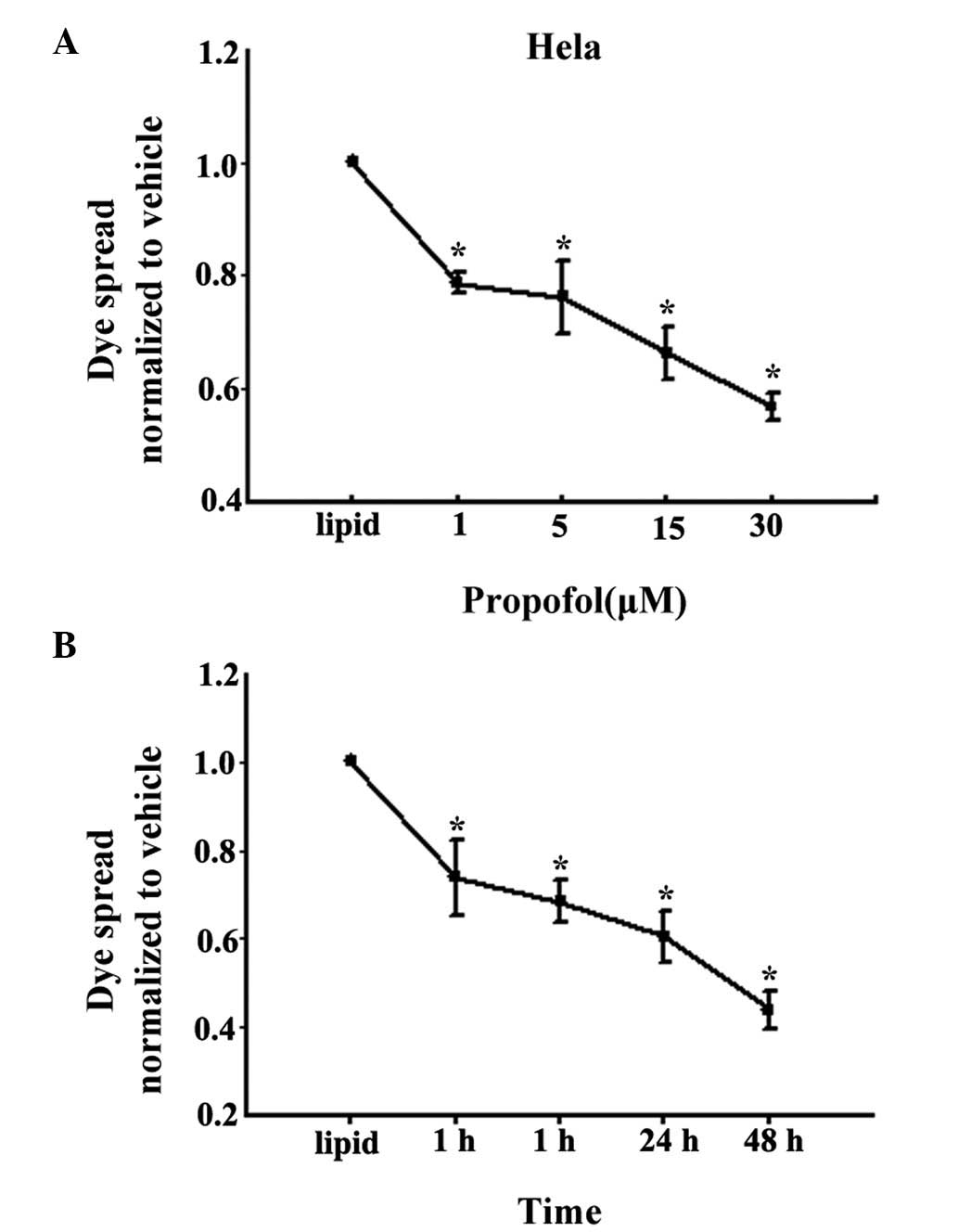
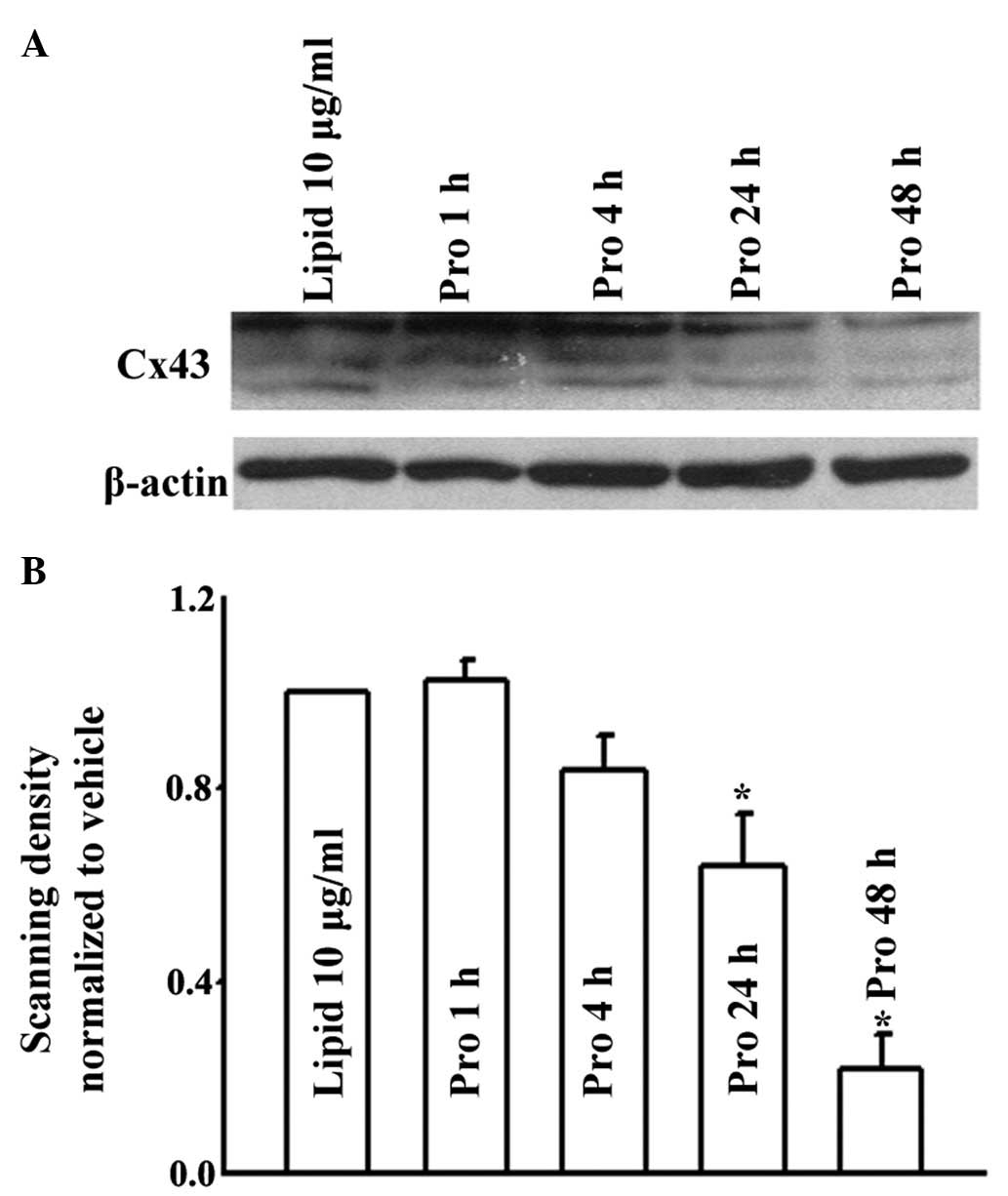
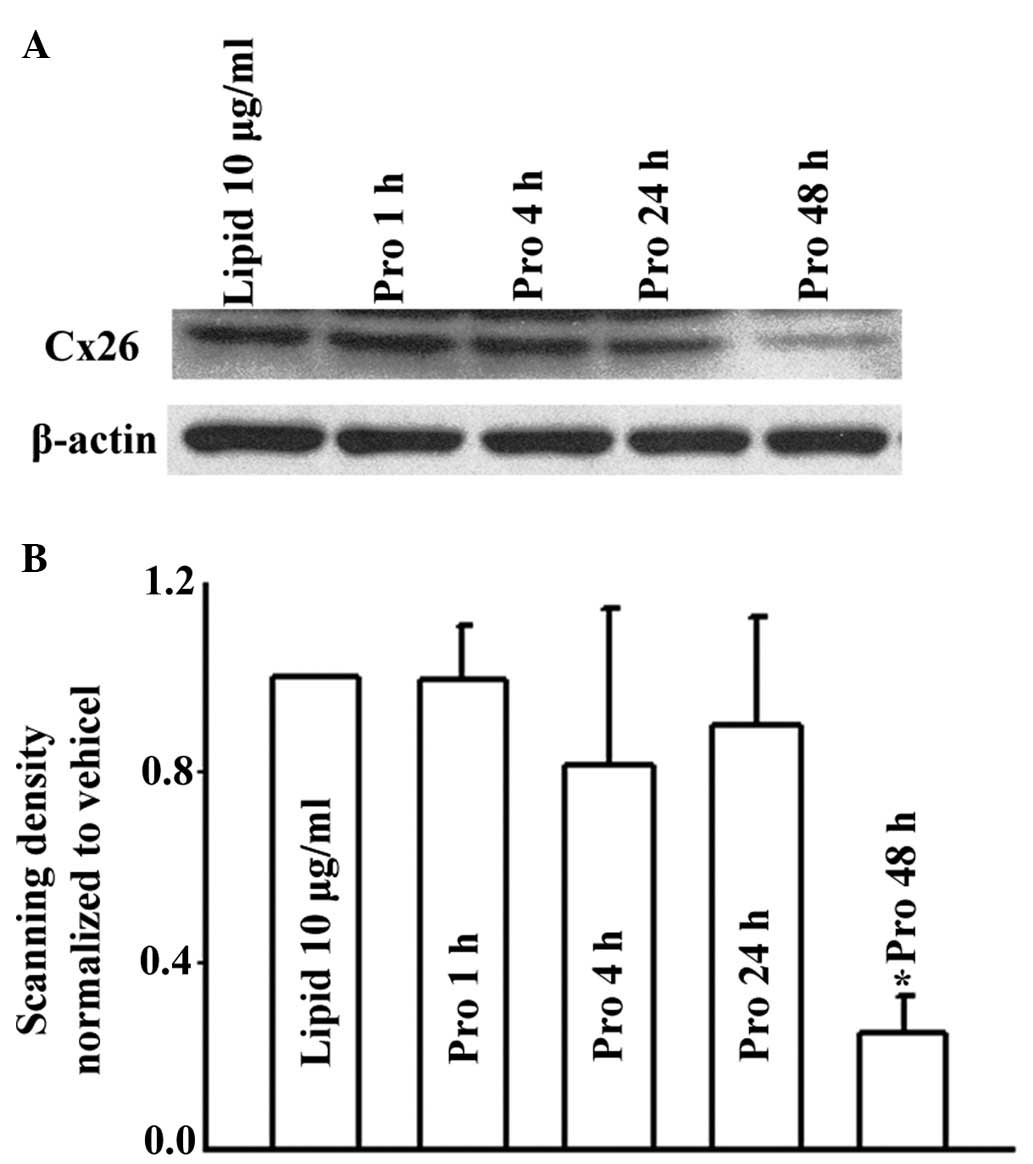
|
1
|
Sosinsky GE and Nicholson BJ: Structural
organization of gap junction channels. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1711:99–125. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Harris AL: Connexin channel permeability
to cytoplasmic molecules. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 94:120–143. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Maeda S and Tsukihara T: Structure of the
gap junction channel and its implications for its biological
functions. Cell Mol Life Sci. 68:1115–1129. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Vinken M, Vanhaecke T, Papeleu P, Snykers
S, Henkens T and Rogiers V: Connexins and their channels in cell
growth and cell death. Cell Signal. 18:592–600. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Cronier L, Crespin S, Strale PO, Defamie N
and Mesnil M: Gap junctions and cancer: New functions for an old
story. Antioxid Redox Signal. 11:323–338. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Kandouz M and Batist G: Gap junctions and
connexins as therapeutic targets in cancer. Expert Opin Ther
Targets. 14:681–692. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Naus CC and Laird DW: Implications and
challenges of connexin connections to cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
10:435–441. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang Q, You T, Yuan D, Han X, Hong X, He
B, Wang L, Tong X, Tao L and Harris AL: Cisplatin and oxaliplatin
inhibit gap junctional communication by direct action and by
reduction of connexin expression, thereby counteracting cytotoxic
efficacy. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 333:903–911. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jensen R and Glazer PM:
Cell-interdependent cisplatin killing by Ku/DNA-dependent protein
kinase signaling transduced through gap junctions. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 101:6134–6139. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Azzam EI, de Toledo SM and Little JB:
Direct evidence for the participation of gap junction-mediated
intercellular communication in the transmission of damage signals
from alpha-particle irradiated to nonirradiated cells. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 98:473–478. 2001.
|
|
11
|
Mesnil M, Piccoli C, Tiraby G, Willecke K
and Yamasaki H: Bystander killing of cancer cells by herpes simplex
virus thymidine kinase gene is mediated by connexins. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 93:1831–1835. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Weiser TG, Regenbogen SE, Thompson KD,
Haynes AB, Lipsitz SR, Berry WR and Gawande AA: An estimation of
the global volume of surgery: A modelling strategy based on
available data. Lancet. 372:139–144. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhu M, Chen J, Yin H, Jiang H, Wen M and
Miao C: Propofol protects human umbilical vein endothelial cells
from cisplatin-induced injury. Vascul Pharmacol. 61:72–79. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Taheri Moghadam G, Hosseini-Zijoud SM,
Heidary Shayesteh T, Ghasemi H and Ranjbar A: Attenuation of
cisplathin-induced toxic oxidative stress by propofol. Anesth Pain
Med. 4:e142212014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Wentlandt K, Carlen PL, Kushnir M, Naus CC
and El-Beheiry H: General anesthetics attenuate gap junction
coupling in P19 cell line. J Neurosci Res. 81:746–752. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Huang F, Li S, Gan X, Wang R and Chen Z:
Propofol inhibits gap junctions by attenuating sevoflurane-induced
cytotoxicity against rat liver cells in vitro. Eur J Anaesthesiol.
31:219–224. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
He B, Tong X, Wang L, Wang Q, Ye H, Liu B,
Hong X, Tao L and Harris AL: Tramadol and flurbiprofen depress the
cytotoxicity of cisplatin via their effects on gap junctions. Clin
Cancer Res. 15:5803–5810. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhao Y, Liu B, Wang Q, Yuan D, Yang Y,
Hong X, Wang X and Tao L: Propofol depresses the cytotoxicity of
X-ray irradiation through inhibition of gap junctions. Anesth
Analg. 112:1088–1095. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Koreen IV, Elsayed WA, Liu YJ and Harris
AL: Tetracycline-regulated expression enables purification and
functional analysis of recombinant connexin channels from mammalian
cells. Biochem J. 383:111–119. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Papazisis KT, Geromichalos GD, Dimitriadis
KA and Kortsaris AH: Optimization of the sulforhodamine B
colori-metric assay. J Immunol Methods. 208:151–158. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Goldberg GS, Bechberger JF and Naus CC: A
pre-loading method of evaluating gap junctional communication by
fluorescent dye transfer. Biotechniques. 18:490–497.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hong X, Wang Q, Yang Y, Zheng S, Tong X,
Zhang S, Tao L and Harris AL: Gap junctions propagate opposite
effects in normal and tumor testicular cells in response to
cisplatin. Cancer Lett. 317:165–171. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
White M and Kenny GN: Intravenous propofol
anaesthesia using a computerised infusion system. Anaesthesia.
45:204–209. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang Y, Wang Q, Zhang S, Zhang Y and Tao
L: Baicalein increases the cytotoxicity of cisplatin by enhancing
gap junction intercellular communication. Mol Med Rep. 10:515–521.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mesnil M, Crespin S, Avanzo JL and
Zaidan-Dagli ML: Defective gap junctional intercellular
communication in the carcinogenic process. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1719:125–145. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Loewenstein WR and Kanno Y: Intercellular
communication and the control of tissue growth: Lack of
communication between cancer cells. Nature. 209:1248–1249. 1966.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Leithe E, Sirnes S, Omori Y and Rivedal E:
Downregulation of gap junctions in cancer cells. Crit Rev Oncog.
12:225–256. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Plante I, Stewart MK, Barr K, Allan AL and
Laird DW: Cx43 suppresses mammary tumor metastasis to the lung in a
Cx43 mutant mouse model of human disease. Oncogene. 30:1681–1692.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Krutovskikh VA, Piccoli C and Yamasaki H:
Gap junction intercellular communication propagates cell death in
cancerous cells. Oncogene. 21:1989–1999. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Czyz J: The stage-specific function of gap
junctions during tumourigenesis. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 13:92–102.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kanczuga-Koda L, Sulkowska M, Koda M,
Rutkowski R and Sulkowski S: Increased expression of gap junction
protein-connexin 32 in lymph node metastases of human ductal breast
cancer. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 45(Suppl 1): S175–S180. 2007.
|
|
32
|
Saito-Katsuragi M, Asada H, Niizeki H,
Katoh F, Masuzawa M, Tsutsumi M, Kuniyasu H, Ito A, Nojima H and
Miyagawa S: Role for connexin 26 in metastasis of human malignant
melanoma: Communication between melanoma and endothelial cells via
connexin 26. Cancer. 110:1162–1172. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tang N, Wang Q, Wu DP, Zhang SZ, Zhang Y
and Tao L: Differential effects of paclitaxel and docetaxel on gap
junctions affects their cytotoxicities in transfected HeLa cells.
Mol Med Rep. 8:638–644. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|