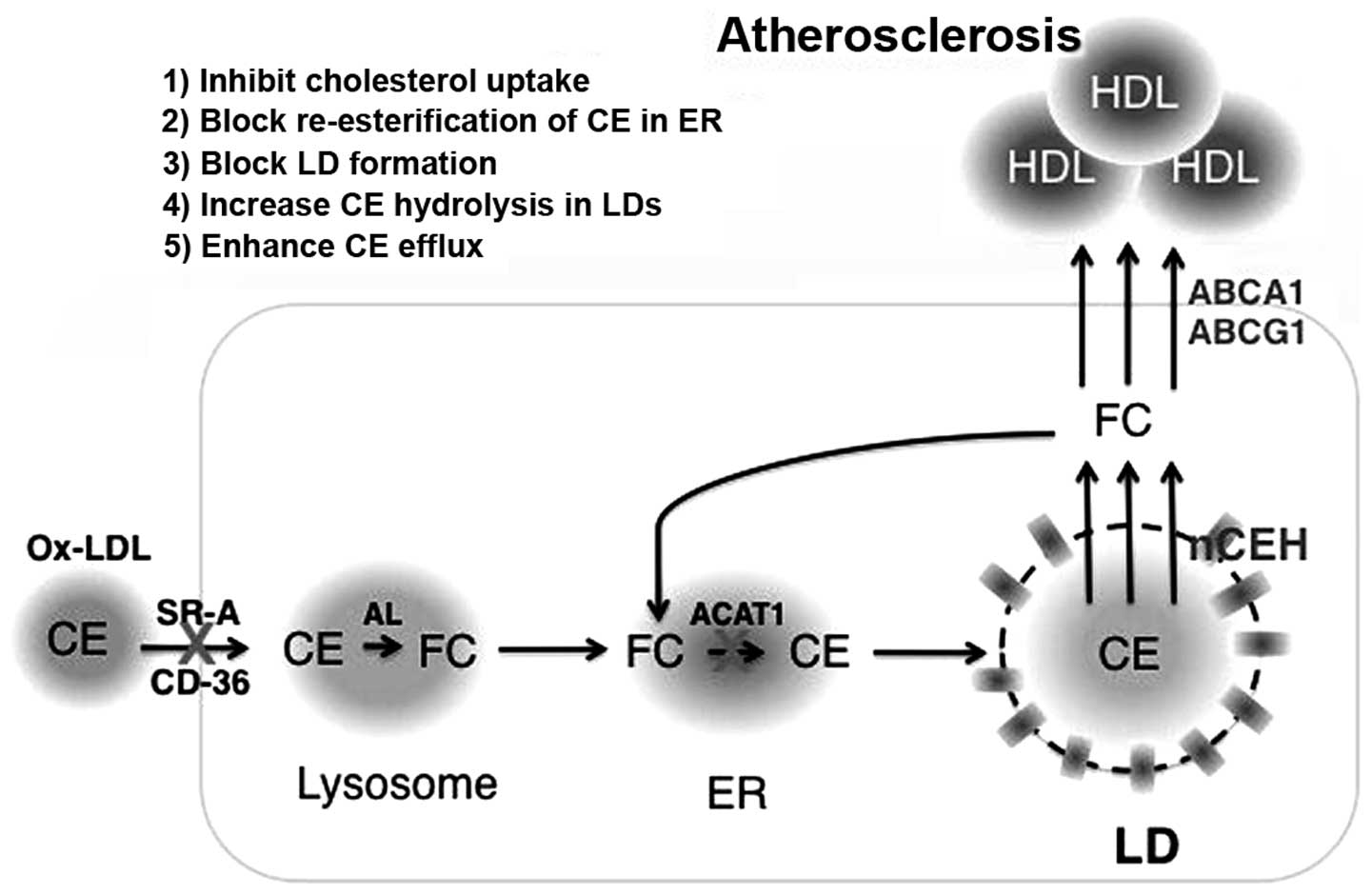
|
1
|
Go AS, Mozaffarian D, Roger VL, Benjamin
EJ, Berry JD, Borden WB, Bravata DM, Dai S, Ford ES, Fox CS, et al:
American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke
Statisics: Executive summary: Heart disease and stroke statistics –
2013 update: A report from the American Heart Association.
Circulation. 127:143–152. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ross R: The pathogenesis of
atherosclerosis: A perspective for the 1990s. Nature. 362:801–809.
1993. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ross R, Glomset J and Harker L: Response
to injury and atherogenesis. Am J Pathol. 86:675–684.
1977.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Williams KJ and Tabas I: The
response-to-retention hypothesis of early atherogenesis.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 15:551–561. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Maxfield FR and van Meer G: Cholesterol,
the central lipid of mammalian cells. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
22:422–429. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Maxfield FR and Tabas I: Role of
cholesterol and lipid organization in disease. Nature. 438:612–621.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Walther TC and Farese RV Jr: The life of
lipid droplets. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1791:459–466. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
8
|
Thiam AR, Farese RV Jr and Walther TC: The
biophysics and cell biology of lipid droplets. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 14:775–786. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu P, Ying Y, Zhao Y, Mundy DI, Zhu M and
Anderson RG: Chinese hamster ovary K2 cell lipid droplets appear to
be metabolic organelles involved in membrane traffic. J Biol Chem.
279:3787–3792. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Umlauf E, Csaszar E, Moertelmaier M,
Schuetz GJ, Parton RG and Prohaska R: Association of stomatin with
lipid bodies. J Biol Chem. 279:23699–23709. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kusminski CM, Shetty S, Orci L, Unger RH
and Scherer PE: Diabetes and apoptosis: Lipotoxicity. Apoptosis.
14:1484–1495. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tabas I: Consequences of cellular
cholesterol accumulation: Basic concepts and physiological
implications. J Clin Invest. 110:905–911. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Herranz P, de Lucas R, Pérez-España L and
Mayor M: Lipodystrophy syndromes. Dermatol Clin. 26:569–578.
ix2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bartz R, Li WH, Venables B, Zehmer JK,
Roth MR, Welti R, Anderson RG, Liu P and Chapman KD: Lipidomics
reveals that adiposomes store ether lipids and mediate phospholipid
traffic. J Lipid Res. 48:837–847. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Buhman KF, Accad M and Farese RV:
Mammalian acyl-CoA:Cholesterol acyltransferases. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1529:142–154. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yen CL, Stone SJ, Koliwad S, Harris C and
Farese RV Jr: Thematic review series: Glycerolipids. DGAT enzymes
and triacylglycerol biosynthesis. J Lipid Res. 49:2283–2301. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Robenek H, Hofnagel O, Buers I, Robenek
MJ, Troyer D and Severs NJ: Adipophilin-enriched domains in the ER
membrane are sites of lipid droplet biogenesis. J Cell Sci.
119:4215–4224. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Robenek MJ, Severs NJ, Schlattmann K,
Plenz G, Zimmer KP, Troyer D and Robenek H: Lipids partition
caveolin-1 from ER membranes into lipid droplets: Updating the
model of lipid droplet biogenesis. FASEB J. 18:866–868.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tauchi-Sato K, Ozeki S, Houjou T, Taguchi
R and Fujimoto T: The surface of lipid droplets is a phospholipid
monolayer with a unique fatty acid composition. J Biol Chem.
277:44507–44512. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ozeki S, Cheng J, Tauchi-Sato K, Hatano N,
Taniguchi H and Fujimoto T: Rab18 localizes to lipid droplets and
induces their close apposition to the endoplasmic reticulum-derived
membrane. J Cell Sci. 118:2601–2611. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Long AP, Manneschmidt AK, VerBrugge B,
Dortch MR, Minkin SC, Prater KE, Biggerstaff JP, Dunlap JR and
Dalhaimer P: Lipid droplet de novo formation and fission are linked
to the cell cycle in fission yeast. Traffic. 13:705–714. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yuan Y, Li P and Ye J: Lipid homeostasis
and the formation of macrophage-derived foam cells in
atherosclerosis. Protein Cell. 3:173–181. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Goo YH, Son SH, Kreienberg PB and Paul A:
Novel lipid droplet-associated serine hydrolase regulates
macrophage cholesterol mobilization. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
34:386–396. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
24
|
Brasaemle DL, Dolios G, Shapiro L and Wang
R: Proteomic analysis of proteins associated with lipid droplets of
basal and lipolytically stimulated 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem.
279:46835–46842. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Brasaemle DL: Thematic review series:
Adipocyte biology. The perilipin family of structural lipid droplet
proteins: Stabilization of lipid droplets and control of lipolysis.
J Lipid Res. 48:2547–2559. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Greenberg AS, Egan JJ, Wek SA, Garty NB,
Blanchette-Mackie EJ and Londos C: Perilipin, a major hormonally
regulated adipocyte-specific phosphoprotein associated with the
periphery of lipid storage droplets. J Biol Chem. 266:11341–11346.
1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Servetnick DA, Brasaemle DL, Gruia-Gray J,
Kimmel AR, Wolff J and Londos C: Perilipins are associated with
cholesteryl ester droplets in steroidogenic adrenal cortical and
Leydig cells. J Biol Chem. 270:16970–16973. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhao X, Gao M, He J, Zou L, Lyu Y, Zhang
L, Geng B, Liu G and Xu G: Perilipin1 deficiency in whole body or
bone marrow-derived cells attenuates lesions in
atherosclerosis-prone mice. PLoS One. 10:e01237382015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Paul A, Chang BH, Li L, Yechoor VK and
Chan L: Deficiency of adipose differentiation-related protein
impairs foam cell formation and protects against atherosclerosis.
Circ Res. 102:1492–1501. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lu X, Gruia-Gray J, Copeland NG, Gilbert
DJ, Jenkins NA, Londos C and Kimmel AR: The murine perilipin gene:
The lipid droplet-associated perilipins derive from
tissue-specific, mRNA splice variants and define a gene family of
ancient origin. Mamm Genome. 12:741–749. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tansey JT, Huml AM, Vogt R, Davis KE,
Jones JM, Fraser KA, Brasaemle DL, Kimmel AR and Londos C:
Functional studies on native and mutated forms of perilipins. A
role in protein kinase A-mediated lipolysis of triacylglycerols. J
Biol Chem. 278:8401–8406. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Zimmermann R, Strauss JG, Haemmerle G,
Schoiswohl G, Birner-Gruenberger R, Riederer M, Lass A, Neuberger
G, Eisenhaber F, Hermetter A and Zechner R: Fat mobilization in
adipose tissue is promoted by adipose triglyceride lipase. Science.
306:1383–1386. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Heid HW, Moll R, Schwetlick I, Rackwitz HR
and Keenan TW: Adipophilin is a specific marker of lipid
accumulation in diverse cell types and diseases. Cell Tissue Res.
294:309–321. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dalen KT, Dahl T, Holter E, Arntsen B,
Londos C, Sztalryd C and Nebb HI: LSDP5 is a PAT protein
specifically expressed in fatty acid oxidizing tissues. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1771:210–227. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Becker L, Gharib SA, Irwin AD, Wijsman E,
Vaisar T, Oram JF and Heinecke JW: A macrophage sterol-responsive
network linked to atherogenesis. Cell Metab. 11:125–135. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jiang HP and Serrero G: Isolation and
characterization of a full-length cDNA coding for an adipose
differentiation-related protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
89:7856–7860. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Masuda Y, Itabe H, Odaki M, Hama K,
Fujimoto Y, Mori M, Sasabe N, Aoki J, Arai H and Takano T:
ADRP/adipophilin is degraded through the proteasome-dependent
pathway during regression of lipid-storing cells. J Lipid Res.
47:87–98. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Xu G, Sztalryd C, Lu X, Tansey JT, Gan J,
Dorward H, Kimmel AR and Londos C: Post-translational regulation of
adipose differentiation-related protein by the ubiquitin/proteasome
pathway. J Biol Chem. 280:42841–42847. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Listenberger LL, Ostermeyer-Fay AG,
Goldberg EB, Brown WJ and Brown DA: Adipocyte
differentiation-related protein reduces the lipid droplet
association of adipose triglyceride lipase and slows
triacylglycerol turnover. J Lipid Res. 48:2751–2761. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Magne J, Aminoff A, Perman Sundelin J,
Mannila MN, Gustafsson P, Hultenby K, Wernerson A, Bauer G,
Listenberger L, Neville MJ, et al: The minor allele of the missense
polymorphism Ser251Pro in perilipin 2 (PLIN2) disrupts an α-helix,
affects lipolysis, and is associated with reduced plasma
triglyceride concentration in humans. FASEB J. 27:3090–3099. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Wolins NE, Skinner JR, Schoenfish MJ,
Tzekov A, Bensch KG and Bickel PE: Adipocyte protein S3-12 coats
nascent lipid droplets. J Biol Chem. 278:37713–37721. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Diaz E and Pfeffer SR: TIP47: A cargo
selection device for mannose 6-phosphate receptor trafficking.
Cell. 93:433–443. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Barbero P, Buell E, Zulley S and Pfeffer
SR: TIP47 is not a component of lipid droplets. J Biol Chem.
276:24348–24351. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Miura S, Gan JW, Brzostowski J, Parisi MJ,
Schultz CJ, Londos C, Oliver B and Kimmel AR: Functional
conservation for lipid storage droplet association among Perilipin,
ADRP and TIP47 (PAT)-related proteins in mammals, Drosophila and
Dictyostelium. J Biol Chem. 277:32253–32257. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Buers I, Robenek H, Lorkowski S, Nitschke
Y, Severs NJ and Hofnagel O: TIP47, a lipid cargo protein involved
in macrophage triglyceride metabolism. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc
Biol. 29:767–773. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Chang BH, Li L, Paul A, Taniguchi S,
Nannegari V, Heird WC and Chan L: Protection against fatty liver
but normal adipogenesis in mice lacking adipose
differentiation-related protein. Mol Cell Biol. 26:1063–1076. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wolins NE, Quaynor BK, Skinner JR, Tzekov
A, Croce MA, Gropler MC, Varma V, Yao-Borengasser A, Rasouli N,
Kern PA, Finck BN and Bickel PE: OXPAT/PAT-1 is a PPAR-induced
lipid droplet protein that promotes fatty acid utilization.
Diabetes. 55:3418–3428. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Li H, Song Y, Li F, Zhang L, Gu Y, Zhang
L, Jiang L, Dong W, Ye J and Li Q: Identification of lipid
droplet-associated proteins in the formation of macrophage-derived
foam cells using micro-arrays. Int J Mol Med. 26:231–239. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zhou Z, Yon Toh S, Chen Z, Guo K, Ng CP,
Ponniah S, Lin SC, Hong W and Li P: Cidea-deficient mice have lean
phenotype and are resistant to obesity. Nat Genet. 35:49–56. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Li JZ, Ye J, Xue B, Qi J, Zhang J, Zhou Z,
Li Q, Wen Z and Li P: Cideb regulates diet-induced obesity, liver
steatosis and insulin sensitivity by controlling lipogenesis and
fatty acid oxidation. Diabetes. 56:2523–2532. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Toh SY, Gong J, Du G, Li JZ, Yang S, Ye J,
Yao H, Zhang Y, Xue B, Li Q, et al: Up-regulation of mitochondrial
activity and acquirement of brown adipose tissue-like property in
the white adipose tissue of fsp27 deficient mice. PLoS One.
3:e28902008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Nishino N, Tamori Y, Tateya S, Kawaguchi
T, Shibakusa T, Mizunoya W, Inoue K, Kitazawa R, Kitazawa S,
Matsuki Y, et al: FSP27 contributes to efficient energy storage in
murine white adipocytes by promoting the formation of unilocular
lipid droplets. J Clin Invest. 118:2808–2821. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Gong J, Sun Z and Li P: CIDE proteins and
metabolic disorders. Curr Opin Lipidol. 20:121–126. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Yeaman SJ: Hormone-sensitive lipase-a
multipurpose enzyme in lipid metabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1052:128–132. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Kraemer FB and Shen WJ: Hormone-sensitive
lipase: Control of intracellular tri-(di-)acylglycerol and
cholesteryl ester hydrolysis. J Lipid Res. 43:1585–1594. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Moore KJ, Kunjathoor VV, Koehn SL, Manning
JJ, Tseng AA, Silver JM, McKee M and Freeman MW: Loss of
receptor-mediated lipid uptake via scavenger receptor A or CD36
pathways does not ameliorate atherosclerosis in hyperlipidemic
mice. J Clin Invest. 115:2192–2201. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Moore KJ, Sheedy FJ and Fisher EA:
Macrophages in atherosclerosis: A dynamic balance. Nat Rev Immunol.
13:709–721. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Ouimet M, Franklin V, Mak E, Liao X, Tabas
I and Marcel YL: Autophagy regulates cholesterol efflux from
macrophage foam cells via lysosomal acid lipase. Cell Metab.
13:655–667. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Goldstein JL, Ho YK, Basu SK and Brown MS:
Binding site on macrophages that mediates uptake and degradation of
acetylated low density lipoprotein, producing massive cholesterol
deposition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 76:333–337. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Kunjathoor VV, Febbraio M, Podrez EA,
Moore KJ, Andersson L, Koehn S, Rhee JS, Silverstein R, Hoff HF and
Freeman MW: Scavenger receptors class A-I/II and CD36 are the
principal receptors responsible for the uptake of modified low
density lipoprotein leading to lipid loading in macrophages. J Biol
Chem. 277:49982–49988. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Suzuki H, Kurihara Y, Takeya M, Kamada N,
Kataoka M, Jishage K, Ueda O, Sakaguchi H, Higashi T, Suzuki T, et
al: A role for macrophage scavenger receptors in atherosclerosis
and susceptibility to infection. Nature. 386:292–296. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Febbraio M, Podrez EA, Smith JD, Hajjar
DP, Hazen SL, Hoff HF, Sharma K and Silverstein RL: Targeted
disruption of the class B scavenger receptor CD36 protects against
atherosclerotic lesion development in mice. J Clin Invest.
105:1049–1056. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Mäkinen PI, Lappalainen JP, Heinonen SE,
Leppänen P, Lähteenvuo MT, Aarnio JV, Heikkilä J, Turunen MP and
Ylä-Herttuala S: Silencing of either SR-A or CD36 reduces
atherosclerosis in hyperlipidaemic mice and reveals reciprocal
upregulation of these receptors. Cardiovasc Res. 88:530–538. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Manning-Tobin JJ, Moore KJ, Seimon TA,
Bell SA, Sharuk M, Alvarez-Leite JI, de Winther MP, Tabas I and
Freeman MW: Loss of SR-A and CD36 activity reduces atherosclerotic
lesion complexity without abrogating foam cell formation in
hyperlipidemic mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 29:19–26. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
65
|
Accad M, Smith SJ, Newland DL, Sanan DA,
King LE Jr, Linton MF, Fazio S and Farese RV Jr: Massive
xanthomatosis and altered composition of atherosclerotic lesions in
hyperlipidemic mice lacking acyl CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase 1.
J Clin Invest. 105:711–719. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Fazio S, Major AS, Swift LL, Gleaves LA,
Accad M, Linton MF and Farese RV Jr: Increased atherosclerosis in
LDL receptor-null mice lacking ACAT1 in macrophages. J Clin Invest.
107:163–171. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Warner GJ, Stoudt G, Bamberger M, Johnson
WJ and Rothblat GH: Cell toxicity induced by inhibition of acyl
coenzyme A:cholesterol acyltransferase and accumulation of
unesterified cholesterol. J Biol Chem. 270:5772–5778. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Larigauderie G, Furman C, Jaye M, Lasselin
C, Copin C, Fruchart JC, Castro G and Rouis M: Adipophilin enhances
lipid accumulation and prevents lipid efflux from THP-1
macrophages: Potential role in atherogenesis. Arterioscler Thromb
Vasc Biol. 24:504–510. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Nuotio K, Isoviita PM, Saksi J, Ijäs P,
Pitkäniemi J, Sonninen R, Soinne L, Saimanen E, Salonen O, Kovanen
PT, et al: Adipophilin expression is increased in symptomatic
carotid atherosclerosis: Correlation with red blood cells and
cholesterol crystals. Stroke. 38:1791–1798. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Son SH, Goo YH, Chang BH and Paul A:
Perilipin 2 (PLIN2)-deficiency does not increase
cholesterol-induced toxicity in macrophages. PLoS One.
7:e330632012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Chen FL, Yang ZH, Wang XC, Liu Y, Yang YH,
Li LX, Liang WC, Zhou WB and Hu RM: Adipophilin affects the
expression of TNF-alpha, MCP-1 and IL-6 in THP-1 macrophages. Mol
Cell Biochem. 337:193–199. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Langlois D, Forcheron F, Li JY, del
Carmine P, Neggazi S and Beylot M: Increased atherosclerosis in
mice deficient in perilipin1. Lipids Health Dis. 10:1692011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Li JZ, Lei Y, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Ye J, Xia
X, Pan X and Li P: Control of cholesterol biosynthesis, uptake and
storage in hepatocytes by Cideb. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1801:577–586. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Brown AJ and Jessup W: Oxysterols and
atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. 142:1–28. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Ishii I, Oka M, Katto N, Shirai K, Saito Y
and Hirose S: Beta-VLDL-induced cholesterol ester deposition in
macrophages may be regulated by neutral cholesterol esterase
activity. Arterioscler Thromb. 12:1139–1145. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Kritharides L, Christian A, Stoudt G,
Morel D and Rothblat GH: Cholesterol metabolism and efflux in human
THP-1 macrophages. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 18:1589–1599.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Escary JL, Choy HA, Reue K and Schotz MC:
Hormone-sensitive lipase overexpression increases cholesteryl ester
hydrolysis in macrophage foam cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
18:991–998. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Buchebner M, Pfeifer T, Rathke N, Chandak
PG, Lass A, Schreiber R, Kratzer A, Zimmermann R, Sattler W,
Koefeler H, et al: Cholesteryl ester hydrolase activity is
abolished in HSL−/− macrophages but unchanged in macrophages
lacking KIAA1363. J Lipid Res. 51:2896–2908. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Sekiya M, Osuga J, Nagashima S, Ohshiro T,
Igarashi M, Okazaki H, Takahashi M, Tazoe F, Wada T, Ohta K, et al:
Ablation of neutral cholesterol ester hydrolase 1 accelerates
atherosclerosis. Cell Metab. 10:219–228. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Escary JL, Choy HA, Reue K, Wang XP,
Castellani LW, Glass CK, Lusis AJ and Schotz MC: Paradoxical effect
on atherosclerosis of hormone-sensitive lipase overexpression in
macrophages. J Lipid Res. 40:397–404. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Choy HA, Wang XP and Schotz MC: Reduced
atherosclerosis in hormone-sensitive lipase transgenic mice
overexpressing cholesterol acceptors. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1634:76–85. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Rothblat GH, de la Llera-Moya M, Atger V,
Kellner-Weibel G, Williams DL and Phillips MC: Cell cholesterol
efflux: Integration of old and new observations provides new
insights. J Lipid Res. 40:781–796. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Allahverdian S, Pannu PS and Francis GA:
Contribution of monocyte-derived macrophages and smooth muscle
cells to arterial foam cell formation. Cardiovasc Res. 95:165–172.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Wang N, Lan D, Chen W, Matsuura F and Tall
AR: ATP-binding cassette transporters G1 and G4 mediate cellular
cholesterol efflux to high-density lipoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 101:9774–9779. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
van Eck M, Bos IS, Kaminski WE, Orsó E,
Rothe G, Twisk J, Böttcher A, Van Amersfoort ES, Christiansen-Weber
TA, Fung-Leung WP, et al: Leukocyte ABCA1 controls susceptibility
to atherosclerosis and macrophage recruitment into tissues. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:6298–6303. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Singaraja RR, Fievet C, Castro G, James
ER, Hennuyer N, Clee SM, Bissada N, Choy JC, Fruchart JC, McManus
BM, et al: Increased ABCA1 activity protects against
atherosclerosis. J Clin Invest. 110:35–42. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Burgess B, Naus K, Chan J,
Hirsch-Reinshagen V, Tansley G, Matzke L, Chan B, Wilkinson A, Fan
J, Donkin J, et al: Overexpression of human ABCG1 does not affect
atherosclerosis in fat-fed ApoE-deficient mice. Arterioscler Thromb
Vasc Biol. 28:1731–1737. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Basso F, Amar MJ, Wagner EM, Vaisman B,
Paigen B, Santamarina-Fojo S and Remaley AT: Enhanced ABCG1
expression increases atherosclerosis in LDLr-KO mice on a western
diet. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 351:398–404. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Baldán A, Pei L, Lee R, Tarr P, Tangirala
RK, Weinstein MM, Frank J, Li AC, Tontonoz P and Edwards PA:
Impaired development of atherosclerosis in hyperlipidemic Ldlr−/−
and ApoE−/− mice transplanted with Abcg1−/− bone marrow.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 26:2301–2307. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Out R, Hoekstra M, Hildebrand RB, Kruit
JK, Meurs I, Li Z, Kuipers F, Van Berkel TJ and Van Eck M:
Macrophage ABCG1 deletion disrupts lipid homeostasis in alveolar
macrophages and moderately influences atherosclerotic lesion
development in LDL receptor-deficient mice. Arterioscler Thromb
Vasc Biol. 26:2295–2300. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Yvan-Charvet L, Ranalletta M, Wang N, Han
S, Terasaka N, Li R, Welch C and Tall AR: Combined deficiency of
ABCA1 and ABCG1 promotes foam cell accumulation and accelerates
atherosclerosis in mice. J Clin Invest. 117:3900–3908.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Sabol SL, Brewer HB Jr and
Santamarina-Fojo S: The human ABCG1 gene: Identification of LXR
response elements that modulate expression in macrophages and
liver. J Lipid Res. 46:2151–2167. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Chawla A, Boisvert WA, Lee CH, Laffitte
BA, Barak Y, Joseph SB, Liao D, Nagy L, Edwards PA, Curtiss LK, et
al: A PPAR gamma-LXR-ABCA1 pathway in macrophages is involved in
cholesterol efflux and atherogenesis. Mol Cell. 7:161–171. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Calkin AC and Tontonoz P: Liver x receptor
signaling pathways and atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc
Biol. 30:1513–1518. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Magana MM and Osborne TF: Two tandem
binding sites for sterol regulatory element binding proteins are
required for sterol regulation of fatty-acid synthase promoter. J
Biol Chem. 271:32689–32694. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Magana MM, Lin SS, Dooley KA and Osborne
TF: Sterol regulation of acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase promoter
requires two interdependent binding sites for sterol regulatory
element binding proteins. J Lipid Res. 38:1630–1638.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Foretz M, Pacot C, Dugail I, Lemarchand P,
Guichard C, Le Lièpvre X, Berthelier-Lubrano C, Spiegelman B, Kim
JB, Ferré P and Foufelle F: ADD1/SREBP-1c is required in the
activation of hepatic lipogenic gene expression by glucose. Mol
Cell Biol. 19:3760–3768. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Cha JY and Repa JJ: The liver X receptor
(LXR) and hepatic lipogenesis. The carbohydrate-response
element-binding protein is a target gene of LXR. J Biol Chem.
282:743–751. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Kim GH, Oh GS, Yoon J, Lee GG, Lee KU and
Kim SW: Hepatic TRAP80 selectively regulates lipogenic activity of
liver X receptor. J Clin Invest. 125:183–193. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
100
|
Zhang XQ, Even-Or O, Xu X, van Rosmalen M,
Lim L, Gadde S, Farokhzad OC and Fisher EA: Nanoparticles
containing a liver X receptor agonist inhibit inflammation and
atherosclerosis. Adv Healthc Mater. 4:228–236. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
101
|
Lim RK, Yu S, Cheng B, Li S, Kim NJ, Cao
Y, Chi V, Kim JY, Chatterjee AK, Schultz PG, et al: Targeted
delivery of LXR agonist using a site-specific antibody-drug
conjugate. Bioconjug Chem. 26:2216–2222. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|