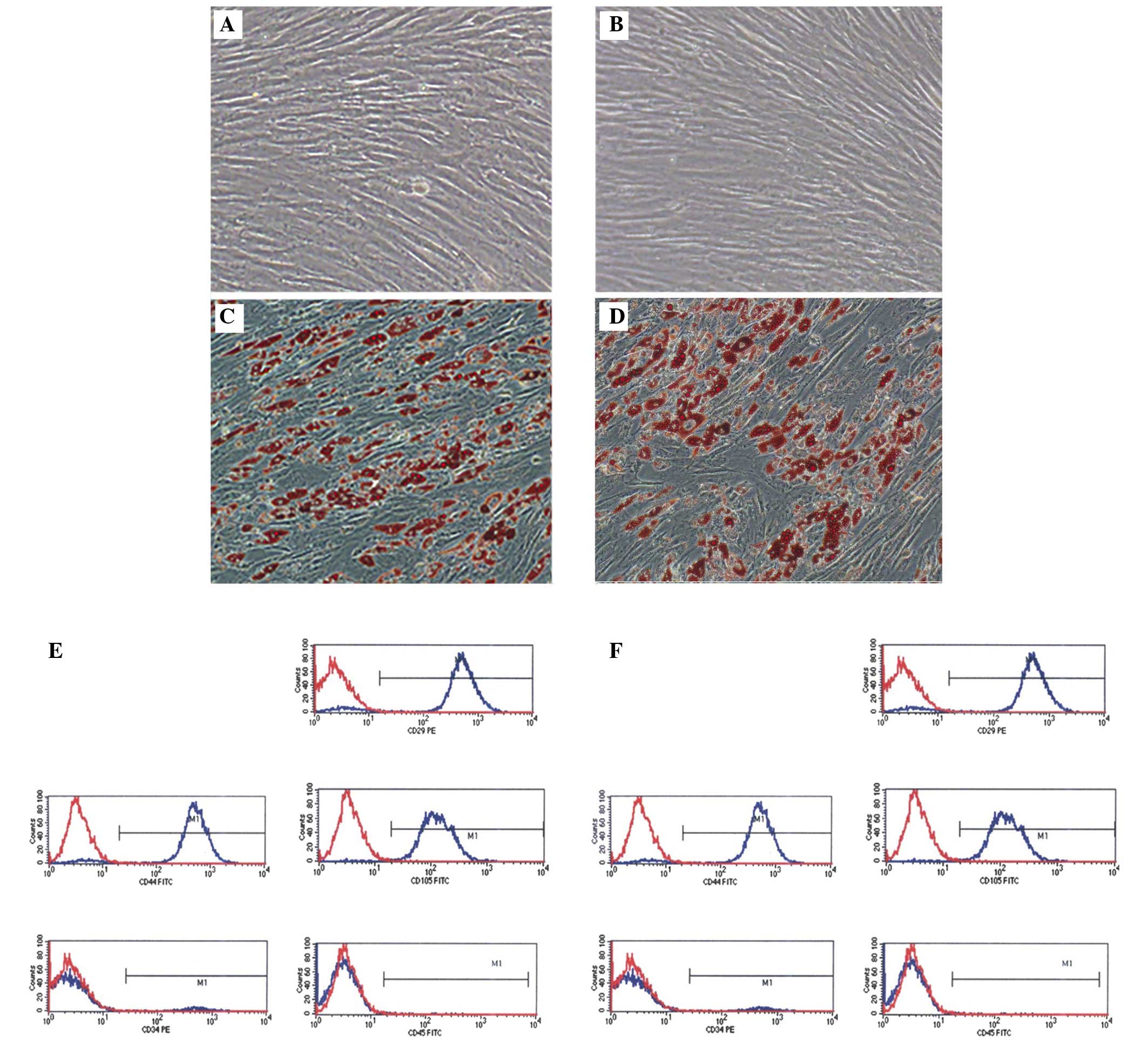
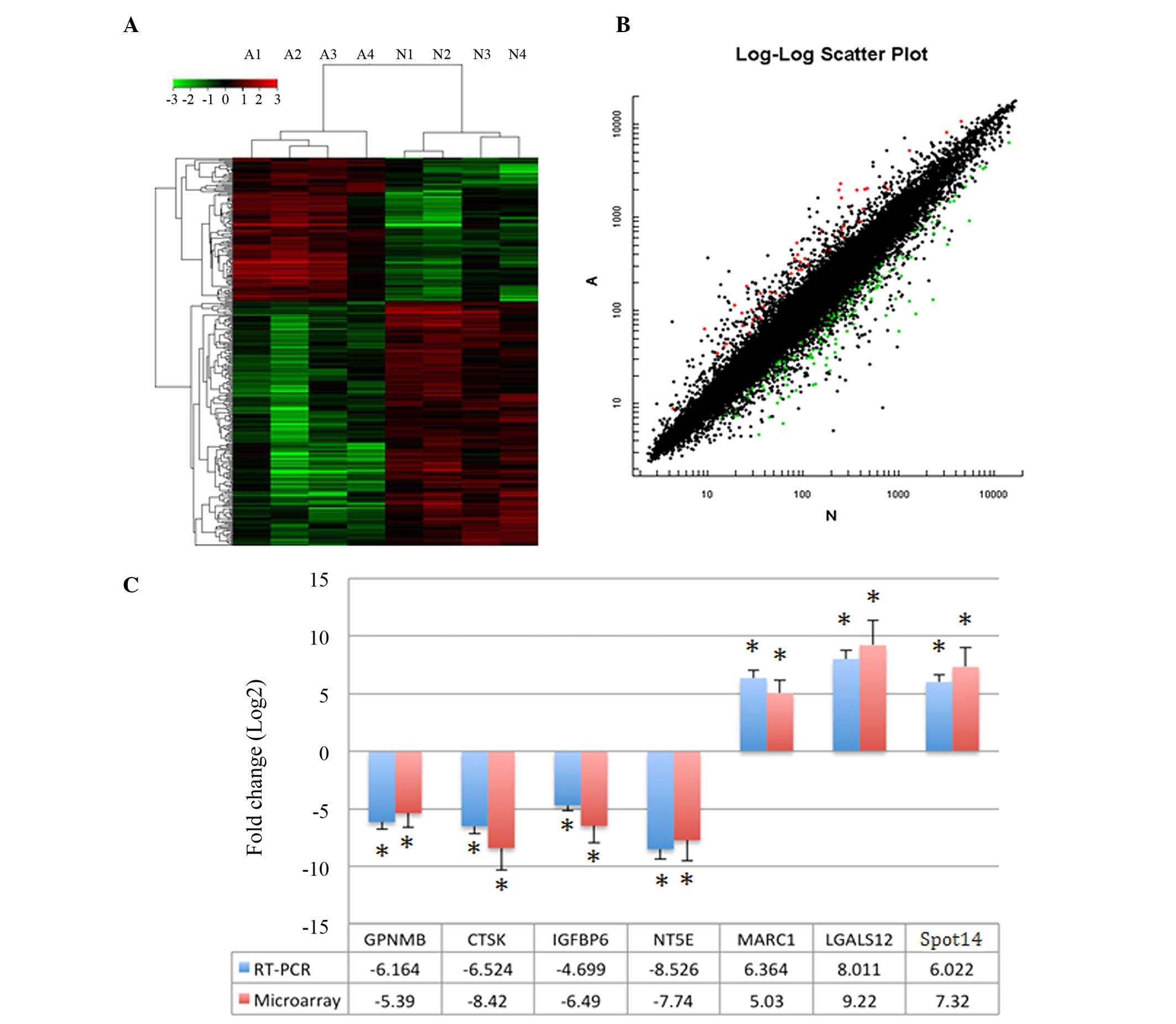
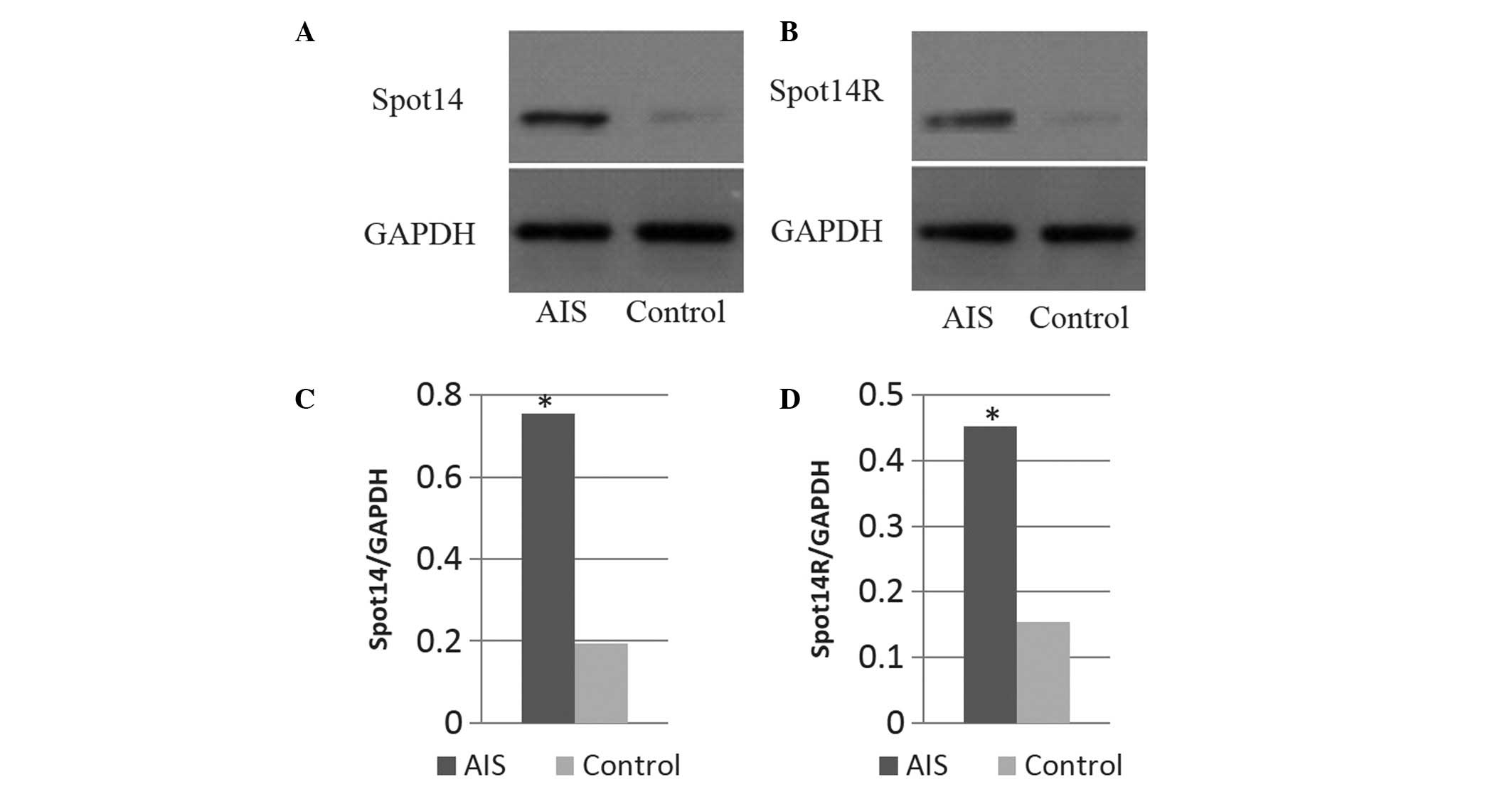
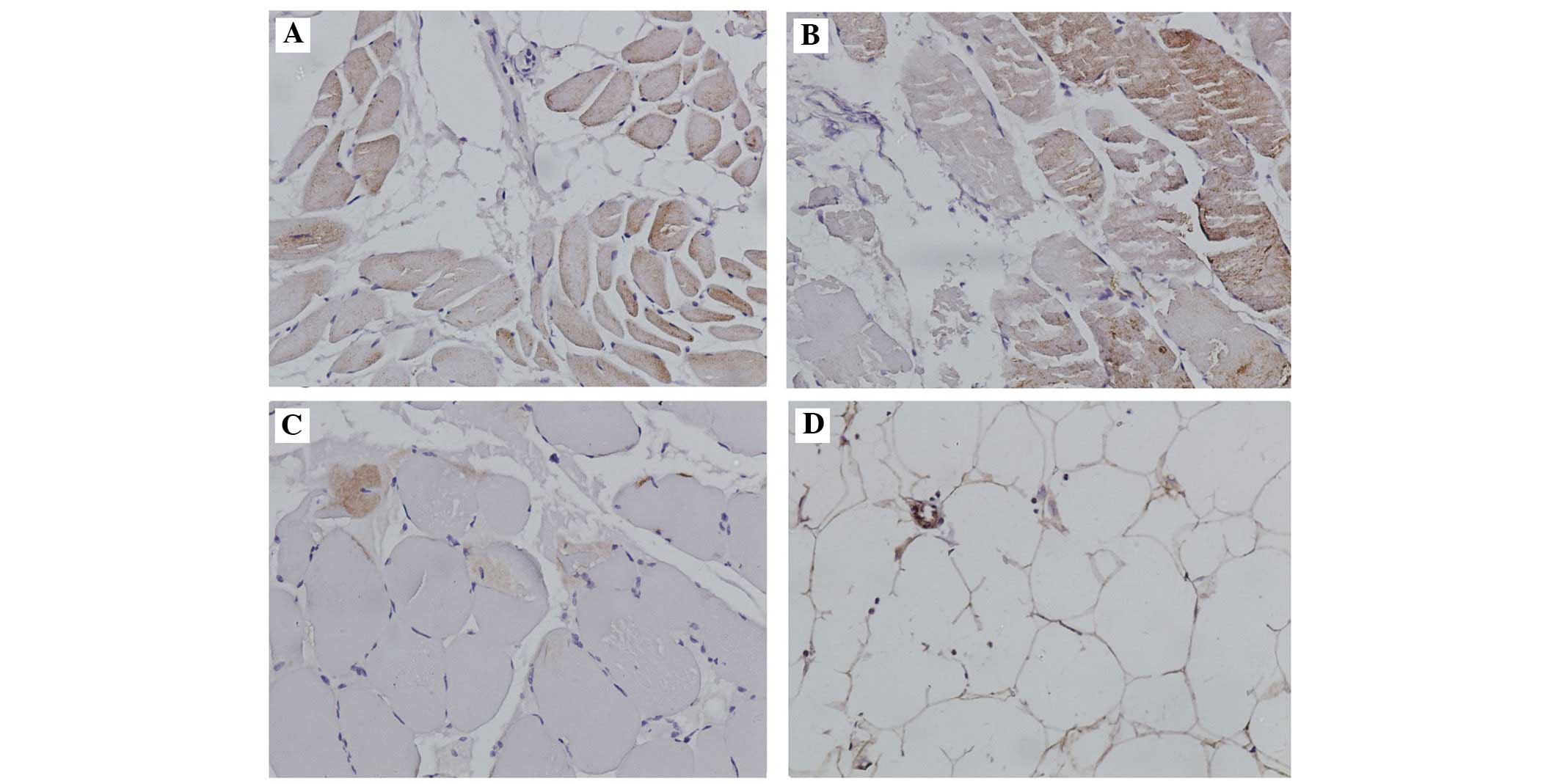
|
1
|
Lonstein JE: Adolescent idiopathic
scoliosis. Lancet. 344:1407–1412. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Weinstein SL, Dolan LA, Cheng JC,
Danielsson A and Morcuende JA: Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis.
Lancet. 371:1527–1537. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Weinstein SL: Adolescent idiopathic
scoliosis: Prevalence and natural history. Instr Course Lect.
38:115–128. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Suh KT, Lee SS, Hwang SH, Kim SJ and Lee
JS: Elevated soluble receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB
ligand and reduced bone mineral density in patients with adolescent
idiopathic scoliosis. Eur Spine J. 16:1563–1569. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lee WT, Cheung CS, Tse YK, Guo X, Qin L,
Ho SC, Lau J and Cheng JC: Generalized low bone mass of girls with
adolescent idiopathic scoliosis is related to inadequate calcium
intake and weight bearing physical activity in peripubertal period.
Osteoporos Int. 16:1024–1035. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cheng JC and Guo X: Osteopenia in
adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. A primary problem or secondary to
the spinal deformity? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 22:1716–1721. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Wang WJ, Hung VW, Lam TP, Ng BK, Qin L,
Lee KM, Qiu Y, Cheng JC and Yeung HY: The association of
disproportionate skeletal growth and abnormal radius dimension
ratio with curve severity in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Eur
Spine J. 19:726–731. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhuang Q, Li J, Wu Z, Zhang J, Sun W, Li
T, Yan Y, Jiang Y, Zhao RC and Qiu G: Differential proteome
analysis of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells from adolescent
idiopathic scoliosis patients. PLoS One. 6:e188342011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chu WC, Lam WM, Ng BK, Tze-Ping L, Lee KM,
Guo X, Cheng JC, Burwell RG, Dangerfield PH and Jaspan T: Relative
shortening and functional tethering of spinal cord in adolescent
scoliosis-Result of asynchronous neuro-osseous growth, summary of
an electronic focus group debate of the IBSE. Scoliosis. 3:82008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Nuttall ME and Gimble JM: Is there a
therapeutic opportunity to either prevent or treat osteopenic
disorders by inhibiting marrow adipogenesis? Bone. 27:177–184.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu Z, Tam EM, Sun GQ, Lam TP, Zhu ZZ, Sun
X, Lee KM, Ng TB, Qiu Y, Cheng JC and Yeung HY: Abnormal leptin
bioavailability in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: An important
new finding. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 37:599–604. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Liang G, Gao W, Liang A, Ye W, Peng Y,
Zhang L, Sharma S, Su P and Huang D: Normal leptin expression,
lower adipogenic ability, decreased leptin receptor and
hyposensitivity to Leptin in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. PLoS
One. 7:e366482012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Colbert CL, Kim CW, Moon YA, Henry L,
Palnitkar M, McKean WB, Fitzgerald K, Deisenhofer J, Horton JD and
Kwon HJ: Crystal structure of Spot 14, a modulator of fatty acid
synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:18820–18825. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Aipoalani DL, O'Callaghan BL, Mashek DG,
Mariash CN and Towle HC: Overlapping roles of the
glucose-responsive genes, S14 and S14R, in hepatic lipogenesis.
Endocrinology. 151:2071–2077. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhu Q, Mariash A, Margosian MR, Gopinath
S, Fareed MT, Anderson GW and Mariash CN: Spot 14 gene deletion
increases hepatic de novo lipogenesis. Endocrinology.
142:4363–4370. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhu Q, Anderson GW, Mucha GT, Parks EJ,
Metkowski JK and Mariash CN: The Spot 14 protein is required for de
novo lipid synthesis in the lactating mammary gland. Endocrinology.
146:3343–3350. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bruford EA, Riise R, Teague PW, Porter K,
Thomson KL, Moore AT, Jay M, Warburg M, Schinzel A, Tommerup N, et
al: Linkage mapping in 29 Bardet-Biedl syndrome families confirms
loci in chromosomal regions 11q13, 15q22.3-q23 and 16q21. Genomics.
41:93–99. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Moreau A, Téruel C, Beylot M, Albalea V,
Tamasi V, Umbdenstock T, Parmentier Y, Sa-Cunha A, Suc B, Fabre JM,
et al: A novel pregnane X receptor and S14-mediated lipogenic
pathway in human hepatocyte. Hepatology. 49:2068–2079. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|