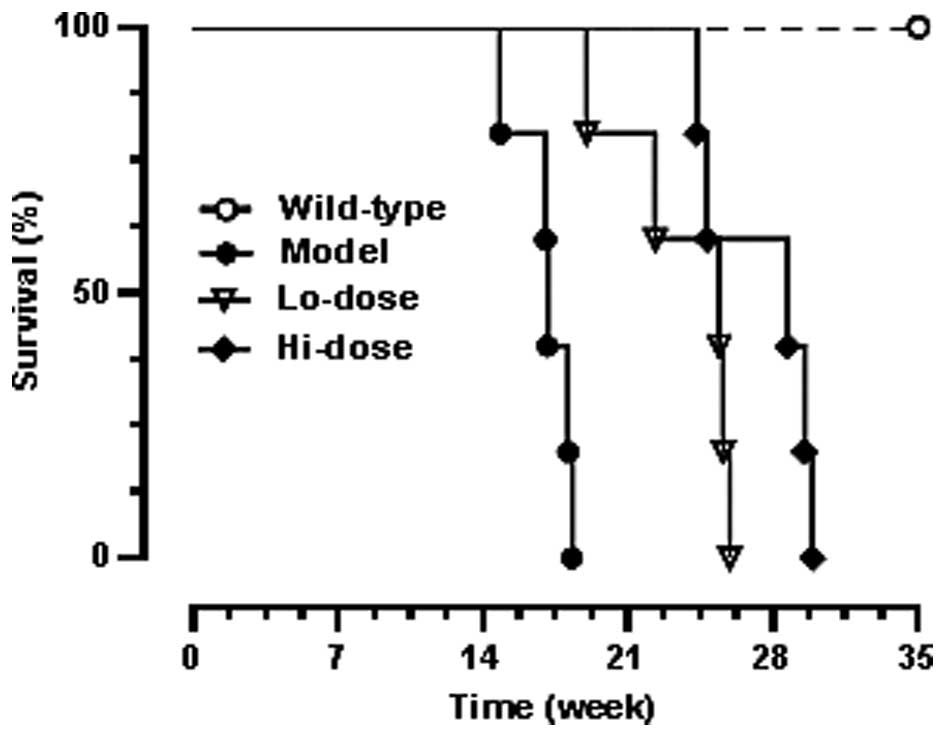
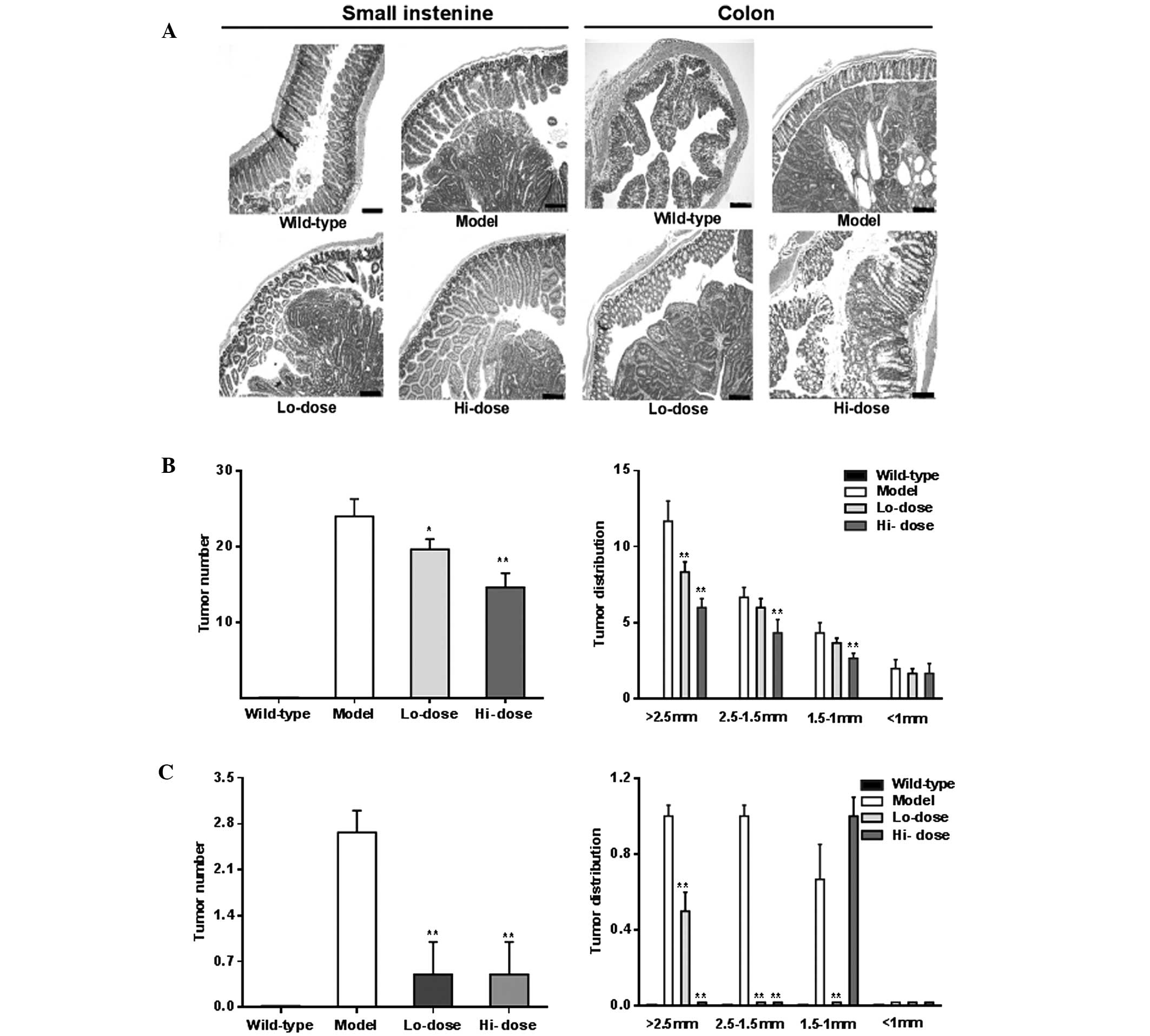
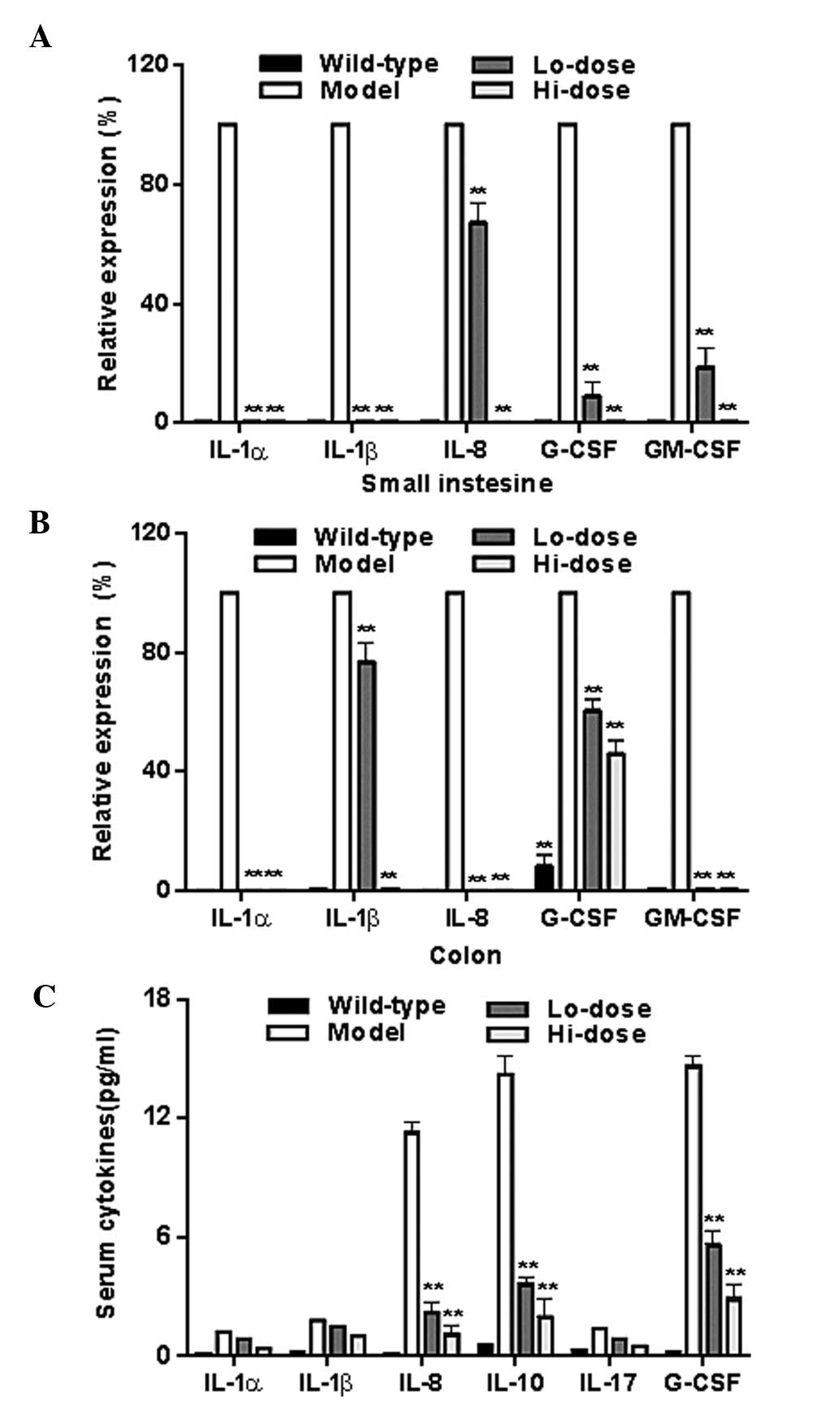
|
1
|
Siegel R, Desantis C and Jemal A:
Colorectal cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:104–117. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
McCarthy N: Tumorigenesis: All together
now. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:148–149. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Madka V and Rao CV: Anti-inflammatory
phytochemicals for chemoprevention of colon cancer. Curr Cancer
Drug Targets. 13:542–557. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Moreno-Jimenez MR, Trujillo-Esquivel F,
Gallegos-Corona MA, Reynoso-Camacho R, González-Laredo RF,
Gallegos-Infante JA, Rocha-Guzmán NE and Ramos-Gomez M:
Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anticarcinogenic activities of
edible red oak (Quercus spp.) infusions in rat colon carcinogenesis
induced by 1,2-dimethylhydrazine. Food Chem Toxicol. 80:144–153.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yu C, Wen XD, Zhang Z, Zhang CF, Wu XH,
Martin A, Du W, He TC, Wang CZ and Yuan CS: American ginseng
attenuates azoxymethane/dextran sodium sulfate-induced colon
carcinogenesis in mice. J Ginseng Res. 39:14–21. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Saleem M: Lupeol, a novel
anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer dietary triterpene. Cancer Lett.
285:109–115. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang X, Song ZJ, He X, Zhang RQ, Zhang CF,
Li F, Wang CZ and Yuan CS: Antitumor and immunomodulatory activity
of genkwanin on colorectal cancer in the APC(Min/+) mice. Int
Immunopharmacol. 29:701–707. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission:
Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China (Part 1) China.
Medical Science Press; Beijing: 2010
|
|
9
|
Bhadra K and Kumar GS: Therapeutic
potential of nucleic acid-binding isoquinoline alkaloids: Binding
aspects and implications for drug design. Med Res Rev. 31:821–862.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Zhang L, Li J, Ma F, Yao S, Li N, Wang J,
Wang Y, Wang X and Yao Q: Synthesis and cytotoxicity evaluation of
13-n-alkyl berberine and palmatine analogues as anticancer agents.
Molecules. 17:11294–11302. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jung J, Choi JS and Jeong CS: Inhibitory
activities of palmatine from coptis chinensis against helicobactor
pylori and gastric damage. Toxicol Res. 30:45–48. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang CZ, Du GJ, Zhang Z, Wen XD, Calway T,
Zhen Z, Musch MW, Bissonnette M, Chang EB and Yuan CS: Ginsenoside
compound K, not Rb1, possesses potential chemo-preventive
activities in human colorectal cancer. Int J Oncol. 40:1970–1976.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang CZ, Zhang Z, Huang WH, Du GJ, Wen XD,
Calway T, Yu C, Nass R, Zhao J, Du W, et al: Identification of
potential anticancer compounds from Oplopanax horridus.
Phytomedicine. 20:999–1006. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fichera A, Guo Y, Romero L, Michelassi F
and Arenas RB: Quantitation of in vivo gene delivery by restriction
enzyme PCR generated polymorphism. J Surg Res. 69:188–192. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mohammed A, Janakiram NB, Li Q, Choi CI,
Zhang Y, Steele VE and Rao CV: Chemoprevention of colon and small
intestinal tumorigenesis in APC (Min/+) mice by licofelone, a novel
dual 5-LOX/COX inhibitor: Potential implications for human colon
cancer prevention. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 4:2015–2026. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Dougherty U, Mustafi R, Wang Y, Musch MW,
Wang CZ, Konda VJ, Kulkarni A, Hart J, Dawson G, Kim KE, et al:
American ginseng suppresses Western diet-promoted tumorigenesis in
model of inflammation-associated colon cancer: Role of EGFR. BMC
Complement Altern Med. 11:1112011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Van der Meer R, Lapré JA, Govers MJAP and
Kleibeuker JH: Mechanisms of the intestinal effects of dietary fats
and milk products on colon carcinogenesis. Cancer Lett. 114:75–83.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jung HA, Yoon NY, Bae HJ, Min BS and Choi
JS: Inhibitory activities of the alkaloids from Coptidis Rhizoma
against aldose reductase. Arch Pharm Res. 31:1405–1412. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang Z, Yu C, Zhang CF, Wu XH, Wen XD,
Anderson S, Du W, Huang WH, Li SP, Wang CZ and Yuan CS:
Chemopreventive effects of oplopantriol A, a novel compound
isolated from Oplopanax horridus, on colorectal cancer. Nutrients.
6:2668–2680. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bin-Hafeez B, Haque R, Parvez S, Pandey S,
Sayeed I and Raisuddin S: Immunomodulatory effects of fenugreek
(Trigonella foenum graecum L.) extract in mice. Int
Immunopharmacol. 3:257–265. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zheng YQ, Wei W, Zhu L and Liu JX: Effects
and mechanisms of Paeoniflorin, a bioactive glucoside from paeony
root, on adjuvant arthritis in rats. Inflamm Res. 56:182–188. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang J, Xie Y, Feng Y, Zhang L, Huang X,
Shen X and Luo X: (−)-Epigallocatechingallate induces apoptosis in
B lymphoma cells via caspase-dependent pathway and Bcl-2 family
protein modulation. Int J Oncol. 46:1507–1515. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Grimoud J, Durand H, de Souza S, Monsan P,
Ouarné F, Theodorou V and Roques C: In vitro screening of
probiotics and synbiotics according to anti-inflammatory and
anti-proliferative effects. Int J Food Microbiol. 144:42–50. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Garcia Rodriguez LA, Cea-Soriano L,
Tacconelli S and Patrignani P: Coxibs: Pharmacology, toxicity and
efficacy in cancer clinical trials. Recent Results Cancer Res.
191:67–93. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Chen S, Qu X, Wan P, Li QW, Wang Z, Guo F,
Bai L, Hu Z, Tan W and Li J: Norcantharidin inhibits
pre-replicative complexes assembly of HepG2 cells. Am J Chin Med.
41:665–682. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu S, Wang XJ, Liu Y and Cui YF:
PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling is involved in
(−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate-induced apoptosis of human
pancreatic carcinoma cells. Am J Chin Med. 41:629–642. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Wang CY, Bai XY and Wang CH: Traditional
Chinese medicine: A treasured natural resource of anticancer drug
research and development. Am J Chin Med. 42:543–559. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yuan A, Chen JJ, Yao PL and Yang PC: The
role of interleukin-8 in cancer cells and microenvironment
interaction. Front Biosci. 10:853–865. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
De Robertis M, Massi E, Poeta ML, Carotti
S, Morini S, Cecchetelli L, Signori E and Fazio VM: The AOM/DSS
murine model for the study of colon carcinogenesis: From pathways
to diagnosis and therapy studies. J Carcinog. 10:92011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wen XD, Wang CZ, Yu C, Zhang Z, Calway T,
Wang Y, Li P and Yuan CS: Salvia miltiorrhiza (dan shen)
significantly ameliorates colon inflammation in dextran sulfate
sodium induced colitis. Am J Chin Med. 41:1097–1108. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gu C, Qiao J, Zhu M, Du J, Shang W, Yin W,
Wang W, Han M and Lu W: Preliminary evaluation of the interactions
of Panax ginseng and Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge with 5-fluorouracil
on pharmacokinetics in rats and pharmacodynamics in human cells. Am
J Chin Med. 41:443–458. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Park EY, Kim MH, Kim EH, Lee EK, Park IS,
Yang DC and Jun HS: Efficacy comparison of Korean ginseng and
American ginseng on body temperature and metabolic parameters. Am J
Chin Med. 42:173–187. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Qi LW, Wang CZ and Yuan CS: Ginsenosides
from American ginseng: Chemical and pharmacological diversity.
Phytochemistry. 72:689–699. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jacoby RF, Seibert K, Cole CE, Kelloff G
and Lubet RA: The cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor celecoxib is a potent
preventive and therapeutic agent in the min mouse model of
adenomatous polyposis. Cancer Res. 60:5040–5044. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yi J, Ye X, Wang D, He K, Yang Y, Liu X
and Li X: Safety evaluation of main alkaloids from Rhizoma
Coptidis. J Ethnopharmacol. 145:303–310. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|