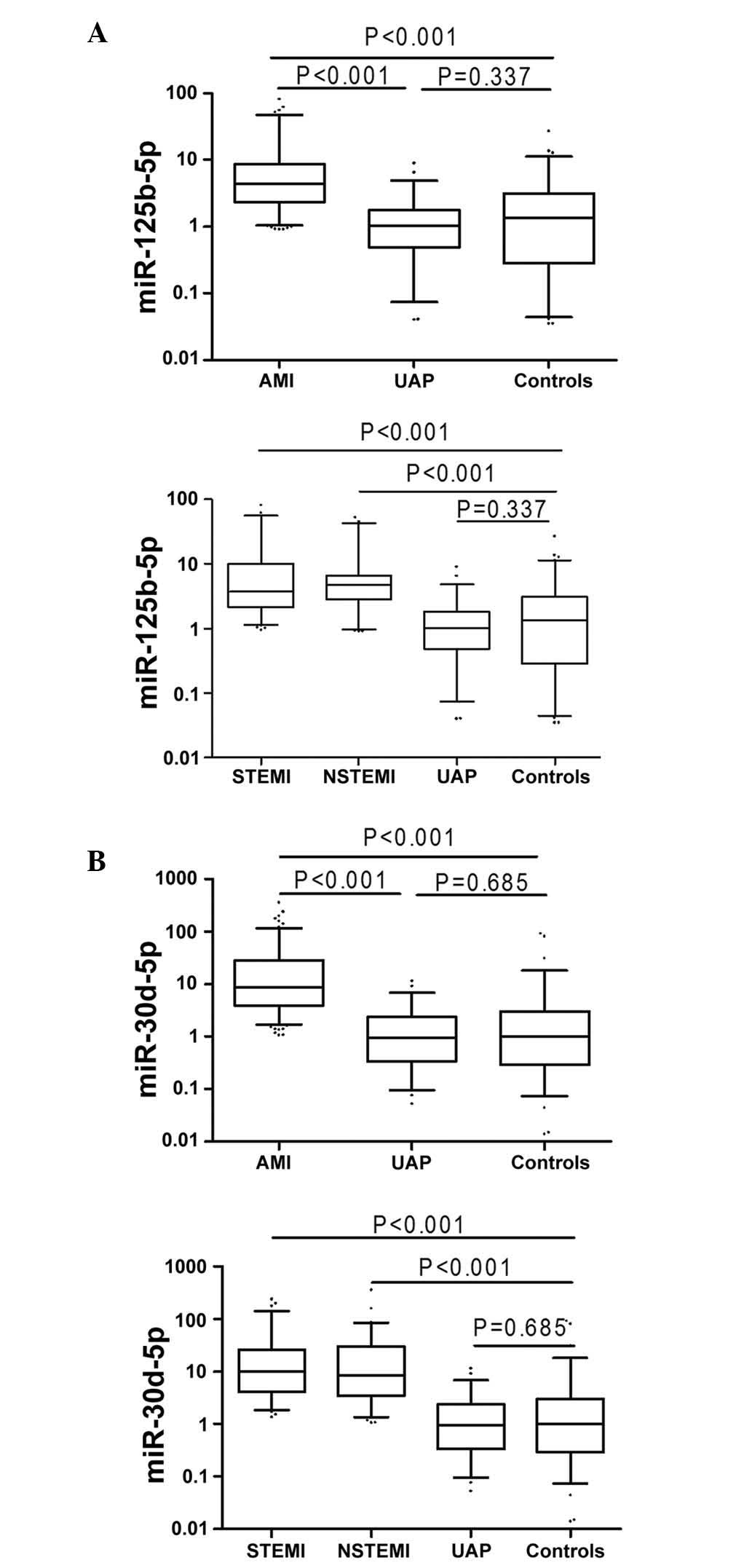
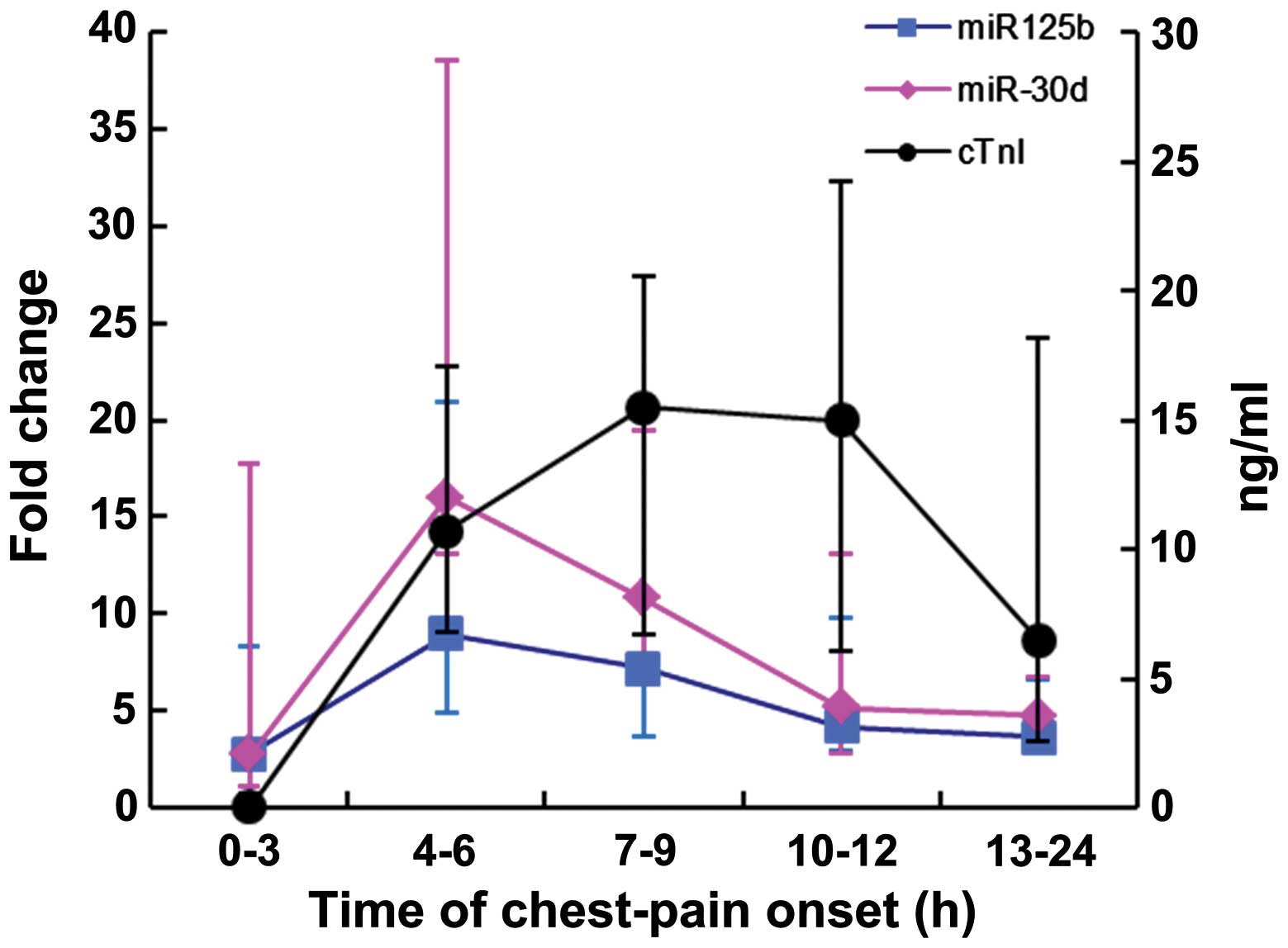
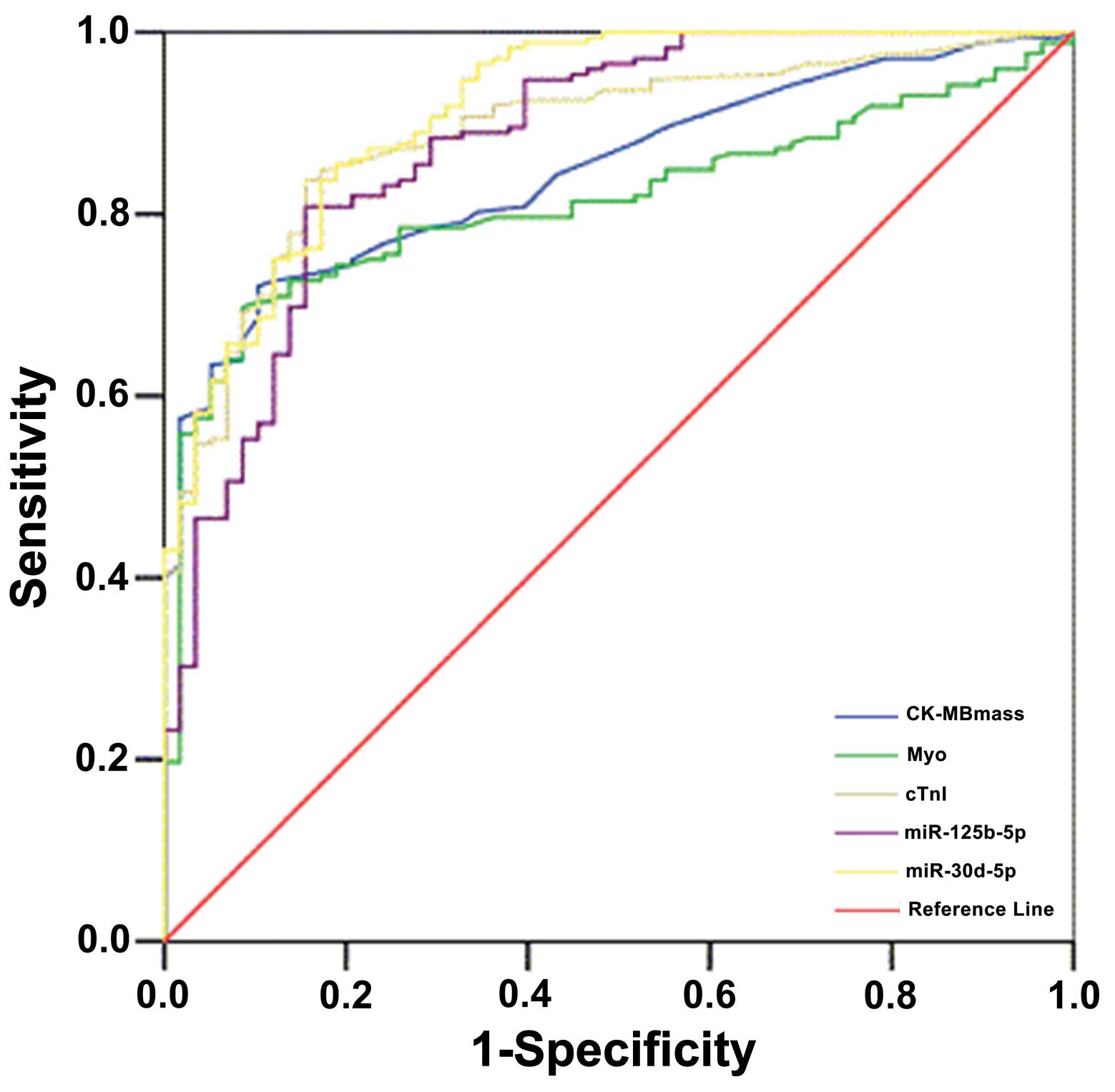
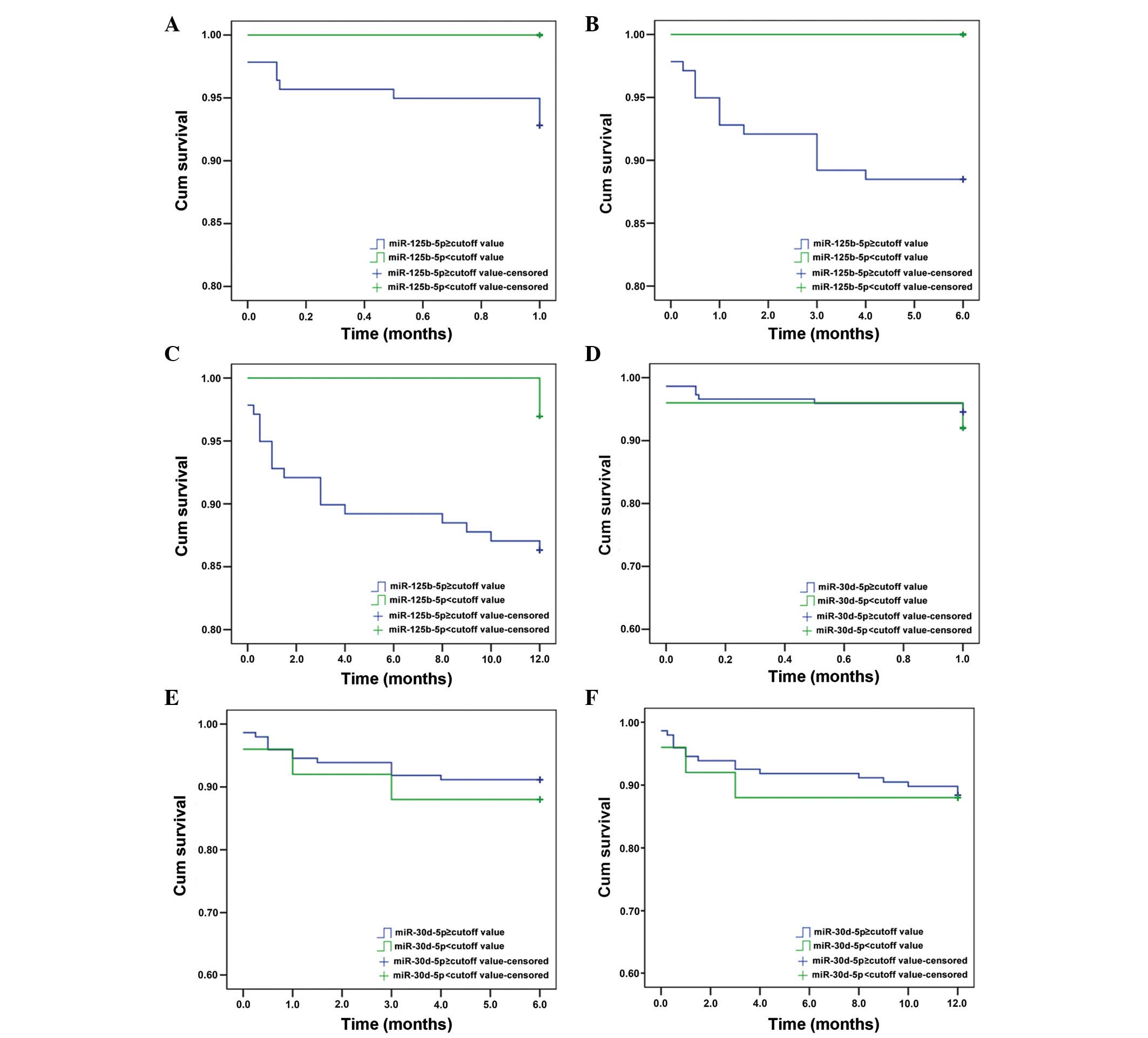
|
1
|
Kumar A and Cannon CP: Acute coronary
syndromes: Diagnosis and management, part I. Mayo Clin Proc.
84:917–938. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Anderson JL, Adams CD, Antman EM, Bridges
CR, Califf RM, Casey DE Jr, Chavey WE 2nd, Fesmire FM, Hochman JS,
Levin TN, et al: ACC/AHA 2007 guidelines for the management of
patients with unstable angina/non-ST-Elevation myocardial
infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 50:e1–e157. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Jneid H, Anderson JL, Wright RS, Adams CD,
Bridges CR, Casey DE Jr, Ettinger SM, Fesmire FM, Ganiats TG,
Lincoff AM, et al: 2012 ACCF/AHA focused update of the guideline
for the management of patients with unstable
angina/Non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction (updating the 2007
guideline and replacing the 2011 focused update. Circulation.
126:875–910. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Amsterdam EA, Wenger NK, Brindis RG, Casey
DE Jr, Ganiats G, Holmes DR Jr, Jaffe AS, Jneid H, Kelly RF, Kontos
MC, et al: 2014 AHA/ACC guideline for the management of patients
with non-ST-elevation acute coronary syndromes. J Am Coll Cardiol.
64:e139–228. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Braunwald E: Unstable angina and non-ST
elevation myocardial infarction. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
185:924–932. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
White HD and Chew DP: Acute myocardial
infarction. Lancet. 372:570–584. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chieffo A, Buchanan GL, Mauri F, Mehilli
J, Vaquerizo B, Moynagh A, Mehran R and Morice MC: ACS and STEMI
treatment: Gender-related issues. EuroIntervention. 8(Suppl P):
P27–P35. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bellbhudder U and Stanfliet JC: Clinicians
ignore best practice guidelines: Prospective audit of cardiac
injury marker ordering in patients with chest pain. S Afr Med J.
104:305–306. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ozturk G, Tavil B, Ozguner M, Ginis Z,
Erden G, Tunc B, Azik MF, Uckan D and Delibas N: Evaluation of
Cardiac Markers in Children Undergoing Hematopoietic Stem Cell
Transplantation. J Clin Lab Anal. 29:259–262. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Jaffe AS, Ravkilde J, Roberts R, Naslund
U, Apple FS, Galvani M and Katus H: It's time for a change to a
troponin standard. Circulation. 102:1216–1220. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Omland T, de Lemos JA, Sabatine MS,
Christophi CA, Rice MM, Jablonski KA, Tjora S, Domanski MJ, Gersh
BJ, Rouleau JL, et al: Prevention of Events with Angiotensin
Converting Enzyme Inhibition (PEACE) Trial Investigators: A
sensitive cardiac troponin T assay in stable coronary artery
disease. N Engl J Med. 361:2538–2547. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Devaux Y, Vausort M, Goretti E, Nazarov
PV, Azuaje F, Gilson G, Corsten MF, Schroen B, Lair ML, Heymans S
and Wagner DR: Use of circulating microRNAs to diagnose acute
myocardial infarction. Clin Chem. 58:559–567. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Keller T, Zeller T, Peetz D, Tzikas S,
Roth A, Czyz E, Bickel C, Baldus S, Warnholtz A, Fröhlich M, et al:
Sensitive troponin I assay in early diagnosis of acute myocardial
infarction. N Engl J Med. 361:868–877. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang GK, Zhu JQ, Zhang JT, Li Q, Li Y, He
J, Qin YW and Jing Q: Circulating microRNA: A novel potential
biomarker for early diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction in
humans. Eur Heart J. 31:659–666. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hsu A, Chen SJ, Chang YS, Chen HC and Chu
PH: Systemic approach to identify serum microRNAs as potential
biomarkers for acute myocardial infarction. BioMed Res Int.
2014:4186282014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Peng L, Chun-guang Q, Bei-fang L, Xue-zhi
D, Zi-hao W, Yun-fu L, Yan-ping D, Yang-gui L, Wei-guo L, Tian-yong
H and Zhen-wen H: Clinical impact of circulating miR-133, miR-1291
and miR-663b in plasma of patients with acute myocardial
infarction. Diagn Pathol. 9:892014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hunter MP, Ismail N, Zhang X, Aguda BD,
Lee EJ, Yu L, Xiao T, Schafer J, Lee ML, Schmittgen TD, et al:
Detection of microRNA expression in human peripheral blood
microvesicles. PLoS One. 3:e36942008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hu SJ, Ren G, Liu JL, Zhao ZA, Yu YS, Su
RW, Ma XH, Ni H, Lei W and Yang ZM: MicroRNA expression and
regulation in mouse uterus during embryo implantation. J Biol Chem.
283:23473–23484. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dweep H and Gretz N: miRWalk2.0: A
comprehensive atlas of microRNA-target interactions. Nat Methods.
12:6972015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fichtlscherer S1, De Rosa S, Fox H,
Schwietz T, Fischer A, Liebetrau C, Weber M, Hamm CW, Röxe T and
Müller-Ardogan M: et al Circulating microRNAs in patients with
coronary artery disease. Circ Res. 107:677–684. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kroh EM, Parkin RK, Mitchell PS and Tewari
M: Analysis of circulating microRNA biomarkers in plasma and serum
using quantitative reverse transcription-PCR (qRT-PCR). Methods.
50:298–301. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Meder B, Keller A, Vogel B, Haas J,
Sedaghat-Hamedani F, Kayvanpour E, Just S, Borries A, Rudloff J,
Leidinger P, et al: MicroRNA signatures in total peripheral blood
as novel biomarkers for acute myocardial infarction. Basic Res
Cardiol. 106:13–23. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Bostjancic E, Zidar N and Glavac D:
MicroRNA microarray expression profiling in human myocardial
infarction. Dis Markers. 27:255–268. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Iguchi H, Kosaka N and Ochiya T: Secretory
microRNAs as a versatile communication tool. Commun Integr Biol.
3:478–481. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zampetaki A, Willeit P, Drozdov I, Kiechl
S and Mayr M: Profiling of circulating microRNAs: From single
biomarkers to re-wired networks. Cardiovasc Res. 93:555–562. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
27
|
Gidlöf O, Andersson P, van der Pals J,
Götberg M and Erlinge D: Cardiospecific microRNA plasma levels
correlate with troponin and cardiac function in patients with ST
elevation myocardial infarction, are selectively dependent on renal
elimination, and can be detected in urine samples. Cardiology.
118:217–226. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Valadi H, Ekström K, Bossios A, Sjöstrand
M, Lee JJ and Lötvall JO: Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and
microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells.
Nat Cell Biol. 9:654–659. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zernecke A, Bidzhekov K, Noels H,
Shagdarsuren E, Gan L, Denecke B, Hristov M, Köppel T, Jahantigh
MN, Lutgens E, et al: Delivery of microRNA-126 by apoptotic bodies
induces CXCL12-dependent vascular protection. Sci Signal.
2:ra812009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|