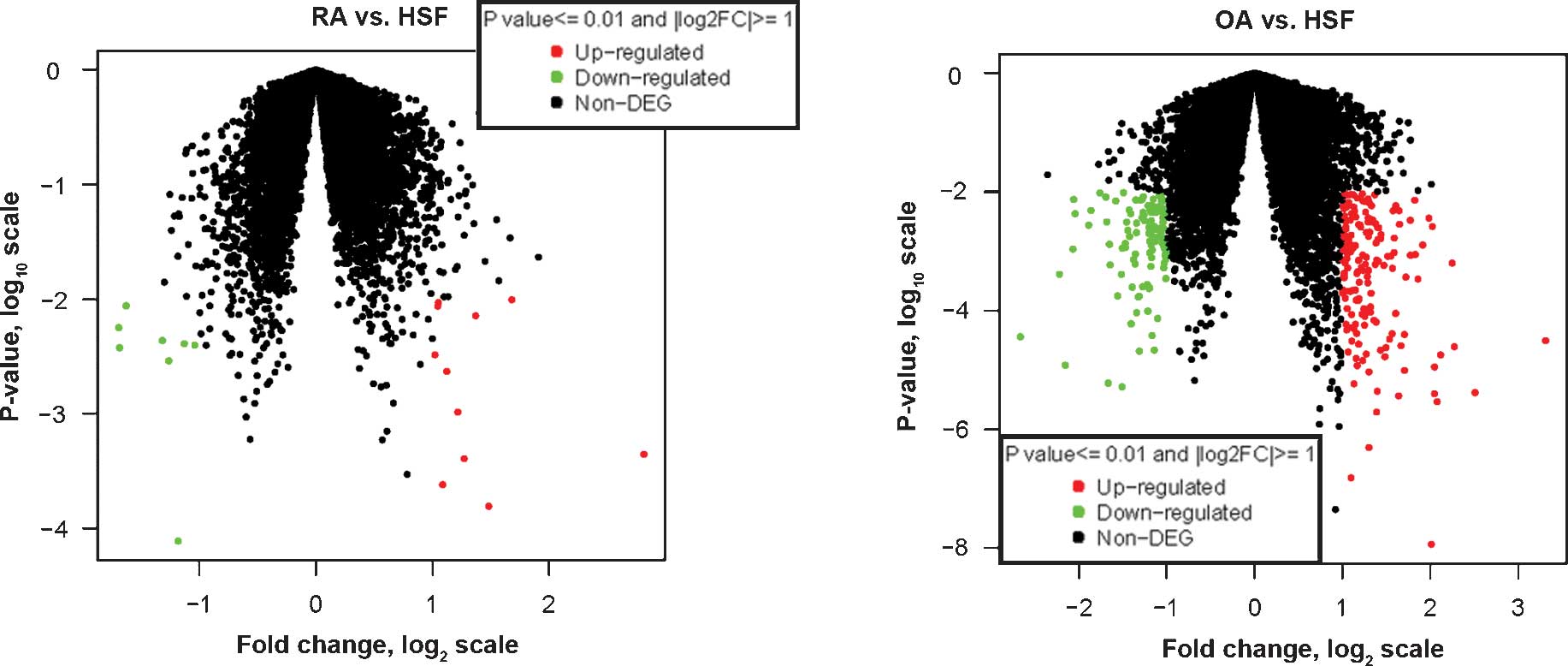
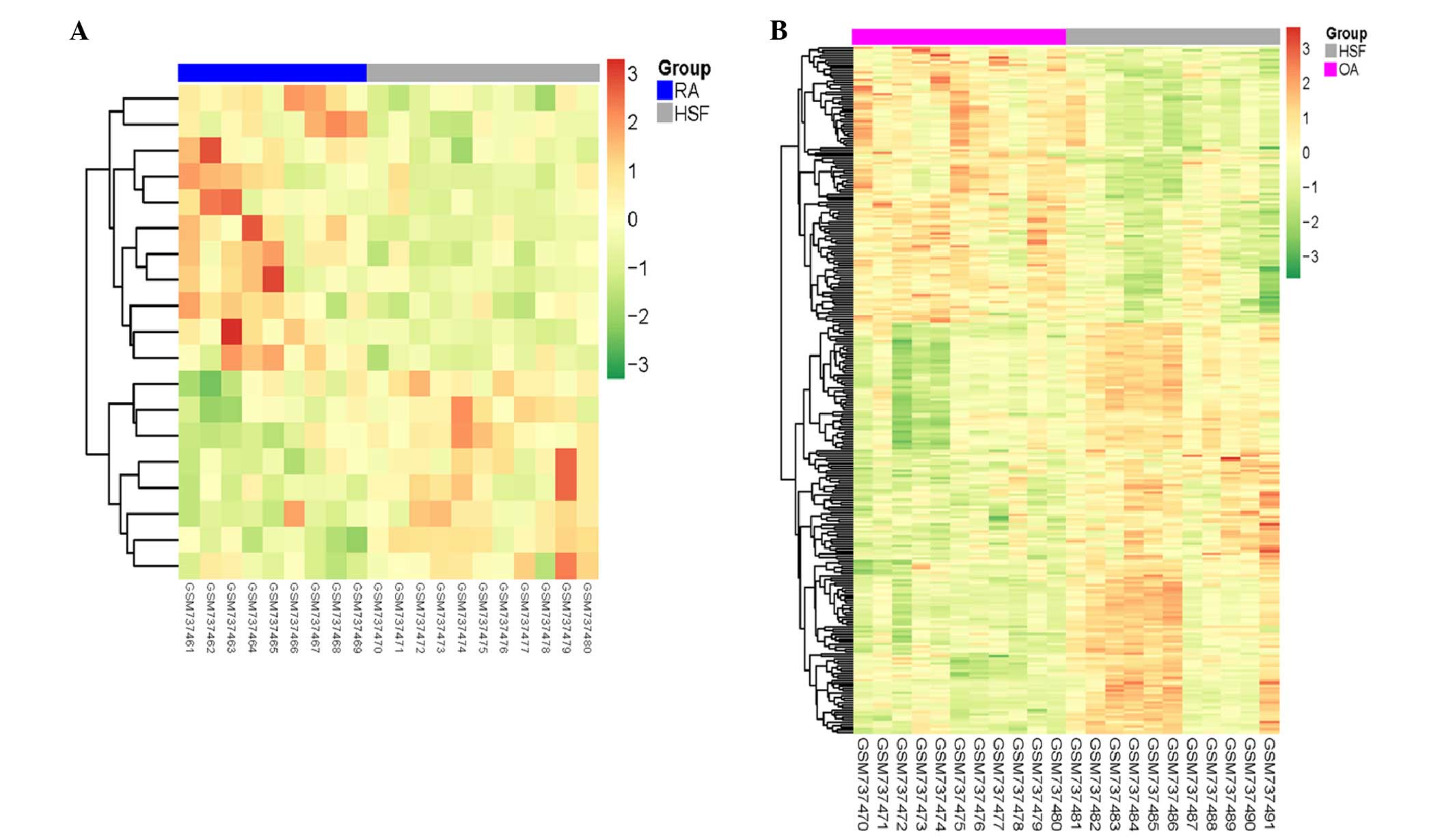
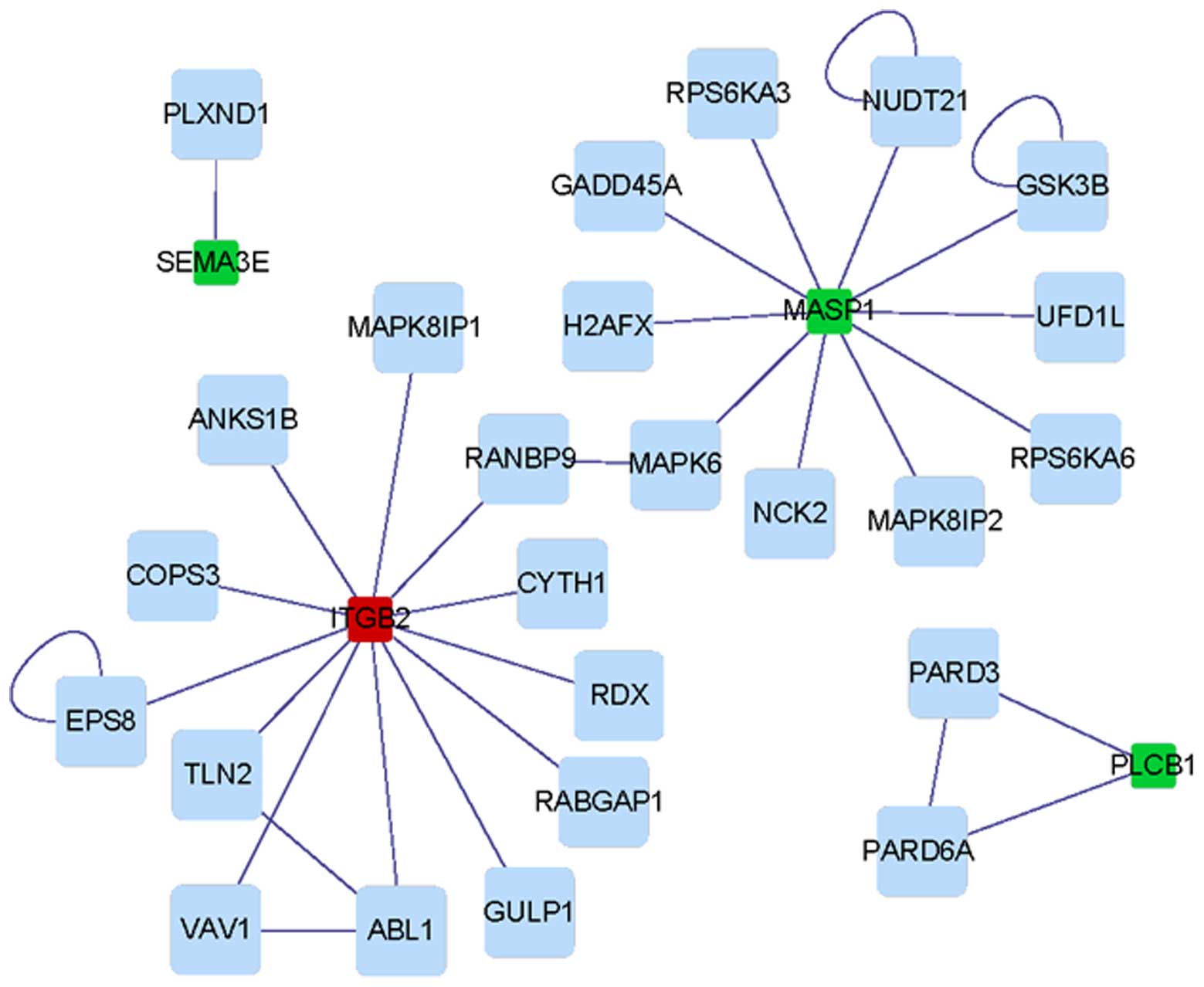
|
1
|
Roivainen A, Söderström KO, Pirilä L, Aro
H, Kortekangas P, Merilahti-Palo R, Yli-Jama T, Toivanen A and
Toivanen P: Oncoprotein expression in human synovial tissue: An
immunohistochemical study of different types of arthritis. Brit J
Rheumatol. 35:933–942. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Pullig O, Weseloh G, Ronneberger D,
Käkönen SM and Swoboda B: Chondrocyte differentiation in human
osteoarthritis: Expression of osteocalcin in normal and
osteoarthritic cartilage and bone. Calcif Tissue Int. 67:230–240.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Drissi H, Zuscik M, Rosier R and O'Keefe
R: Transcriptional regulation of chondrocyte maturation: Potential
involvement of transcription factors in OA pathogenesis. Mol
Aspects Med. 26:169–179. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kwon DR and Park GY: Intra-articular
injections for the treatment of osteoarthritis: Focus on the
clinical use of several regimens. Osteoarthritis-Diagnosis,
Treatment and Surgery. Chen Q: InTech; Rijeka: pp. 67–100. 2012
|
|
5
|
Nakagawa K, Sakiyama H, Tsuchida T,
Yamaguchi K, Toyoguchi T, Masuda R and Moriya H: Complement C1 s
activation in degenerating articular cartilage of rheumatoid
arthritis patients: Immunohistochemical studies with an active form
specific antibody. Ann Rheum Dis. 58:175–181. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen M, Daha MR and Kallenberg CG: The
complement system in systemic autoimmune disease. J Autoimmun.
34:J276–J286. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Bartok B and Firestein GS: Fibroblast-like
synoviocytes: Key effector cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol
Rev. 233:233–255. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Izquierdo E, Cañete JD, Celis R, Del Rey
MJ, Usategui A, Marsal S, Sanmartí R, Criado G and Pablos JL:
Synovial fibroblast hyperplasia in rheumatoid arthritis:
Clinicopathologic correlations and partial reversal by anti-tumor
necrosis factor therapy. Arthritis Rheum. 63:2575–2583. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Stanczyk J, Ospelt C, Karouzakis E, Filer
A, Raza K, Kolling C, Gay R, Buckley CD, Tak PP, Gay S and Kyburz
D: Altered expression of microRNA-203 in rheumatoid arthritis
synovial fibroblasts and its role in fibroblast activation.
Arthritis Rheum. 63:373–381. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Karouzakis E, Gay RE, Gay S and Neidhart
M: Epigenetic control in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts.
Nat Rev Rheumatol. 5:266–272. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Van Baarsen LG, Wijbrandts CA, Timmer TC,
Van Der Pouw Kraan TC, Tak PP and Verweij CL: Synovial tissue
heterogeneity in rheumatoid arthritis in relation to disease
activity and biomarkers in peripheral blood. Arthritis Rheum.
62:1602–1607. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kasperkovitz PV, Timmer TC, Smeets TJ,
Verbeet NL, Tak PP, van Baarsen LG, Baltus B, Huizinga TW,
Pieterman E, Fero M, et al: Fibroblast-like synoviocytes derived
from patients with rheumatoid arthritis show the imprint of
synovial tissue heterogeneity: Evidence of a link between an
increased myofibroblast like phenotype and high-inflammation
synovitis. Arthritis Rheum. 52:430–441. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Del Rey MJ, Usategui A, Izquierdo E,
Cañete JD, Blanco FJ, Criado G and Pablos JL: Transcriptome
analysis reveals specific changes in osteoarthritis synovial
fibroblasts. Ann Rheum Dis. 71:275–280. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Ritchie ME, Silver J, Oshlack A, Holmes M,
Diyagama D, Holloway A and Smyth GK: A comparison of background
correction methods for two-colour microarrays. Bioinformatics.
23:2700–2707. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Smyth GK and Speed T: Normalization of
cDNA microarray data. Methods. 31:265–273. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Smyth GK: Limma: Linear models for
microarray data. Bioinformatics and computational biology solutions
using R and Bioconductor. Gentleman R, Carey VJ, Huber W, Irizarry
RA and Dudoit S: Springer; New York: pp. 397–420. 2005, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Franceschini A, Szklarczyk D, Frankild S,
Kuhn M, Simonovic M, Roth A, Lin J, Minguez P, Bork P, von Mering C
and Jensen LJ: STRING v9. 1: Protein-protein interaction networks,
with increased coverage and integration. Nucleic Acids Res.
41(Database issue): D808–D815. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
19
|
Nepusz T, Yu H and Paccanaro A: Detecting
overlapping protein complexes in protein-protein interaction
networks. Nat Methods. 9:471–472. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
McLaughlin S, Wang J, Gambhir A and Murray
D: PIP(2) and proteins: Interactions, organization, and information
flow. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 31:151–175. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pruzanski W, Keystone EC, Sternby B,
Bombardier C, Snow KM and Vadas P: Serum phospholipase A2
correlates with disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. J
Rheumatol. 15:1351–1355. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lin M, Farewell V, Vadas P, Bookman AA,
Keystone EC and Pruzanski W: Secretory phospholipase A2 as an index
of disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Prospective double
blind study of 212 patients. J Rheumatol. 23:1162–1166.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Vignon E, Balblanc JC, Mathieu P, Louisot
P and Richard M: Metalloprotease activity, phospholipase A2
activity and cytokine concentration in osteoarthritis synovial
fluids. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 1:115–120. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Berg KA, Maayani S and Clarke WP:
Interactions between effectors linked to serotonin receptors. Ann
NY Acad Sci. 861:111–120. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Jang BC, Sung SH, Park JG, Park JW, Bae
JH, Shin DH, Park GY, Han SB and Suh SI: Glucosamine hydrochloride
specifically inhibits COX-2 by preventing COX-2 N-glycosylation and
by increasing COX-2 protein turnover in a proteasome-dependent
manner. J Biol Chem. 282:27622–27632. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rollin R, Marco F, Camafeita E, Calvo E,
López Durán L, Jover J, López JA and Fernández-Gutiérrez B:
Differential proteome of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells from
osteoarthritis patients. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 16:929–935.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li T, Xiao J, Wu Z and Qiu G:
Over-expression of c-maf by chondrocytes in osteoarthritis. J Int
Med Res. 37:129–135. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Maclean HE, Kim JI, Glimcher MJ, Wang J,
Kronenberg HM and Glimcher LH: Absence of transcription factor
c-maf causes abnormal terminal differentiation of hypertrophic
chondrocytes during endochondral bone development. Dev Biol.
262:51–63. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Huang W, Lu N, Eberspaecher H and De
Crombrugghe B: A new long form of c-Maf cooperates with Sox9 to
activate the type II collagen gene. J Biol Chem. 277:50668–50675.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Goeldner I, Skare T, Boldt AB, Nass FR,
Messias-Reason IJ and Utiyama SR: Association of MASP-2 levels and
MASP2 gene polymorphisms with rheumatoid arthritis in patients and
their relatives. PLoS One. 9:e909792014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Rioja I, Clayton CL, Graham SJ, Life PF
and Dickson MC: Gene expression profiles in the rat streptococcal
cell wall-induced arthritis model identified using microarray
analysis. Arthritis Res Ther. 7:R101–R117. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Nikkari L, Aho H, Yli-Jama T, Larjava H,
Jalkanen M and Heino J: Expression of integrin family of cell
adhesion receptors in rheumatoid synovium. Alpha 6 integrin subunit
in normal and hyperplastic synovial lining cell layer. Am J Pathol.
142:1019–1027. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Rinaldi N, Schwarz-Eywill M, Weis D,
Leppelmann-Jansen P, Lukoschek M, Keilholz U and Barth TF:
Increased expression of integrins on fibroblast-like synoviocytes
from rheumatoid arthritis in vitro correlates with enhanced binding
to extracellular matrix proteins. Ann Rheum Dis. 56:45–51. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ishikawa H, Hirata S, Andoh Y, Kubo H,
Nakagawa N, Nishibayashi Y and Mizuno K: An immunohistochemical and
immunoelectron microscopic study of adhesion molecules in synovial
pannus formation in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int. 16:53–60.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Del Rey MJ, Izquierdo E, Usategui A,
Gonzalo E, Blanco FJ, Acquadro F and Pablos JL: The transcriptional
response of normal and rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts to
hypoxia. Arthritis Rheum. 62:3584–3594. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|