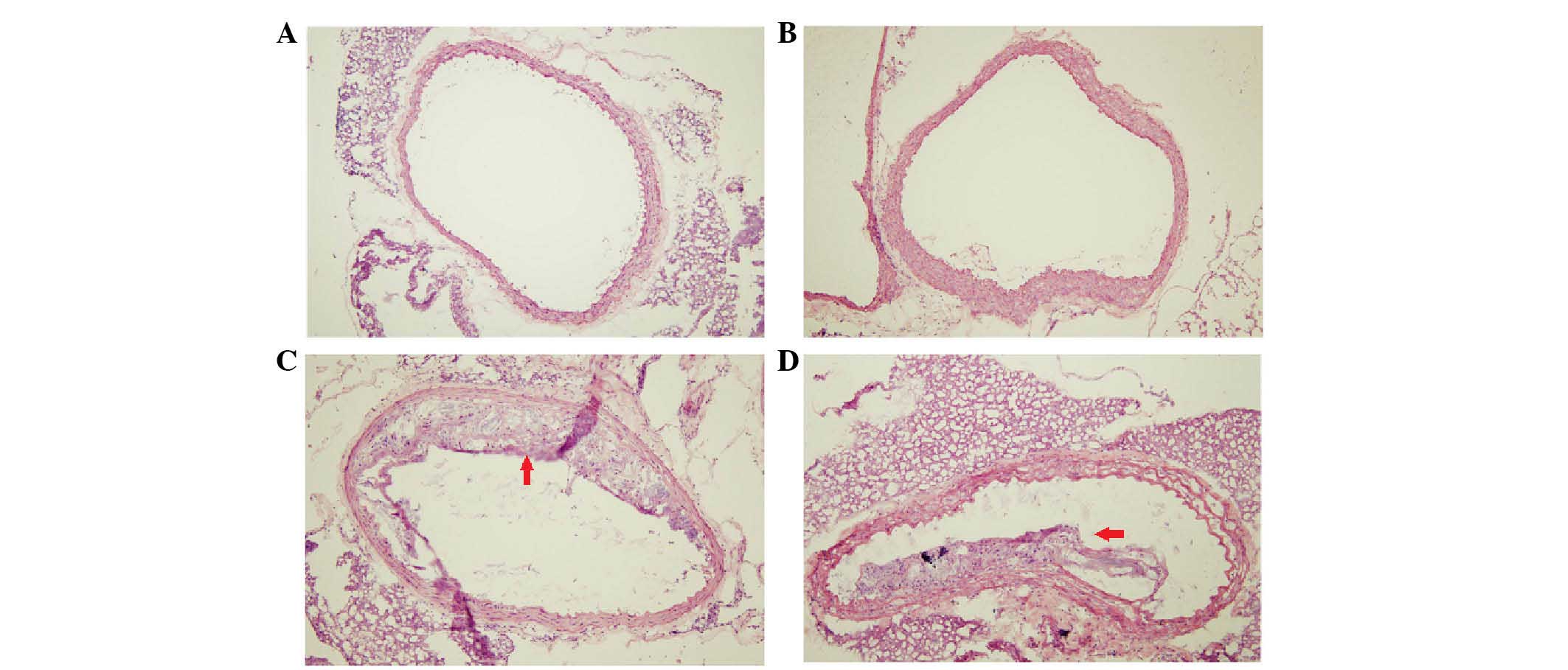
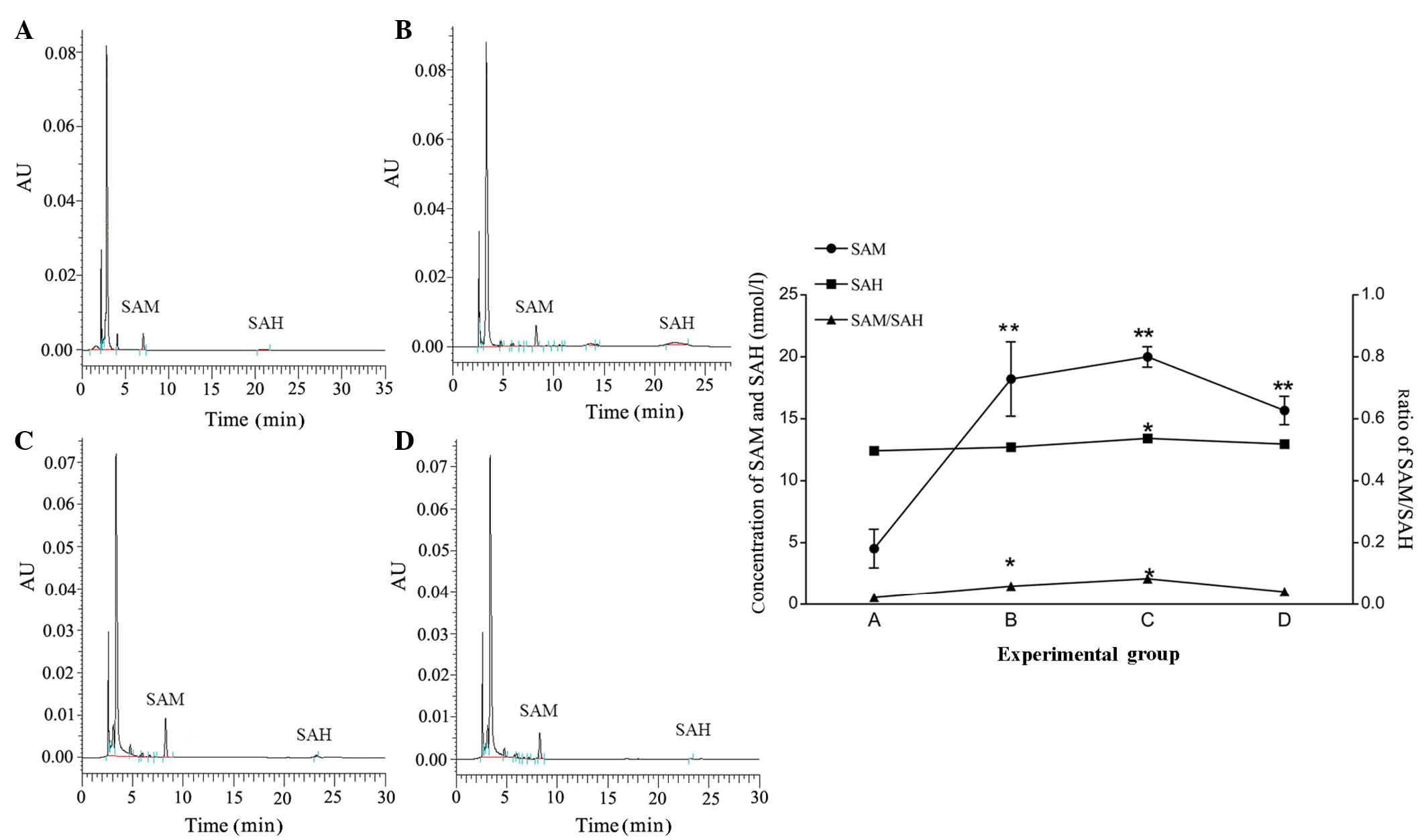
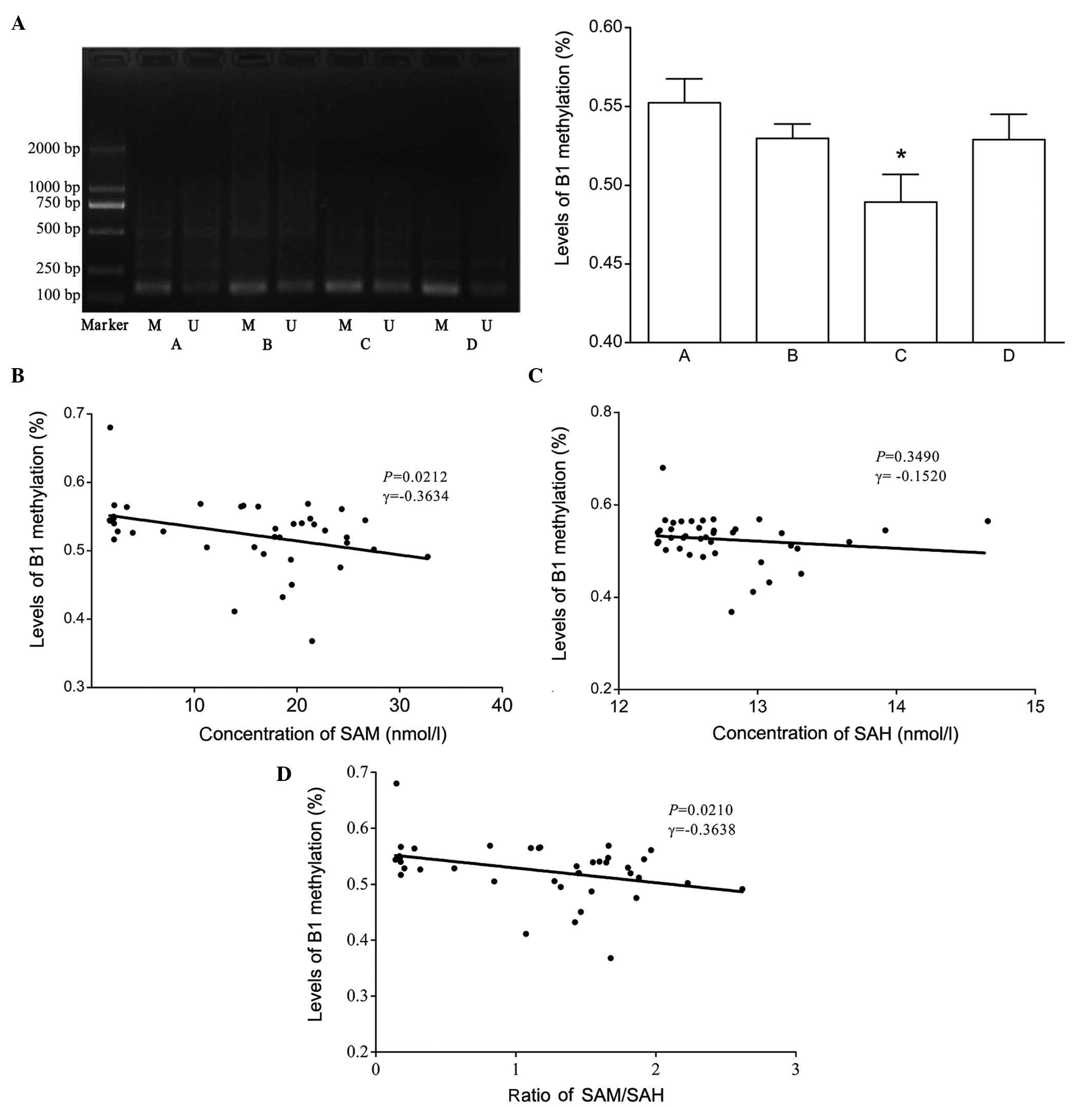
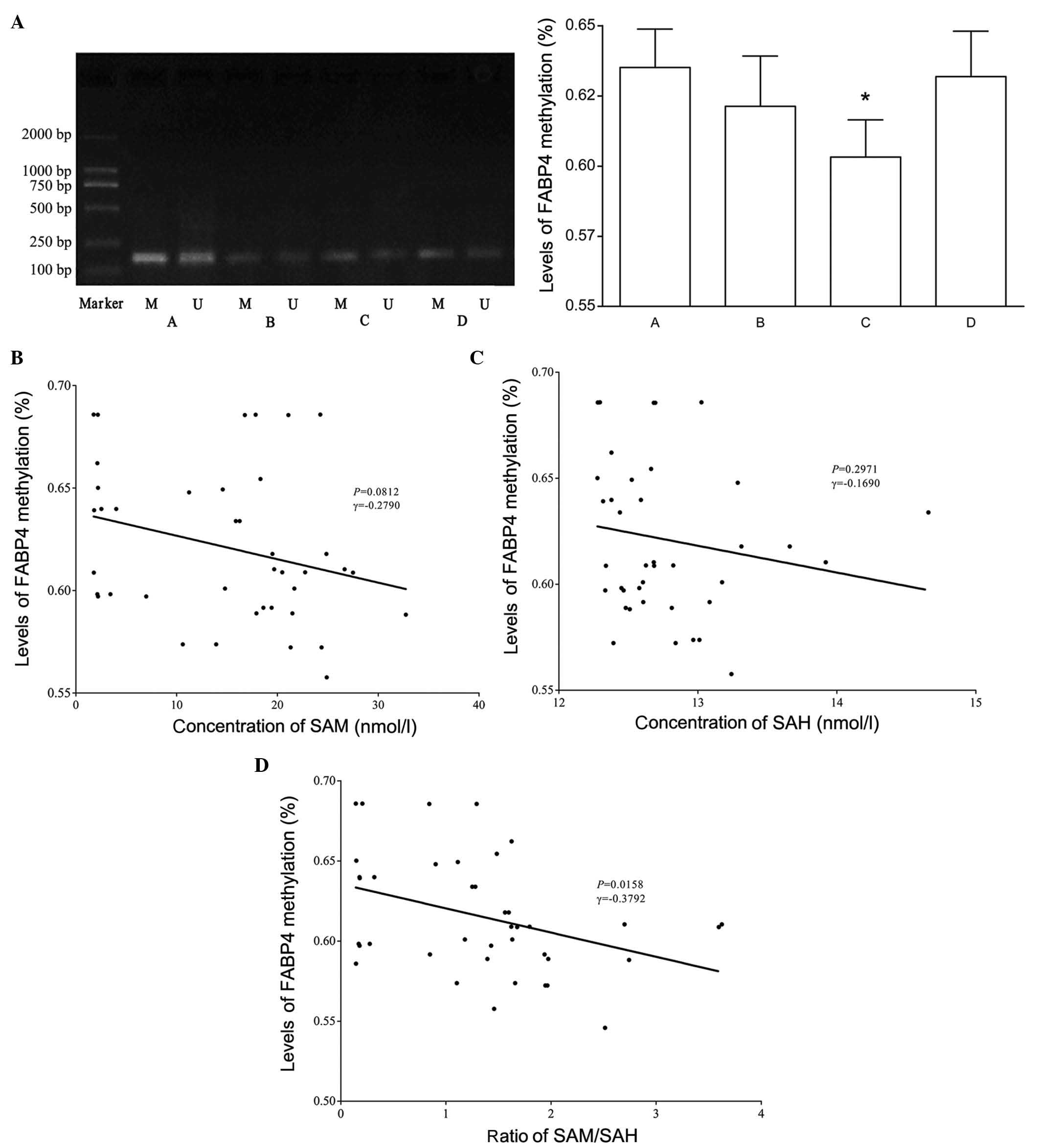
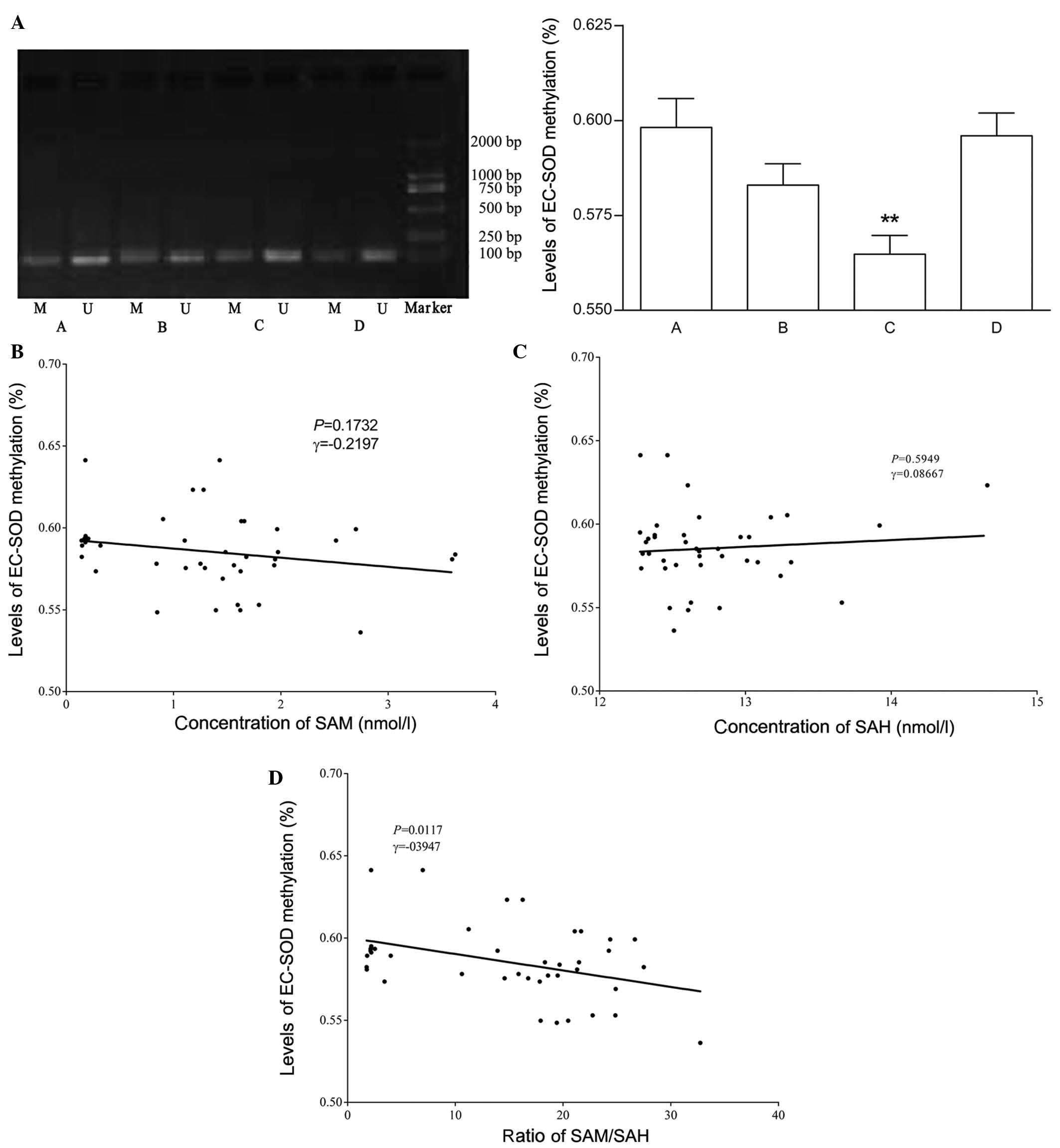
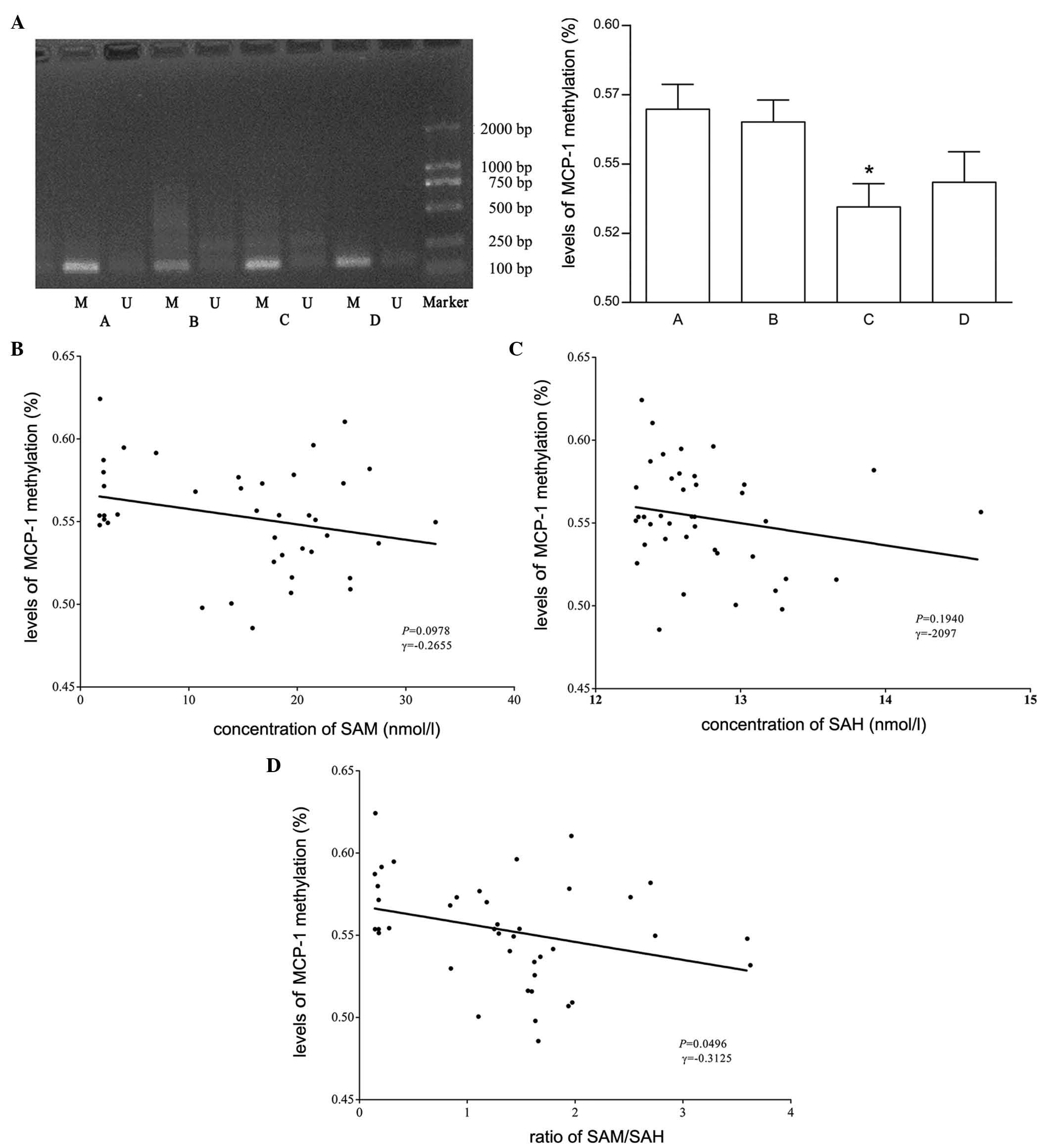
|
1
|
Segers D, Lipton JA, Leenen PJ, Cheng C,
Tempel D, Pasterkamp G, Moll FL, de Crom R and Krams R:
Atherosclerotic plaque stability is affected by the chemokine
CXCL10 in both mice and humans. Int J Inflam. 2011:9361092011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Orbay H, Hong H, Zhang Y and Cai W:
Positron emission tomography imaging of atherosclerosis.
Theranostics. 3:894–902. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ma S, Zhang H, Sun W, Gong H, Wang Y, Ma
C, Wang J, Cao C, Yang X, Tian J and Jiang Y: Hyperhomocysteinemia
induces cardiac injury by up-regulation of p53-dependent Noxa and
Bax expression through the p53 DNA methylation in
ApoE−/− mice. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai).
45:391–400. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Green TJ, Skeaff CM, McMahon JA, Venn BJ,
Williams SM, Devlin AM and Innis SM: Homocysteine-lowering vitamins
do not lower plasma S-adenosylhomocysteine in older people with
elevated homocysteine concentrations. Br J Nutr. 103:1629–1634.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pizzolo F, Blom HJ, Choi SW, Girelli D,
Guarini P, Martinelli N, Stanzial AM, Corrocher R, Olivieri O and
Friso S: Folic acid effects on s-adenosylmethionine,
s-adenosylhomocysteine, and DNA methylation in patients with
intermediate hyperhomocysteinemia. J Am Coll Nutr. 30:11–18. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ma SL, Tang NL and Lam LC: Association of
gene expression and methylation of UQCRC1 to the predisposition of
Alzheimer's disease in a Chinese population. J Psychiatr Res.
76:143–147. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sipkens JA, Hahn NE, Blom HJ, Lougheed SM,
Stehouwer CD, Rauwerda JA, Krijnen PA, van Hinsbergh VW and Niessen
HW: S-Adenosylhomocysteine induces apoptosis and
phosphatidyl-serine exposure in endothelial cells independent of
homocysteine. Atherosclerosis. 221:48–54. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Tehlivets O: Homocysteine as a risk factor
for atherosclerosis: Is its conversion to s-adenosyl-L-homocysteine
the key to deregulated lipid metabolism? J Lipids. 2011:7028532011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kerins DM, Koury MJ, Capdevila A, Rana S
and Wagner C: Plasma S-adenosylhomocysteine is a more sensitive
indicator of cardiovascular disease than plasma homocysteine. Am J
Clin Nutr. 74:723–729. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Loehrer FM, Schwab R, Angst CP, Haefeli WE
and Fowler B: Influence of oral S-adenosyl-methionine on plasma
5-methyl-tetrahydrofolate, S-adenosylhomocysteine, homocysteine and
methionine in healthy humans. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 282:845–850.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Loehrer FM, Haefeli WE, Angst CP, Browne
G, Frick G and Fowler B: Effect of methionine loading on
5-methyltetrahydro-folate, 5-adenosyl-methionine and
S-adenosylhomocysteine in plasma of healthy humans. Clin Sci.
91:79–86. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Loehrer FM, Angst CP, Brunner FP, Haefeli
WE and Fowler B: Evidence for disturbed S-adenosylmethionine:
S-adenosylhomocysteine ratio in patients with end-stage renal
failure: A cause for disturbed methylation reactions? Nephrol Dial
Transplant. 13:656–661. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Meehan RR and Stancheva I: DNA methylation
and control of gene expression in vertebrate development. Essays
Biochem. 37:59–70. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Chen NC, Yang F, Capecci LM, Gu Z, Schafer
AI, Durante W, Yang XF and Wang H: Regulation of homocysteine
metabolism and methylation in human and mouse tissues. FASEB J.
24:2804–2817. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bird A: DNA methylation patterns and
epigenetic memory. Genes Dev. 16:6–21. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fukushige S and Horii A: DNA methylation
in cancer: A gene silencing mechanism and the clinical potential of
its biomarkers. Tohoku J Exp Med. 229:173–185. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lakshmi SV, Naushad SM, Reddy CA, Saumya
K, Rao DS, Kotamraju S and Kutala VK: Oxidative stress in coronary
artery disease: Epigenetic perspective. Mol Cell Biochem.
374:203–211. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Liu ZH, Chen LL, Deng XL, Song HJ, Liao
YF, Zeng TS, Zheng J and Li HQ: Methylation status of CpG sites in
the MCP-1 promoter is correlated to serum MCP-1 in Type 2 diabetes.
J Endocrinol Invest. 35:585–589. 2012.
|
|
19
|
Jiang Y, Zhang H, Sun T, Wang J, Sun W,
Gong H, Yang B, Shi Y and Wei J: The comprehensive effects of
hyperlipidemia and hyperhomocy-steinemia on pathogenesis of
atherosclerosis and DNA hypomethylation in ApoE−/− mice.
Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 44:866–875. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Zulli A, Widdop RE, Hare DL, Buxton BF and
Black MJ: High methionine and cholesterol diet abolishes
endothelial relaxation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
23:1358–1363. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jiang Y, Sun T, Xiong J, Cao J, Li G and
Wang S: Hyperhomo cysteinemia-mediated DNA hypomethylation and its
potential epigenetic role in rats. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin
(Shanghai). 39:657–667. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Hagebeuk EE, Duran M, Abeling NG, Vyth A
and Poll-The BT: S-adenosylmethionine and S-adenosylhomocysteine in
plasma and cerebrospinal fluid in Rett syndrome and the effect of
folinic acid supplementation. J Inherit Metab Dis. 36:967–972.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Agardh HE, Gertow K, Salvado DM,
Hermansson A, van Puijvelde GH, Hansson GK, N-Berne GP and
Gabrielsen A: Fatty acid binding protein 4 in circulating
leucocytes reflects atherosclerotic lesion progression in
Apoe(−/−) mice. J Cell Mol Med. 17:303–310. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Maksimenko AV and Vavaev AV: Antioxidant
enzymes as potential targets in cardioprotection and treatment of
cardiovascular diseases. Enzyme antioxidants: The next stage of
pharmacological counterwork to the oxidative stress. Heart Int.
7:e32012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Linic IS, Sosa I, Kovacevic M, Ivancic A,
Trobonjaca Z, Ledic D, Grubesic A, Dvornik S and Stifter S:
Predicting carotid restenosis by comparison of plaque MCP-1 mRNA
expression and serum levels. Med Hypotheses. 80:26–28. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Ikkruthi S, Rajappa M, Nandeesha H,
Satheesh S, Sundar I, Ananthanarayanan PH and Harichandrakumar KT:
Hyperhomocysteinemia and hyperlipoproteinemia (a) in obese south
indian men: An indication for increased cardiovascular risk. Acta
Physiol Hung. 101:13–20. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Ajith TA and Ranimenon: Homocysteine in
ocular diseases. Clin Chim Acta. 450:316–321. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang Y, Chen S, Yao T, Li D, Wang Y, Li Y,
Wu S and Cai J: Homocysteine as a risk factor for hypertension: A
2-year follow-up study. PLoS One. 9:e1082232014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang D, Wen X, Wu W, Xu E, Zhang Y and
Cui W: Homocysteine-related hTERT DNA demethylation contributes to
shortened leukocyte telomere length in atherosclerosis.
Atherosclerosis. 231:173–179. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Griffiths HR, Aldred S, Dale C, Nakano E,
Kitas GD, Grant MG, Nugent D, Taiwo FA, Li L and Powers HJ:
Homocysteine from endothelial cells promotes LDL nitration and
scavenger receptor uptake. Free Radic Biol Med. 40:488–500. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hagebeuk EE, Duran M, Abeling NG, Vyth A
and Poll-The BT: S-adenosylmethionine and S-adenosylhomocysteine in
plasma and cerebrospinal fluid in Rett syndrome and the effect of
folinic acid supplementation. J Inherit Metab Dis. 36:967–972.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yideng J, Jianzhong Z, Ying H, Juan S,
Jinge Z, Shenglan W, Xiaoqun H and Shuren W: Homocysteine-mediated
expression of SAHH, DNMTs, MBD2, and DNA hypomethylation potential
pathogenic mechanism in VSMCs. DNA Cell Biol. 26:603–611. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yang XL, Tian J, Liang Y, Ma CJ, Yang AN,
Wang J, Ma SC, Cheng Y, Hua X and Jiang YD: Homocysteine induces
blood vessel global hypomethylation mediated by LOX-1. Genet Mol
Res. 13:3787–3799. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Enneman AW, van der Velde N, de Jonge R,
Heil SG, Stolk L, Hofman A, Rivadeneira F, Zillikens MC,
Uitterlinden AG and van Meurs JB: The association between plasma
homocysteine levels, methylation capacity and incident osteoporotic
fractures. Bone. 50:1401–1405. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Maegawa S, Hinkal G, Kim HS, Shen L, Zhang
L, Zhang J, Zhang N, Liang S, Donehower LA and Issa JP: Widespread
and tissue specific age-related DNA methylation changes in mice.
Genome Res. 20:332–340. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Holm S, Ueland T, Dahl TB, Michelsen AE,
Skjelland M, Russell D, Nymo SH, Krohg-Sørensen K, Clausen OP, Atar
D, et al: Fatty acid binding protein 4 is associated with carotid
atherosclerosis and outcome in patients with acute ischemic stroke.
PLoS One. 6:e287852011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Orekhov AN, Sobenin IA, Gavrilin MA,
Gratchev A, Kotyashova SY, Nikiforov NG and Kzhyshkowska J:
Macrophages in immunopathology of atherosclerosis: A target for
diagnostics and therapy. Curr Pharm Des. 21:1172–1179. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
38
|
Shepard CW and Steinberger J: Premature
atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in childhood cancer
survivors. Prog Pediatr Cardiol. 39:59–66. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Cash HL, McGarvey ST, Houseman EA, Marsit
CJ, Hawley NL, Lambert-Messerlian GM, Viali S, Tuitele J and Kelsey
KT: Cardiovascular disease risk factors and DNA methylation at the
LINE-1 repeat region in peripheral blood from Samoan Islanders.
Epigenetics. 6:1257–1264. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Connelly JJ, Cherepanova OA, Doss JF,
Karaoli T, Lillard TS, Markunas CA, Nelson S, Wang T, Ellis PD,
Langford CF, et al: Epigenetic regulation of COL15A1 in smooth
muscle cell replicative aging and atherosclerosis. Hum Mol Genet.
22:5107–5120. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Terra X, Quintero Y, Auguet T, Porras JA,
Hernández M, Sabench F, Aguilar C, Luna AM, Del Castillo D and
Richart C: FABP 4 is associated with inflammatory markers and
metabolic syndrome in morbidly obese women. Eur J Endocrinol.
164:539–547. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lisanti S, Omar WA, Tomaszewski B, De
Prins S, Jacobs G, Koppen G, Mathers JC and Langie SA: Comparison
of methods for quantification of global DNA methylation in human
cells and tissues. PLoS One. 8:e790442013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
Wagner C and Koury MJ:
S-Adenosylhomocysteine: A better indicator of vascular disease than
homocysteine? Am J Clin Nutr. 86:1581–1595. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Girona J, Rosales R, Plana N, Saavedra P,
Masana L and Vallvé JC: FABP4 induces vascular smooth muscle cell
proliferation and migration through a MAPK-dependent pathway. PLoS
One. 8:e819142013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yang AN, Zhang HP, Sun Y, Yang XL, Wang N,
Zhu G, Zhang H, Xu H, Ma SC, Zhang Y, et al: High-methionine diets
accelerate atherosclerosis by HHcy-mediated FABP4 gene
demethylation pathway via DNMT1 in ApoE(−/−) mice. FEBS Lett.
589:3998–4009. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Laukkanen MO, Kivelä A, Rissanen T,
Rutanen J, Karkkainen MK, Leppanen O, Bräsen JH and Yla-Herttuala
S: Adenovirus-mediated extracellular superoxide dismutase gene
therapy reduces neointima formation in balloon-denuded rabbit
aorta. Circulation. 106:1999–2003. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Giovannone R, Busetto GM, Antonini G, De
Cobelli O, Ferro M, Tricarico S, Del Giudice F, Ragonesi G, Conti
SL, Lucarelli G, et al: Hyperhomocysteinemia as an early predictor
of erectile dysfunction: International Index of Erectile Function
(IIEF) and penile doppler ultrasound correlation with plasma levels
of homocysteine. Medicine (Baltimore). 94:e15562015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Kim SJ, Choe YH and Bang OY;
Chaos-Biomarker Collaborators: Are stroke biomarkers seeing brain
vessels in patients with ischemic stroke?: A C-reactive protein and
homocysteine study. Stroke. 42:1464–1468. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Cummings DM, King DE, Mainous AG and
Geesey ME: Combining serum biomarkers: The association of
C-reactive protein, insulin sensitivity, and homocysteine with
cardiovascular disease history in the general US population. Eur J
Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil. 13:180–185. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Liu C, Wang Q, Guo H, Xia M, Yuan Q, Hu Y,
Zhu H, Hou M, Ma J, Tang Z and Ling W: Plasma
S-adenosylhomocysteine is a better biomarker of atherosclerosis
than homocysteine in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice fed high
dietary methionine. J Nutr. 138:311–315. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Han XB, Zhang HP, Cao CJ, Wang YH, Tian J,
Yang XL, Yang AN, Wang J, Jiang YD and Xu H: Aberrant DNA
methylation of the PDGF gene in homocysteine-mediated VSMC
proliferation and its underlying mechanism. Mol Med Rep.
10:947–954. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Perng W, Villamor E, Shroff MR, Nettleton
JA, Pilsner JR, Liu Y and Diez-Roux AV: Dietary intake, plasma
homocysteine, and repetitive element DNA methylation in the
Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA). Nutr Metab Cardiovasc
Dis. 24:614–622. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zhao J, Forsberg CW, Goldberg J, Smith NL
and Vaccarino V: MAOA promoter methylation and susceptibility to
carotid atherosclerosis: Role of familial factors in a monozygotic
twin sample. BMC Med Genet. 13:1002012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wilson AS, Power BE and Molloy PL: DNA
hypomethylation and human diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1775:138–162. 2007.
|